北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (3): 518-522. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2021.03.013
2015—2017年北京市2型糖尿病患者骨关节炎患病的相关因素
吴俊慧1,陈泓伯1,2,武轶群1,吴瑶1,王紫荆1,吴涛1,王梦莹1,王斯悦1,王小文1,王伽婷1,于欢1,胡永华1,Δ( )
)
- 1.北京大学公共卫生学院流行病与卫生统计学系,北京 100191
2.北京大学护理学院老年护理与康复教研室,北京 100191
Prevalence and risk factors of osteoarthritis in patients with type 2 diabetes in Beijing, China from 2015 to 2017
WU Jun-hui1,CHEN Hong-bo1,2,WU Yi-qun1,WU Yao1,WANG Zi-jing1,WU Tao1,WANG Meng-ying1,WANG Si-yue1,WANG Xiao-wen1,WANG Jia-ting1,YU Huan1,HU Yong-hua1,Δ( )
)
- 1. Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, Peking University School of Public Health, Beijing 100191, China
2. Department of Geriatric Nursing and Rehabilitation, Peking University School of Nursing, Beijing 100191, China
摘要:
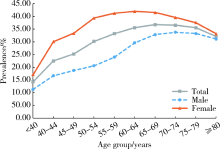
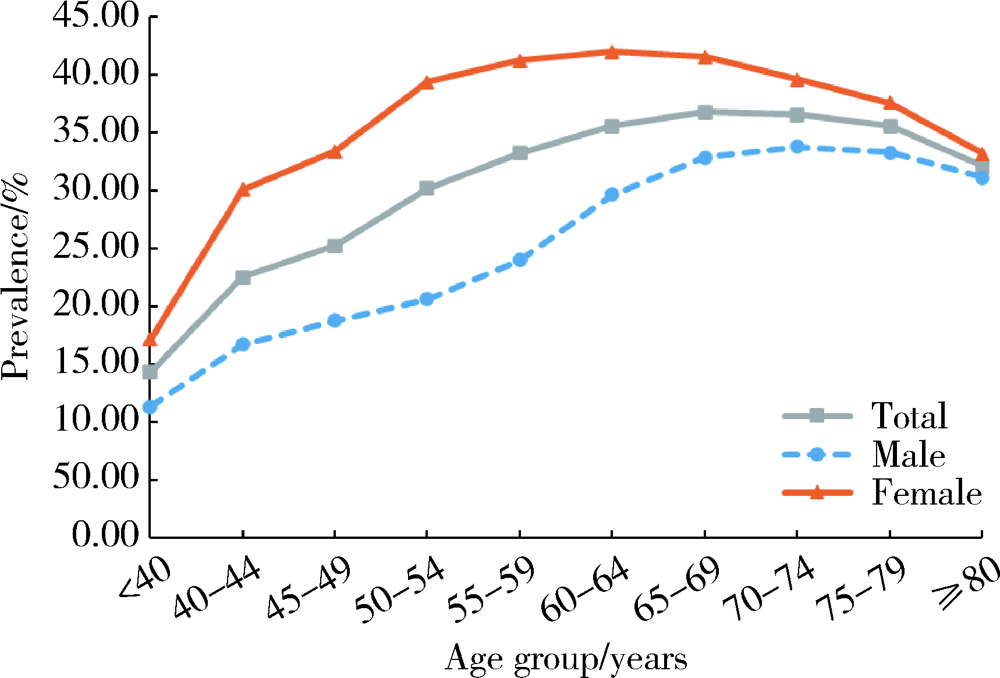
目的: 利用大数据对2型糖尿病患者骨关节炎的患病情况和相关因素进行探究,为该类合并症的防治工作提供科学依据。方法: 利用2015—2017年北京市所有定点医疗机构的就诊数据,收集成年2型糖尿病患者的相关资料进行描述性分析,采用Logistic回归模型探究2型糖尿病患者骨关节炎患病的相关因素。结果: 共纳入1 046 264例成年2型糖尿病患者,平均年龄63.07岁,男性占50.78%。2型糖尿病患者中患有骨关节炎的病例341 561人,患病率为32.65%;女性患病率(38.05%)高于男性(27.41%),差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。2型糖尿病患者骨关节炎在各个年龄段均有发生,骨关节炎患病率最高的年龄组为65~69岁组(36.76%),患病率最低的年龄组为≤44岁组(14.3%),70岁前患病率随年龄组的升高而增加。进一步分析2型糖尿病患者骨关节炎患病的影响因素,发现女性(OR=1.62,95%CI:1.61~1.63)、年龄(OR=1.01,95%CI:1.01~1.01)、患有其他合并症(OR=1.19,95%CI:1.18~1.21)、使用降糖药(OR=0.79,95%CI:0.78~0.80)、患有心血管疾病(OR=1.13,95%CI:1.11~1.15)、患有脑血管疾病(OR=1.25,95%CI:1.23~1.28)、患有糖尿病肾病(OR=1.61,95%CI:1.51~1.71)等因素与2型糖尿病人群患骨关节炎有关。结论: 北京地区2型糖尿病患者骨关节炎的患病率较高,应对中老年患者加强健康宣教与疾病监测工作,重点关注绝经期妇女,尽早开展合并症筛查工作。
中图分类号:
- R181.3
| [1] |
Hunter DJ, Bierma-Zeinstra S. Osteoarthritis[J]. Lancet, 2019,393(10182):1745-1759.
doi: S0140-6736(19)30417-9 pmid: 31034380 |
| [2] |
Hunter DJ, Schofield D, Callander E. The individual and socio-economic impact of osteoarthritis[J]. Nat Rev Rheumatol, 2014,10(7):437-441.
doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2014.44 pmid: 24662640 |
| [3] |
Neogi T. The epidemiology and impact of pain in osteoarthritis[J]. Osteoarthritis Cartilage, 2013,21(9):1145-1153.
doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2013.03.018 |
| [4] | 王华军, 陈均源, 罗斯敏, 等. 糖尿病与骨关节炎相关性的Meta分析[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志, 25(11):994-998. |
| [5] |
Veronese N, Cooper C, Reginster JY, et al. Type 2 diabetes mellitus and osteoarthritis[J]. Semin Arthritis Rheum, 2019,49(1):9-19.
doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2019.01.005 |
| [6] | Asfandiyarova NS, Nizov AA, Nekhaeva TI, et al. Osteoarthrosis in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. Terapevticheski Arkhiv, 2013,85(5):44. |
| [7] | 刘爱武, 王秋萍, 杜娜, 等. 住院患者2型糖尿病与膝骨关节炎流行病学的研究[J]. 中国社区医师, 2019,35(9):165-169. |
| [8] | 曾雁冰, 袁志鹏, 方亚. 中国老年人就医行为及其影响因素研究[J]. 中国卫生统计, 2020,37(2):199-205. |
| [9] |
Liu Y, Zhang HF, Liang NX. Prevalence and associated factors of knee osteoarthritis in a rural Chinese adult population: An epidemiological survey[J]. BMC Public Health, 2015,16(1):94.
doi: 10.1186/s12889-016-2782-x |
| [10] |
Lee SG, Kim SJ. Prevalence of knee osteoarthritis, risk factors, and quality of life: the Fifth Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey[J]. Int J Rheum Dis, 2017,20(7):809-817.
doi: 10.1111/apl.2017.20.issue-7 |
| [11] |
Nieves-Plaza M, Castro-Santana LE, Font YM, et al. Association of hand or knee osteoarthritis with diabetes mellitus in a population of Hispanics from Puerto Rico[J]. J Clin Rheumatol, 2013,19(1):1-6.
doi: 10.1097/RHU.0b013e31827cd578 pmid: 23319016 |
| [12] |
Prieto-Alhambra D, Judge A, Javaid MK, et al. Incidence and risk factors for clinically diagnosed knee, hip and hand osteoarthritis: Influences of age, gender and osteoarthritis affecting other joints[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2014,73(9):1659-1664.
doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-203355 |
| [13] |
Rosa SC, Goncalves J, Judas F, et al. Impaired glucose trans-porter-1 degradation and increased glucose transport and oxidative stress in response to high glucose in chondrocytes from osteo-arthritic versus normal human cartilage[J]. Arthritis Res Ther, 2009,11(3):R80.
doi: 10.1186/ar2713 |
| [14] |
Courties A, Sellam J. Osteoarthritis and type 2 diabetes mellitus: What are the links?[J]. Diabetes Res Clin Pract, 2016,122:198-206.
doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2016.10.021 |
| [15] |
Findlay DM. Vascular pathology and osteoarthritis[J]. Rheumatology (Oxford), 2007,46(12):1763-1768.
pmid: 17693442 |
| [16] |
Johnson EO, Soultanis K, Soucacos PN. Vascular anatomy and microcirculation of skeletal zones vulnerable to osteonecrosis: Vascularization of the femoral head[J]. Orthop Clin North Am, 2004,35(3):285-291.
doi: 10.1016/j.ocl.2004.03.002 |
| [1] | 曾媛媛,谢云,陈道南,王瑞兰. 脓毒症患者发生正常甲状腺性病态综合征的相关因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 526-532. |
| [2] | 李红光,韩玮华,吴训,冯继玲,李刚,孟娟红. 关节腔冲洗联合液态浓缩生长因子注射治疗单侧颞下颌关节骨关节炎的初步研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 338-344. |
| [3] | 林咏惟,周雅琳,赵润茏,许雅君,刘燕萍. 孕早期女性铁营养状况及其影响因素分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 600-605. |
| [4] | 傅强,高冠英,徐雁,林卓华,孙由静,崔立刚. 无症状髋关节前上盂唇撕裂超声与磁共振检查的对比研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 665-669. |
| [5] | 栗占国,任立敏. 侵蚀性骨关节炎:一种值得关注的疾病[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(5): 829-831. |
| [6] | 柯岩,张蔷,马云青,李儒军,陶可,桂先革,李克鹏,张洪,林剑浩. 全髋关节置换术治疗脊柱骨骺发育不良患者Tönnis 3级髋关节骨关节炎的早期疗效[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(1): 175-182. |
| [7] | 耿研,宋志博,张晓慧,邓雪蓉,王昱,张卓莉. 银屑病关节炎抑郁和焦虑患病情况及相关因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(6): 1048-1055. |
| [8] | 许璐,陈璐,樊东升,冯菁楠,刘立立,詹思延,王胜锋. 基于15省城镇医疗保险数据测算我国成人进行性肌萎缩患病率[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(3): 521-526. |
| [9] | 邓思危,陈则亦,刘志科,王健,卓琳,高双庆,余家阔,詹思延. 基于城镇医保数据库骨关节伤病的流行病学研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(3): 527-534. |
| [10] | 张晓盈,彭嘉婧,刘传慧,蔡小燕,张江林,梅轶芳,靳洪涛,王晓非,磨红,栗占国. 骨关节炎患者用药治疗现状的全国多中心大样本现场调查[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(6): 1044-1048. |
| [11] | 王丹丹,甘业华,马绪臣,孟娟红. ADAMTS14基因单核苷酸多态性与汉族女性颞下颌关节骨关节炎的相关性研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(2): 279-283. |
| [12] | 石慧峰, 张敬旭, 张嵘, 王晓莉. 中国0~6岁儿童孤独症谱系障碍患病率的meta分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(5): 798-806. |
| [13] | 张英泽. 观察、思考与创新在我国骨科发展中的重要作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2016, 48(2): 189-190. |
| [14] | 潘利平,曹永平,文立成,柴卫兵,杜军保,金红芳,柳佳,杨昕,孟志超,刘恒,崔云鹏,王瑞,吴浩,周星彤,李翔,李卓扬,塔拉提百克. 软骨中硫化氢含量及其对白介素1β诱导的软骨细胞基质金属蛋白酶13表达的抑制作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2016, 48(2): 194-201. |
| [15] | 李志昌,姜龙,张舒,秦雪英,Daniel K. White PT,侯云飞,周之伟,林剑浩. 终末期骨关节炎患者全膝关节置换术前的躯体功能客观测定[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2016, 48(2): 257-262. |
|
||