北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (6): 1068-1073. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2022.06.002
类风湿关节炎临床分层及其特征的横断面研究
蔡文心1,李仕成2,3,刘一鸣1,4,梁如玉1,李静1,郭建萍1,胡凡磊1,孙晓麟1,李春1,刘栩1,叶华1,邓立宗3,*( ),李茹1,*(
),李茹1,*( ),栗占国1,*(
),栗占国1,*( )
)
- 1. 北京大学人民医院风湿免疫科,北京 100044
2. 苏州大学附属第二医院肿瘤科,江苏苏州 215123
3. 中国医学科学院系统医学研究院/苏州系统医学研究所,江苏苏州 215123
4. 郑州大学第五附属医院风湿免疫科,郑州 450052
A cross-sectional study on the clinical phenotypes of rheumatoid arthritis
Wen-xin CAI1,Shi-cheng LI2,3,Yi-ming LIU1,4,Ru-yu LIANG1,Jing LI1,Jian-ping GUO1,Fan-lei HU1,Xiao-lin SUN1,Chun LI1,Xu LIU1,Hua YE1,Li-zong DENG3,*( ),Ru LI1,*(
),Ru LI1,*( ),Zhan-guo LI1,*(
),Zhan-guo LI1,*( )
)
- 1. Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, Peking University People's Hospital, Beijing 100044, China
2. Department of Oncology, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Suzhou 215123, Jiangsu, China
3. Institute of Systems Medicine, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College, Suzhou Institute of Systems Medicine, Suzhou 215123, Jiangsu, China
4. Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, the Fifth Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450052, China
摘要:
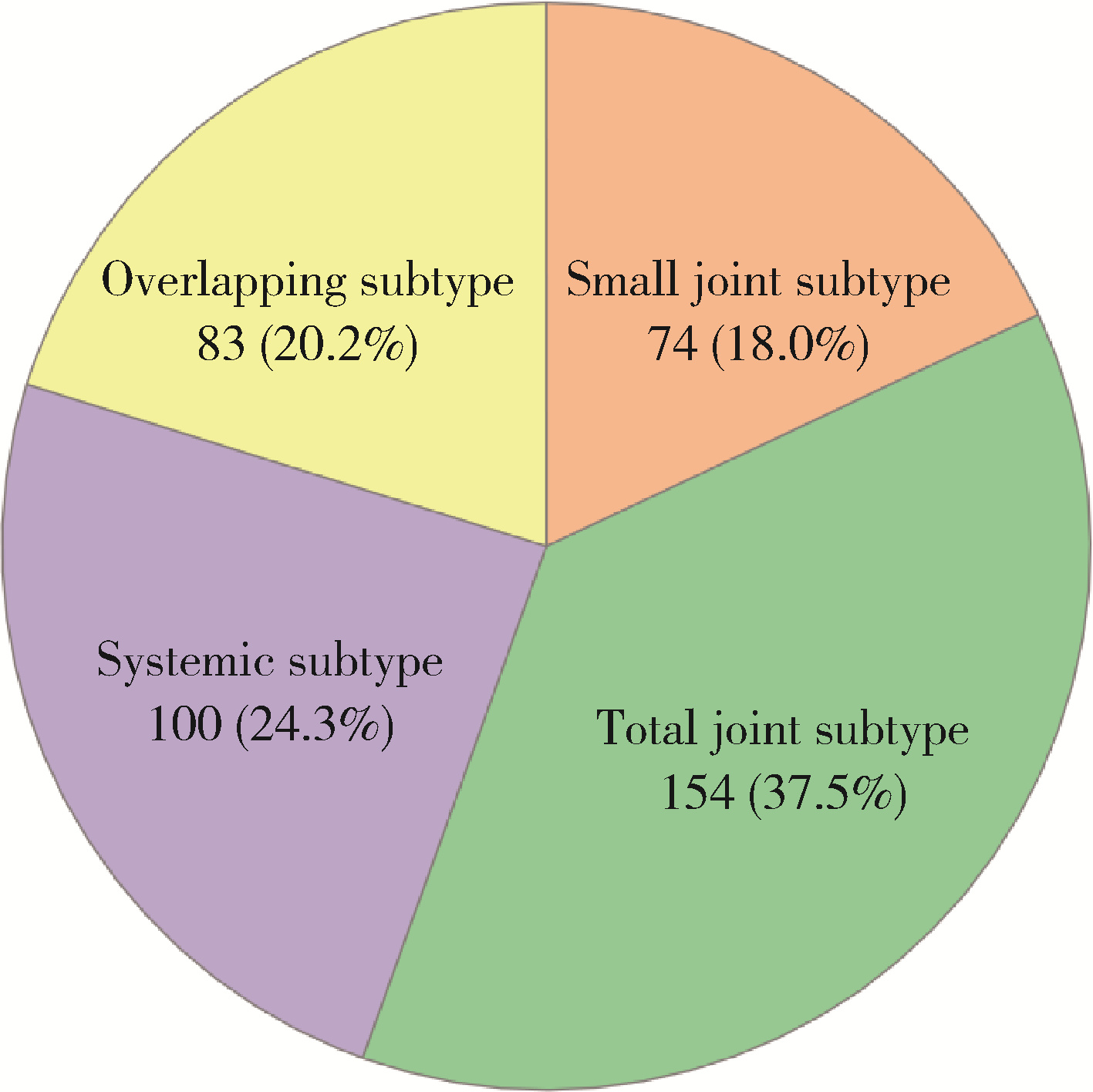
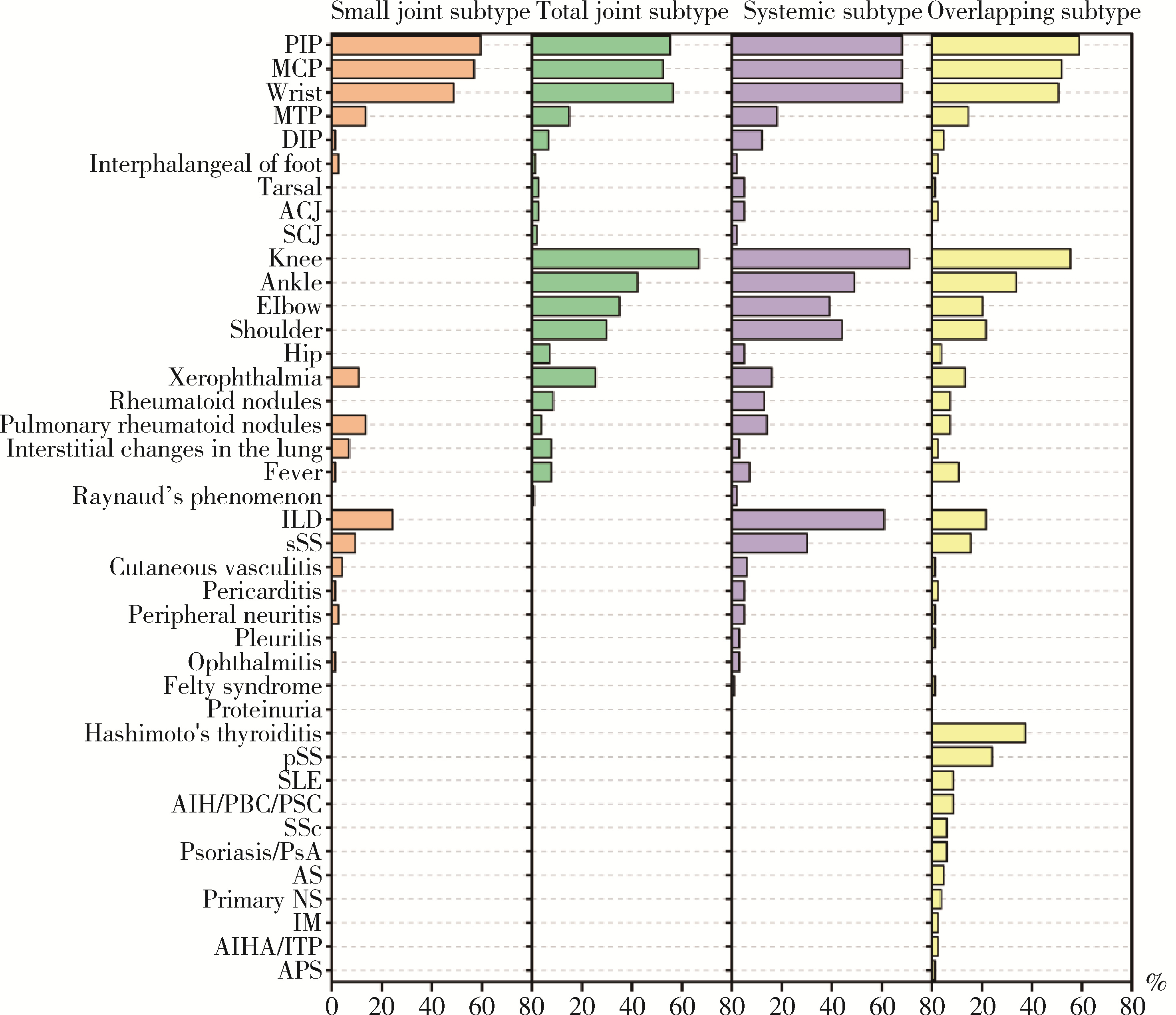
目的: 探索类风湿关节炎(rheumatoid arthritis, RA)临床分层及其特征,为RA的发病机制、临床诊治和转归评估提供依据。方法: 选择2018—2021年于北京大学人民医院就诊的RA患者,收集患者一般情况、关节受累部位及数量、关节外表现、合并症及实验室检查结果等信息,采用统计及生物信息分析的方法,以受累关节部位、有无系统受累或合并其他自身免疫性疾病等进行临床分层,并对各亚型患者的特征进行分析。结果: 共纳入411例RA患者,平均年龄(48.84±15.17)岁,其中女性346例(84.2%)。患者被分为小关节型(74,18.0%)、全关节型(154, 37.5%)、系统型(100, 24.3%)、重叠型(83,20.2%)4个亚型。小关节型者无中大关节受累,其中35.1%有系统表现,红细胞沉降率(erythrocyte sedimentation rate, ESR)及C反应蛋白(C-reaction protein, CRP)水平和血小板计数较其他亚型低,而IgA及IgG类风湿因子阳性率较高;全关节型者中大关节和小关节均可受累,关节外表现少见,晨僵发生率和抗核抗体(antinuclear antibodies, ANA)阳性率显著低于其他亚型,而ESR及CRP水平相对较高;系统型者以合并肺间质纤维化和口、眼干燥症状常见, 病情活动指数高;重叠型至少合并另一种风湿病或自身免疫性疾病,以桥本甲状腺炎和原发性干燥综合征最为常见,与其他亚型相比,女性多见,高免疫球蛋白血症、低补体血症和斑点型ANA为其特征。结论: 根据类风湿关节炎的临床特征,可初步将其分为小关节型、全关节型、系统型、重叠型4个亚型,各有其临床和实验室特征,有助于进一步认识RA和为患者进行个体化治疗提供依据。
中图分类号:
- R593.22
| 1 |
Turesson C , O'Fallon WM , Crowson CS , et al. Extra-articular disease manifestations in rheumatoid arthritis: Incidence trends and risk factors over 46 years[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2003, 62 (8): 722- 727.
doi: 10.1136/ard.62.8.722 |
| 2 |
Li R , Sun J , Ren LM , et al. Epidemiology of eight common rheumatic diseases in China: A large-scale cross-sectional survey in Beijing[J]. Rheumatology (Oxford), 2012, 51 (4): 721- 729.
doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/ker370 |
| 3 |
Zhou Y , Wang X , An Y , et al. Disability and health-related quality of life in Chinese patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A cross-sectional study[J]. Int J Rheum Dis, 2018, 21 (9): 1709- 1715.
doi: 10.1111/1756-185X.13345 |
| 4 |
Aletaha D , Neogi T , Silman AJ , et al. 2010 rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: An American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative[J]. Arthritis Rheum, 2010, 62 (9): 2569- 2581.
doi: 10.1002/art.27584 |
| 5 |
Vij R , Strek ME . Diagnosis and treatment of connective tissue disease-associated interstitial lung disease[J]. Chest, 2013, 143 (3): 814- 824.
doi: 10.1378/chest.12-0741 |
| 6 |
Linn-Rasker SP , van der Helm-van Mil AHM , Breedveld FC , et al. Arthritis of the large joints, in particular, the knee, at first presentation is predictive for a high level of radiological destruction of the small joints in rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2007, 66 (5): 646- 650.
doi: 10.1136/ard.2006.066704 |
| 7 |
Drossaers-Bakker KW , Kroon HM , Zwinderman AH , et al. Radiographic damage of large joints in long-term rheumatoid arthritis and its relation to function[J]. Rheumatology (Oxford), 2000, 39 (9): 998- 1003.
doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/39.9.998 |
| 8 |
Lockshin MD , Levine AB , Erkan D . Patients with overlap autoimmune disease differ from those with 'pure' disease[J]. Lupus Sci Med, 2015, 2 (1): e000084.
doi: 10.1136/lupus-2015-000084 |
| 9 |
Wallace ZS , Zhang Y , Perugino CA , et al. Clinical phenotypes of IgG4-related disease: An analysis of two international cross-sectional cohorts[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2019, 78 (3): 406- 412.
doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2018-214603 |
| 10 |
Tarn JR , Howard-Tripp N , Lendrem DW , et al. Symptom-based stratification of patients with primary Sjögren's syndrome: Multi-dimensional characterisation of international observational cohorts and reanalyses of randomised clinical trials[J]. Lancet Rheum, 2019, 1 (2): E85- E94.
doi: 10.1016/S2665-9913(19)30042-6 |
| 11 |
Platzer A , Alasti F , Smolen JS , et al. Trajectory clusters of radiographic progression in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: Associations with clinical variables[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2022, 81 (2): 175- 183.
doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2021-220331 |
| 12 |
Vergne-Salle P , Pouplin S , Trouvin AP , et al. The burden of pain in rheumatoid arthritis: Impact of disease activity and psychological factors[J]. Eur J Pain, 2020, 24 (10): 1979- 1989.
doi: 10.1002/ejp.1651 |
| 13 |
Lee YC , Frits ML , Iannaccone CK , et al. Subgrouping of patients with rheumatoid arthritis based on pain, fatigue, inflammation, and psychosocial factors[J]. Arthritis Rheum, 2014, 66 (8): 2006- 2014.
doi: 10.1002/art.38682 |
| 14 |
Terao C , Hashimoto M , Yamamoto K , et al. Three groups in the 28 joints for rheumatoid arthritis synovitis: Analysis using more than 17 000 assessments in the KURAMA database[J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8 (3): e59341.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0059341 |
| 15 |
Curtis JR , Weinblatt M , Saag K , et al. Data-driven patient clustering and differential clinical outcomes in the brigham and women's rheumatoid arthritis sequential study registry[J]. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken), 2021, 73 (4): 471- 480.
doi: 10.1002/acr.24471 |
| [1] | 刘东武, 陈杰, 高明利, 于静. 类风湿关节炎伴发淋巴结Castleman样病理改变1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 928-931. |
| [2] | 黄会娜,赵静,赵祥格,白自然,李霞,王冠. 乳酸对类风湿关节炎患者外周血CD4+T细胞亚群的调控作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 519-525. |
| [3] | 汤晓菲,李永红,丁秋玲,孙卓,张阳,王育梅,田美伊,刘坚. 类风湿关节炎患者下肢深静脉血栓发病率及危险因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 279-283. |
| [4] | 邹雪,白小娟,张丽卿. 艾拉莫德联合托法替布治疗难治性中重度类风湿关节炎的疗效[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 1013-1021. |
| [5] | 吴琦,蔡月明,何娟,黄文蒂,王庆文. 血脂异常与类风湿关节炎肺间质病变的相关性分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 982-992. |
| [6] | 张警丰,金银姬,魏慧,姚中强,赵金霞. 体重指数与类风湿关节炎临床特征的相关性分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 993-999. |
| [7] | 金银姬,孙琳,赵金霞,刘湘源. 血清IgA型抗鼠科肉瘤病毒癌基因同源物B1抗体在类风湿关节炎中的意义[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 631-635. |
| [8] | 程昉,杨邵英,房星星,王璇,赵福涛. CCL28-CCR10通路在类风湿关节炎单核细胞迁移中的作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1074-1078. |
| [9] | 刘蕊,赵金霞,闫良. 类风湿关节炎合并下肢静脉血栓患者的临床特点[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1079-1085. |
| [10] | 张警丰,金银姬,魏慧,姚中强,赵金霞. 类风湿关节炎患者生活质量与疾病活动度的横断面研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1086-1093. |
| [11] | 高超,陈立红,王莉,姚鸿,黄晓玮,贾语博,刘田. 类风湿关节炎合并纤维肌痛简易分类标准的临床验证[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(2): 278-282. |
| [12] | 娄雪,廖莉,李兴珺,王楠,刘爽,崔若玫,徐健. 类风湿关节炎患者外周血TWEAK基因启动子区甲基化状态及其表达[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(6): 1020-1025. |
| [13] | 钟华,徐丽玲,白明欣,苏茵. 类风湿关节炎患者趋化因子CXCL9和CXCL10在骨侵蚀中的作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(6): 1026-1031. |
| [14] | 罗靓,霍文岗,张钦,李春. 类风湿关节炎合并角膜溃疡的临床特点和相关因素分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(6): 1032-1036. |
| [15] | 张璐,胡小红,陈澄,蔡月明,王庆文,赵金霞. 类风湿关节炎初治患者颈椎失稳情况及临床特征[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(6): 1049-1054. |
|
||