北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (4): 652-657. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2023.04.014
脊髓髓内海绵状血管瘤患者不同治疗方式的预后
- 北京大学第三医院神经外科,北京 100191
Prognosis of patients with spinal intramedullary cavernous hemangioma by different treatments
Bin CHEN,Chao WU,Bin LIU,Tao YU,Zhen-yu WANG*( )
)
- Department of Neurosurgery, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
摘要:
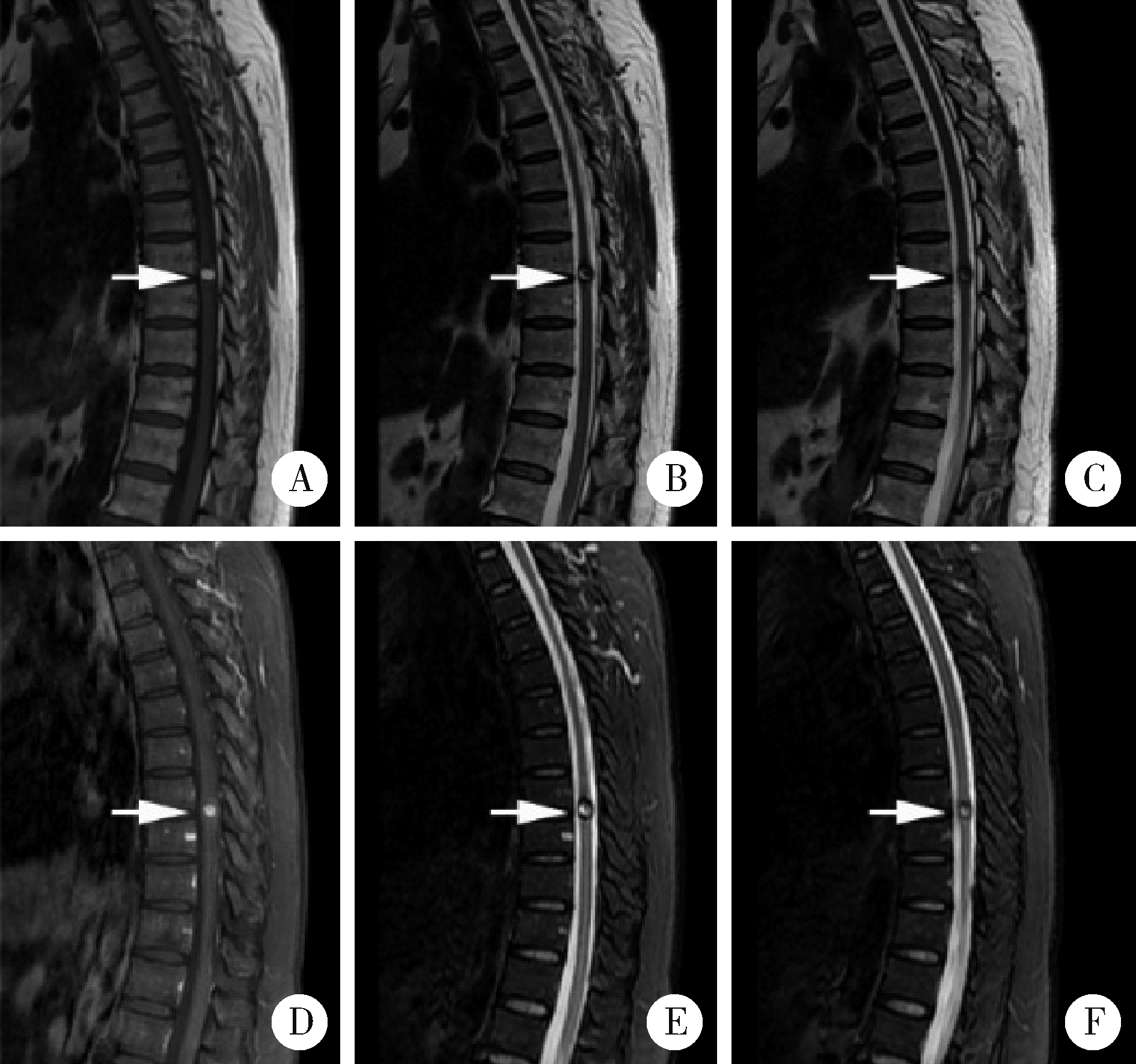
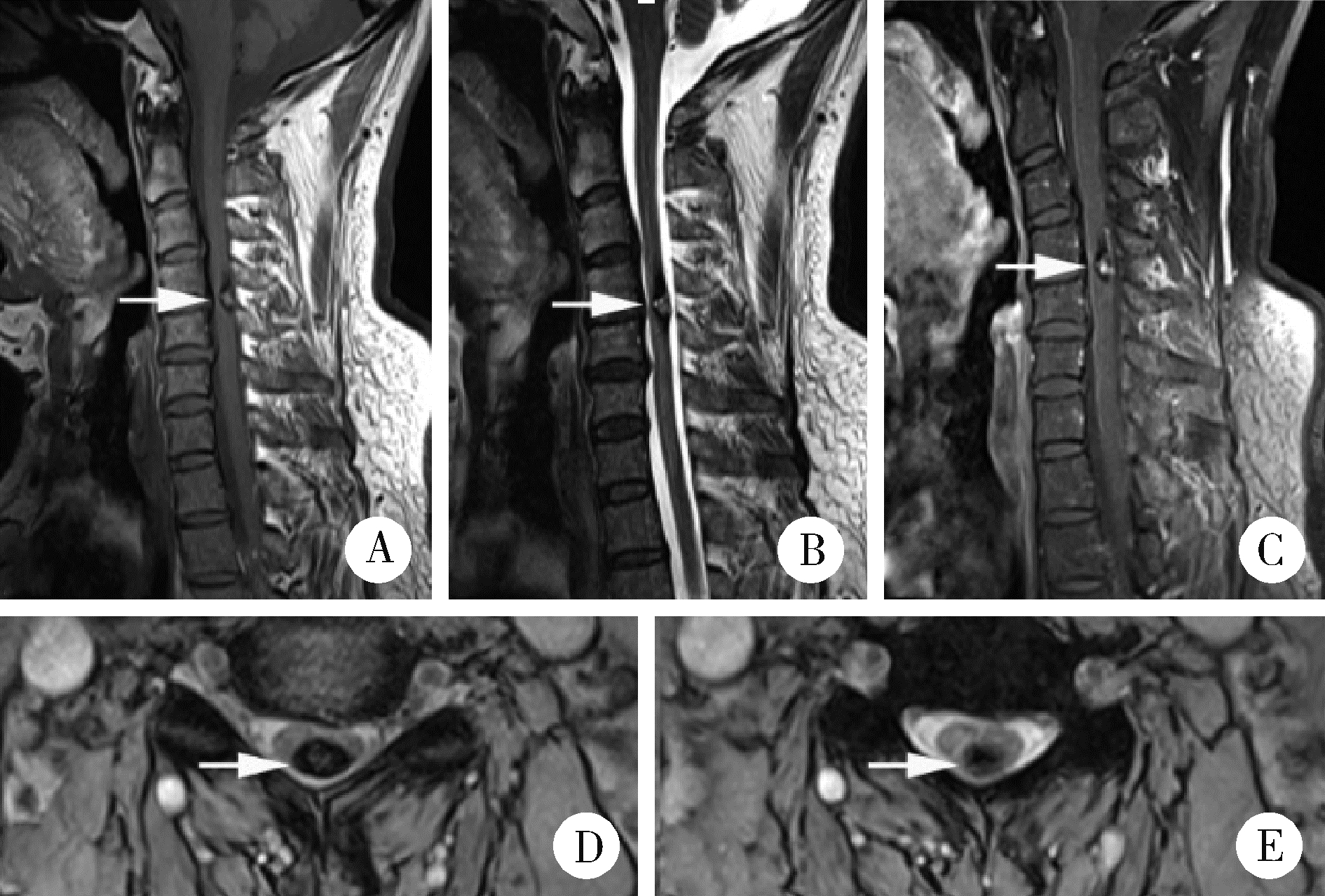
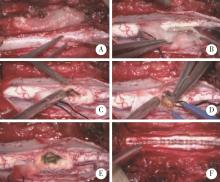
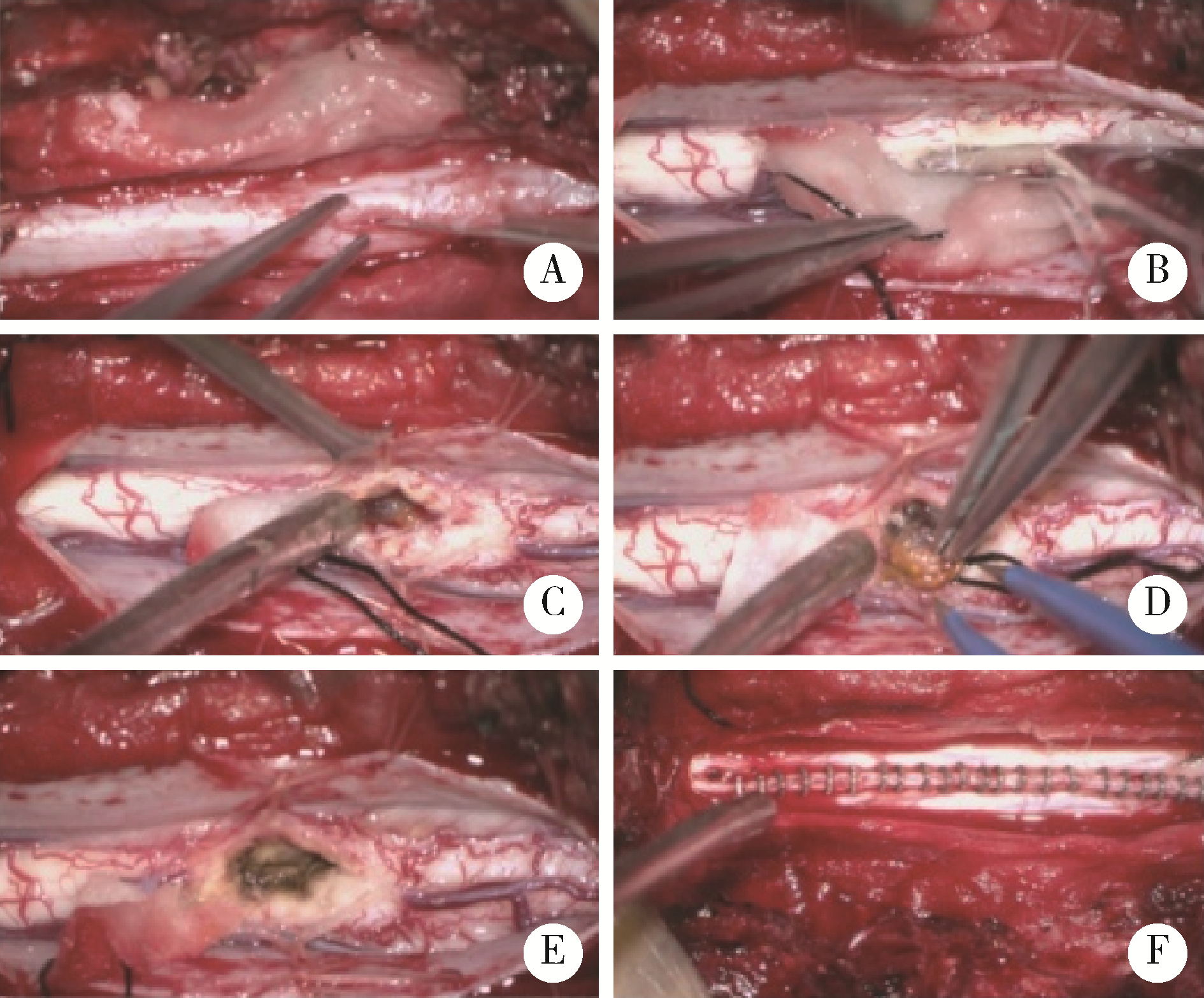
目的: 探讨采取不同治疗方式的脊髓髓内海绵状血管瘤患者末次随访时的脊髓功能改善情况。方法: 回顾性研究2007年1月至2018年12月就诊于北京大学第三医院的30例脊髓髓内海绵状血管瘤患者,总结脊髓髓内海绵状血管瘤患者的性别、年龄、临床症状、影像学表现,采用欧洲脊髓病评分(European myelopathy score, EMS)评估患者治疗前后脊髓功能状态,分析手术治疗及保守治疗患者的预后。结果: 30例患者中,男性患者14例,女性患者16例(1 ∶ 1.14),患者平均年龄为(48.1±13.6)岁(18~81岁)。单纯感觉障碍者3例,单纯肌力下降者2例,单纯疼痛者1例,肌力下降伴疼痛者1例,感觉障碍伴有肌力下降者5例,感觉障碍、肌力下降、二便异常者3例,感觉障碍、肌力下降、疼痛者3例,感觉障碍伴疼痛者8例,感觉障碍、疼痛、二便异常者1例,感觉障碍、疼痛、肌力下降、二便异常者1例,无症状者2例。共有11例患者病变位于颈椎区域,2例患者病变位于颈胸交界处,15例患者病变位于胸椎区域,2例患者病变位于腰椎区域。血管瘤最大径平均为(10.90±4.87) mm, 磁共振成像表现常为T2WI混杂信号及高信号,T1WI等信号或混杂信号。随访时间为(27.4±8.7)个月,包括手术治疗患者19例及保守治疗患者11例。手术治疗患者末次随访时脊髓功能较初次就诊时得到明显改善,差异具有统计学意义(P < 0.05),保守治疗患者1例患者症状改善,2例患者症状加重,余患者保持平稳,治疗前后脊髓功能无明显改变,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。结论: 脊髓髓内海绵状血管瘤手术治疗效果确切,预后较好;保守治疗总体改善率较低,并且有加重风险。
中图分类号:
- R651.2
| 1 |
ZevgaridisD,MedeleR J,HamburgerC,et al.Cavernous haemangiomas of the spinal cord. A review of 117 cases[J].Acta Neurochir,1999,141(3):237-245.
doi: 10.1007/s007010050293 |
| 2 |
BadhiwalaJH,FarrokhyarF,AlhazzaniW,et al.Surgical outcomes and natural history of intramedullary spinal cord cavernous malformations: A single-center series and meta-analysis of indivi-dual patient data: Clinic article[J].J Neurosurg Spine,2014,21(4):662-676.
doi: 10.3171/2014.6.SPINE13949 |
| 3 |
DalitzK,VitzthumHE.Evaluation of five scoring systems for cervical spondylogenic myelopathy[J].Spine J,2019,19(2):e41-e46.
doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2008.05.005 |
| 4 |
SchermanDB,RaoPJ,VarikattW,et al.Clinical presentation and surgical outcomes of an intramedullary C2 spinal cord cavernoma: A case report and review of the relevant literature[J].J Spine Surg,2016,2(2):139-142.
doi: 10.21037/jss.2016.04.01 |
| 5 |
PétillonP,WilmsG,RaftopoulosC,et al.Spinal intradural extramedullary cavernous hemangioma[J].Neuroradiology,2018,60(10):1085-1087.
doi: 10.1007/s00234-018-2073-6 |
| 6 |
NieQB,ChenZ,JianFZ,et al.Cavernous angioma of the cauda equina: A case report and systematic review of the literature[J].J Int Med Res,2012,40(5):2001-2008.
doi: 10.1177/030006051204000542 |
| 7 |
LiangJT,BaoYH,ZhangHQ,et al.Management and prognosis of symptomatic patients with intramedullary spinal cord cavernoma: Clinical article[J].J Neurosurg Spine,2011,15(4):447-456.
doi: 10.3171/2011.5.SPINE10735 |
| 8 |
ArdeshiriA,ÖzkanN,ChenB,et al.A retrospective and consecutive analysis of the epidemiology and management of spinal cavernomas over the last 20 years in a single center[J].Neurosurg Rev,2016,39(2):269-276.
doi: 10.1007/s10143-015-0674-7 |
| 9 | BaldvinsdóttirB,ErlingsdóttirG,Kjartanssonó,et al.Extrame-dullar cavernous hemangioma with intra- and extradural growth and clinical symptoms of Brown-Séquard syndrome: Case report and review of the literature[J].World Neurosurg,2016,98(11):881. e5-881. e8. |
| 10 | OttenM,McCormickP.Natural history of spinal cavernous malformations[J].Handb Clin Neurol,2017,143,233-239. |
| 11 | MithaAP,TurnerJD,SpetzlerRF.Surgical approaches to intramedullary cavernous malformations of the spinal cord[J].Neurosurgery,2011,68(2):317-324. |
| 12 |
ZhangL,YangW,JiaW,et al.Comparison of outcome between surgical and conservative management of symptomatic spinal cord cavernous malformations[J].Neurosurgery,2016,78(4):552-561.
doi: 10.1227/NEU.0000000000001075 |
| 13 |
ReitzM,BurkhardtT,VettorazziE,et al.Intramedullary spinal cavernoma: Clinical presentation, microsurgical approach, and long-term outcome in a cohort of 48 patients[J].Neurosurg Focus,2015,39(2):E19.
doi: 10.3171/2015.5.FOCUS15153 |
| 14 |
AoyamaT,HidaK,HoukinK.Intramedullary cavernous angiomas of the spinal cord: Clinical characteristics of 13 lesions[J].Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo),2011,51(8):561-566.
doi: 10.2176/nmc.51.561 |
| 15 | 李熊辉,王振宇,刘彬.脊髓髓内海绵状血管瘤的诊疗现状[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2017,27(3):276-279. |
| 16 |
AzadTD,VeeravaguA,LiA,et al.Long-term effectiveness of gross-total resection for symptomatic spinal cord cavernous malformations[J].Neurosurgery,2018,83(6):1201-1208.
doi: 10.1093/neuros/nyx610 |
| 17 | 董伟杰,刘馨蔓,苏月焦,等.脊髓髓内海绵状血管瘤的显微手术治疗[J].中华显微外科杂志,2018,41(2):105-108. |
| [1] | 王薇,蔡林,高莹,郭晓蕙,张俊清. 原发性醛固酮增多症术后持续性重度高钾血症1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(2): 376-380. |
| [2] | 洪鹏,田晓军,赵小钰,杨飞龙,刘茁,陆敏,赵磊,马潞林. 肾移植术后双侧乳头状肾癌1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(4): 811-813. |
| [3] | 杨洁,张然,刘宇楠,王佃灿. 表现为耳后区巨大肿物的口外型舌下腺囊肿1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(1): 193-195. |
| [4] | 唐琦,林榕城,姚林,张争,郝瀚,张崔建,蔡林,李学松,何志嵩,周利群. 肾癌术后局部复发患者的临床病理特征及预后分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(4): 628-631. |
|
||