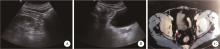
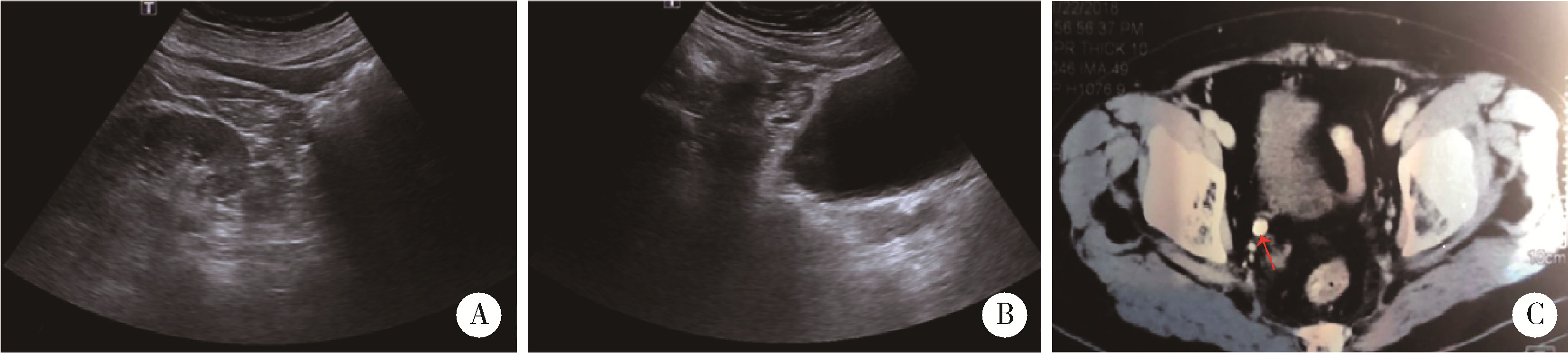
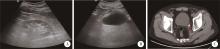
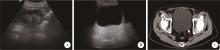
北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (5): 939-942. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2023.05.025
无症状无积水输尿管结石4例患者的诊治
- 北京大学人民医院泌尿外科, 北京 100044
Diagnosis and treatment of four cases of asymptomatic and non-hydrous ureteral calculi
Cai-peng QIN,Fei WANG,Yi-qing DU,Xiao-wei ZHANG,Qing LI,Shi-jun LIU,Tao XU*( )
)
- Department of Urology, Peking Univesity People's Hospital, Beijing 100044, China
中图分类号:
- R693.4
| 1 | Wimpissinger F , Türk C , Kheyfets O , et al. The silence of the stones: Asymptomatic ureteral calculi[J]. J Urol, 2007, 178 (4 Pt 1): 1341- 1344. |
| 2 |
Marchini GS , Vicentini FC , Monga M , et al. Irreversible renal function impairment due to silent ureteral stones[J]. Urology, 2016, 93, 33- 39.
doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2016.02.042 |
| 3 | He L , Yang H , Fan L , et al. Comparison of symptomatic versus asymptomatic urolithiasis: Surgical outcomes and medium-term follow-up[J]. Int J Clin Exp Med, 2016, 9 (2): 4300- 4307. |
| 4 |
Wimpissinger F , Springer C , Kurtaran A , et al. Functional aspects of silent ureteral stones investigated with MAG-3 renal scintigraphy[J]. BMC Urol, 2014, 14 (1): 1- 5.
doi: 10.1186/1471-2490-14-1 |
| 5 |
Marchini GS , Vicentini FC , Mazzucchi E , et al. Silent ureteral stones: Impact on kidney function: Can treatment of silent ureteral stones preserve kidney function?[J]. Urology, 2012, 79 (2): 304- 308.
doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2011.07.1436 |
| 6 |
Weizer AZ , Auge BK , Silverstein AD , et al. Routine postoperative imaging is important after ureteroscopic stone manipulation[J]. J Urol, 2002, 168 (1): 46- 50.
doi: 10.1016/S0022-5347(05)64829-X |
| 7 |
Glowacki LS , Beecroft ML , Cook RJ , et al. The natural history of asymptomatic urolithiasis[J]. J Urol, 1992, 147 (2): 319- 321.
doi: 10.1016/S0022-5347(17)37225-7 |
| 8 |
Khaitan A , Gupta NP , Hemal AK , et al. Post-ESWL, clinically insignificant residual stones: Reality or myth?[J]. Urology, 2002, 59 (1): 20- 24.
doi: 10.1016/S0090-4295(01)01494-7 |
| 9 |
Shokeir AA . Renal colic: Pathophysiology, diagnosis and treatment[J]. Eur Urol, 2001, 39 (3): 241- 249.
doi: 10.1159/000052446 |
| 10 | Sfakianakis GN , Cohen DJ , Braunstein RH , et al. MAG3-F0 scintigraphy in decision making for emergency intervention in renal colic after helical CT positive for a urolith[J]. J Nucl Med, 2000, 41 (11): 1813- 1822. |
| 11 |
Lanzone JA , Gulmi FA , Chou SY , et al. Renal hemodynamics in acute unilateral ureteral obstruction: Contribution of endothelium-derived relaxing factor[J]. J Urol, 1995, 153 (6): 2055- 2059.
doi: 10.1016/S0022-5347(01)67401-9 |
| 12 |
Zabihi N , Teichman JM . Dealing with the pain of renal colic[J]. Lancet, 2001, 358 (9280): 437- 438.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(01)05668-9 |
| 13 | Miller OF , Kane CJ . Time to stone passage for observed ureteral calculi: A guide for patient education[J]. J Urol, 1999, 162 (3 Pt 1): 688- 690. |
| 14 |
German I , Lantsberg S , Crystal P , et al. Non contrast compu-terized tomography and dynamic renal scintigraphy in the evaluation of patients with renal colic: Are both necessary?[J]. Eur Urol, 2002, 42 (2): 188- 191.
doi: 10.1016/S0302-2838(02)00271-3 |
| 15 |
Eisner BH , Pedro R , Namasivayam S , et al. Differences in stone size and ureteral dilation between obstructing proximal and distal ureteral calculi[J]. Urology, 2008, 72 (3): 517- 520.
doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2008.03.034 |
| 16 |
Kelleher JP , Plail RO , Dave SM , et al. Sequential renography in acute urinary tract obstruction due to stone disease[J]. Br J Urol, 1991, 67 (2): 125- 128.
doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.1991.tb15092.x |
| 17 |
Gandolpho L , Sevillano M , Barbieri A , et al. Scintigraphy and Doppler ultrasonography for the evaluation of obstructive urinary calculi[J]. Braz J Med Biol Res, 2001, 34 (6): 745- 751.
doi: 10.1590/S0100-879X2001000600007 |
| [1] | 傅强,高冠英,徐雁,林卓华,孙由静,崔立刚. 无症状髋关节前上盂唇撕裂超声与磁共振检查的对比研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 665-669. |
| [2] | 王磊,韩天栋,江卫星,李钧,张道新,田野. 主动迁移技术与原位碎石技术在输尿管软镜治疗1~2 cm输尿管上段结石中的安全性和有效性比较[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 553-557. |
| [3] | 李金勇,孙宏亮,叶志东,樊雪强,刘鹏. 颈动脉斑块成分和体积的多排螺旋计算机断层扫描血管成像技术评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(5): 833-839. |
| [4] | 叶海云,许清泉,马凯,黄晓波. 内镜治疗的输尿管结石患者治疗前结石位置和输尿管扩张特点分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(4): 622-625. |
| [5] | 张力杰, 叶雄俊, 黄晓波, 熊六林, 马凯, 李建兴, 王晓峰. 无管化经皮肾镜和输尿管镜碎石术处理最大径线1.5 cm以上输尿管上段结石的比较[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2015, 47(1): 170-174. |
| [6] | 王澍, 施永康, 黄晓波, 马凯, 许清泉, 熊六林, 李建兴, 王晓峰. 上尿路结石合并感染的细菌培养及药物敏感性分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2014, 46(5): 798-801. |
| [7] | 熊六林,叶雄俊,马凯,黄晓波,王晓峰. 无管化24 F通道经皮肾镜治疗肾输尿管上段结石的初步探讨[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2013, 45(4): 575-. |
| [8] | 熊六林, 黄晓波, 叶雄俊, 马凯, 许清泉, 李建兴, 王晓峰. CQS-01超声气压弹道碎石清石系统在经皮肾镜手术中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2012, 44(4): 575-578. |
| [9] | 熊六林, 黄晓波, 李建兴, 许清泉, 叶雄俊, 杨波, 马凯, 陈亮, 胡卫国, 王晓峰. CQS-01与EMS-Ⅲ超声气压弹道碎石清石系统的临床有效性和安全性对照试验研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2011, 43(4): 548-555. |
|
||