北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (6): 1013-1021. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2023.06.009
艾拉莫德联合托法替布治疗难治性中重度类风湿关节炎的疗效
- 1. 山西医科大学附属汾阳医院, 山西省汾阳医院风湿免疫科, 山西汾阳 032200
2. 苏州永鼎医院消化内科, 江苏苏州 215100
Effectiveness of tofacitinib combined with iguratimod in the treatment of difficult-to-treat moderate-to-severe rheumatoid arthritis
Xue ZOU1,2,Xiao-juan BAI1,Li-qing ZHANG1,*( )
)
- 1. Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, Fenyang Hospital Affiliated to Shanxi Medical University, Shanxi Province Fenyang Hospital, Fenyang 032200, Shanxi, China
2. Department of Gastroenterology, Suzhou Yongding Hospital, Suzhou 215100, Jiangsu, China
摘要:
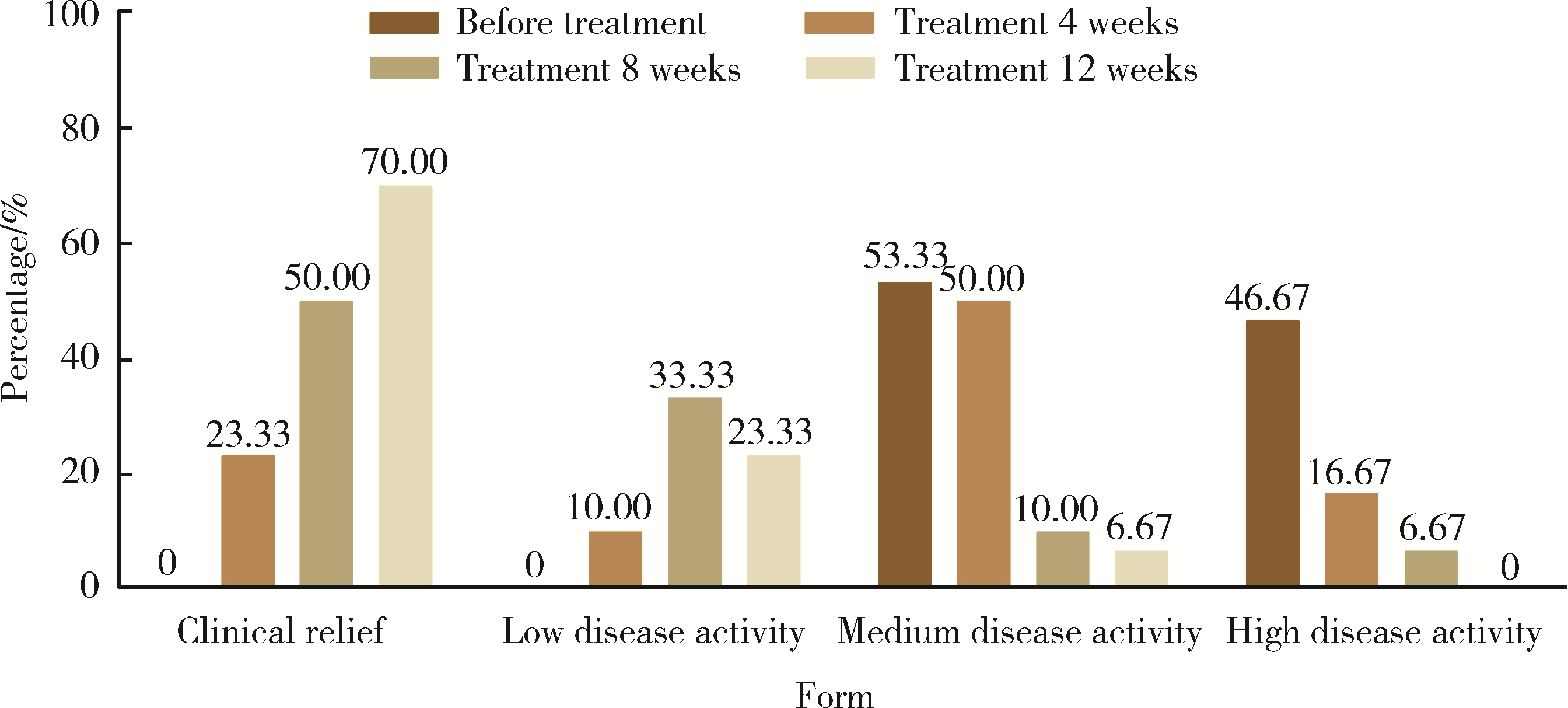
目的: 探讨艾拉莫德联合托法替布在难治性中重度类风湿关节炎(rheumatoid arthritis, RA)患者中的疗效和安全性。方法: 选择2021年9月至2022年6月规律就诊于山西省汾阳医院风湿免疫科的难治性中重度活动性RA患者30例进行前瞻性临床研究,其中,23例患者采用≥2种传统合成改善病情抗风湿药(disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs,DMARDs)(至少包括甲氨蝶呤或来氟米特)治疗6个月以上,7例患者采用传统合成DMARDs联合肿瘤坏死因子拮抗剂治疗。将DMARDs调整为艾拉莫德联合托法替布,共治疗12周,收集患者治疗前,治疗4周、8周及12周时的临床资料:肿胀关节数(swollen joints count,SJC)、疼痛关节数(tender joints count,TJC)、晨僵时间、临床疾病活动指数(clinical disease activity index,CDAI)、健康状况评估问卷(health status assessment questionnaire,HAQ)、28个关节计数的疾病活动评分(28-joint disease activity score,DAS28)。记录患者的红细胞沉降率(erythrocyte sedimentation rate, ESR)、C反应蛋白(C-reactive protein, CRP)、血小板(platelet, PLT)、类风湿因子(rheumatoid factor, RF)、球蛋白、抗环瓜氨酸肽(cyclic citrullinated peptide, CCP)抗体等实验室检查结果,记录患者的用药情况,比较患者疾病活动指标的变化情况,记录药物不良反应。结果: 比较治疗前后的ESR、CRP、RF、PLT、SJC、TJC、基于ESR的DAS28(DAS28-ESR)、晨僵时间、HAQ、CDAI、抗CCP抗体,差异均有统计学意义(P < 0.05),而治疗前后的球蛋白比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。艾拉莫德联合托法替布治疗期间,所有患者均未发生白细胞减少、肝酶明显升高、过敏、血栓栓塞等严重不良反应。结论: 艾拉莫德联合托法替布治疗难治性中重度RA,可通过降低炎性指标改善患者的近期临床症状,且安全性良好。
中图分类号:
- R593.22
| 1 |
Smolen JS , Landewé RBM , Bijlsma JWJ , et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs: 2019 update[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2020, 79 (6): 685- 699.
doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2019-216655 |
| 2 | de Hair MJH , Jacobs JWG , Schoneveld JLM , et al. Difficult-to-treat rheumatoid arthritis: An area of unmet clinical need[J]. Rheumatology (Oxford), 2018, 57 (7): 1135- 1144. |
| 3 |
Buch MH . Defining refractory rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2018, 77 (7): 966- 969.
doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2017-212862 |
| 4 |
Smolen JS , Aletaha D , Mcinnes IB . Rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Lancet, 2016, 388 (10055): 2023- 2038.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30173-8 |
| 5 |
Aletaha D , Neogi T , Silman AJ , et al. 2010 rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: An American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism Collaborative initiative[J]. Arthritis Rheum, 2010, 62 (9): 2569- 2581.
doi: 10.1002/art.27584 |
| 6 |
Wu D , Luo Y , Li T , et al. Systemic complications of rheumatoid arthritis: Focus on pathogenesis and treatment[J]. Front Immunol, 2022, 13, 1051082.
doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1051082 |
| 7 |
Sun X , Li R , Cai Y , et al. Clinical remission of rheumatoid arthritis in a multi center real-world study in Asia-Pacific region[J]. Lancet Reg Health West Pac, 2021, 15, 100240.
doi: 10.1016/j.lanwpc.2021.100240 |
| 8 | 李宏超, 徐丽玲, 苏茵. 难治性类风湿关节炎诊治探讨[J]. 中华风湿病学杂志, 2019, 23 (10): 689- 693. |
| 9 |
Nagy G , Roodenrijs NMT , Welsing PM , et al. EULAR definition of difficult-to-treat rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2021, 80 (1): 31- 35.
doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-217344 |
| 10 |
Xie S , Li S , Tian J , et al. Iguratimod as a new drug for rheumatoid arthritis: Current landscape[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2020, 11, 73.
doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00073 |
| 11 | Xu Y , Zhu Q , Song J , et al. Regulatory effect of iguratimod on the balance of Th subsets and inhibition of inflammatory cytokines in patients with rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Mediators Inflamm, 2015, 2015, 356040. |
| 12 | Wen L , Jiang W , Zhou M , et al. Effect of combined application of iguratimod in the treatment of active rheumatoid arthritis on bone metabolism, Th17 cells and Treg cells[J]. Am J Transl Res, 2021, 13 (3): 1676- 1684. |
| 13 |
Liu S , Song LP , Li RB , et al. Iguratimod promotes transformation of mononuclear macrophages in elderly patients with rheumatoid arthritis by nuclear factor-κB pathway[J]. World J Clin Cases, 2021, 9 (10): 2181- 2191.
doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i10.2181 |
| 14 |
Li CH , Ma ZZ , Jian LL , et al. Iguratimod inhibits osteoclastoge-nesis by modulating the RANKL and TNF-α signaling pathways[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2021, 90, 107219.
doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107219 |
| 15 |
Kondo N , Kuroda T , Kobayashi D . Cytokine networks in the pa-thogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22 (20): 10922.
doi: 10.3390/ijms222010922 |
| 16 | Malemud CJ . The role of the JAK/STAT signal pathway in rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis, 2018, 10 (5/6): 117- 127. |
| 17 | 疏金玲, 张玲玲, 魏伟. 酪氨酸激酶抑制剂治疗类风湿关节炎研究进展[J]. 中国药理学与毒理学杂志, 2020, 34 (9): 713- 720. |
| 18 |
Puigdevall L , Michiels C , Stewardson C , et al. JAK/STAT: Why choose a classical or an alternative pathway when you can have both?[J]. J Cell Mol Med, 2022, 26 (7): 1865- 1875.
doi: 10.1111/jcmm.17168 |
| 19 | 戴冰冰, 刘佳丽, 李宁宁, 等. 托法替布治疗难治性中重度类风湿关节炎的疗效及安全性[J]. 实用临床医药杂志, 2022, 26 (11): 122- 126. |
| 20 |
Zheng N , Guo C , Wu R . Iguratimod is effective in refractory rheumatoid arthritis patients with inadequate response to metho-trexate-cyclosporin A-hydroxychloroquine-prednisone[J]. Scand J Rheumatol, 2018, 47 (5): 422- 424.
doi: 10.1080/03009742.2017.1376109 |
| 21 |
Mizutani S , Kodera H , Sato Y , et al. Clinical effectiveness of iguratimod based on real-world data of patients with rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Clin Rheumatol, 2021, 40 (1): 123- 132.
doi: 10.1007/s10067-020-05208-y |
| 22 | Inoue A , Nozaki Y , Hirooka Y , et al. The effectiveness and retention rate of iguratimod in Japanese rheumatoid arthritis patients with/without methotrexate in daily medical care[J]. Life (Basel), 2020, 10 (11): 261. |
| 23 | Ouyang D , Ma YZ , Zou J , et al. Effectiveness and safety of iguratimod monotherapy or combined with methotrexate in treating rheumatoid arthritis: A aystematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2022, 13, 911810. |
| 24 | Smolen JS , Landewe R , Breedveld FC , et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 2013 update[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2014, 73 (3): 492- 509. |
| 25 | Angelini J , Talotta R , Roncato R , et al. JAK-inhibitors for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: A focus on the present and an outlook on the future[J]. Biomolecules, 2020, 10 (7): 1002. |
| 26 | 张春燕, 范小冬, 秦元, 等. JAK抑制剂托法替布治疗类风湿性关节炎效果的Meta分析[J]. 第三军医大学学报, 2018, 40 (6): 543- 550. |
| 27 | Sands BE , Taub PR , Armuzzi A , et al. Tofacitinib treatment is associated with modest and reversible increases in serum lipids in patients with ulcerative colitis[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2020, 18 (1): 123- 132.e3. |
| 28 | Taylor PC , Kremer JM , Emery P , et al. Lipid profile and effect of statin treatment in pooled phase Ⅱ and phase Ⅲ baricitinib studies[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2018, 77 (7): 988- 995. |
| [1] | 刘东武, 陈杰, 高明利, 于静. 类风湿关节炎伴发淋巴结Castleman样病理改变1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 928-931. |
| [2] | 刘佐相,陈晓薇,赵厚宇,詹思延,孙凤. 真实世界中2型糖尿病患者二甲双胍联用西格列汀的心血管安全性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 424-430. |
| [3] | 黄会娜,赵静,赵祥格,白自然,李霞,王冠. 乳酸对类风湿关节炎患者外周血CD4+T细胞亚群的调控作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 519-525. |
| [4] | 何珊,陈炘,程琦,朱灵江,张培玉,童淑婷,薛静,杜燕. 托法替布通过JAK/STAT3通路抑制肺成纤维细胞向肌成纤维细胞转化[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 505-511. |
| [5] | 汤晓菲,李永红,丁秋玲,孙卓,张阳,王育梅,田美伊,刘坚. 类风湿关节炎患者下肢深静脉血栓发病率及危险因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 279-283. |
| [6] | 李文菁,张保宙,李恒,赖良鹏,杜辉,孙宁,龚晓峰,李莹,王岩,武勇. 胫距跟融合治疗终末期踝和后足病变的中短期临床结果[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 299-306. |
| [7] | 吴琦,蔡月明,何娟,黄文蒂,王庆文. 血脂异常与类风湿关节炎肺间质病变的相关性分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 982-992. |
| [8] | 张警丰,金银姬,魏慧,姚中强,赵金霞. 体重指数与类风湿关节炎临床特征的相关性分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 993-999. |
| [9] | 薛蔚,董樑,钱宏阳,费笑晨. 前列腺癌新辅助治疗与辅助治疗的现状及进展[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 775-780. |
| [10] | 邱敏,宗有龙,王滨帅,杨斌,徐楚潇,孙争辉,陆敏,赵磊,卢剑,刘承,田晓军,马潞林. 腹腔镜肾部分切除术治疗中高复杂程度肾肿瘤的效果[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 833-837. |
| [11] | 金银姬,孙琳,赵金霞,刘湘源. 血清IgA型抗鼠科肉瘤病毒癌基因同源物B1抗体在类风湿关节炎中的意义[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 631-635. |
| [12] | 王磊,韩天栋,江卫星,李钧,张道新,田野. 主动迁移技术与原位碎石技术在输尿管软镜治疗1~2 cm输尿管上段结石中的安全性和有效性比较[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 553-557. |
| [13] | 蔡文心,李仕成,刘一鸣,梁如玉,李静,郭建萍,胡凡磊,孙晓麟,李春,刘栩,叶华,邓立宗,李茹,栗占国. 类风湿关节炎临床分层及其特征的横断面研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1068-1073. |
| [14] | 程昉,杨邵英,房星星,王璇,赵福涛. CCL28-CCR10通路在类风湿关节炎单核细胞迁移中的作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1074-1078. |
| [15] | 刘蕊,赵金霞,闫良. 类风湿关节炎合并下肢静脉血栓患者的临床特点[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1079-1085. |
|
||