北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (1): 32-38. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2024.01.006
基于转录组测序探索口腔扁平苔藓局部激素治疗敏感性相关分子特征
- 北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院口腔黏膜科,国家口腔医学中心,国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心,口腔生物材料和数字诊疗装备国家工程研究中心,口腔数字医学北京市重点实验室,国家卫生健康委员会口腔医学计算机应用工程技术研究中心,国家药品监督管理局口腔生物材料重点实验室,北京 100081
Detection of molecular affecting sensitivity to local glucocorticoid therapy in oral lichen planus through transcriptome sequencing
Xiaomeng REN,Kaiyi LI,Chunlei LI*( )
)
- Department of Oral Medicine, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Center of Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Research Center of Oral Biomaterials and Digital Medical Devices & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology & NHC Research Center of Engineering and Technology for Computerized Dentistry & NMPA Key Laboratory for Dental Materials, Beijing 100081, China
摘要:
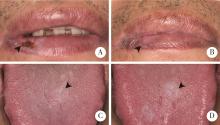
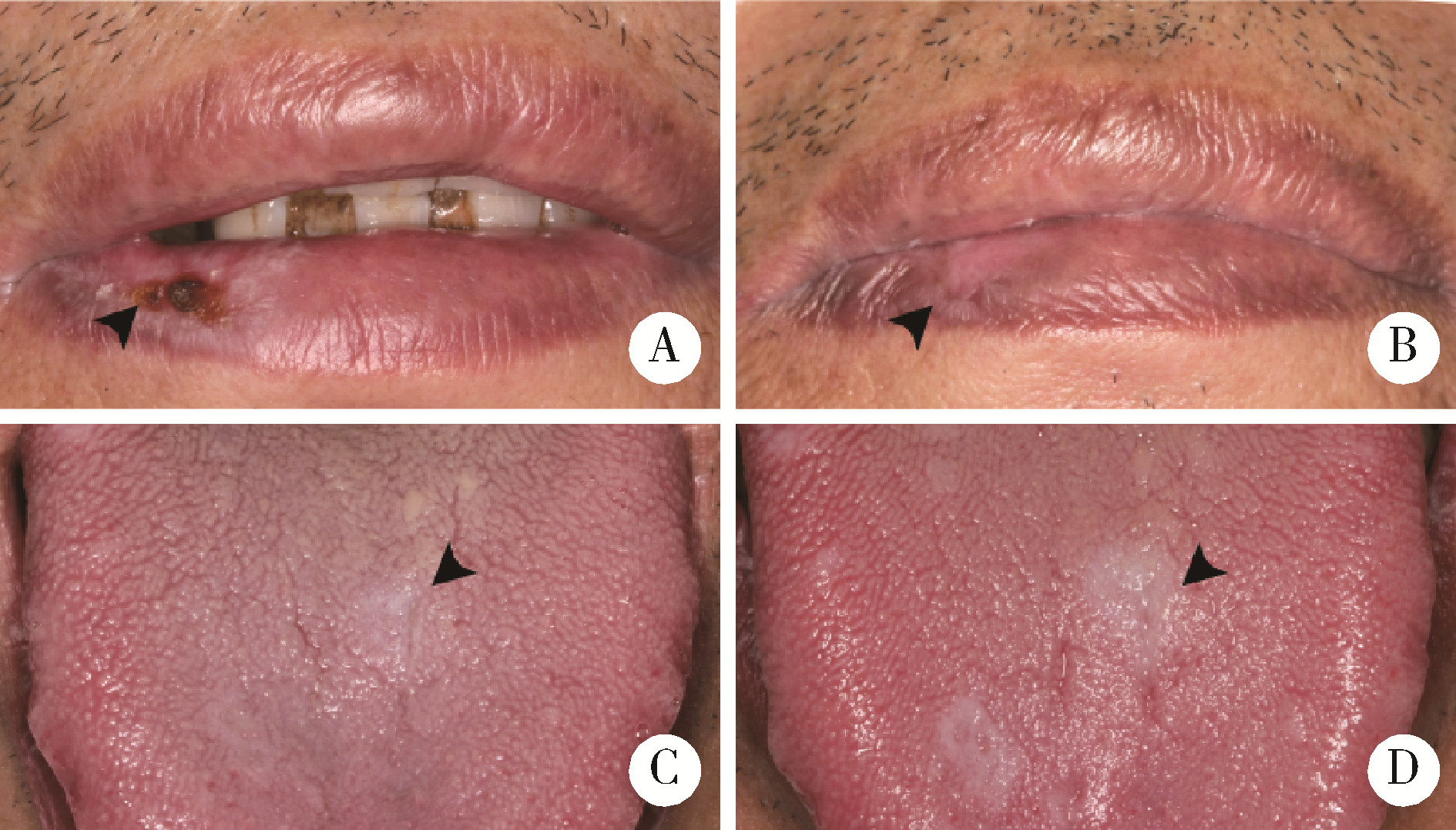
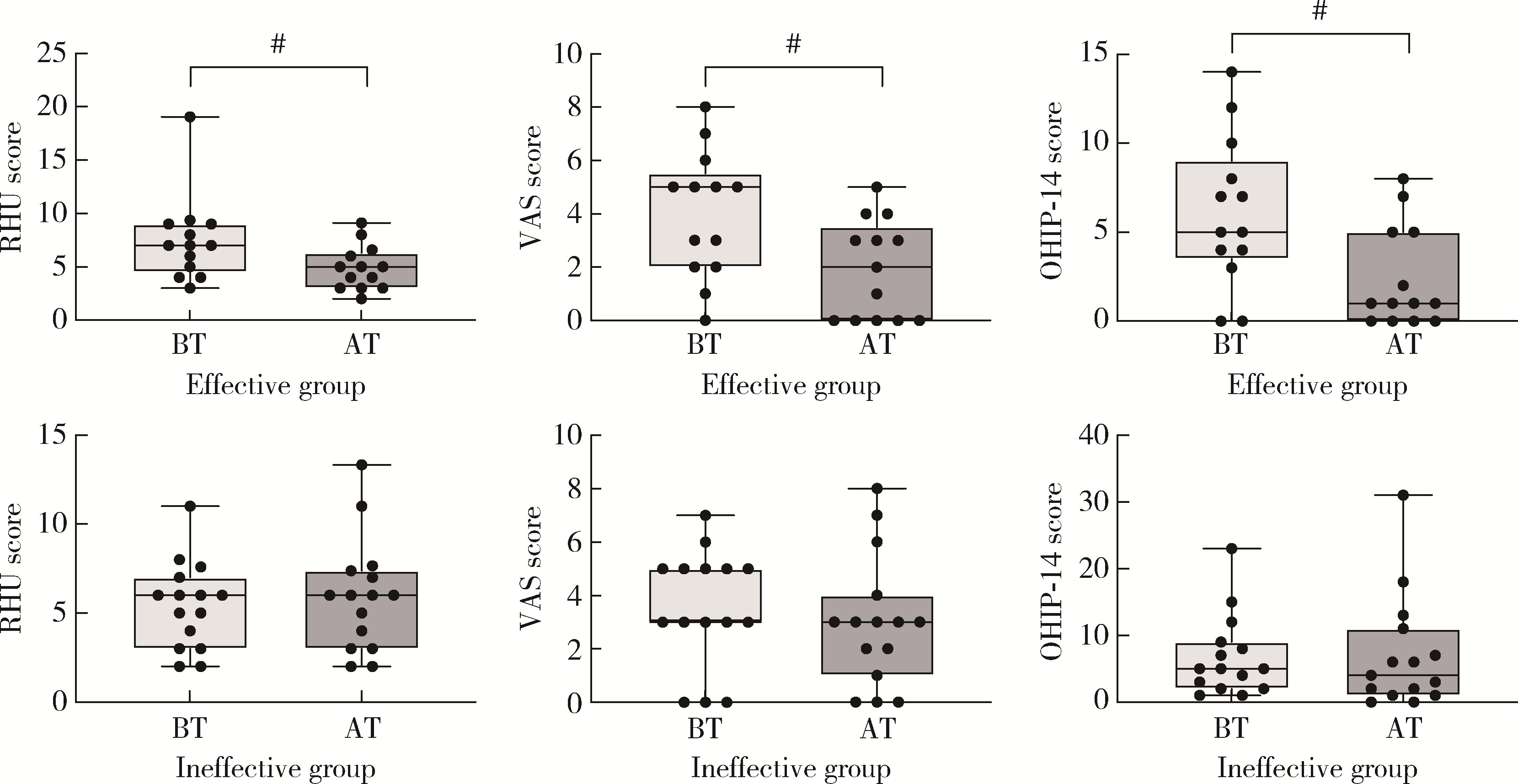
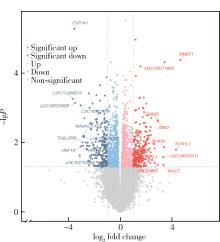
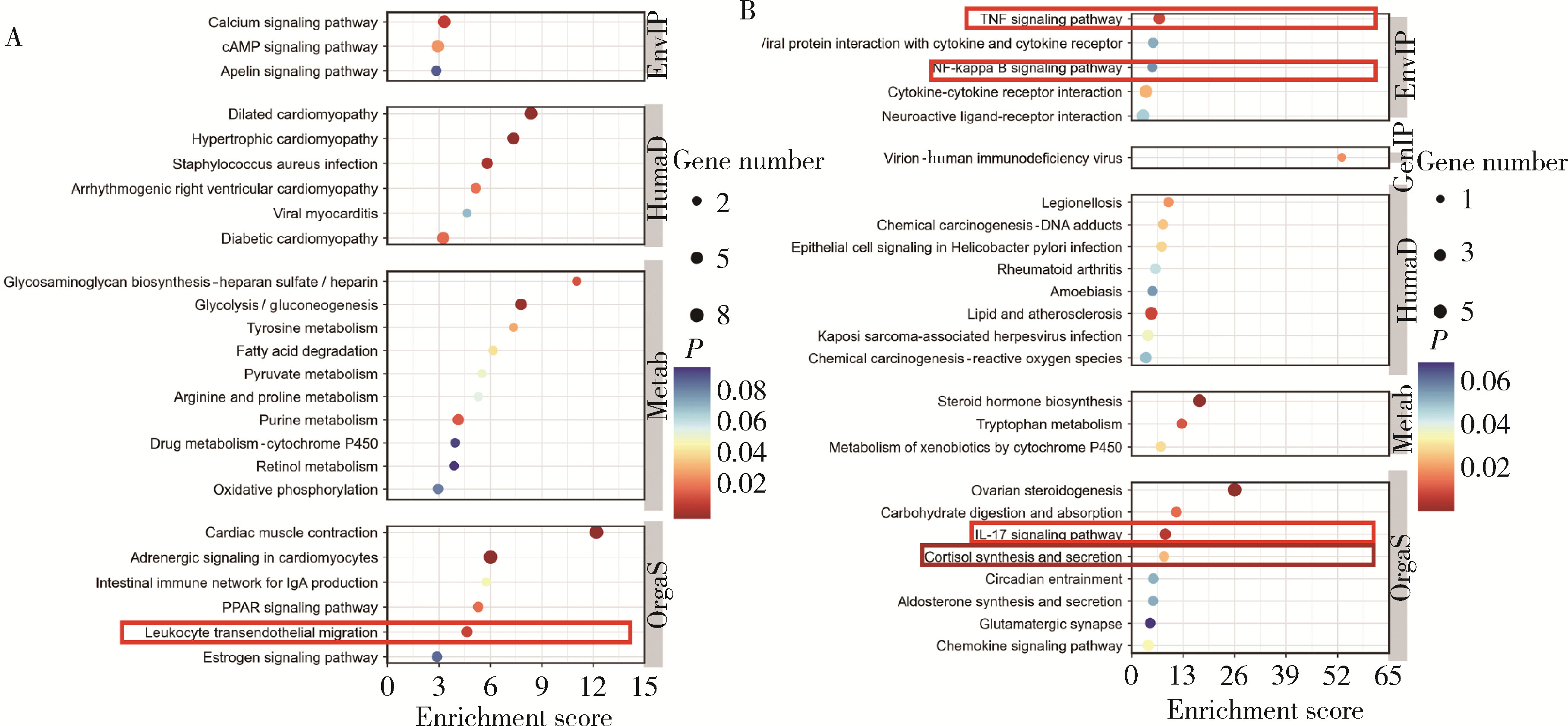
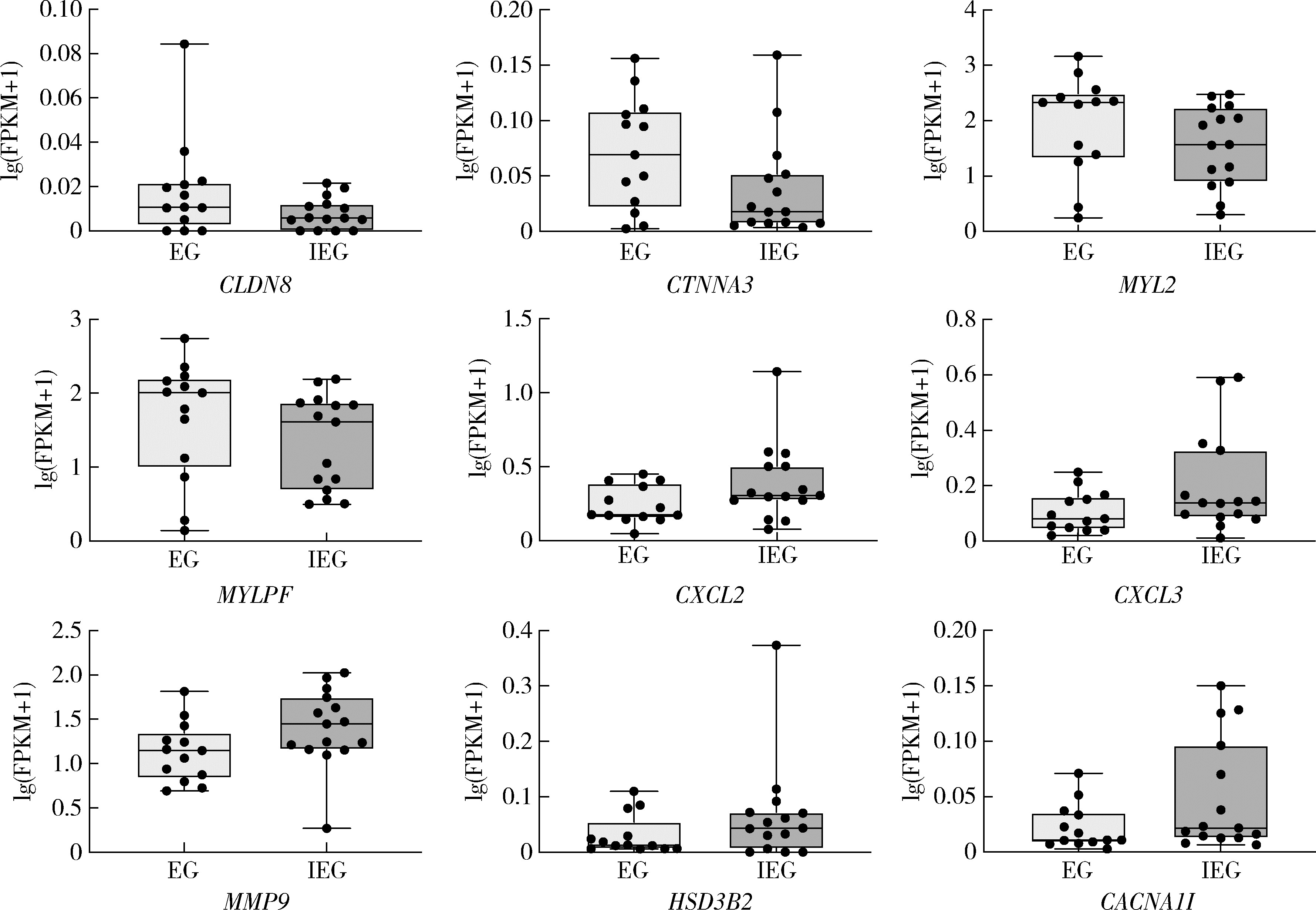
目的: 探索影响口腔扁平苔藓(oral lichen planus, OLP)局部糖皮质激素治疗敏感性相关分子。方法: 本研究为前瞻性研究,纳入2019年11月至2023年3月就诊于北京大学口腔医院口腔黏膜科28例有症状的OLP患者,采用0.1 g/L(mg/mL)地塞米松局部涂擦,每日3次,每次1 min,治疗4周后根据其临床效果(体征记分、疼痛症状记分、口腔健康程度量表)将OLP分为激素有效组和激素无效组。治疗前收集受试者口腔黏膜组织,提取组织总核糖核酸(ribonucleic acid, RNA)后进行转录组测序。对测序获得的基因表达数据,使用R软件中的DESeq2包进行差异分析,基于超几何分布算法对差异表达基因(differentially expressed genes, DEGs)进行京都基因和基因组百科全书(Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes, KEGG)通路富集分析,从而筛选可能影响局部地塞米松治疗敏感性的相关分子。结果: 28例OLP患者经过局部地塞米松治疗4周后,13例患者在治疗前后客观体征记分分别为7.0(4.5,9.0)和5.0(3.0,6.3),疼痛症状记分分别为5.0(2.0,5.5)和2.0(0.0,3.5),口腔健康影响程度分别为5.0(3.5,9.0)和1.0(0.0,5.0),均显著降低(P<0.01)(有效组),15例患者治疗后上述指标与治疗前差异无统计学意义(无效组),两组患者的一般情况及治疗前疾病严重程度差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。两组患者转录组学测序共鉴定出499个DEGs,其中有效组中274个基因上调,225个基因下调。KEGG富集分析显示有效组上调基因显著富集于白细胞穿血管内皮迁移通路(CLDN8、CTNNA3、MYL2、MYLPF),而下调基因显著富集于肿瘤坏死因子(tumor necrosis factor, TNF)、白介素-17(interleukin-17, IL-17)、核因子κB(nuclear factor kappa B, NF-κB)及皮质醇合成和分泌信号通路。结论: CLDN8、CTNNA3、MYL2、MYLPF高表达的OLP患者对局部糖皮质激素治疗效果较好,而对TNF、IL-17、NF-κB等炎症通路相关基因及皮质醇合成分泌相关基因高表达的患者治疗效果较差。
中图分类号:
- R781.5
| 1 |
Li C , Tang X , Zheng X , et al. Global prevalence and incidence estimates of oral lichen planus: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. JAMA Dermatol, 2020, 156 (2): 172- 181.
doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2019.3797 |
| 2 |
Li JW , Li KY , Chan BWA , et al. Rate of malignant transformation differs based on diagnostic criteria for oral lichenoid conditions: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 24 277 patients[J]. Cancers (Basel), 2023, 15 (9): 2537.
doi: 10.3390/cancers15092537 |
| 3 |
Zhu ZD , Ren XM , Zhou MM , et al. Salivary cytokine profile in patients with oral lichen planus[J]. J Dent Sci, 2022, 17 (1): 100- 105.
doi: 10.1016/j.jds.2021.06.013 |
| 4 |
Ioannides D , Vakirlis E , Kemeny L , et al. European S1 guidelines on the management of lichen planus: A cooperation of the european dermatology forum with the european academy of dermatology and venereology[J]. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol, 2020, 34 (7): 1403- 1414.
doi: 10.1111/jdv.16464 |
| 5 |
中华口腔医学会口腔黏膜病学专业委员会, 中华口腔医学会中西医结合专业委员会. 口腔扁平苔藓诊疗指南(修订版)[J]. 中华口腔医学杂志, 2022, 57 (2): 115- 121.
doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112144-20211115-00505 |
| 6 | 左雯鑫, 李晓宇, 蔡淦英, 等. 他克莫司含漱液治疗糜烂型口腔扁平苔藓的随机单盲对照研究[J]. 上海口腔医学, 2013, 22 (6): 708- 710. |
| 7 |
Jajarm HH , Falaki F , Mahdavi O . A comparative pilot study of low intensity laser versus topical corticosteroids in the treatment of erosive-atrophic oral lichen planus[J]. Photomed Laser Surg, 2011, 29 (6): 421- 425.
doi: 10.1089/pho.2010.2876 |
| 8 |
Qing M , Zhou Y , Peng J , et al. The interleukin-6 family in tissues is closely related to the clinical outcomes of oral lichen planus[J]. J Oral Pathol Med, 2023, 52 (2): 161- 168.
doi: 10.1111/jop.13366 |
| 9 |
van der Meij EH , van der Waal I . Lack of clinicopathologic correlation in the diagnosis of oral lichen planus based on the presently available diagnostic criteria and suggestions for modifications[J]. J Oral Pathol Med, 2003, 32 (9): 507- 512.
doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0714.2003.00125.x |
| 10 |
Wu Y , Xu H , Wang Y , et al. An improved scoring system for monitoring oral lichen planus: A preliminary clinical study[J]. Oral Dis, 2023, 29 (8): 3337- 3345.
doi: 10.1111/odi.14273 |
| 11 |
Hashem AS , Issrani R , Elsayed TEE , et al. Topical hyaluronic acid in the management of oral lichen planus: A comparative study[J]. J Investig Clin Dent, 2019, 10 (2): e12385.
doi: 10.1111/jicd.12385 |
| 12 |
Vilar-Villanueva M , Gándara-Vila P , Blanco-Aguilera E , et al. Psychological disorders and quality of life in oral lichen planus patients and a control group[J]. Oral Dis, 2019, 25 (6): 1645- 1651.
doi: 10.1111/odi.13106 |
| 13 |
中华口腔医学会口腔黏膜病专业委员会. 口腔扁平苔藓(萎缩型、糜烂型)疗效评价标准(试行)[J]. 中华口腔医学杂志, 2005, 40 (2): 92- 93.
doi: 10.3760/j.issn:1002-0098.2005.02.002 |
| 14 |
Bindakhil M , Akintoye S , Corby P , et al. Influence of topical corticosteroids on malignant transformation of oral lichen planus[J]. J Oral Pathol Med, 2022, 51 (2): 188- 193.
doi: 10.1111/jop.13257 |
| 15 |
Chung HS , Kim Y , Oh SJ , et al. A synthetic compound, 4-acetyl-3-methyl-6-(3, 4, 5-trimethoxyphenyl)pyrano[3, 4-c]pyran-1, 8-dione, ameliorates ovalbumin-induced asthma[J]. Bioorg Med Chem, 2013, 21 (21): 6359- 6365.
doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2013.08.045 |
| 16 |
Chen YT , Li J , Chang JN , et al. Transcriptomic analysis of world trade center particulate matter-induced pulmonary inflammation and drug treatments[J]. Environ Int, 2023, 177, 108027.
doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2023.108027 |
| 17 | Matos Leitão M , Euclides Silva-Filho S , Arena AC , et al. Antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory properties of aqueous extract obtained from serjania marginata casar leaves[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2023, 304, 116018. |
| 18 |
Valdez R , Cavinder CA , Varner DD , et al. Dexamethasone downregulates expression of several genes encoding orphan nuclear receptors that are important to steroidogenesis in stallion testes[J]. J Biochem Mol Toxicol, 2019, 33 (6): e22309.
doi: 10.1002/jbt.22309 |
| 19 |
Paulusová V , Laco J , Drízhal I , et al. Expression of matrix metalloproteinase 9 in patients with oral lichen planus[J]. Acta Medica (Hradec Kralove), 2012, 55 (1): 23- 26.
doi: 10.14712/18059694.2015.70 |
| 20 | Wang H , Guan X , Luo Z , et al. The association and potentially destructive role of Th9/IL-9 is synergistic with Th17 cells by elevating mmp9 production in local lesions of oral lichen planus[J]. J Oral Pathol Med, 2018, 47 (4): 425- 433. |
| 21 | Kylmäniemi M , Oikarinen A , Oikarinen K , et al. Effects of dexamethasone and cell proliferation on the expression of matrix metalloproteinases in human mucosal normal and malignant cells[J]. J Dent Res, 1996, 75 (3): 919- 926. |
| 22 | Villa A , Sankar V , Bassani G , et al. Dexamethasone solution and dexamethasone in mucolox for the treatment of oral lichen planus: A preliminary study[J]. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol, 2020, 129 (6): 585- 590. |
| [1] | 朱正达,高岩,何汶秀,方鑫,刘洋,魏攀,闫志敏,华红. 红色诺卡氏菌细胞壁骨架治疗糜烂型口腔扁平苔藓的疗效及安全性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(5): 964-969. |
| [2] | 刘洋,高岩,陈学杰,华红. 脱落细胞DNA 定量分析在口腔潜在恶性疾病诊断中的准确性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(1): 16-20. |
| [3] | 李纯青, 王东信, 程彤, 郑雪宜. 近期上呼吸道感染史对儿童围术期呼吸系统不良事件的影响:前瞻性队列研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(5): 814-818. |
| [4] | 郭雨思,李硕,吕鸣樾,杨迪,华红. 口腔扁平苔藓患者C型行为特征分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(1): 120-124. |
| [5] | 姚林, 张雷, 范宇, 张政, 徐燕鹏, 刘茗洁, 何志嵩, 龚侃, 李学松, 张争, 张崔健, 周利群. 前瞻随机对照研究:新技术对硬性膀胱镜患者舒适度的提高[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2014, 46(4): 635-637. |
|
||