北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (3): 375-383. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2024.03.001
• 论著 • 下一篇
短期大气颗粒物暴露和MTNR1B基因多态性对甘油三酯-葡萄糖指数影响的家系研究
郭煌达1,彭和香1,王斯悦1,侯天姣1,李奕昕1,章涵宇1,王梦莹2,3,武轶群1,3,秦雪英1,3,唐迅1,3,李劲1,3,陈大方1,3,胡永华1,3,吴涛1,3,*( )
)
- 1. 北京大学公共卫生学院流行病与卫生统计学系, 北京 100191
2. 北京大学公共卫生学院营养与食品卫生学系, 北京 100191
3. 重大疾病流行病学教育部重点实验室(北京大学), 北京 100191
A ssociations of short-term ambient particulate matter exposure and MTNR1B gene with triglyceride-glucose index: A family-based study
Huangda GUO1,Hexiang PENG1,Siyue WANG1,Tianjiao HOU1,Yixin LI1,Hanyu ZHANG1,Mengying WANG2,3,Yiqun WU1,3,Xueying QIN1,3,Xun TANG1,3,Jing LI1,3,Dafang CHEN1,3,Yonghua HU1,3,Tao WU1,3,*( )
)
- 1. Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, Peking University School of Public Health, Beijing 100191, China
2. Department of Nutrition and Food Hygiene, Peking University School of Public Health, Beijing, 100191, China
3. Key Laboratory of Epidemiology of Major Diseases(Peking University), Ministry of Education, Beijing 100191, China
摘要:
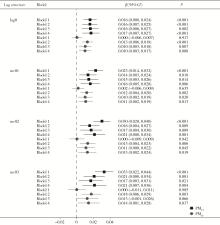
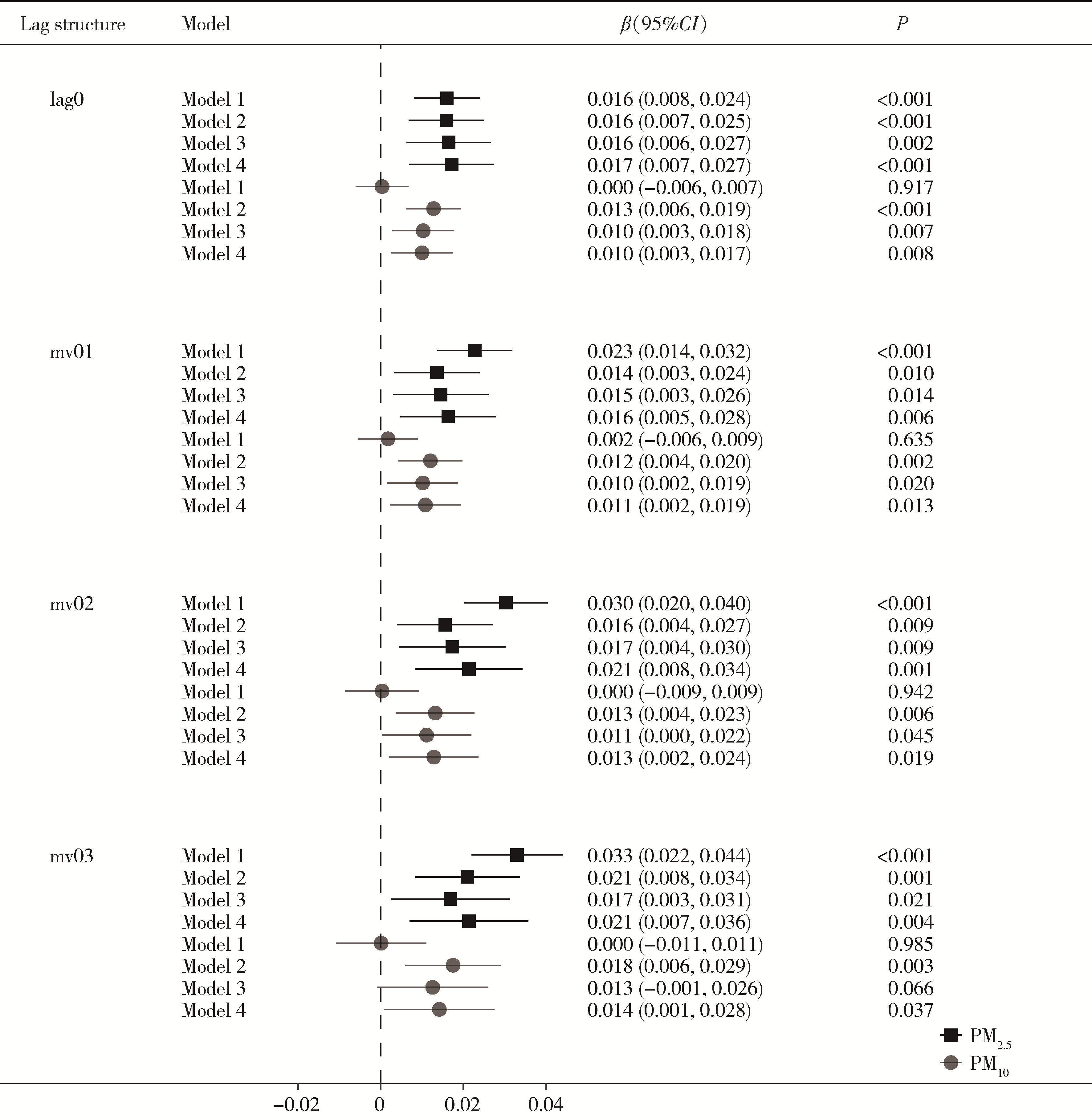
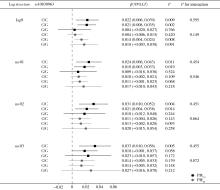
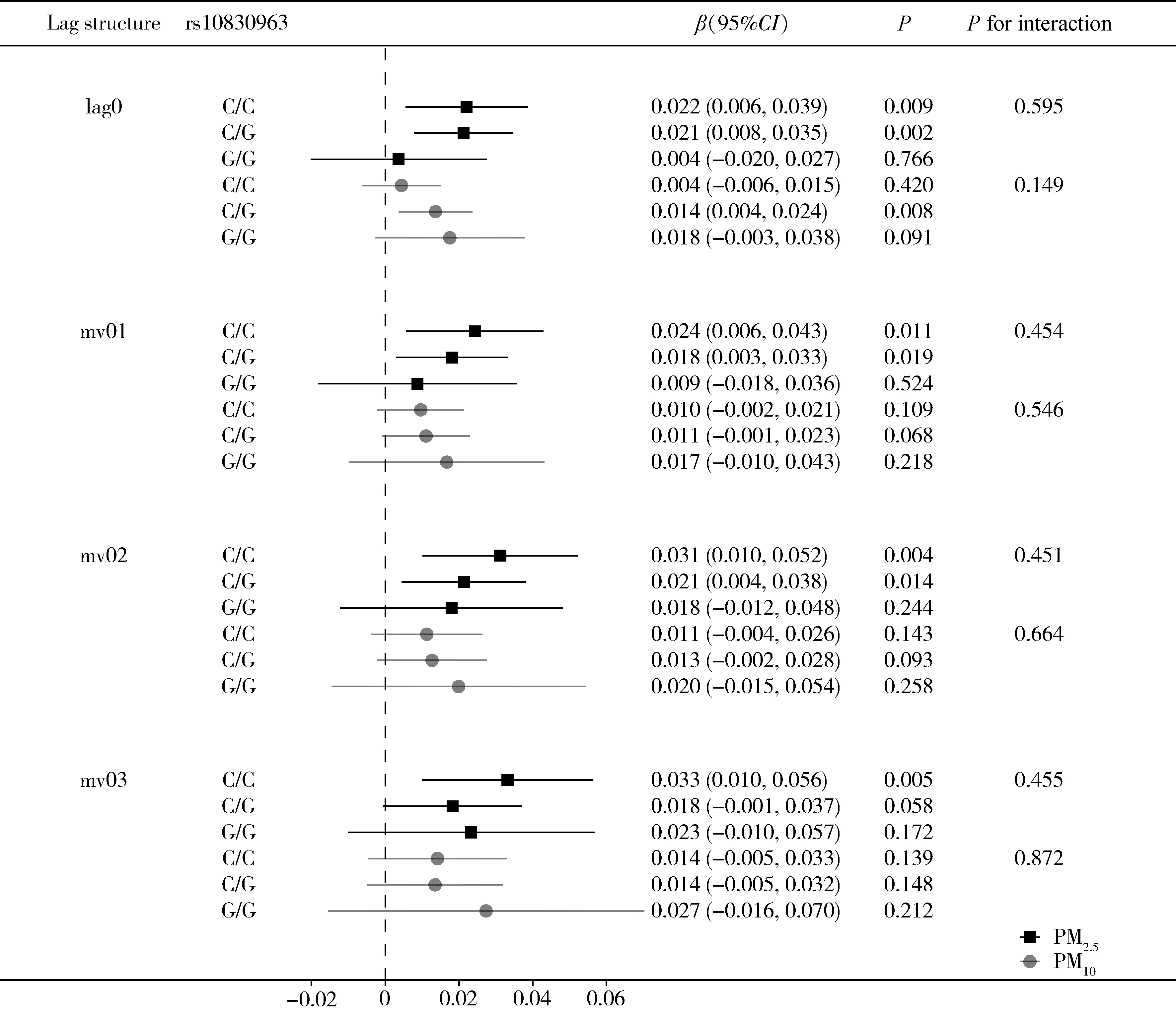
目的: 利用北京房山家系队列研究资料, 探索短期大气颗粒物(particulate matter, PM)暴露和褪黑素受体1B(melatonin receptor 1 B, MTNR1B)基因多态性对甘油三酯-葡萄糖(triglyceride-glucose, TyG)指数的影响。方法: 纳入来自北京市房山区9个乡镇的先证者及其亲属作为研究对象, 使用混合线性模型评估短期PM暴露和MTNR1B基因rs10830963位点多态性与TyG指数的关联,进一步利用最大似然法进行基因-环境交互作用分析, 探索rs10830963位点多态性在PM与TyG指数关联中的效应修饰作用。结果: 共纳入来自2 084个家系的4 395名参与者,研究对象平均年龄(58.98 +8.68)岁, 女性占比53.90%。关联分析结果显示, PM2.5浓度每升高10 μg/m3, TyG指数升高0.017(95% Cl: 0.007~ 0.027), 而PM10。每升高10 μg/m3, TyG指数升高0.010(95% CI: O. 003 ~0.017), 且关联均存在滞后效应。此外, rs10830963位点与TyG指数存在阳性关联。每增加一个风险等位基因G, TyG指数升高0.040(95% CI: 0. 004 ~0.076)。与CC基因型携带者相比, GG基因型携带者的TyG指数高0.079(95% CI: 0. 005 ~0. 152)。未发现该位点多态性与PM暴露的交互作用具有统计学意义。结论: PM2.5和PM10。短期暴露与较高的TyG指数相关, MTNR1B基因的rs10830963位点G等位基因与TyG指数升高相关联。
中图分类号:
- R122.2
| 1 |
Xiao D , Sun H , Chen L , et al. Assessment of six surrogate insulin resistance indexes for predicting cardiometabolic multimorbidity incidence in Chinese middle-aged and older populations: Insights from the China health and retirement longitudinal study[J]. Diabetes Metab Res Rev, 2024, 40 (1): e3764.
doi: 10.1002/dmrr.3764 |
| 2 |
Guerrero-Romero F , Simental-Mendía LE , González-Ortiz M , et al. The product of triglycerides and glucose, a simple measure of insulin sensitivity. Comparison with the euglycemic-hyperinsulinemic clamp[J]. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2010, 95 (7): 3347- 3351.
doi: 10.1210/jc.2010-0288 |
| 3 |
Zhang J , Yin B , Xi Y , et al. Triglyceride-glucose index is a risk factor for breast cancer in China: A cross-sectional study[J]. Lipids Health Dis, 2024, 23 (1): 29.
doi: 10.1186/s12944-024-02008-0 |
| 4 |
Hao B , Lyu L , Xu J , et al. The relationship between triglyceride-glucose index and prospective key clinical outcomes in patients hospitalised for coronary artery disease[J]. Cardiovasc Diabetol, 2024, 23 (1): 40.
doi: 10.1186/s12933-024-02132-2 |
| 5 |
Su W , Wang J , Chen K , et al. A higher TyG index level is more likely to have enhanced incidence of T2DM and HTN comorbidity in elderly Chinese people: A prospective observational study from the reaction study[J]. Diabetol Metab Syndr, 2024, 16 (1): 29.
doi: 10.1186/s13098-024-01258-3 |
| 6 | Dong W , Gong Y , Zhao J , et al. A combined analysis of TyG index, SII index, and SIRI index: Positive association with CHD risk and coronary atherosclerosis severity in patients with NAFLD[J]. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne), 2023, 14, 1281839. |
| 7 |
Peng H , Wang M , Wang S , et al. KCNQ1 rs2237892 polymorphism modify the association between short-term ambient particulate matter exposure and fasting blood glucose: A family-based study[J]. Sci Total Environ, 2023, 876, 162820.
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.162820 |
| 8 |
Wu Y , Tian Y , Wang M , et al. Short-term exposure to air pollution and its interaction effects with two ABO SNPs on blood lipid levels in northern China: A family-based study[J]. Chemosphere, 2020, 249, 126120.
doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126120 |
| 9 | Wang S , Wang M , Peng H , et al. Synergism of cell adhesion re-gulatory genes and instant air pollutants on blood pressure elevation[J]. Chemosphere, 2023, 312 (Pt 1): 136992. |
| 10 | Guo H , Wang M , Ye Y , et al. Short-term exposure to nitrogen dioxide modifies genetic predisposition in blood lipid and fasting plasma glucose: A pedigree-based study[J]. Biology (Basel), 2023, 12 (12): 1470. |
| 11 |
Pan M , Liu F , Zhang K , et al. Independent and interactive associations between greenness and ambient pollutants on novel glycolipid metabolism biomarkers: A national repeated measurement study[J]. Environ Res, 2023, 233, 116393.
doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2023.116393 |
| 12 | Liu F , Chen G , Huo W , et al. Associations between long-term exposure to ambient air pollution and risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Environ Pollut, 2019, 252 (Pt B): 1235- 1245. |
| 13 |
Prokopenko I , Langenberg C , Florez JC , et al. Variants in MTNR1B influence fasting glucose levels[J]. Nat Genet, 2009, 41 (1): 77- 81.
doi: 10.1038/ng.290 |
| 14 |
Lyssenko V , Nagorny CL , Erdos MR , et al. Common variant in MTNR1B associated with increased risk of type 2 diabetes and impaired early insulin secretion[J]. Nat Genet, 2009, 41 (1): 82- 88.
doi: 10.1038/ng.288 |
| 15 |
Prokopenko I , Poon W , Mägi R , et al. A central role for GRB10 in regulation of islet function in man[J]. PLoS Genet, 2014, 10 (4): e1004235.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004235 |
| 16 |
Garaulet M , Lopez-Minguez J , Dashti HS , et al. Interplay of dinner timing and MTNR1B type 2 diabetes risk variant on glucose tolerance and insulin secretion: A randomized crossover trial[J]. Diabetes Care, 2022, 45 (3): 512- 519.
doi: 10.2337/dc21-1314 |
| 17 | Xu XH , Kou LC , Wang HM , et al. Genetic polymorphisms of melatonin receptors 1A and 1B may result in disordered lipid metabolism in obese patients with polycystic ovary syndrome[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2019, 19 (3): 2220- 2230. |
| 18 |
Wang M , Wang S , Wang X , et al. Carotid intima-media thickness, genetic risk, and ischemic stroke: A family-based study in rural China[J]. Int J Environ Res Public Health, 2020, 18 (1): 119.
doi: 10.3390/ijerph18010119 |
| 19 |
Tian Y , Liu H , Zhao Z , et al. Association between ambient air pollution and daily hospital admissions for ischemic stroke: A nationwide time-series analysis[J]. PLoS Med, 2018, 15 (10): e1002668.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1002668 |
| 20 |
Zhan M , Li Z , Li X , et al. Effect of short-term ambient PM2.5 exposure on fasting blood glucose levels: A longitudinal study among 47 471 people in eastern China[J]. Environ Pollut, 2021, 290, 117983.
doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2021.117983 |
| 21 |
Chen L , Zhou Y , Li S , et al. Air pollution and fasting blood glucose: A longitudinal study in China[J]. Sci Total Environ, 2016, 541, 750- 755.
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.09.132 |
| 22 |
Chen J , Wu L , Yang G , et al. The influence of PM2.5 exposure on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Life Sci, 2021, 270, 119135.
doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119135 |
| 23 |
Glencross DA , Ho TR , Camiña N , et al. Air pollution and its effects on the immune system[J]. Free Radic Biol Med, 2020, 151, 56- 68.
doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2020.01.179 |
| 24 |
Peng C , Bind MC , Colicino E , et al. Particulate air pollution and fasting blood glucose in nondiabetic individuals: Associations and epigenetic mediation in the normative aging study, 2000-2011[J]. Environ Health Perspect, 2016, 124 (11): 1715- 1721.
doi: 10.1289/EHP183 |
| 25 |
Ning R , Li Y , Du Z , et al. The mitochondria-targeted antioxidant MitoQ attenuated PM2.5-induced vascular fibrosis via regulating mitophagy[J]. Redox Biol, 2021, 46, 102113.
doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2021.102113 |
| 26 |
Sabatti C , Service SK , Hartikainen AL , et al. Genome-wide association analysis of metabolic traits in a birth cohort from a founder population[J]. Nat Genet, 2009, 41 (1): 35- 46.
doi: 10.1038/ng.271 |
| 27 |
Tuomi T , Nagorny CLF , Singh P , et al. Increased melatonin signaling is a risk factor for type 2 diabetes[J]. Cell Metab, 2016, 23 (6): 1067- 1077.
doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2016.04.009 |
| 28 |
Li C , Zhou Y , Qiao B , et al. Association between a melatonin receptor 1b genetic polymorphism and its protein expression in gestational diabetes mellitus[J]. Reprod Sci, 2019, 26 (10): 1382- 1388.
doi: 10.1177/1933719118765983 |
| 29 |
Garaulet M , Gómez-Abellán P , Rubio-Sastre P , et al. Common type 2 diabetes risk variant in MTNR1B worsens the deleterious effect of melatonin on glucose tolerance in humans[J]. Metabolism, 2015, 64 (12): 1650- 1657.
doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2015.08.003 |
| 30 |
Xia AY , Zhu H , Zhao ZJ , et al. Molecular mechanisms of the melatonin receptor pathway linking circadian rhythm to type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. Nutrients, 2023, 15 (6): 1406.
doi: 10.3390/nu15061406 |
| 31 |
Dubocovich ML , Delagrange P , Krause DN , et al. International union of basic and clinical pharmacology. LXXV. Nomenclature, classification, and pharmacology of G protein-coupled melatonin receptors[J]. Pharmacol Rev, 2010, 62 (3): 343- 380.
doi: 10.1124/pr.110.002832 |
| 32 | Mühlbauer E , Albrecht E , Bazwinsky-Wutschke I , et al. Melatonin influences insulin secretion primarily via MT(1) receptors in rat insulinoma cells (INS-1) and mouse pancreatic islets[J]. J Pineal Res, 2012, 52 (4): 446- 459. |
| 33 |
Stumpf I , Mühlbauer E , Peschke E . Involvement of the cGMP pathway in mediating the insulin-inhibitory effect of melatonin in pancreatic beta-cells[J]. J Pineal Res, 2008, 45 (3): 318- 327.
doi: 10.1111/j.1600-079X.2008.00593.x |
| [1] | 阎腾龙,胥嘉钰,陈田,杨鑫,王伟伟,周淑佩,牛丕业,贾光,夏交. 亚慢性PM2.5和O3共同暴露对大鼠鼻黏膜ATP总量及ATP酶活性的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 687-692. |
| [2] | 白枫,何倚帆,牛亚楠,杨若娟,曹静. 超细颗粒物对大鼠离体灌注心脏功能的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(2): 240-245. |
| [3] | 郑鸿尘,薛恩慈,王雪珩,陈曦,王斯悦,黄辉,江锦,叶莺,黄春兰,周筠,高文静,余灿清,吕筠,吴小玲,黄小明,曹卫华,严延生,吴涛,李立明. 基于大家系设计的静息心率与常见慢性病双表型遗传度估计[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(3): 432-437. |
| [4] | 楚梦天,董伟,迟锐,潘璐,李宏宇,胡大宇,杨玄,邓芙蓉,郭新彪. 高效空气过滤净化器对北京市冬季某区居民室内PM2.5及其组分的净化效果[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(3): 482-487. |
| [5] | 吴筱音,李国星,王旭英,梁凤超,潘小川. 北京市大气污染与呼吸系统疾病死亡的相关性——基于卫星遥感数据的时空分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(3): 409-417. |
| [6] | 曹宇,刘徽,张俊,黄克武,赵厚宇,杨羽,詹思延. 北京市颗粒物污染对慢性阻塞性肺疾病急性加重住院的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(3): 403-408. |
| [7] | 张怡,宋晓明,赵茜,王童,李丽娟,陈婕,徐洪兵,刘贝贝,孙晓燕,贺蓓,黄薇. 大气颗粒物及多环芳烃暴露与慢性阻塞性肺疾病患者全身性氧化应激水平[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(3): 394-402. |
| [8] | 范爱琴,冯金秋,刘伟,张敏佳,刘坦,周雅琳,许雅君. 槲皮素拮抗大气细颗粒物PM2.5对大鼠胚胎毒性的体外研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(3): 388-393. |
| [9] | 潘小川. 关注中国大气灰霾(PM2.5)对人群健康影响的新常态[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2015, 47(3): 377-379. |
| [10] | 易铁慈, 李建平. 超细颗粒物对心血管系统的不良影响及其机制[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2014, 46(6): 996-1000. |
| [11] | 倪洋, 涂星莹, 朱一丹, 郭新彪, 邓芙蓉. 北京市某地区冬季大气细颗粒物和超细颗粒物污染水平及影响因素分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2014, 46(3): 389-394. |
| [12] | 郭新彪, 邓芙蓉. 大气PM 2.5与健康:针对复杂系统的复杂科学研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2014, 46(3): 341-342. |
| [13] | 董凤鸣, 莫运政, 李国星, 胥美美, 潘小川. 大气颗粒物(PM10/PM 2.5)与人群循环系统疾病死亡关系的病例交叉研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2013, 45(03): 398-404. |
| [14] | 卢秀玲, 张馨如, 邓芙蓉, 郭新彪. 气管滴注大气可吸入颗粒物对大鼠的系统性氧化应激作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2011, 43(3): 352-355. |
| [15] | 王欣, 邓芙蓉, 吴少伟, 郑迎东, 孙秀明, 刘红, 郭新彪. 北京市某区大气可吸入颗粒物和细颗粒物对儿童肺功能的短期影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2010, 42(3): 340-344. |
|
||