北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (3): 424-430. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2024.03.008
真实世界中2型糖尿病患者二甲双胍联用西格列汀的心血管安全性
刘佐相1,2,陈晓薇1,2,赵厚宇1,2,詹思延1,2,3,*( ),孙凤1,2,4,*(
),孙凤1,2,4,*( )
)
- 1. 北京大学公共卫生学院流行病与卫生统计学系,北京 100191
2. 重大疾病流行病学教育部重点实验室(北京大学),北京 100191
3. 北京大学第三医院临床流行病学研究中心,北京 100191
4. 海南省真实世界数据研究院,海南琼海 571437
Cardiovascular safety of sitagliptin added to metformin in real world patients with type 2 diabetes
Zuoxiang LIU1,2,Xiaowei CHEN1,2,Houyu ZHAO1,2,Siyan ZHAN1,2,3,*( ),Feng SUN1,2,4,*(
),Feng SUN1,2,4,*( )
)
- 1. Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, Peking University School of Public Health, Beijing 100191, China
2. Key Laboratory of Epidemiology of Major Diseases (Peking University), Ministry of Education, Beijing 100191, China
3. Clinical Epidemiology Research Center, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
4. Hainan Institute of Real World Data, Qionghai 571437, Hainan, China
摘要:
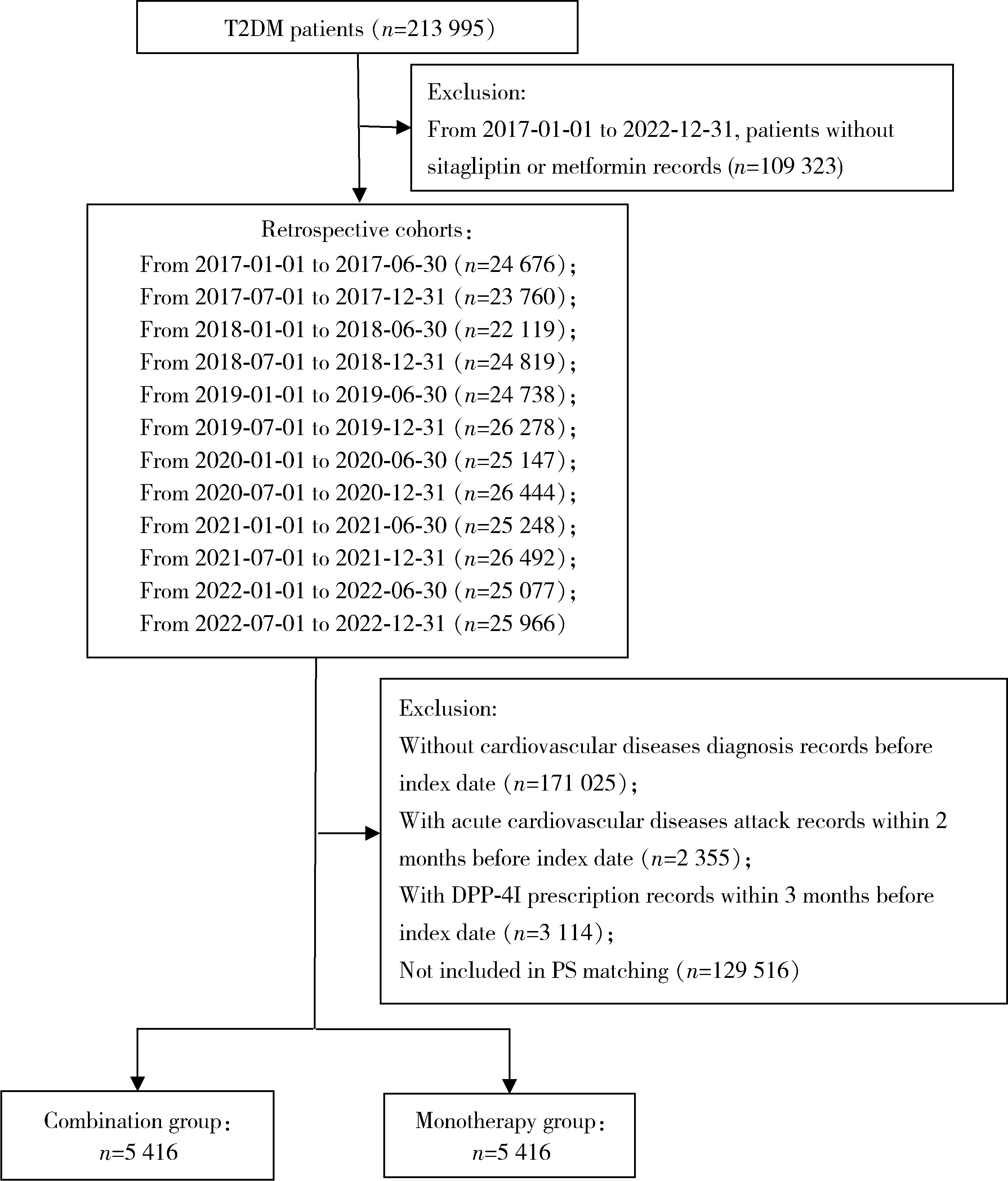
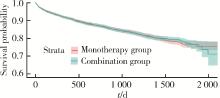
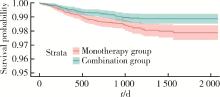
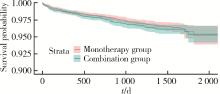
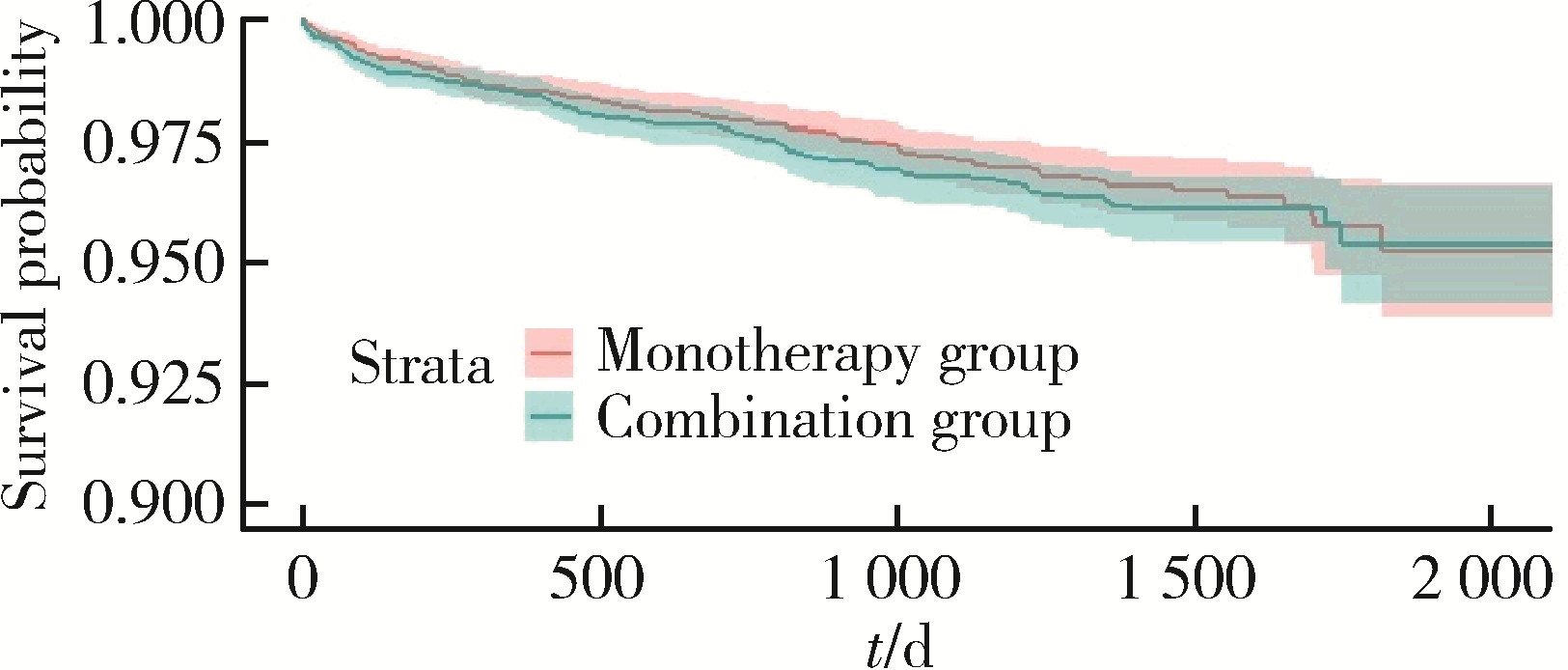
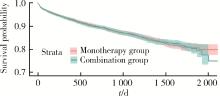
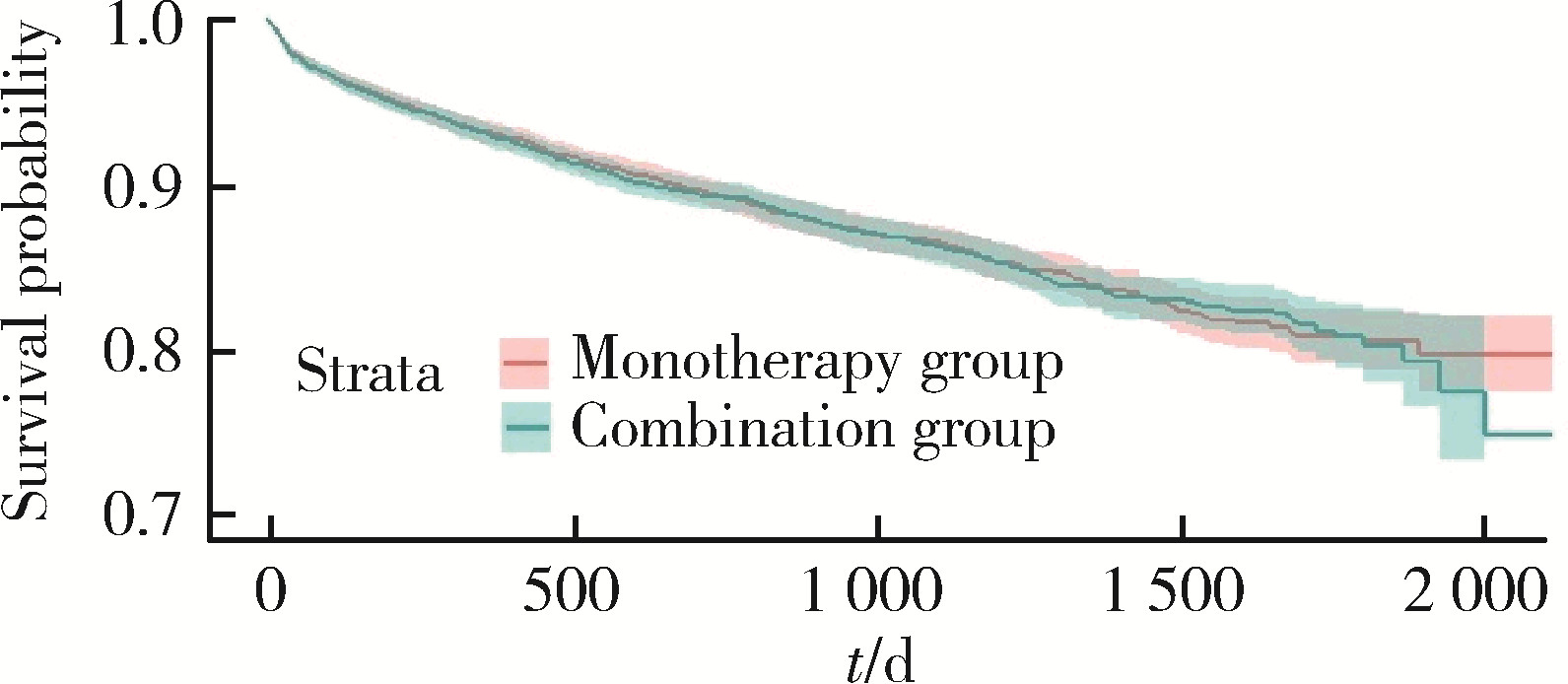
目的: 评估真实世界中2型糖尿病(type 2 diabetes mellitus,T2DM)患者在二甲双胍治疗基础上联用西格列汀对心血管不良事件的发生风险的影响。方法: 使用来自宁波市鄞州区域健康信息平台的真实世界数据,选取2017年1月1日至2022年12月31日期间,在平台中具有诊疗记录的T2DM患者。根据其用药情况,将其分二甲双胍联用西格列汀组(联用组)以及二甲双胍单用药组(单用组)。根据用药索引日期构建一系列回顾性队列,并使用倾向性评分匹配,将可能与结局有关的基线协变量纳入模型,用单用组研究对象匹配联用组研究对象,以增加组间基线特征的可比性,构建最终的回顾性队列。随访终止时间为结局发生、死亡或者是研究结束时间(2022年12月31日),以先发生者为准。观察结束后使用Cox比例风险模型估算两组间三点主要心血管不良事件(3-point major adverse cardiovascular events,3P-MACE)复合结局(心血管死亡、心肌梗死、卒中)以及各次要结局发生的风险比(hazard ratio,HR)及其95%置信区间(confidence interval,CI)。结果: 倾向性评分匹配前,联用组基线使用胰岛素、α糖苷酶抑制剂、钠-葡萄糖转运体2抑制剂(sodium-glucose transporter 2 inhibitors,SGLT-2I)、格列奈类降糖药的患者比例大于单用组,且联用组基线空腹血糖(fasting blood glucose,FBG)与糖化血红蛋白(hemoglobin A1c,HbA1c)水平高于单用组。在倾向性评分匹配后,联用组和单用组各纳入5 416例研究对象,组间基线特征均得到有效平衡。两组3P-MACE的发病密度分别为6.41/100人年和6.35/100人年。与单用组相比,联用组3P-MACE发生风险不增加也不降低(HR=1.00,95% CI:0.91~1.10)。次要结局比较,联用组患者心血管死亡发生率低于单用组(HR=0.59,95% CI:0.41~0.85),未发现二甲双胍联用西格列汀与心肌梗死和卒中发生风险的关联(HR=1.12,95% CI:0.89~1.41;HR=0.99,95% CI:0.91~1.12)。结论: 在我国宁波市鄞州区T2DM患者中,与单用二甲双胍相比,二甲双胍联用西格列汀治疗可能降低心血管死亡的发生风险,且不增加或减少总体心血管事件发生风险,研究结果可为西格列汀的心血管安全性评价提供真实世界证据。
中图分类号:
- R195.4
| 1 |
中华医学会糖尿病学分会. 中国2型糖尿病防治指南(2020年版)[J]. 国际内分泌代谢杂志, 2021, 41 (5): 482- 548.
doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121383-20210825-08063 |
| 2 |
Ji L , Hu D , Pan C , et al. Primacy of the 3B approach to control risk factors for cardiovascular disease in type 2 diabetes patients[J]. Am J Med, 2013, 126 (10): 925.e11- 925.e 22.
doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2013.02.035 |
| 3 |
Schmidt AM . Diabetes mellitus and cardiovascular disease[J]. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, 2019, 39 (4): 558- 568.
doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.119.310961 |
| 4 |
Goldfine AB . Assessing the cardiovascular safety of diabetes therapies[J]. N Engl J Med, 2008, 359 (11): 1092- 1095.
doi: 10.1056/NEJMp0805758 |
| 5 |
Griffin SJ , Leaver JK , Irving GJ . Impact of metformin on cardiovascular disease: A meta-analysis of randomised trials among people with type 2 diabetes[J]. Diabetologia, 2017, 60 (9): 1620- 1629.
doi: 10.1007/s00125-017-4337-9 |
| 6 |
Garber AJ , Abrahamson MJ , Barzilay JI , et al. Consensus statement by the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and American College of Endocrinology on the comprehensive Type 2 diabetes management algorithm: 2020 executive summary[J]. Endocr Pract, 2020, 26 (1): 107- 139.
doi: 10.4158/CS-2019-0472 |
| 7 |
余学锋, 王爱红. 基层医疗机构二肽基肽酶4抑制剂临床应用常见问题专家指导建议[J]. 中国糖尿病杂志, 2022, 30 (2): 81- 85.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6187.2022.02.001 |
| 8 |
Fei Y , Tsoi MF , Cheung BMY . Cardiovascular outcomes in trials of new antidiabetic drug classes: A network meta-analysis[J]. Cardiovasc Diabetol, 2019, 18 (1): 112.
doi: 10.1186/s12933-019-0916-z |
| 9 |
Green JB , Bethel MA , Armstrong PW , et al. Effect of sitagliptin on cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes[J]. N Engl J Med, 2015, 373 (3): 232- 242.
doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1501352 |
| 10 |
El Sanadi CE , Ji X , Kattan MW . 3-point major cardiovascular event outcome for patients with T2D treated with dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor or glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist in addition to metformin monotherapy[J]. Ann Transl Med, 2020, 8 (21): 1345.
doi: 10.21037/atm-20-4063 |
| 11 |
Zhao H , Chen X , Sun Y , et al. Associations between thiazolidi-nediones use and incidence of rheumatoid arthritis: A retrospective population-based cohort study[J]. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken), 2024, 76 (4): 486- 496.
doi: 10.1002/acr.25277 |
| 12 |
Lin H , Tang X , Shen P , et al. Using big data to improve cardiovascular care and outcomes in China: A protocol for the Chinese electronic health records research in Yinzhou (CHERRY) study[J]. BMJ Open, 2018, 8 (2): e019698.
doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2017-019698 |
| 13 |
Robins JM , Hernán MA , Rotnitzky A . Effect modification by time-varying covariates[J]. Am J Epidemiol, 2007, 166 (9): 994- 1002.
doi: 10.1093/aje/kwm231 |
| 14 |
Borah BJ , Moriarty JP , Crown WH , et al. Applications of propensity score methods in observational comparative effectiveness and safety research: Where have we come and where should we go?[J]. J Comp Eff Res, 2014, 3 (1): 63- 78.
doi: 10.2217/cer.13.89 |
| 15 |
中国医师协会内分泌代谢科医师分会. DPP-4抑制剂临床应用专家共识[J]. 中华内分泌代谢杂志, 2018, 34 (11): 899- 903.
doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1000-6699.2018.11.001 |
| 16 |
Ussher JR , Drucker DJ . Cardiovascular biology of the incretin system[J]. Endocr Rev, 2012, 33 (2): 187- 215.
doi: 10.1210/er.2011-1052 |
| 17 |
Mccormick LM , Kydd AC , Read PA , et al. Chronic dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibition with sitagliptin is associated with sustained protection against ischemic left ventricular dysfunction in a pilot study of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and coronary artery disease[J]. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging, 2014, 7 (2): 274- 281.
doi: 10.1161/CIRCIMAGING.113.000785 |
| 18 |
Anderluh M , Kocic G , Tomovic K , et al. Cross-talk between the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 and stromal cell-derived factor-1 in stem cell homing and myocardial repair: Potential impact of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors[J]. Pharmacol Ther, 2016, 167, 100- 107.
doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2016.07.009 |
| 19 |
Ussher JR , Drucker DJ . Cardiovascular actions of incretin-based therapies[J]. Circ Res, 2014, 114 (11): 1788- 1803.
doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.114.301958 |
| 20 |
Scirica BM , Bhatt DL , Braunwald E , et al. Saxagliptin and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. N Engl J Med, 2013, 369 (14): 1317- 1326.
doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1307684 |
| 21 |
Zheng SL , Roddick AJ , Aghar-Jaffar R , et al. Association between use of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors, glucagon-like peptide 1 agonists, and dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors with all-cause mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Jama, 2018, 319 (15): 1580- 1591.
doi: 10.1001/jama.2018.3024 |
| 22 |
Kaneko M , Narukawa M . Meta-analysis of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors use and cardiovascular risk in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. Diabetes Res Clin Pract, 2016, 116, 171- 182.
doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2016.04.012 |
| 23 |
Giugliano D , Longo M , Signoriello S , et al. The effect of DPP-4 inhibitors, GLP-1 receptor agonists and SGLT-2 inhibitors on cardiorenal outcomes: A network meta-analysis of 23 CVOTs[J]. Cardiovasc Diabetol, 2022, 21 (1): 42.
doi: 10.1186/s12933-022-01474-z |
| 24 |
Ou SM , Shih CJ , Chao PW , et al. Effects on clinical outcomes of adding dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors versus sulfonylureas to metformin therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. Ann Intern Med, 2015, 163 (9): 663- 672.
doi: 10.7326/M15-0308 |
| 25 |
Baksh S , Wen J , Mansour O , et al. Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhi-bitor cardiovascular safety in patients with type 2 diabetes, with cardiovascular and renal disease: A retrospective cohort study[J]. Sci Rep, 2021, 11 (1): 16637.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-95687-z |
| 26 |
Noguchi Y , Yoshizawa S , Tachi T , et al. Effect of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors vs. metformin on major cardiovascular events using spontaneous reporting system and real-world database study[J]. J Clin Med, 2022, 11 (17): 4988.
doi: 10.3390/jcm11174988 |
| 27 |
Ray WA . Evaluating medication effects outside of clinical trials: New-user designs[J]. Am J Epidemiol, 2003, 158 (9): 915- 920.
doi: 10.1093/aje/kwg231 |
| [1] | 侯天姣,周治波,王竹青,王梦莹,王斯悦,彭和香,郭煌达,李奕昕,章涵宇,秦雪英,武轶群,郑鸿尘,李静,吴涛,朱洪平. 转化生长因子β信号通路与非综合征型唇腭裂发病风险的基因-基因及基因-环境交互作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 384-389. |
| [2] | 陈平,黎泽明,郭怡,孙昕霙,Edwin B.FISHER. 基于大五人格理论应用潜在剖面分析探究2型糖尿病患者的用药依从性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(3): 530-535. |
| [3] | 许璐,陈璐,樊东升,冯菁楠,刘立立,詹思延,王胜锋. 基于15省城镇医疗保险数据测算我国成人进行性肌萎缩患病率[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(3): 521-526. |
| [4] | 杨羽, 赵厚宇, 詹思延. 队列数据共享的必要性与可行性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(2): 381-385. |
| [5] | 任巧萌,王丽敏,彭丹璐,郭岩. 中国成人糖尿病患者病情知晓对行为的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(3): 451-454. |
|
||