北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (6): 956-962. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2024.06.003
血清趋化因子CXCL-10和涎液化糖链抗原6水平在类风湿关节炎合并肺间质病变患者中的诊断和病情评估价值
闫蕊1, 柯丹1, 张妍1, 李丽1, 苏焕然1, 陈伟2, 孙明霞2, 刘晓敏1,*( ), 罗靓3,*(
), 罗靓3,*( )
)
- 1. 北京市顺义区医院风湿免疫科,北京 101300
2. 北京市顺义区医院放射科,北京 101300
3. 重庆市渝北区人民医院中医科,重庆 401120
Diagnostic significance of serum chemokine CXCL-10 and Krebs von den lungen-6 level in patients with rheumatoid arthritis associated interstitial lung disease
Rui YAN1, Dan KE1, Yan ZHANG1, Li LI1, Huanran SU1, Wei CHEN2, Mingxia SUN2, Xiaomin LIU1,*( ), Liang LUO3,*(
), Liang LUO3,*( )
)
- 1. Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, Beijing Shunyi Hospital, Beijing 101300, China
2. Department of Radiology, Beijing Shunyi Hospital, Beijing 101300, China
3. Department of Chinese Medicine, the People' s Hospital of Yubei District of Chongqing, Chongqing 401120, China
摘要:
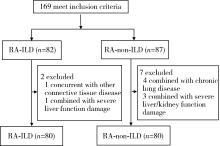
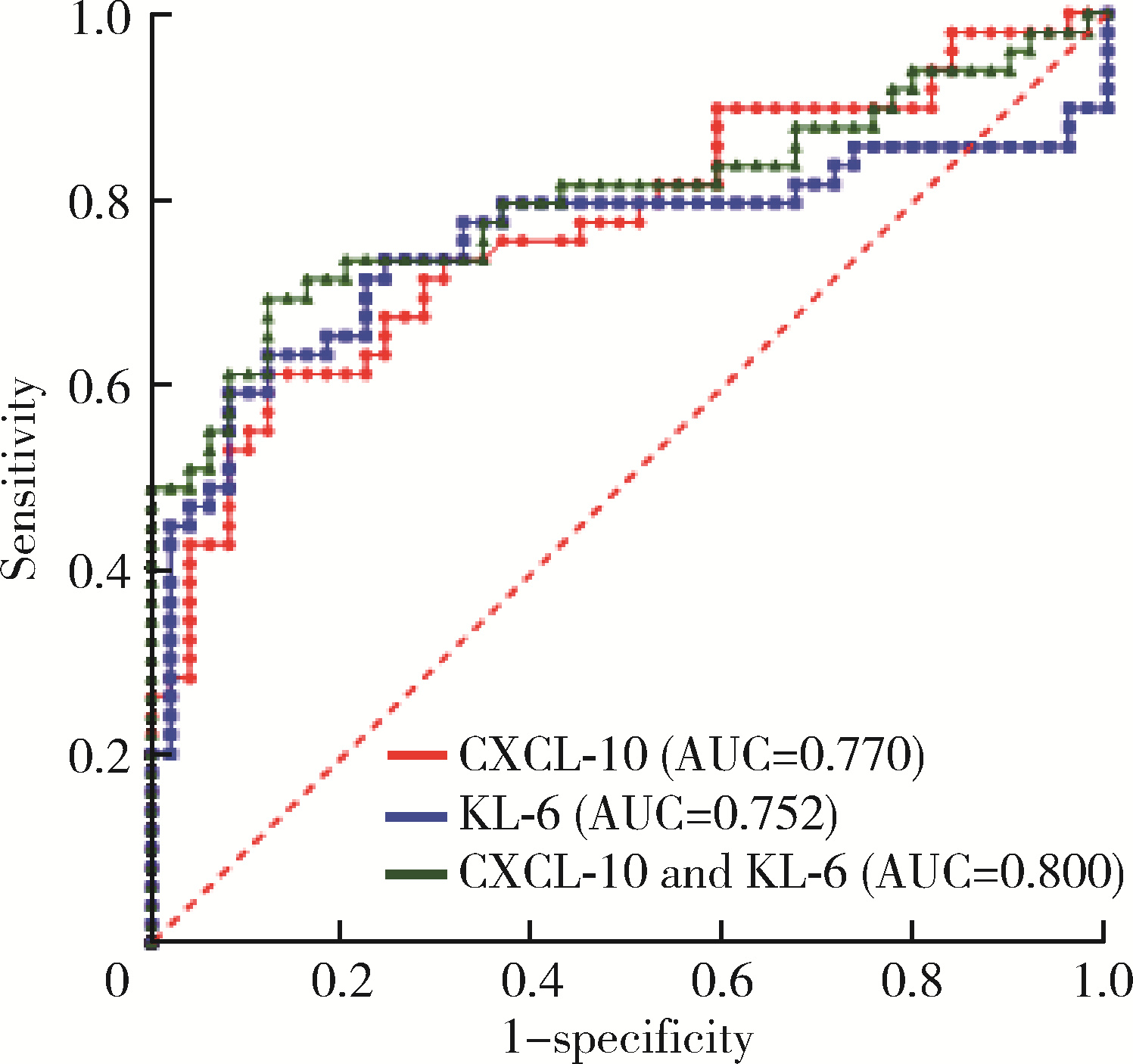
目的: 检测CXC趋化因子配体10(CXC motif chemokine 10, CXCL-10)和涎液化糖链抗原6(Krebs von den lungen-6, KL-6)在类风湿关节炎合并肺间质病变(rheumatoid arthritis associated interstitial lung disease, RA-ILD)患者血清中的表达水平,分析其与RA-ILD的相关性,探讨CXCL-10和KL-6对RA-ILD患者病情评价的意义。方法: 选择2021年5月至2023年10月在北京市顺义区医院风湿免疫科住院及门诊治疗的169例类风湿关节炎(rheumatoid arthritis,RA)患者的病例资料进行回顾性分析,根据是否合并ILD分为RA-ILD组82例和RA-non-ILD组87例,根据入排标准最终筛选出两组各80例。采用酶联免疫吸附试验检测所有患者血清CXCL-10和KL-6水平,通过1 ∶ 1倾向性评分匹配法(propensity score matching, PSM)对两组患者进行匹配,得到组间协变量均衡的样本。比较匹配后的组间差异,分析血清CXCL-10、KL-6与ILD评分(Warrick评分)、临床实验室及肺功能参数之间的相关性,利用二元Logistic回归分析RA患者发生ILD的危险因素,并判断CXCL-10、KL-6对RA-ILD的预测价值。结果: 经1 ∶ 1 PSM匹配出RA-ILD组和RA-non-ILD组患者各49例。RA-ILD组血清CXCL-10、KL-6水平显著高于RA-non-ILD组[CXCL-10水平64.36(34.01, 110.18) ng/L vs. 29.80(16.89, 40.55) ng/L,P<0.001;KL-6水平360.70(236.35, 715.05) U/mL vs. 210.69(159.98, 255.50) U/mL, P<0.001]。RA-ILD患者血清CXCL-10水平与Warrick评分呈正相关(r=0.378,P=0.007),与用力肺活量(forced vital capacity, FVC)占正常预计值的百分比(FVC%)呈负相关(r=-0.338,P=0.018);KL-6与类风湿因子(rheumatoid factor,RF)呈正相关(r=0.296,P=0.039),与FVC%(r=-0.436,P=0.002)和一氧化碳弥散量(diffusion lung carbon monoxide, DLCO)占预计值的百分比(DLCO%,r=-0.426,P=0.002)呈负相关。单因素和多因素二元Logistic回归分析均提示CXCL-10(OR值分别为1.035、1.023,P均<0.05)、KL-6水平(OR值分别为1.004、1.005,P均<0.05)与ILD呈正相关。分别用CXCL-10和KL-6绘制ROC曲线,曲线下面积分别为0.770和0.752,联合检测曲线下面积可增加至0.800。结论: RA-ILD患者血清CXCL-10和KL-6水平明显升高,与ILD患者ILD严重程度有一定的相关性,两者联合检测对诊断RA-ILD有较高的参考价值。
中图分类号:
- R593.22
| 1 |
Kakutani T , Hashimoto A , Tominaga A , et al. Related factors, increased mortality and causes of death in patients with rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease[J]. Mod Rheumatol, 2020, 30 (3): 458- 464.
doi: 10.1080/14397595.2019.1621462 |
| 2 | Zamora-Legoff JA , Krause ML , Crowson CS , et al. Patterns of interstitial lung disease and mortality in rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Rheumatology (Oxford), 2017, 56 (3): 344- 350. |
| 3 |
Natalini JG , Swigris JJ , Morisset J , et al. Understanding the determinants of health-related quality of life in rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease[J]. Respir Med, 2017, 127, 1- 6.
doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2017.04.002 |
| 4 |
McDermott GC , Doyle TJ , Sparks JA . Interstitial lung disease throughout the rheumatoid arthritis disease course[J]. Curr Opin Rheumatol, 2021, 33 (3): 284- 291.
doi: 10.1097/BOR.0000000000000787 |
| 5 |
Raimundo K , Solomon JJ , Olson AL , et al. Rheumatoid arthritis-interstitial lung disease in the United States: Prevalence, incidence, and healthcare costs and mortality[J]. J Rheumatol, 2019, 46 (4): 360- 369.
doi: 10.3899/jrheum.171315 |
| 6 |
Shimizu S , Yoshinouchi T , Niimi T , et al. Differing distributions of CXCR3- and CCR4-positive cells among types of interstitial pneumonia associated with collagen vascular diseases[J]. Virchows Arch, 2007, 450 (1): 51- 58.
doi: 10.1007/s00428-006-0330-2 |
| 7 |
Kameda M , Otsuka M , Chiba H , et al. CXCL9, CXCL10, and CXCL11; biomarkers of pulmonary inflammation associated with autoimmunity in patients with collagen vascular diseases-associated interstitial lung disease and interstitial pneumonia with autoimmune features[J]. PLoS One, 2020, 15 (11): e0241719.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0241719 |
| 8 |
Kim HC , Choi KH , Jacob J , et al. Prognostic role of blood KL-6 in rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease[J]. PLoS One, 2020, 15 (3): e0229997.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0229997 |
| 9 |
Raghu G , Rochwerg B , Zhang Y , et al. An official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT clinical practice guideline: Treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. An update of the 2011 clinical practice guideline[J]. Am J Respir Crit Care Med, 2015, 192 (2): e3- e19.
doi: 10.1164/rccm.201506-1063ST |
| 10 | Warrick JH , Bhalla M , Schabel SI , et al. High resolution com-puted tomography in early scleroderma lung disease[J]. J Rheumatol, 1991, 18 (10): 1520- 1528. |
| 11 | Shin S , Park EH , Kang EH , et al. Sex differences in clinical characteristics and their influence on clinical outcomes in an observational cohort of patients with rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Joint Bone Spine, 2021, 88 (3): 105124. |
| 12 |
Kronzer VL , Westerlind H , Alfredsson L , et al. Respiratory diseases as risk factors for seropositive and seronegative rheumatoid arthritis and in relation to smoking[J]. Arthritis Rheumatol, 2021, 73 (1): 61- 68.
doi: 10.1002/art.41491 |
| 13 |
Kiely P , Busby AD , Nikiphorou E , et al. Is incident rheumatoid arthritis interstitial lung disease associated with methotrexate treatment? Results from a multivariate analysis in the ERAS and ERAN inception cohorts[J]. BMJ Open, 2019, 9 (5): e028466.
doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2018-028466 |
| 14 |
Paulin F , Secco A , Benavidez F , et al. Lung involvement prevalence in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis without known pulmonary disease: A multicentric cross sectional study[J]. Adv Rheumatol, 2021, 61 (1): 52.
doi: 10.1186/s42358-021-00209-0 |
| 15 |
Ke Y , Dai X , Xu D , et al. Features and outcomes of elderly rheumatoid arthritis: Does the age of onset matter? A comparative study from a single center in China[J]. Rheumatol Ther, 2021, 8 (1): 243- 254.
doi: 10.1007/s40744-020-00267-8 |
| 16 |
Samhouri BF , Vassallo R , Achenbach SJ , et al. Incidence, risk factors, and mortality of clinical and subclinical rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease: A population-based cohort[J]. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken), 2022, 74 (12): 2042- 2049.
doi: 10.1002/acr.24856 |
| 17 |
Duarte AC , Porter JC , Leandro MJ . The lung in a cohort of rheumatoid arthritis patients-an overview of different types of involvement and treatment[J]. Rheumatology (Oxford), 2019, 58 (11): 2031- 2038.
doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kez177 |
| 18 |
McFarlane IM , Zhaz SY , Bhamra MS , et al. Assessment of interstitial lung disease among black rheumatoid arthritis patients[J]. Clin Rheumatol, 2019, 38 (12): 3413- 3424.
doi: 10.1007/s10067-019-04760-6 |
| 19 |
Hyldgaard C , Hilberg O , Pedersen AB , et al. A population-based cohort study of rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease: Comorbidity and mortality[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2017, 76 (10): 1700- 1706.
doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2017-211138 |
| 20 | Meyer KC . Pulmonary fibrosis, part Ⅰ: Epidemiology, patho-genesis, and diagnosis[J]. Expert Rev Respir Med, 2017, 11 (5): 343- 359. |
| 21 |
King TE Jr , Bradford WZ , Castro-Bernardini S , et al. A phase 3 trial of pirfenidone in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis[J]. N Engl J Med, 2014, 370 (22): 2083- 2092.
doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1402582 |
| 22 |
Mollica Poeta V , Massara M , Capucetti A , et al. Chemokines and chemokine receptors: New targets for cancer immunotherapy[J]. Front Immunol, 2019, 10, 379.
doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00379 |
| 23 |
Pandya JM , Lundell AC , Andersson K , et al. Blood chemokine profile in untreated early rheumatoid arthritis: CXCL10 as a disease activity marker[J]. Arthritis Res Ther, 2017, 19 (1): 20.
doi: 10.1186/s13075-017-1224-1 |
| 24 |
Yu R , Liu X , Deng X , et al. Serum CHI3L1 as a biomarker of interstitial lung disease in rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Front Immunol, 2023, 14, 1211790.
doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1211790 |
| 25 | 吴雪, 武丽君, 罗采南, 等. 涎液化糖链抗原-6在结缔组织病相关间质性肺病诊断中的应用价值[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2019, 99 (40): 3172- 3175. |
| 26 | Lee YS , Kim HC , Lee BY , et al. The value of biomarkers as predictors of outcome in patients with rheumatoid arthritis-associated usual interstitial pneumonia[J]. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis, 2016, 33 (3): 216- 223. |
| 27 |
Chen F , Lu X , Shu X , et al. Predictive value of serum markers for the development of interstitial lung disease in patients with polymyositis and dermatomyositis: A comparative and prospective study[J]. Intern Med J, 2015, 45 (6): 641- 647.
doi: 10.1111/imj.12754 |
| [1] | 贾霈雯, 杨迎, 邹耀威, 欧阳志明, 林建子, 马剑达, 杨葵敏, 戴冽. 类风湿关节炎患者低肌肉量综合征的临床特征及其对躯体功能的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(6): 1009-1016. |
| [2] | 马豆豆, 卢哲敏, 郭倩, 朱莎, 古今, 丁艳, 石连杰. 小剂量利妥昔单抗成功治疗类风湿关节炎合并重症肌无力1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(6): 1110-1114. |
| [3] | 赵亮, 史成龙, 马柯, 赵静, 王潇, 邢晓燕, 莫万星, 练益瑞, 高超, 李玉慧. 抗合成酶综合征重叠类风湿关节炎患者的免疫学特征[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(6): 972-979. |
| [4] | 韩艺钧, 陈小莉, 李常虹, 赵金霞. 甲氨蝶呤在类风湿关节炎患者中的应用现状[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(6): 994-1000. |
| [5] | 刘东武, 陈杰, 高明利, 于静. 类风湿关节炎伴发淋巴结Castleman样病理改变1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 928-931. |
| [6] | 柴晓东,孙子文,李海爽,朱靓怡,刘小旦,刘延涛,裴斐,常青. 髓母细胞瘤分子亚型中CD8+T淋巴细胞浸润的临床病理特点[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 512-518. |
| [7] | 黄会娜,赵静,赵祥格,白自然,李霞,王冠. 乳酸对类风湿关节炎患者外周血CD4+T细胞亚群的调控作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 519-525. |
| [8] | 汤晓菲,李永红,丁秋玲,孙卓,张阳,王育梅,田美伊,刘坚. 类风湿关节炎患者下肢深静脉血栓发病率及危险因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 279-283. |
| [9] | 邹雪,白小娟,张丽卿. 艾拉莫德联合托法替布治疗难治性中重度类风湿关节炎的疗效[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 1013-1021. |
| [10] | 吴琦,蔡月明,何娟,黄文蒂,王庆文. 血脂异常与类风湿关节炎肺间质病变的相关性分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 982-992. |
| [11] | 张警丰,金银姬,魏慧,姚中强,赵金霞. 体重指数与类风湿关节炎临床特征的相关性分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 993-999. |
| [12] | 金银姬,孙琳,赵金霞,刘湘源. 血清IgA型抗鼠科肉瘤病毒癌基因同源物B1抗体在类风湿关节炎中的意义[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 631-635. |
| [13] | 蔡文心,李仕成,刘一鸣,梁如玉,李静,郭建萍,胡凡磊,孙晓麟,李春,刘栩,叶华,邓立宗,李茹,栗占国. 类风湿关节炎临床分层及其特征的横断面研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1068-1073. |
| [14] | 程昉,杨邵英,房星星,王璇,赵福涛. CCL28-CCR10通路在类风湿关节炎单核细胞迁移中的作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1074-1078. |
| [15] | 刘蕊,赵金霞,闫良. 类风湿关节炎合并下肢静脉血栓患者的临床特点[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1079-1085. |
|
||