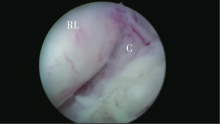
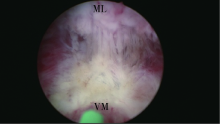
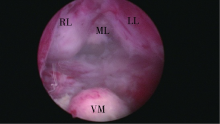
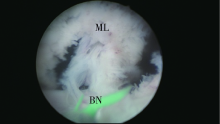
Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences) ›› 2019, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (6): 1159-1164. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2019.06.032
Previous Articles Next Articles
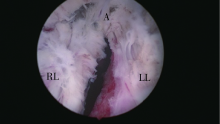
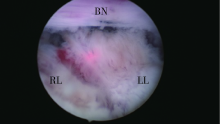
Low power seven-step two-lobe holmium laser enucleation of the prostate technique for surgical treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia
Ke LIU,Fan ZHANG,Chun-lei XIAO( ),Hai-zhui XIA,Yi-chang HAO,Hai BI,Lei ZHAO,Yu-qing LIU,Jian LU,Lu-lin MA
),Hai-zhui XIA,Yi-chang HAO,Hai BI,Lei ZHAO,Yu-qing LIU,Jian LU,Lu-lin MA
- Department of Urology, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
CLC Number:
- R697 +.3
| [1] | Vincent MW, Gilling PJ . HoLEP has come of age[J]. World J Urol, 2015,33(4):487-493. |
| [2] | Cornu JN, Ahyai S, Bachmann A , et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of functional outcomes and complications following transurethral procedures for lower urinary tract symptoms resulting from benign prostatic obstruction: an update[J]. Eur Urol, 2015,67(6):1066-1096. |
| [3] | Robert G, Cornu JN, Fourmarier M , et al. Multicentre prospective evaluation of the learning curve of holmium laser enucleation of the prostate (HoLEP)[J]. BJU Int, 2016,117(3):495-499. |
| [4] | 刘宁, 黄广林, 满立波 , 等. 缩短钬激光前列腺剜除术学习曲线的方法[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2015,4(1):720-723. |
| [5] | Becker B, Gross AJ, Netsch C . Safety and efficacy using a low-powered holmium laser for enucleation of the prostate (HoLEP): 12-month results from a prospective low-power HoLEP series[J]. World J Urol, 2018,36(3):441-447. |
| [6] | Gong YG, He DL, Wang MZ , et al. Holmium laser enucleation of the prostate: A modified enucleation technique and initial results[J]. J Urol, 2012,187(4):1336-1340. |
| [7] | Minagawa S, Okada S, Morikawa H . Safety and effectiveness of holmium laser enucleation of the prostate using a low-power laser[J]. Urology, 2017,110:51-55. |
| [8] | Scoffone CM, Cracco CM . High-power HoLEP: No thanks![J]. World J Urol, 2018,36(5):837-838. |
| [9] | 刘可, 肖春雷, 马潞林 . 钬激光前列腺剜除术治疗良性前列腺增生的自学学习曲线[J]. 中国微创外科杂志, 2016,16(1):31-34. |
| [10] | Scoffone CM, Cracco CM . The en-bloc no-touch holmium laser enucleation of the prostate (HoLEP) technique[J]. World J Urol, 2016,34(8):1175-1181. |
| [11] | Kim M, Lee HE, Oh SJ . Technical aspects of holmium laser enucleation of the prostate for benign prostatic hyperplasia[J]. Korean J Urol, 2013,54(9):570-579. |
| [12] | Endo F, Shiga Y, Minagawa S , et al. Anteroposterior dissection HoLEP: A modification to prevent transient stress urinary incontinence[J]. Urology, 2010,76(6):1451-1455. |
| [13] | Elkoushy MA, Elshal AM, Elhiralli MM . Reoperation after hol-mium laser enucleation of the prostate for management of benign prostate hyperplasia: Assessment of risk factors with time to event analysis[J]. J Endourol, 2015,29(7):797-804. |
| [1] | Deng-gao LIU,Dan-ni ZHENG,Ya-ning ZHAO,Ya-qiong ZHANG,Xin YE,Li-qi ZHANG,Xiao-yan XIE,Lei ZHANG,Zu-yan ZHANG,Guang-yan YU. Recent progress in the treatment of intractable sialolithiasis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(1): 8-12. |
| [2] | WANG Xiang-xi,LI Zhen-zhen,LAI Yan-yun,YANG Li,SHI Lin-li,ZHONG Shao-min,WU Yan. Clinical efficacy of 585 nm Q-switched laser treatment on inflammatory lesion and postinflammatory erythema of acne vulgaris [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(2): 283-288. |
| [3] | MA Ke-nan,CHEN Hu,SHEN Yan-ru,ZHOU Yong-sheng,WANG Yong,SUN Yu-chun. Finite element analyses of retention of removable partial denture circumferential clasps manufactured by selective laser melting [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(1): 105-112. |
| [4] | LI Wen-jin,DING Qian,YUAN Fu-song,Sun Feng-bo,ZHENG Jian-qiao,BAO Rui,Zhang Lei. Effects of femtosecond laser treatment on surface characteristics and flexural strength of zirconia [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(4): 770-775. |
| [5] | XIU Qian, CHEN Xi, LIU Tong,CHEN Ming-xing, YAO Ping, XIN Wei-hong. Analysis of 2 cases of dyspnea happening after tracheotomy and the clinical application of Mimics 10.01 [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2018, 50(5): 924-927. |
| [6] | SUI Hua-xin, LV Pei-jun, WANG Yong, FENG Yu-chi. Effects of low level laser irradiation on the osteogenic capacity of sodium alginate/gelatin/human adipose-derived stem cells 3D bio-printing construct [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2018, 50(5): 868-875. |
| [7] | HAO Yi-chang, CHEN Kun, LIU Yu-qing, LU Jian, XIAO Chun-lei, MA Lu-lin. Transurethral flexible ureteroscopic holmium laser resection for tumors of renal pelvis: 6 cases report and literature review [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2018, 50(5): 816-821. |
| [8] | CHENG Ming-xuan, JIANG Ting, SUN Yu-chun, ZHANG Hao-yu. Influence of intraoral scan and dental cast scan on occlusal quantitative analysis of virtual dental model [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2018, 50(1): 136-140. |
| [9] | LIU Jing-yin, CHEN Fei, GE Yan-jun, WEI Ling, PAN Shao-xia, FENG Hai-lan. Influence of implants prepared by selective laser melting on early bone healing [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2018, 50(1): 117-122. |
| [10] | SUI Hua-xin, LV Pei-jun, WANG Yu-guang, WANG Yong, SUN Yu-chun. Effect of lowlevel laser irradiation on proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human adipose-derived stromal cells [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2017, 49(2): 337-343. |
| [11] | SU Zheng, BAI Yu-hao, HOU Xiao-mei. Effects of different techniques on removal of vapor lock in the apical region of curved canals: a cone-beam computed tomography study [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2017, 49(1): 76-080. |
| [12] | GUO Yi-dan, ZHANG Sun. Preliminary research of Er:YAG laser used for pulpotomy of Beagle dogs [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2016, 48(4): 714-719. |
| [13] | WANG Ying, Obada BARRY, Gerhard WAHL, CHEN Bo, LIN Ye. Pilot study of laser-doppler flowmetry measurement of oral mucosa blood flow [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2016, 48(4): 697-701. |
| [14] | QU Chun-na, KANG Jun, LUAN Qing-xian. Effects of Er, Cr: YSGG laser on the root surface of periodontitis and healthy teeth [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2016, 48(1): 71-75. |
| [15] | LIU Ke, XIAO Chun-Lei, LIU Yu-Qing, HAO Yi-Chang, ZHANG Shu-Dong, TIAN Yu, MA Lu-Lin. Management of calyceal diverticular calculi with stenotic infundibulum by flexible ureteroscopic holmium laser infundibulectomy and lithotripsy [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2015, 47(4): 618-621. |
|
||