Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2025, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (4): 644-649. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2025.04.003
Previous Articles Next Articles
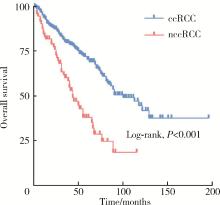
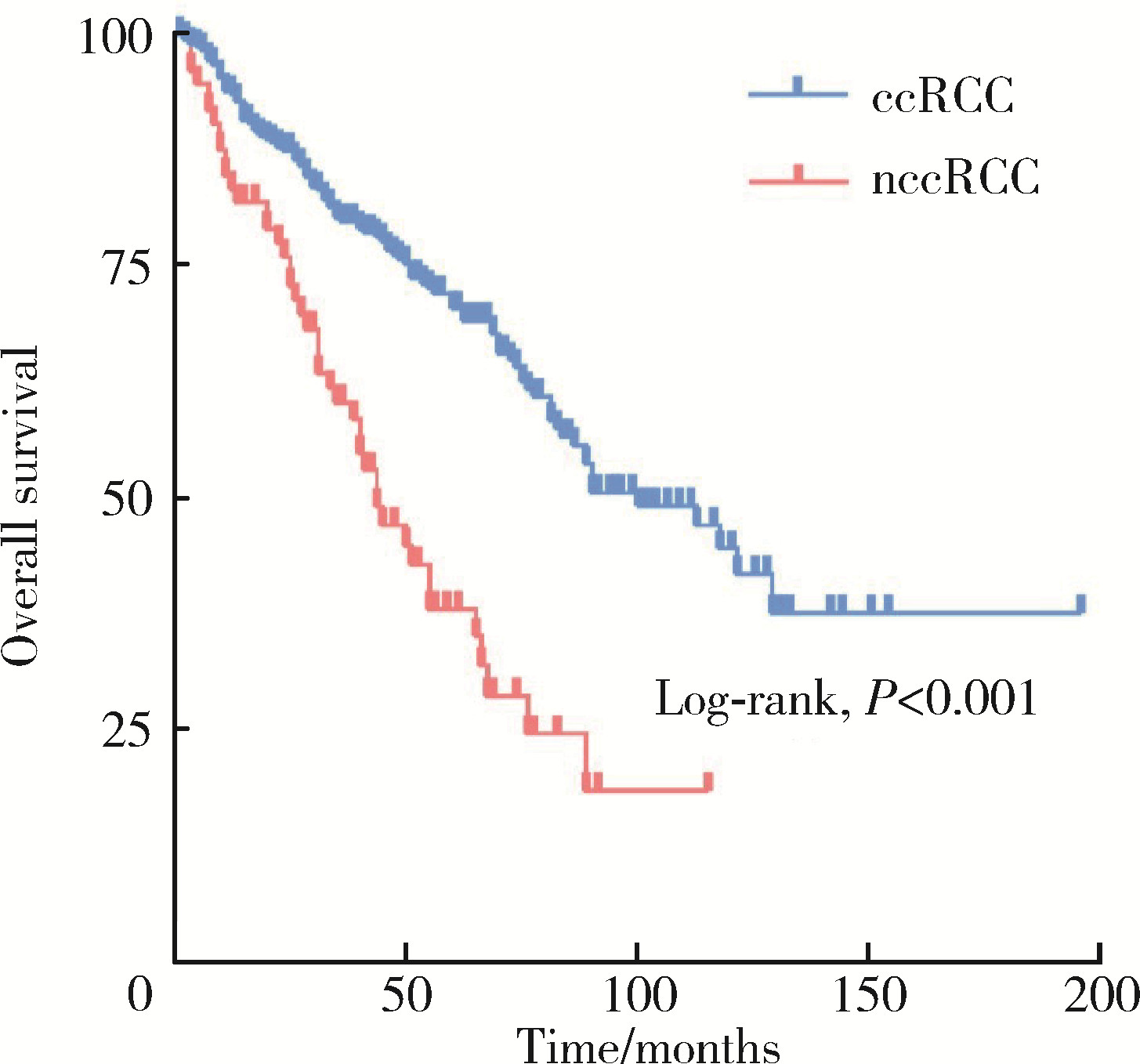
Clinicopathological and prognostic differences between clear cell and non-clear cell renal cell carcinoma with venous tumor thrombus
Boda GUO1, Min LU2, Guoliang WANG1, Hongxian ZHANG1, Lei LIU1, Xiaofei HOU1, Lei ZHAO1, Xiaojun TIAN1, Shudong ZHANG1,*( )
)
- 1. Department of Urology, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
2. Department of Pathology, Peking University Third Hospital, Peking University School of Basic Medical Sciences, Beijing, 100191, China
CLC Number:
- R737.11
| 1 |
|
| 2 |
|
| 3 |
|
| 4 |
|
| 5 |
|
| 6 |
|
| 7 |
|
| 8 |
|
| 9 |
|
| 10 |
薛子璇, 唐世英, 邱敏, 等. 青年肾肿瘤伴瘤栓的临床病理特征及预后分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55 (5): 802- 811.
doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2023.05.005 |
| 11 |
|
| 12 |
|
| 13 |
|
| 14 |
|
| 15 |
|
| 16 |
|
| 17 |
|
| [1] | Zhanyi ZHANG, Min LU, Yuehao SUN, Jinghan DONG, Xiaofei HOU, Chunlei XIAO, Guoliang WANG, Xiaojun TIAN, Lulin MA, Hongxian ZHANG, Shudong ZHANG. Clinicopathological features and survival analysis of TFE3-rearranged renal cell carcinoma with venous tumor thrombus [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2025, 57(4): 650-661. |
| [2] | Zezhen ZHOU, Liyuan GE, Fan ZHANG, Shaohui DENG, Ye YAN, Hongxian ZHANG, Guoliang WANG, Lei LIU, Yi HUANG, Shudong ZHANG. A retrospective matching study of partial nephrectomy and radical nephrectomy for pathological T3a stage renal cell carcinoma [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2025, 57(4): 704-710. |
| [3] | Weihao LI, Jing LI, Xuemin ZHANG, Wei LI, Qingle LI, Xiaoming ZHANG. Effect of intraoperative blood salvage autotransfusion on the prognosis of patients after carotid body tumor resection [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2025, 57(2): 272-276. |
| [4] | Yaqing MAO, Zhen CHEN, Yao YU, Wenbo ZHANG, Yang LIU, Xin PENG. Impact of type 2 diabetes mellitus on the prognosis of patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(6): 1089-1096. |
| [5] | Junyong OU,Kunming NI,Lulin MA,Guoliang WANG,Ye YAN,Bin YANG,Gengwu LI,Haodong SONG,Min LU,Jianfei YE,Shudong ZHANG. Prognostic factors of patients with muscle invasive bladder cancer with intermediate-to-high risk prostate cancer [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 582-588. |
| [6] | Shuai LIU,Lei LIU,Zhuo LIU,Fan ZHANG,Lulin MA,Xiaojun TIAN,Xiaofei HOU,Guoliang WANG,Lei ZHAO,Shudong ZHANG. Clinical treatment and prognosis of adrenocortical carcinoma with venous tumor thrombus [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 624-630. |
| [7] | Binshuai WANG,Min QIU,Qianjin ZHANG,Maofeng TIAN,Lei LIU,Guoliang WANG,Min LU,Xiaojun TIAN,Shudong ZHANG. Experience in diagnosis and treatment of 6 cases of renal Ewing's sarcoma with venous thrombus [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 636-639. |
| [8] | Le YU,Shaohui DENG,Fan ZHANG,Ye YAN,Jianfei YE,Shudong ZHANG. Clinicopathological characteristics and prognosis of multilocular cystic renal neoplasm of low malignant potential [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 661-666. |
| [9] | Fan SHU,Yichang HAO,Zhanyi ZHANG,Shaohui DENG,Hongxian ZHANG,Lei LIU,Guoliang WANG,Xiaojun TIAN,Lei ZHAO,Lulin MA,Shudong ZHANG. Functional and oncologic outcomes of partial nephrectomy for cystic renal cell carcinoma: A single-center retrospective study [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 667-672. |
| [10] | Zezhen ZHOU,Shaohui DENG,Ye YAN,Fan ZHANG,Yichang HAO,Liyuan GE,Hongxian ZHANG,Guoliang WANG,Shudong ZHANG. Predicting the 3-year tumor-specific survival in patients with T3a non-metastatic renal cell carcinoma [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 673-679. |
| [11] | Yangyi FANG,Qiang LI,Zhigao HUANG,Min LU,Kai HONG,Shudong ZHANG. Well-differentiated papillary mesothelial tumour of the tunica vaginalis: A case report [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 741-744. |
| [12] | Yuanyuan ZENG,Yun XIE,Daonan CHEN,Ruilan WANG. Related factors of euthyroid sick syndrome in patients with sepsis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(3): 526-532. |
| [13] | Jian-bin LI,Meng-na LYU,Qiang CHI,Yi-lin PENG,Peng-cheng LIU,Rui WU. Early prediction of severe COVID-19 in patients with Sjögren’s syndrome [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(6): 1007-1012. |
| [14] | Yun-chong LIU,Zong-long WU,Li-yuan GE,Tan DU,Ya-qian WU,Yi-meng SONG,Cheng LIU,Lu-lin MA. Mechanism of nuclear protein 1 in the resistance to axitinib in clear cell renal cell carcinoma [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 781-792. |
| [15] | Huan-rui LIU,Xiang PENG,Sen-lin LI,Xin GOU. Risk modeling based on HER-2 related genes for bladder cancer survival prognosis assessment [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 793-801. |
|
||