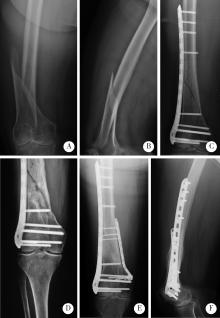
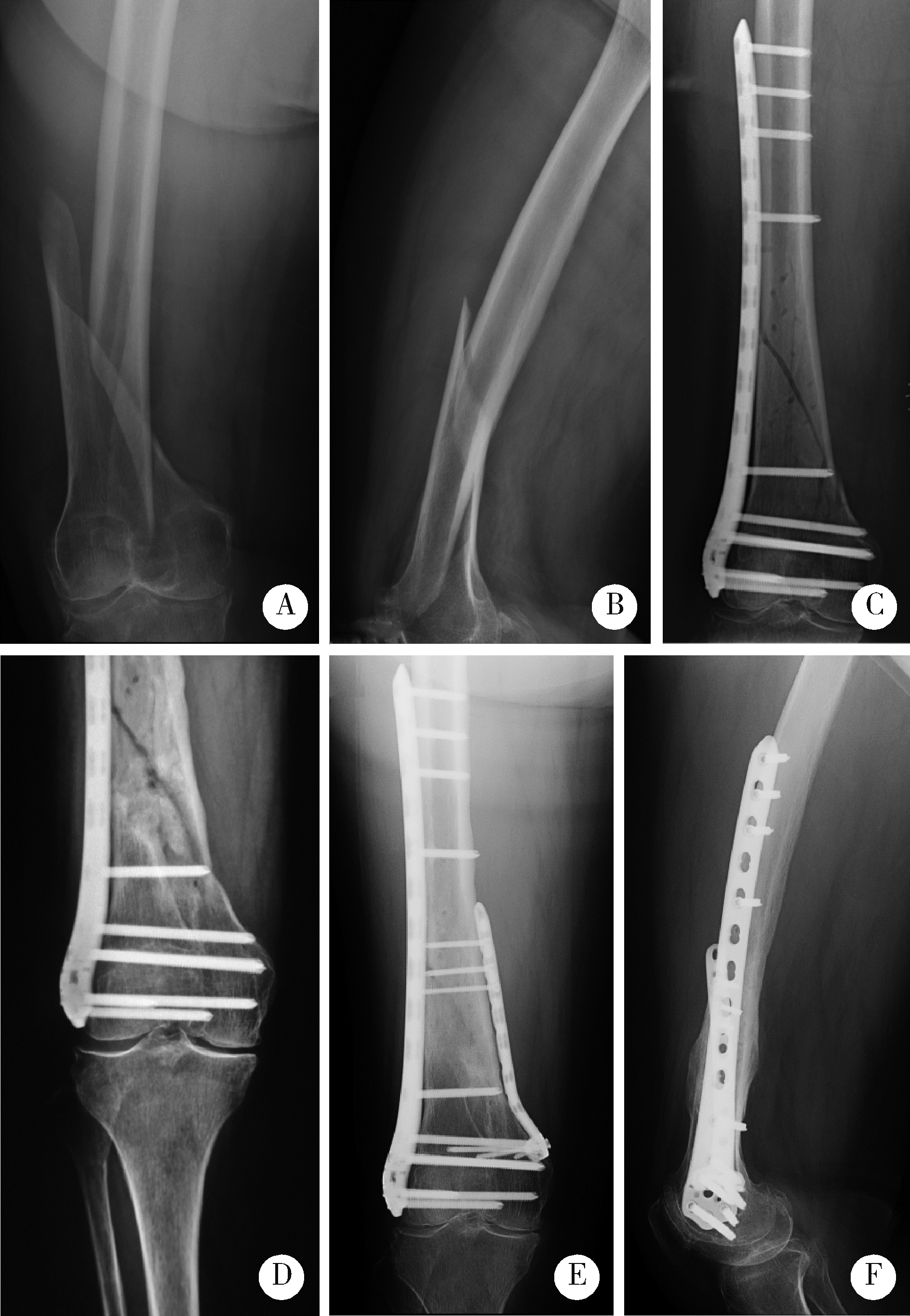
Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2022, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (6): 1172-1177. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2022.06.019
Previous Articles Next Articles
Related factors of revision of distal femoral fractures treated with lateral locking plate
Guo-jin HOU,Fang ZHOU*( ),Yun TIAN,Hong-quan JI,Zhi-shan ZHANG,Yan GUO,yang LV,Zhong-wei YANG
),Yun TIAN,Hong-quan JI,Zhi-shan ZHANG,Yan GUO,yang LV,Zhong-wei YANG
- Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
CLC Number:
- R683.4
| 1 |
Court-Brown CM , Caesar B . Epidemiology of adult fractures: A review[J]. Injury, 2006, 37 (8): 691- 697.
doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2006.04.130 |
| 2 | Martinet O , Cordey J , Harder Y , et al. The epidemiology of fractures of the distal femur[J]. Injury, 2000, 31 (3): 62- 63. |
| 3 |
Hoffmann MF , Jones CB , Sietsema DL , et al. Clinical outcomes of locked plating of distal femoral fractures in a retrospective cohort[J]. J Orthop Surg Res, 2013, 8 (1): 43.
doi: 10.1186/1749-799X-8-43 |
| 4 | Consortium SF . LCP versus LISS in the treatment of open and closed distal femur fractures: does it make a difference?[J]. J Orthop Trauma, 2016, 30 (6): e212- e216. |
| 5 | Henderson CE , Kuhl LL , Fitzpatrick DC , et al. Locking plates for distal femur fractures: Is there a problem with fracture healing?[J]. J Orthop Trauma, 2011, 25 (Suppl 1): 8- 14. |
| 6 |
Rodriguez EK , Boulton C , Weaver MJ , et al. Predictive factors of distal femoral fracture nonunion after lateral locked plating: A retrospective multicenter case-control study of 283 fractures[J]. Injury, 2014, 45 (3): 554- 559.
doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2013.10.042 |
| 7 |
MoreLand JR , Bassett LW , Hanker GJ . Radiographic analysis of the axial alignment of the lower extremity[J]. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1987, 69 (5): 745- 749.
doi: 10.2106/00004623-198769050-00016 |
| 8 | 李景学, 孙鼎元. 骨关节X线诊断学[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 1992: 176. |
| 9 |
Syed AA , Agarwal M , Giannoudis PV , et al. Distal femoral fractures: Long-term outcome following stabilisation with the LISS[J]. Injury, 2004, 35 (6): 599- 607.
doi: 10.1016/S0020-1383(03)00247-X |
| 10 | Kregor PJ , Stannard JA , Zlowodzki M , et al. Treatment of distal femur fractures using the less invasive stabilization system[J]. J Orthop Trauma, 2014, 18 (8): 509- 520. |
| 11 |
Lujan T , Henderson CE , Madey SM , et al. Locked plating of distal femur fractures leads to inconsistent and asymmetric callus formation[J]. J Orthop Trauma, 2010, 24 (3): 156- 162.
doi: 10.1097/BOT.0b013e3181be6720 |
| 12 |
Ebraheim NA , Liu J , Hashmi SZ , et al. High complication rate in locking plate fixation of lower periprosthetic distal femur fractures in patients with total knee arthroplasties[J]. J Arthroplasty, 2012, 27 (5): 809- 813.
doi: 10.1016/j.arth.2011.08.007 |
| 13 |
Hak DJ , Toker S , Yi C , et al. The influence of fracture fixation biomechanics on fracture healing[J]. Orthopedics, 2010, 33 (10): 752- 755.
doi: 10.3928/01477447-20100826-20 |
| 14 | Fulkerson E , Egol KA , Kubiak EN , et al. Fixation of diaphyseal fractures with a segmental defect: A biomechanical comparison of locked and conventional plating techniques[J]. Trauma, 2006, 60 (4): 830- 835. |
| 15 |
Ricci WM , Streubel PN , Morshed S , et al. Risk factors for failure of locked plate fixation of distal femur fractures: an analysis of 335 cases[J]. J Orthop Trauma, 2014, 28 (2): 83- 89.
doi: 10.1097/BOT.0b013e31829e6dd0 |
| 16 |
Steinberg EL , Elis J , Steinberg Y , et al. A double-plating approach to distal femur fracture: A clinical study[J]. Injury, 2017, 48 (10): 2260- 2265.
doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2017.07.025 |
| 17 | Jagodzinski M , Krettek C . Effect of mechanical stability on fracture healing: An update[J]. Injury, 2007, 38 (Suppl 1): 3- 10. |
| 18 | Peschiera V , Staletti L , Cavanna M , et al. Predicting the failure in distal femur fractures[J]. Injury, 2018, 49 (Suppl 3): 2- 7. |
| 19 |
Tan SL , Balogh ZJ . Indications and limitations of locked plating[J]. Injury, 2009, 40 (7): 683- 691.
doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2009.01.003 |
| 20 | 宁鹏, 赵铭, 张月东. 下肢骨折锁定加压钢板内固定失败的Logistic回归分析[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志, 2014, 22 (24): 2238- 2243. |
| 21 |
Elkins J , Marsh JL , Lujan T , et al. Motion predicts clinical callus formation: Construct-specific finite element analysis of supracondylar femoral fractures[J]. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 2016, 98 (4): 276- 284.
doi: 10.2106/JBJS.O.00684 |
| 22 | 程建岗, 袁志, 刘建, 等. 锁定接骨板动力化治疗股骨远端骨折经锁定接骨板内固定术后骨不连的效果[J]. 国际骨科学杂志, 2019, 40 (1): 57- 59. |
| [1] | Ying TANG, Yongbo ZHANG, Danhong WU, Yanhong LIN, Fenghua LAN. Detection of pathogenic gene mutations in thirteen cases of congenital bilateral absence of vas deferens infertility patients [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(5): 763-774. |
| [2] | Ying HUANG,Zhi-yuan WU,Xing-hong ZHOU,Zhi-gang CAI,Jie ZHANG. Category of facial symmetry perception after maxillary reconstruction using anterolateral thigh flap [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(4): 708-715. |
| [3] | Shi-kai XIONG,Wei-li SHI,An-hong WANG,Xing XIE,Qin-wei GUO. Radiographic diagnosis of distal fibula avulsion fractures: Comparison of ankle X-ray and three-dimensional reconstruction of CT [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(1): 156-159. |
| [4] | Shan YE,Ping-ping JIN,Nan ZHANG,Hai-bo WU,Lin SHI,Qiang ZHAO,Kun YANG,Hui-shu YUAN,Dong-sheng FAN. Cortical thickness and cognitive impairment in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(6): 1158-1162. |
| [5] | Jia-peng ZHENG,Qi XIAO,Hui-yun DENG,Qing-quan WU,Wen-liang ZHAI,Da-sheng LIN. Arthroscopic classification and management for the popliteal hiatus of the lateral meniscus tears [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(5): 891-895. |
| [6] | HONG Peng,TIAN Xiao-jun,ZHAO Xiao-yu,YANG Fei-long,LIU Zhuo,LU Min,ZHAO Lei,MA Lu-lin. Bilateral papillary renal cell carcinoma following kidney transplantation: A case report [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(4): 811-813. |
| [7] | Jun-hui ZHANG,Yi-hang JIANG,Yu-guang JIANG,Ji-qing ZHANG,Ning KANG. Clinical outcomes of simultaneous bilateral endoscopic surgery for bilateral upper urinary tract calculi [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(4): 672-677. |
| [8] | Shun-ji WANG,Wen-bo ZHANG,Yao YU,Xiao-yan XIE,Hong-yu YANG,Xin PENG. Application of computer-assisted design for anterolateral thigh flap in oral and maxillofacial reconstruction [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2020, 52(1): 119-123. |
| [9] | Sen-lei LI,Xian-teng YANG,Xiao-bin TIAN,Li SUN. Early functional recovery of direct anterior approach versus anterolateral approach for total hip arthroplasty [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(2): 268-272. |
| [10] | LIU Zhong-di, MA Ming-tai, CHEN Jian-hai, FU Zhong-guo, JIANG Bao-guo. “Time-angle measurement” reduction evaluation technique and clinical evaluation of proximal humerus fracture [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2017, 49(6): 1003-1007. |
| [11] | LI Xu, LI Feng-long, LU Yi, ZHU Yi-ming, GUO Si-yi, LI Yi-jun, JIANG Chun-yan. Clinical study on locking plate for the treatment of non-osteoporotic complex proximal humeral fractures [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2017, 49(5): 855-860. |
| [12] | XU Jie, ZHUANG Wei-da, LI Xin-wei, YU Guo-yu, LIN Yuan, LUO Fen-qi, XIAO Yu-hua. Comparison of the effects of total hip arthroplasty via direct anterior approach and posterolateral piriformis-sparing approach [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2017, 49(2): 214-220. |
| [13] | YANG Yi, CAI Bin, FAN Dong-sheng△. Expression of microRNA-29b in mice with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2015, 47(5): 733-736. |
| [14] | XIE Hua-Shun- , MA Fu-Rong, FAN Dong-Sheng, WANG Li-Ping, YAN Yan, LU Pei-Quan. Acoustic analysis for 21 patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis complaining of dysarthria [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2014, 46(5): 751-755. |
|
||