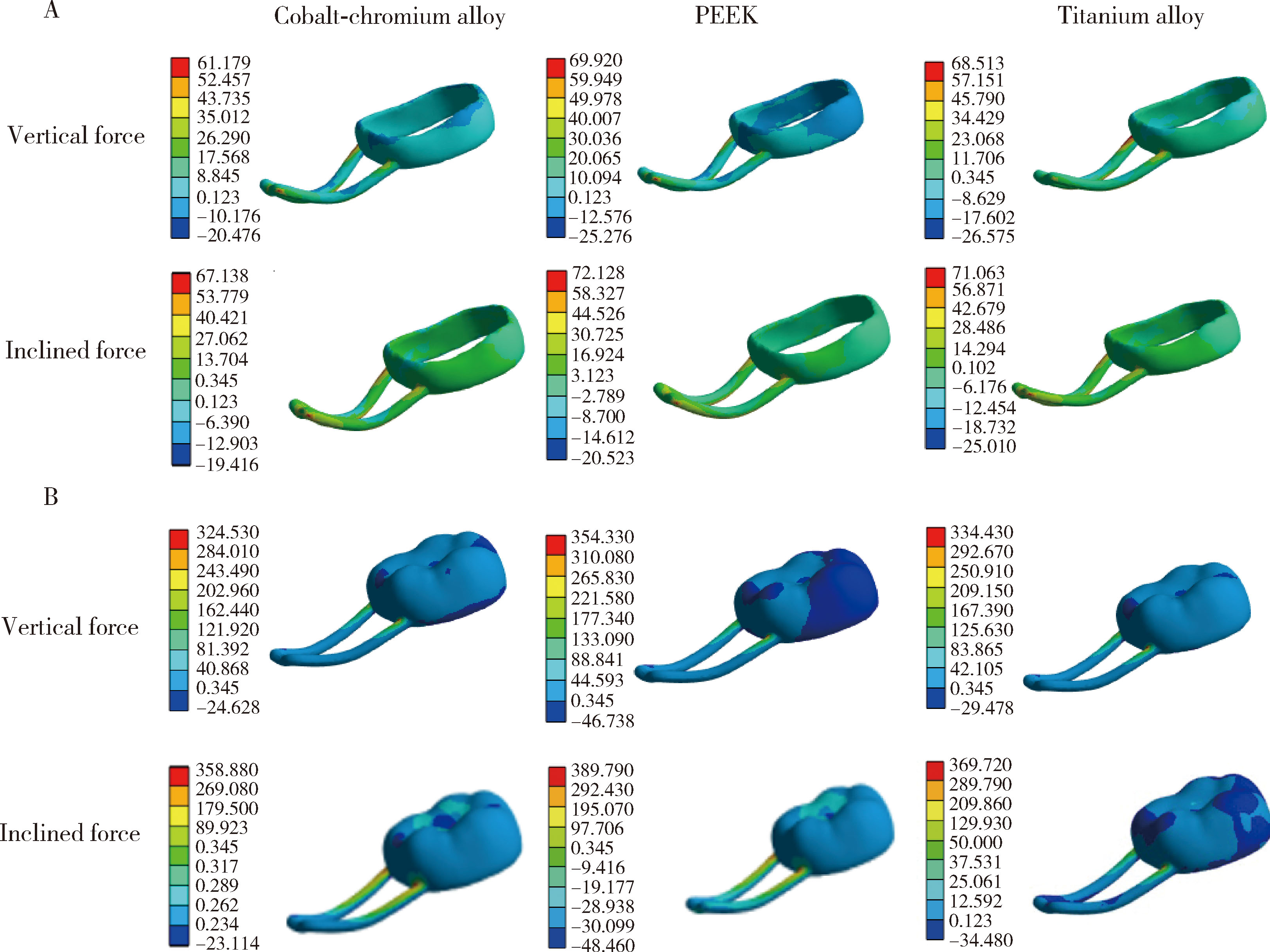
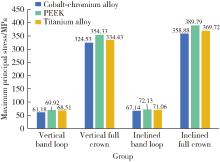
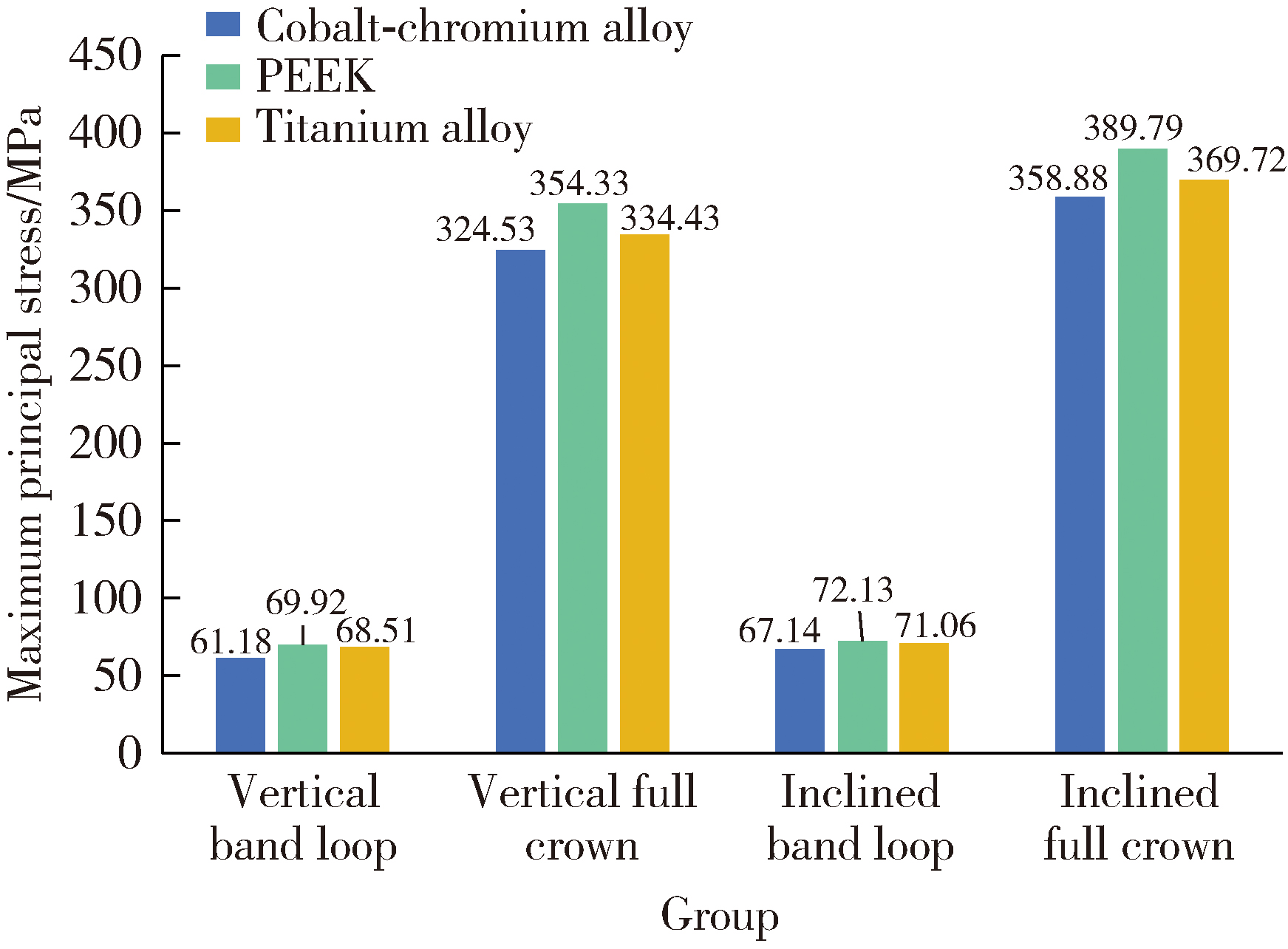
Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2025, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (2): 376-383. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2025.02.024
Previous Articles Next Articles
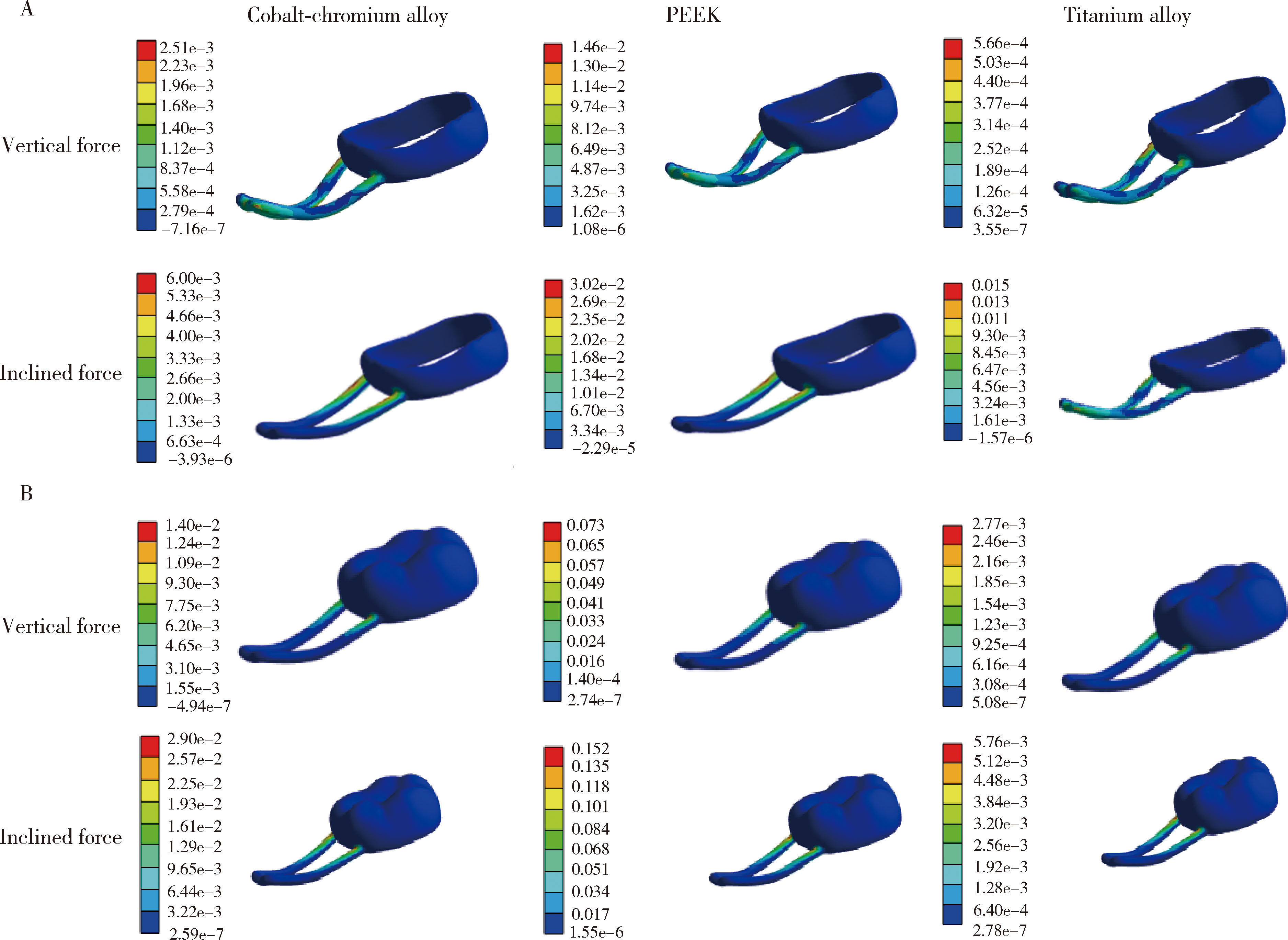
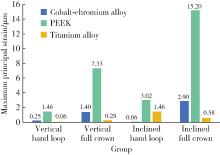
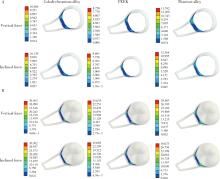
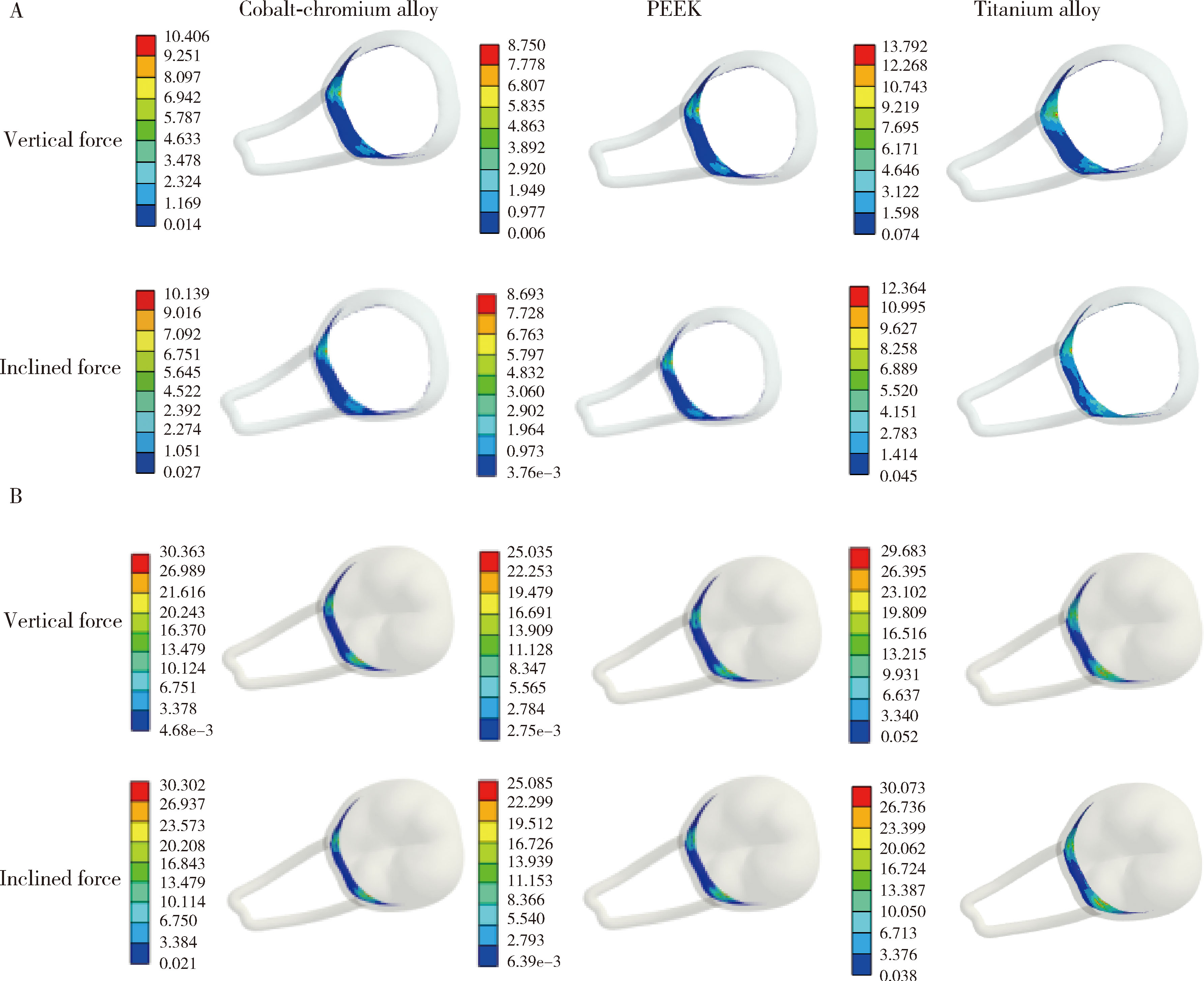
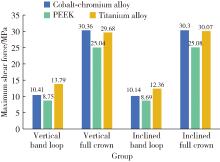
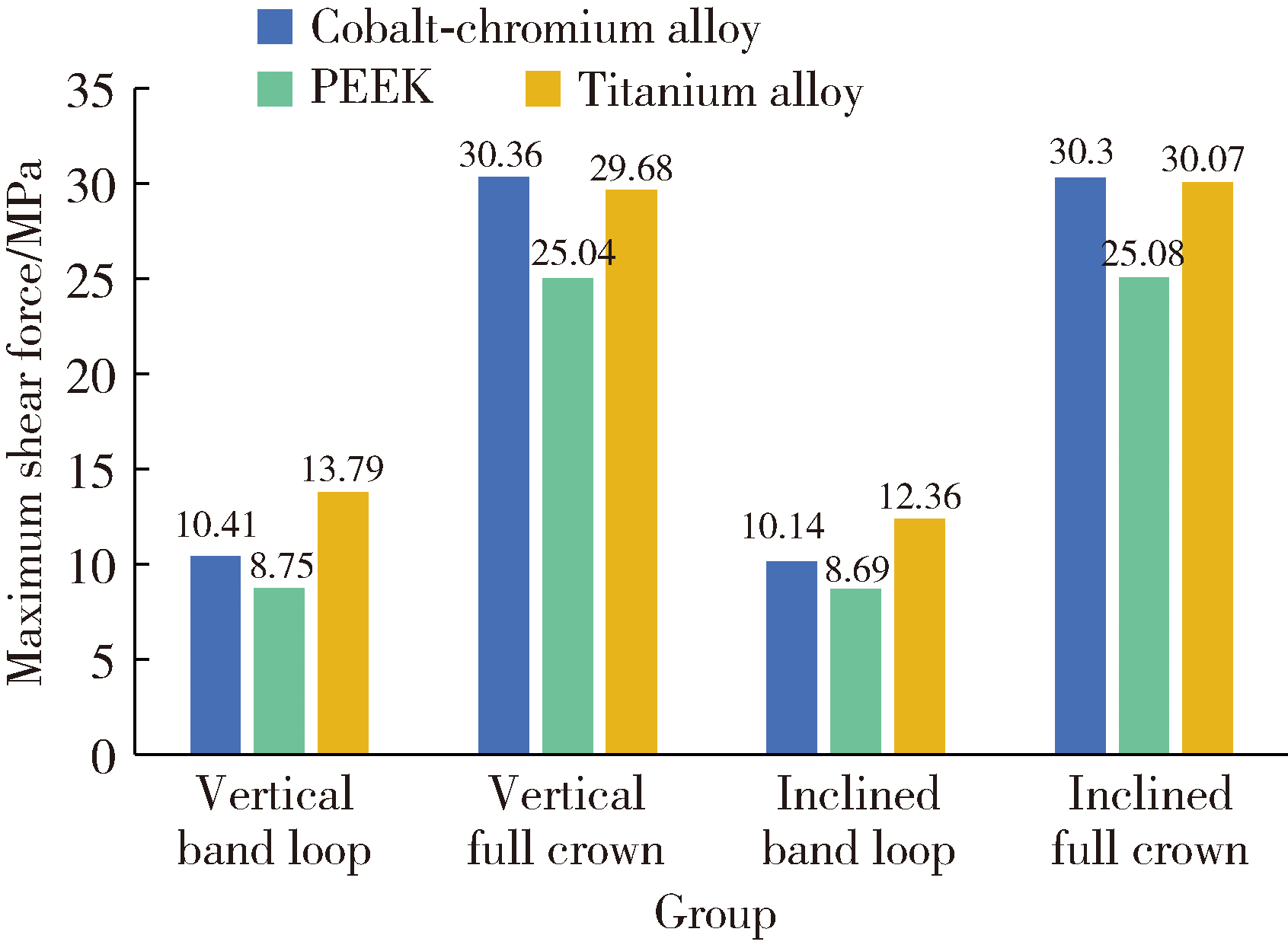
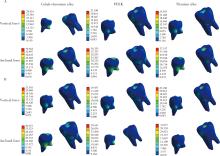
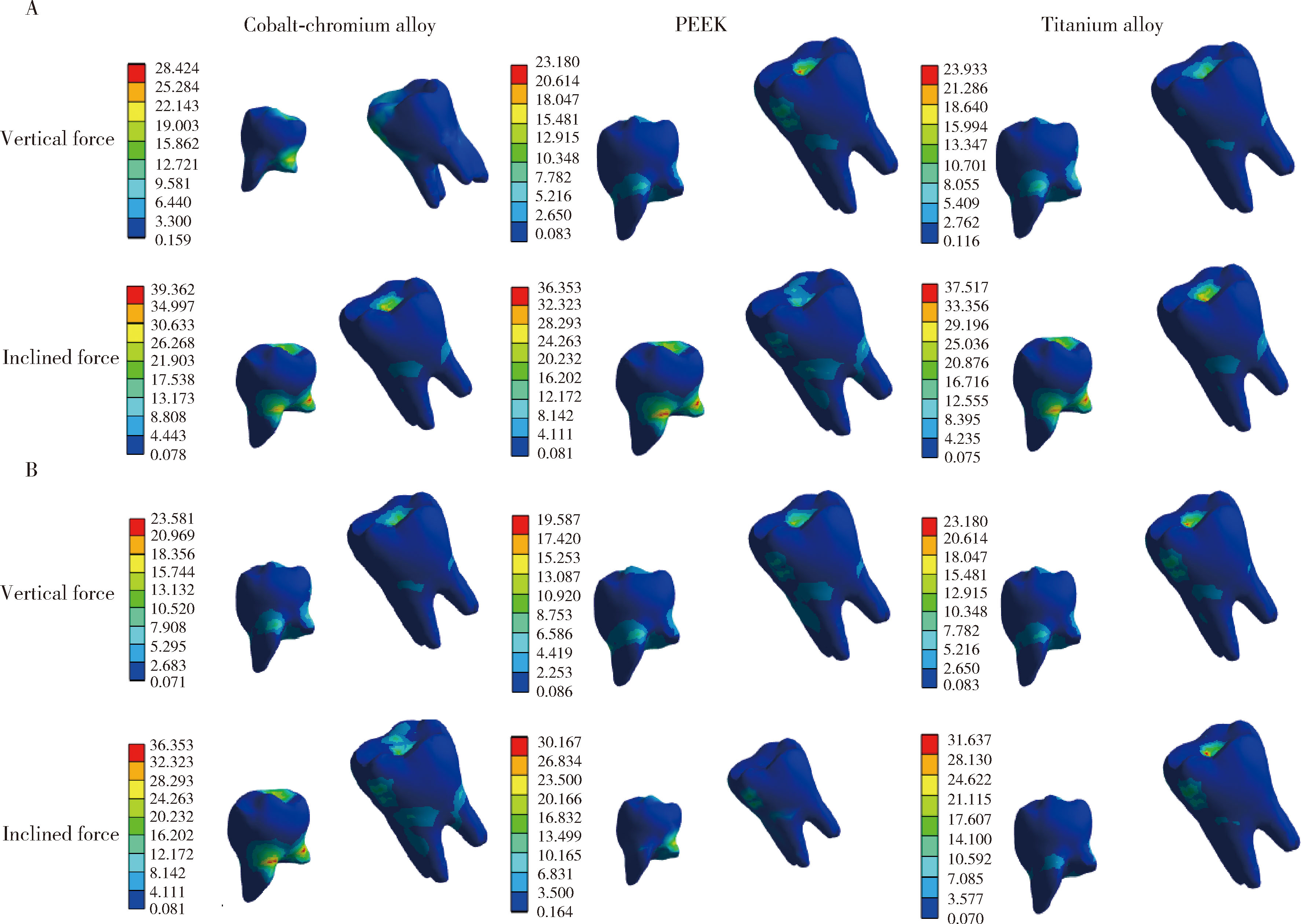
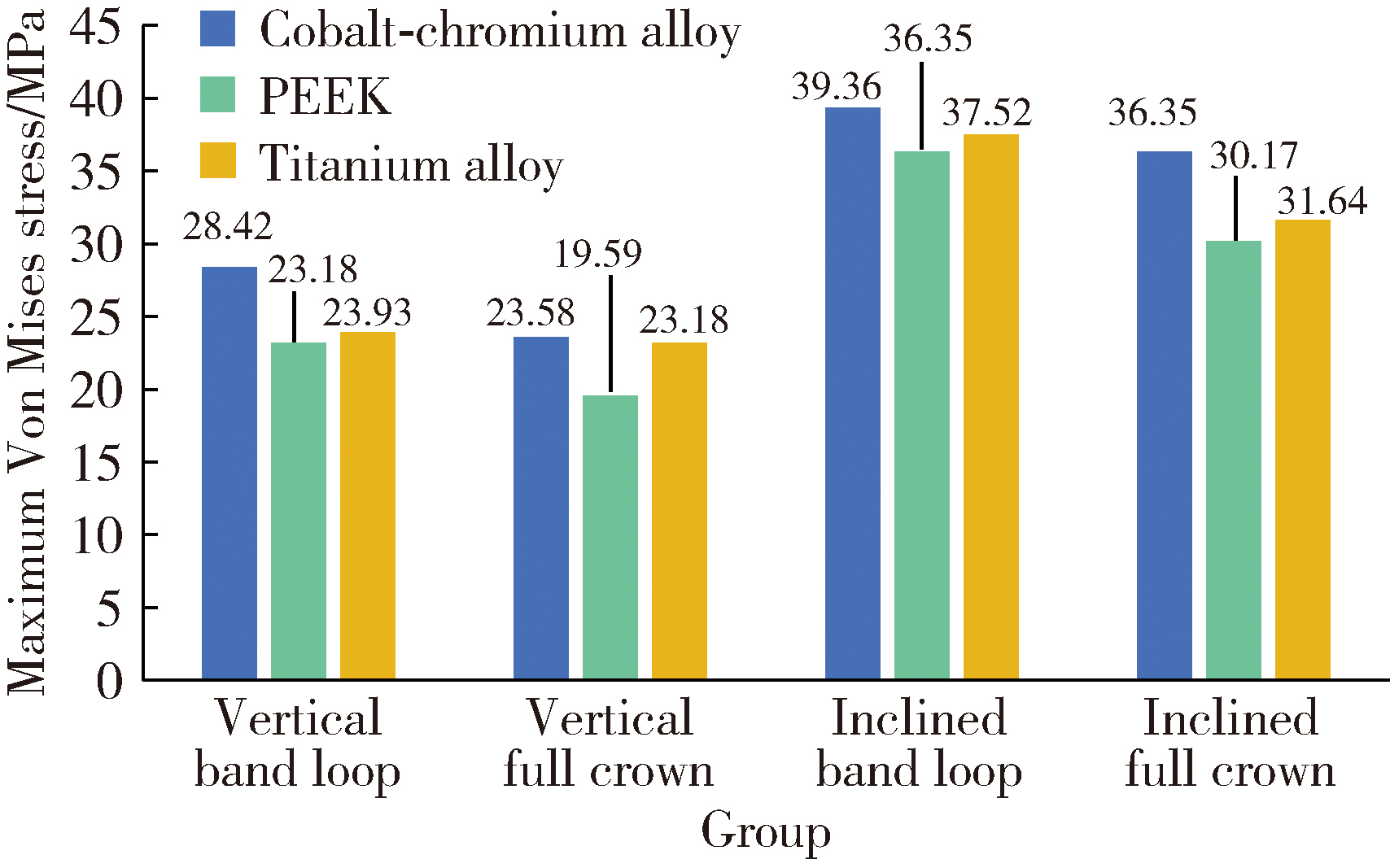
Three-dimensional finite element analysis of digital wire loop space maintainers for missing deciduous teeth
Lijuan MA1,2, Yonghui TENG3, Yong WANG1, Yijiao ZHAO1,4,△( ), Xinyue ZHANG1, Qingzhao QIN1, Dong YIN2
), Xinyue ZHANG1, Qingzhao QIN1, Dong YIN2
- 1. Center for Digital Dentistry, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Center for Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Research Center of Oral Biomaterials and Digi-tal Medical Devices & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology & NHC Research Center of Engineering and Technology for Computerized Dentistry, Beijing 100081, China
2. Department of Stomatology, People's Hospital of Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region(Ningxia Medical University), Yinchuan 750002, China
3. Department of Orthodontic, Yinchuan Stomatological Hospital, Yinchuan 750002, China
4. Institute of Medical Technology, Peking University Health Science Center, Beijing 100191, China
CLC Number:
- R783.2
| 1 | Slabkovskaya A , Abramova M , Morozova N , et al. Biomechanics of changing the position of permanent teeth with early loss of the first temporary molars[J]. Georgian Med News, 2021 (316/317): 89- 96. |
| 2 |
Jayachandar D , Gurunathan D , Jeevanandan G . Prevalence of early loss of primary molars among children aged 5-10 years in Chennai: A cross-sectional study[J]. J Indian Soc Pedod Prev Dent, 2019, 37 (2): 115- 119.
doi: 10.4103/1319-2442.261340 |
| 3 |
Sabeti AK , Karimizadeh Z , Rafatjou R . Maximum equivalent stress induced and the displacement of the developing permanent first molars after the premature loss of primary second molars: A finite element analysis[J]. Dent Med Probl, 2020, 57 (4): 401- 409.
doi: 10.17219/dmp/122041 |
| 4 | 秦庆钊, 胡嘉, 陈小贤, 等. 儿童带环丝圈式间隙保持器的椅旁数字化设计与制作方法初探[J]. 华西口腔医学杂志, 2024, 42 (2): 234- 241. |
| 5 |
冀堃, 朱顶贵, 陆伟, 等. 聚醚酮酮数字化乳牙早失间隙保持器的临床应用观察[J]. 中华口腔医学研究杂志(电子版), 2019, 13 (6): 368- 372.
doi: 10.3877/cma.j.issn.1674-1366.2019.06.008 |
| 6 |
张静兰, 莫伟兰, 刘芳, 等. 三种间隙保持器的临床效果评价[J]. 新医学, 2021, 52 (10): 768- 771.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-9802.2021.10.009 |
| 7 |
Tokuc M , Yilmaz H . Comparison of fit accuracy between conventional and CAD/CAM-fabricated band-loop space maintainers[J]. Int J Paediatr Dent, 2022, 32 (5): 764- 771.
doi: 10.1111/ipd.12955 |
| 8 |
Trivedi G , Singh PP , Oinam AS , et al. Cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) dose optimization technique and image quality assessment scoring[J]. J Cancer Res Ther, 2024, 20 (1): 71- 78.
doi: 10.4103/jcrt.jcrt_1130_22 |
| 9 |
Rees JS , Jacobsen PH . Elastic modulus of the periodontal ligament[J]. Biomaterials, 1997, 18 (14): 995- 999.
doi: 10.1016/S0142-9612(97)00021-5 |
| 10 |
Hart RT , Hennebel VV , Thongpreda N , et al. Modeling the biomechanics of the mandible: A three-dimensional finite element study[J]. J Biomech, 1992, 25 (3): 261- 286.
doi: 10.1016/0021-9290(92)90025-V |
| 11 |
Nishigawa G , Matsunaga T , Maruo Y , et al. Finite element analysis of the effect of the bucco-lingual position of artificial posterior teeth under occlusal force on the denture supporting bone of the edentulous patient[J]. J Oral Rehabil, 2003, 30 (6): 646- 652.
doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2842.2003.01110.x |
| 12 |
Eskitascioglu G , Usumez A , Sevimay M , et al. The influence of occlusal loading location on stresses transferred to implant-supported prostheses and supporting bone: A three-dimensional finite element study[J]. J Prosthet Dent, 2004, 91 (2): 144- 150.
doi: 10.1016/j.prosdent.2003.10.018 |
| 13 | W.A. 纳什. 材料力学[M]. 4版. 赵志岗, 译. 北京: 科学出版社, 2002: 20. |
| 14 |
Heravi F , Salari S , Tanbakuchi B , et al. Effects of crown-root angle on stress distribution in the maxillary central incisors' PDL during application of intrusive and retraction forces: A three-dimensional finite element analysis[J]. Prog Orthod, 2013, 14, 26.
doi: 10.1186/2196-1042-14-26 |
| 15 |
Hedayati Z , Shomali M . Maxillary anterior en masse retraction using different antero-posterior position of mini screw: A 3D finite element study[J]. Prog Orthod, 2016, 17 (1): 31.
doi: 10.1186/s40510-016-0143-z |
| 16 |
Yi Q , Feng X , Zhang C , et al. Comparison of dynamic mechanical properties of dentin between deciduous and permanent teeth[J]. Connect Tissue Res, 2021, 62 (4): 402- 410.
doi: 10.1080/03008207.2020.1758684 |
| 17 |
Saillard E , Gardegaront M , Levillain A , et al. Finite element models with automatic computed tomography bone segmentation for failure load computation[J]. Sci Rep, 2024, 14 (1): 16576.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-66934-w |
| 18 | Braun S , Hnat WP , Freudenthaler JW , et al. A study of maximum bite force during growth and development[J]. Angle Or-thod, 1996, 66 (4): 261- 264. |
| 19 |
Owais AI , Shaweesh M , Abu Alhaija ES . Maximum occusal bite force for children in different dentition stages[J]. Eur J Orthod, 2013, 35 (4): 427- 433.
doi: 10.1093/ejo/cjs021 |
| 20 |
Christensen J , Matzen LH , Hedegaard M , et al. Scout images acquired prior to cone beam CT acquisitions: Reproducibility of findings and added diagnostic information[J]. Dentomaxillofac Ra-diol, 2024, 53 (8): 527- 534.
doi: 10.1093/dmfr/twae039 |
| 21 | Abdin M , Ahmed E , Hamad R , et al. Success rates and failures of fixed and removable space maintainers after the premature loss of primary molars[J]. Quintessence Int, 2024, 55 (4): 304- 312. |
| 22 |
Gomes MC , Perazzo MF , Neves ÉTB , et al. Premature primary tooth loss and oral health-related quality of life in preschool children[J]. Int J Environ Res Public Health, 2022, 19 (19): 12163.
doi: 10.3390/ijerph191912163 |
| 23 | 刘磊, 马方方, 夏彬, 等. 聚醚醚酮/碳化硅复合材料的结构及性能[J]. 高分子材料科学与工程, 2023, 39 (11): 75- 81. |
| 24 |
李思媛, 薛雅娟. 聚醚醚酮材料的性能及在儿童口腔中的应用[J]. 医疗装备, 2023, 36 (21): 162- 164.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2376.2023.21.052 |
| 25 | 戴丽, 冀堃, 廖莹, 等. 聚醚酮酮数字化乳牙早失间隙保持器的临床效果及满意度[J]. 中国临床研究, 2021, 34 (12): 1670- 1672. |
| [1] | Shuang REN, Huijuan SHI, Zixuan LIANG, Si ZHANG, Xiaoqing HU, Hongshi HUANG, Yingfang AO. Biomechanics during cutting movement in individuals after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(5): 868-873. |
| [2] | Han ZHAO,Yan WEI,Xuehui ZHANG,Xiaoping YANG,Qing CAI,Chengyun NING,Mingming XU,Wenwen LIU,Ying HUANG,Ying HE,Yaru GUO,Shengjie JIANG,Yunyang BAI,Yujia WU,Yusi GUO,Xiaona ZHENG,Wenjing LI,Xuliang DENG. Bionic design, preparation and clinical translation of oral hard tissue restorative materials [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(1): 4-8. |
| [3] | Xinyu XU,Ling WU,Fengqi SONG,Zili LI,Yi ZHANG,Xiaojing LIU. Mandibular condyle localization in orthognathic surgery based on mandibular movement trajectory and its preliminary accuracy verification [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(1): 57-65. |
| [4] | Sui LI,Wenjie MA,Shimin WANG,Qian DING,Yao SUN,Lei ZHANG. Trueness of different digital design methods for incisal guidance of maxillary anterior implant-supported single crowns [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(1): 81-87. |
| [5] | Meng-en OU,Yun DING,Wei-feng TANG,Yong-sheng ZHOU. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of cement flow in abutment margin-crown platform switching [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(3): 548-552. |
| [6] | Jing WEN,Xiang-ying OUYANG,Xi-yan PEI,Shan-yong QIU,Jian-ru LIU,Wen-yi LIU,Cai-fang CAO. Multivariable analysis of tooth loss in subjects with severe periodontitis over 4-year natural progression [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(1): 70-77. |
| [7] | FENG Sha-wei,GUO Hui,WANG Yong,ZHAO Yi-jiao,LIU He. Initial establishment of digital reference standardized crown models of the primary teeth [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(2): 327-334. |
| [8] | TIAN Jing,QIN Man,CHEN Jie,XIA Bin. Early loss of primary molar and permanent tooth germ caused by the use of devitalizer during primary molar root canal therapy: Two cases report [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(2): 381-385. |
| [9] | LI Yi,WONG Lai U,LIU Xiao-qiang,ZHOU Ti,LYU Ji-zhe,TAN Jian-guo. Marginal features of CAD/CAM laminate veneers with different materials and thicknesses [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(1): 140-145. |
| [10] | QIU Shu-ting,ZHU Yu-jia,WANG Shi-min,WANG Fei-long,YE Hong-qiang,ZHAO Yi-jiao,LIU Yun-song,WANG Yong,ZHOU Yong-sheng. Preliminary clinical application verification of complete digital workflow of design lips symmetry reference plane based on posed smile [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(1): 193-199. |
| [11] | XU Xiao-xiang,CAO Ye,ZHAO Yi-jiao,JIA Lu,XIE Qiu-fei. In vitro evaluation of the application of digital individual tooth tray in the impression making of mandibular full-arch crown abutments [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(1): 54-61. |
| [12] | YUE Zhao-guo,ZHANG Hai-dong,YANG Jing-wen,HOU Jian-xia. Comparison of residual cement between CAD/CAM customized abutments and stock abutments via digital measurement in vitro [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(1): 69-75. |
| [13] | LI Zheng,LIU Yu-shu,WANG Shi-min,ZHANG Rui,JIA Lu,YE Hong-qiang,HU Wen-jie,ZHAO Wen-yan,LIU Yun-song,ZHOU Yong-sheng. Application of biocopy function of temporary crown occlusal morphology in patients with severe attrition [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(1): 62-68. |
| [14] | FANG Shuo-bo,YANG Guang-ju,KANG Yan-feng,SUN Yu-chun,XIE Qiu-fei. Method and accuracy of determining the jaw position of repositioning splint with the aid of digital technique [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(1): 76-82. |
| [15] | Lang YOU,Ke-hui DENG,Wei-wei LI,Yi-jiao ZHAO,Yu-chun SUN,Yong-sheng ZHOU. Visual sensitivity threshold of lateral view of nasolabial Angle changes in edentulous jaw patients [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2020, 52(1): 107-112. |
|
||