Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2020, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (2): 308-316. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2020.02.019
Previous Articles Next Articles
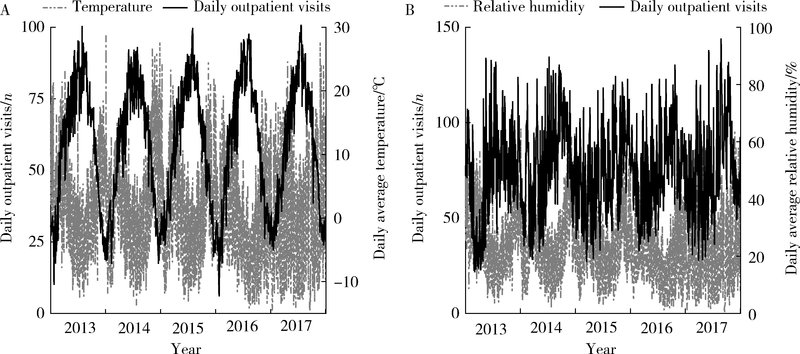
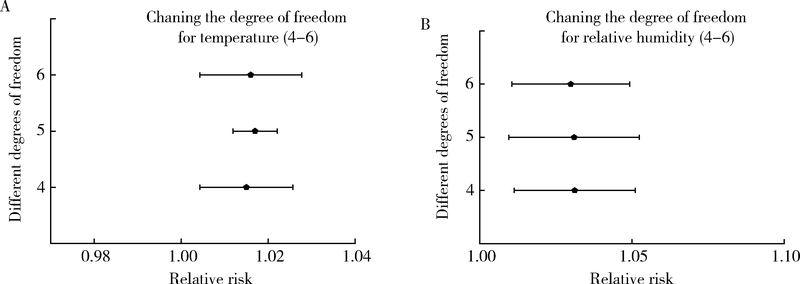
Effects of temperature and relative humidity on the number of outpatients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and their interaction effect in Lanzhou, China
Hai-rong BAO1,Xiao-ju LIU1,En-li TAN1,Juan SHU1,Ji-yuan DONG2,△( ),Sheng LI3
),Sheng LI3
- 1. Department of Gerontal Respiratory Medicine, The First Hospital of Lanzhou University, Lanzhou 730000, China
2. Institute of Occupational and Environmental Health, School of Public Health, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou 730000, China
3. Lanzhou Center for Disease Prevention and Control, Lanzhou 730030, China
CLC Number:
- R122.7
| [1] | 曾运红, 郭兰萍, 张羽 , 等. 慢性阻塞性肺疾病发病性院与气候因素的关系[J]. 广东医学, 2003,24(11):1230-1231. |
| [2] | 阴俊, 谈建国, 竺丽明 , 等. 不同地区慢性阻塞性肺病与气象因子相关性分析[J]. 气象科技, 2007,35(6):841-844. |
| [3] | 李耀宁, 陶立新, 张子曰 , 等. 慢性阻塞性肺病与气象因素相关性分析[J]. 气象与环境学报, 2010,26(6):13-17 |
| [4] | 陈新, 刘特, 王树越 , 等. 日平均气温对医院慢性阻塞性肺疾病急性加重患者住院人次的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(医学版), 2015,41(2):389-392 |
| [5] | Liang WM, Liu WP, Kuo HW . Diurnal temperature range and emergency room admissions for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in Taiwan[J]. Int J Biometeorol, 2009,53(1):17-23. |
| [6] | Donaldson GC, Golderoing JJ, Wedzicha JA . Influence of season on exacerbation characteristics in patients with COPD[J]. Chest, 2012,141(1):94-100. |
| [7] | Ferrari U, Exner T, Wanka ER , et al. Influence of air pressure, humidity, solar radiation, temperature, and wind speed on ambulatory visits due to chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in Bava-ria, Germany[J]. Int J Biometeorol, 2012,56(1):137-143. |
| [8] | Jenkings CR, Celli B, Aanerson JA , et al. Seasonality and determinants of moderate and severe COPD exacerbations in the TORCH study[J]. Eur Respir J, 2012,39(1):38-45. |
| [9] | Tseng CM ,Chen YT,Ou SM, et al.The effect of cold temperature on increased exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a nationwide study.[J]. PLoS One, 2013,8(3):1-7. |
| [10] | Almagrop P, Hernandez C, Martinex-Camblor P , et al. Seasonality, ambient temperatures and hospitalizations for acute exacerbation of COPD: A population-based study in a metropolitan area[J]. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis, 2015,10(1):899-908. |
| [11] | Hansel NN, Mccormack MC, Kim V . The Effects of Air Pollution and Temperature on COPD[J]. COPD, 2016,13(3):372-379. |
| [12] | Mccormack MC, Paulin LM, Gummerson CE , et al. Colder temperature is associated with increased COPD morbidity[J]. Eur Respir J, 2017,49(6):1-7. |
| [13] | 景文超, 马玉霞 . 兰州市呼吸道疾病与气象要素关系分析[C]// 第28届中国气象学会年会: S14气候环境变化与人体健. 厦门: 中国气象学会, 2011: 1-15. |
| [14] | 李银娟, 方秋红 . 住院慢性阻塞性肺疾病急性加重期患者季候分布特点调查及气象影响因素分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2015(14):1695-1699 |
| [15] | 周先锋, 于思雨, 阮晓楠 , 等. 气象因素对慢性阻塞性肺疾病患者门诊就诊人次的影响[J]. 环境与职业医学, 2015,32(8):711-716 |
| [16] | 王敏珍, 郑山, 王式功 , 等. 气温与湿度的交互作用对呼吸系统疾病的影响[J]. 中国环境科学, 2016,36(2):581-588 |
| [17] | 付桂琴, 刘华悦, 贾俊妹 . 石家庄地区气温对慢性阻塞性肺病住院人次的影响[J]. 气象与环境学报, 2017,33(2):102-106 |
| [18] | 杨慧慧 . 合肥市2010-2012 年温度和湿度对儿童手足口病的影响及其交互效应[D]. 合肥: 安徽医科大学, 2016 |
| [19] | 赵雨馨 . 长春市气温变化和天气环流型对慢性阻塞性肺病的影响研究[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2018 |
| [20] | Gasparrini A, Armstrong B, Kenward MG . Distributed lag non linear models[J]. Stat Med, 2010,29(21):2224-2234. |
| [21] | Gasparrini A . Distributed lag linear and non-linear models in R: the package dlnm[J]. J Stat Softw, 2011,43(8):1-20. |
| [22] | Gasparrini A, Armstrong B, Kenward MG . Reducing and meta-analyzing estimates from distributed lag non-linear models[J]. BMC Med Res Methodol, 2013,13(1):1. |
| [23] | Gasparrini A . Modeling exposure-lag-response associations with distributed lag non-linear models[J]. Stat Med, 2014,33(5):881-899. |
| [24] | Mukaka M . Statistics Corner: A guide to appropriate use of correlation coefficient in medical research[J]. J Med Asso Malawi, 2012,24(3):69-71. |
| [25] | 郭亮, 王烨菁, 贾晓东 , 等. 气温对上海市某中心城区医院急诊内科就诊量的影响[J]. 环境与职业医学, 2017,34(4):321-325. |
| [26] | 王金玉, 李盛, 李普 , 等. 2014-201年兰州市气温与死亡人次关系的时间序列研究[J]. 环境与职业医学, 2018,35(12):1076-1082 |
| [27] | 韦性富, 郑山, 翁俊 , 等. 甘肃省金昌市气温变化对高血压门急诊就诊人次影响的时间序列分析[J]. 环境与职业医学, 2019,36(5):452-458. |
| [28] | Ye XF . The effects of hot and cold temperatures on emergency hospital admissions in Brisbane, Australia[D]. Australia: Queensland University of Technology, 2013. |
| [29] | 李骊 . 广州市大气污染,气象与逐日人群死亡数的关系研究[D]. 广州: 南方医科大学, 2015. |
| [30] | 甘肃省体育局. 2014年甘肃省国民体质监测报告[M]. 兰州: 甘肃人民出版社, 2017: 80-100. |
| [1] | Yuxin WANG, Ru CAO, Jing HUANG, Ponsawansong Pitakchon, Tawatsupa Benjawan, Xiaochuan PAN, Prapamontol Tippawan, Guoxing LI. Impact of fine particulate matter exposure on non-accidental mortality under different apparent temperature levels [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(5): 820-827. |
| [2] | Qingxin ZHOU,Qingqing YANG,Shuyuan SHI,Pei LI,Feng SUN. Association between serum uric acid and airflow obstruction based on the health-checkup population [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 693-699. |
| [3] | Xiang CAI,Rendong WANG,Shijia WANG,Ziqi REN,Qiuhong YU,Dongguo LI. Dynamic trajectory and cell communication of different cell clusters in malignant progression of glioblastoma [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(2): 199-206. |
| [4] | Zi-kai WANG,Jia-li MO,Meng ZHANG,Ji-ping LIAO. Epidemiology and hospitalization costs analysis of female inpatients with acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in Beijing from 2013 to 2020 [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(6): 1074-1081. |
| [5] | Su-huan XU,Bei-bei WANG,Qiu-ying PANG,Li-jun ZHONG,Yan-ming DING,Yan-bo HUANG,Xin-yan CHE. Effect of equal temperature bladder irrigation in patients with transurethral resection of prostate: A meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(4): 676-683. |
| [6] | Xue-heng WANG,Si-yue WANG,He-xiang PENG,Meng FAN,Huang-da GUO,Tian-jiao HOU,Meng-ying WANG,Yi-qun WU,Xue-ying QIN,Xun TANG,Jin LI,Da-fang CHEN,Yong-hua HU,Tao WU. Genotype-environment interaction on arterial stiffness: A pedigree-based study [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(3): 400-407. |
| [7] | Ruo-qing ZHONG,Meng-qian ZHU,Ying-long LI,Jie PAN. Antibacterial effect of low-temperature plasma on Enterococcus faecalis in dentinal tubules in vitro [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(1): 38-43. |
| [8] | Ruo-tong YANG,Meng-ying WANG,Chun-nan LI,Huan YU,Xiao-wen WANG,Jun-hui WU,Si-yue WANG,Jia-ting WANG,Da-fang CHEN,Tao WU,Yong-hua HU. Interaction between ischemic stroke risk loci identified by genome-wide association studies and sleep habits [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(3): 412-420. |
| [9] | Xi CHEN,Si-yue WANG,En-ci XUE,Xue-heng WANG,He-xiang PENG,Meng FAN,Meng-ying WANG,Yi-qun WU,Xue-ying QIN,Jing LI,Tao WU,Hong-ping ZHU,Jing LI,Zhi-bo ZHOU,Da-fang CHEN,Yong-hua HU. Exploring the association between de novo mutations and non-syndromic cleft lip with or without palate based on whole exome sequencing of case-parent trios [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(3): 387-393. |
| [10] | ZHU Xiao-ling,LI Wen-jing,WANG Xian-e,SONG Wen-li,XU Li,ZHANG Li,FENG Xiang-hui,LU Rui-fang,SHI Dong,MENG Huan-xin. Gene polymorphisms of cytochrome B-245 alpha chain (CYBA) and cholesteryl ester transfer protein (CETP) and susceptibility to generalized aggressive periodontitis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(1): 18-22. |
| [11] | Jiao HE,Ge-heng YUAN,Jun-qing ZHANG,Xiao-hui GUO. Approach to creating early diabetic peripheral neuropathy rat model [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(6): 1150-1154. |
| [12] | Yuan ZHANG,Jian-min HAN,Lin LIU,Xu-liang DENG. Study of bond strength of one-piece glass fiber posts-and-cores with flared root canals in vitro [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(2): 327-334. |
| [13] | Jiang XIE,Fei LI. Association of sleep overlap syndrome with type 2 diabetes in a cross-sectional study [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(2): 252-255. |
| [14] | WANG Jin-yu, LI Sheng, DONG Ji-yuan, LI Shou-yu, LI Pu, JIA Qing, WANG Ling-qing, CHANG Xu-hong. Distributed lag effects on the relationship between daily mean temperature and the incidence of bacillary dysentery in Lanzhou city [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2018, 50(5): 861-867. |
| [15] | YUAN Yuan, WANG Ping, WU-CHOU Yah-huei YE Xiao-qian, HUANG Shang-zhi, SHI Bing, WANG Ke, WANG Zhu-qing, LIU Dong-jing, WANG Zi-fan9,WU Tao, WANG Hong. Association study between candidate genes involved in cell-cell adhesion and non-syndromic cleft lip with or without cleft palate in Chinese population [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2016, 48(3): 403-408. |
|
||