Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2023, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (1): 120-123. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2023.01.018
Previous Articles Next Articles
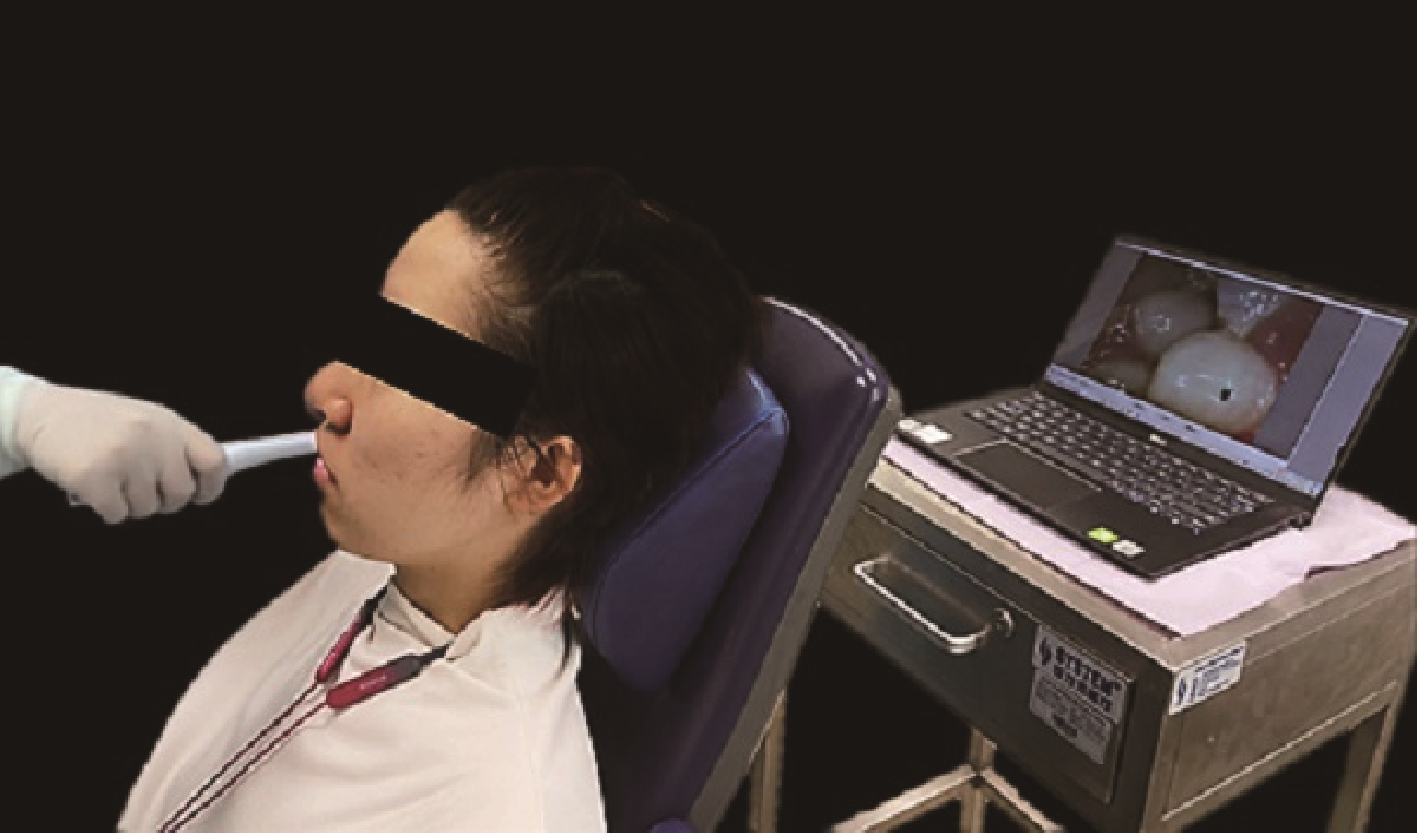
A study on the application of intraoral camera in the identification of oral anatomical landmarks
Shu-ting CHIU,Ebrahimi FARAZ,Xiao ZHANG,Hong-qiang YE*( ),Yun-song LIU*(
),Yun-song LIU*( )
)
- Department of Prosthodontics, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Center of Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Research Center of Oral Biomaterials and Digi-tal Medical Devices & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology & NHC Research Center of Engineering and Technology for Computerized Dentistry & NMPA Key Laboratory for Dental Materials, Beijing 100081, China
CLC Number:
- R781.0
| 1 | 周永胜. 口腔修复学[M]. 3版 北京: 北京大学医学出版社, 2020: 289- 292. |
| 2 | 孙玉春, 王勇, 邓珂慧, 等. 功能易适数字化全口义齿的自主创新研发[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52 (2): 390- 394. |
| 3 | 张志愿. 口腔颌面外科学[M]. 8版 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2020: 45- 49. |
| 4 |
刘济远, 唐休发, 王了, 等. 口腔内窥镜在牙槽外科临床实习教学中的应用初探[J]. 中国继续医学教育, 2020, 12 (35): 54- 57.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-9308.2020.35.015 |
| 5 |
Wander P , Ireland RS . Dental photography in record keeping and litigation[J]. Br Dent J, 2014, 217 (3): 133- 137.
doi: 10.1038/sj.bdj.2014.649 |
| 6 |
Christensen GJ . Important clinical uses for digital photography[J]. J Am Dent Assoc, 2005, 136 (1): 77- 79.
doi: 10.14219/jada.archive.2005.0030 |
| 7 | Ferrazzano GF , Orlando S , Cantile T , et al. An experimental in vivo procedure for the standardised assessment of sealants retention over time[J]. Eur J Paediatr Dent, 2016, 17 (3): 176- 180. |
| 8 |
Alzayyat NA , Hafez RM , Yassen AA , et al. Accuracy of the light-induced fluorescent intraoral camera in occlusal caries detection[J]. J Contemp Dent Pract, 2021, 22 (4): 365- 372.
doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-3082 |
| 9 |
Signori C , Collares K , Cumerlato CBF , et al. Validation of assessment of intraoral digital photography for evaluation of dental restorations in clinical research[J]. J Dent, 2018, 71, 54- 60.
doi: 10.1016/j.jdent.2018.02.001 |
| 10 | Vetchaporn S , Rangsri W , Ittichaicharoen J , et al. Validity and reliability of intraoral camera with fluorescent aids for oral potentially malignant disorders screening in teledentistry[J]. Int J Dent, 2021, 2021, 6814027. |
| 11 | 马莎, 朱文卓, 赵豫梅, 等. 基于当代医患关系对医学生医德教育的思考与探讨[J]. 中国继续医学教育, 2022, 14 (13): 162- 165. |
| 12 | 王姝侠, 彭雪寒, 孟忆贫, 等. 论医学生爱伤意识的培养[J]. 重庆医学, 2013, 42 (25): 3068- 3069. |
| 13 | 董向辉, 靳占奎. PBL方法联合SEGUE量表提升骨科规培医师医患沟通能力的应用效果[J]. 中国当代医药, 2022, 29 (27): 157- 161. |
| [1] | Chen CHEN,Yuhong LIANG. Root canal therapy of maxillary molars with atypical canals: A report of three cases [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(1): 190-195. |
| [2] | Han ZHAO,Yan WEI,Xuehui ZHANG,Xiaoping YANG,Qing CAI,Chengyun NING,Mingming XU,Wenwen LIU,Ying HUANG,Ying HE,Yaru GUO,Shengjie JIANG,Yunyang BAI,Yujia WU,Yusi GUO,Xiaona ZHENG,Wenjing LI,Xuliang DENG. Bionic design, preparation and clinical translation of oral hard tissue restorative materials [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(1): 4-8. |
| [3] | Tuan-feng ZHOU,Xue YANG,Rui-jie WANG,Ming-xuan CHENG,Hua ZHANG,Jin-qi WEI. A clinical application study of digital manufacturing simple intraoral Gothic arch-tracing device in determining the centric relation of complete dentures [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(1): 101-107. |
| [4] | Wei YONG,Kun QIAN,Wen-hao ZHU,Xiao-yi ZHAO,Chang LIU,Jie PAN. X-ray evaluation of pulp calcification in adult permanent teeth after pulpotomy [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(1): 88-93. |
| [5] | Wei-wei LI,Hu CHEN,Yong WANG,Yu-chun SUN. Research on friction and wear behaviors of silicon-lithium spray coating on zirconia ceramics [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(1): 94-100. |
| [6] | PENG Li, WANG Zu-hua, SUN Yu-chun, QU Wei,HAN Yang, LIANG Yu-hong. Computer aided design and three-dimensional printing forapicoectomy guide template [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2018, 50(5): 905-910. |
| [7] | TAN Jing, WEI Xiu-xia, ZHANG Qing-hui, ZHOU Yong-sheng. Three-year clinical effects of a modified semi-fixed bridge on restoring a missing posterior tooth [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2018, 50(2): 314-317. |
| [8] | JIAO Yang, WANG Ji-de, DENG Jiu-peng. Effect of different surface treatments on the crystal structure and properties of zirconia [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2018, 50(1): 49-52. |
| [9] | LIAO Yu, LIU Xiao-qiang, CHEN Li, ZHOU Jian-feng, TAN Jian-guo. Effects of different surface treatments on the zirconia-resin cement bond strength [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2018, 50(1): 53-57. |
| [10] | ZHANG Hao-yu, JIANG Ting, CHENG Ming-xuan, ZHANG Yu-wei. Wear intensity and surface roughness of microhybrid composite and ceramic occlusal veneers on premolars after the thermocycling and cyclic mechanical loading tests [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2018, 50(1): 73-77. |
| [11] | TANG Lin, ZHANG Yi, LI Hao, LIU Yu-hua, ZHOU Yong-sheng, LI Bo-wen, WU Wei-yi, WANG Si-wen. Influence of EDC ethanol solution on dentin shear bond strength with a self-etch adhesive system [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2017, 49(6): 1055-1059. |
| [12] | LI Hao, LIU Yu-hua, LUO Zhi-qiang. Effects of bioactive glass on reducing the hypersensitivity after full crown preparation [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2017, 49(4): 709-713. |
| [13] | ZHAO Yi-jiao, LIU Yi, SUN Yu-chun, WANG Yong. Three-dimensional data fusion method for tooth crown and root based on curvature continuity algorithm#br# [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2017, 49(4): 719-723. |
|
||