北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2019, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (3): 430-438. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2019.03.009
非线性动力学方法可预警直立倾斜试验中血管迷走性晕厥的发生
李凡1,王汉斌2,彭清1,孙云闯1,张冉2,庞博2,方竞2,张珏2△( ),黄一宁1△(
),黄一宁1△( )
)
- 1. 北京大学第一医院神经内科,北京 100034
2. 北京大学前沿交叉学科研究院,北京 100871
Prediction of syncope with nonlinear dynamic analysis during head-up tilt in vasovagal syncope patients
Fan LI1,Han-bin WANG2,Qing PENG1,Yun-chuang SUN1,Ran ZHANG2,Bo PANG2,Jing FANG2,Jue ZHANG2△( ),Yi-ning HUANG1△(
),Yi-ning HUANG1△( )
)
- 1. Department of Neurology, Peking University First Hospital, Beijing 100034, China
2. Academy of Advanced Interdisciplinary Study, Peking University, Beijing 100871, China
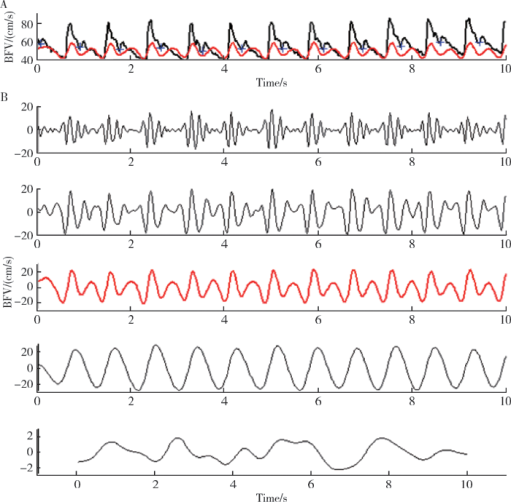
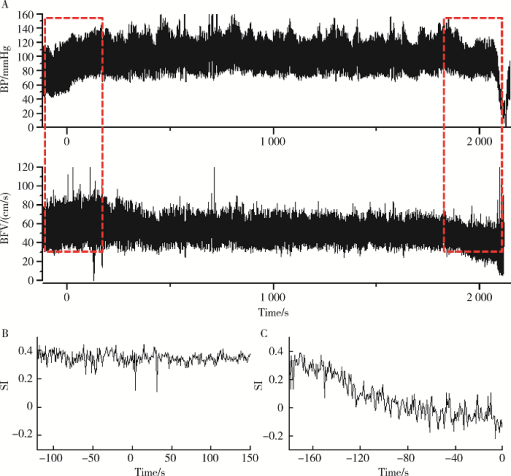
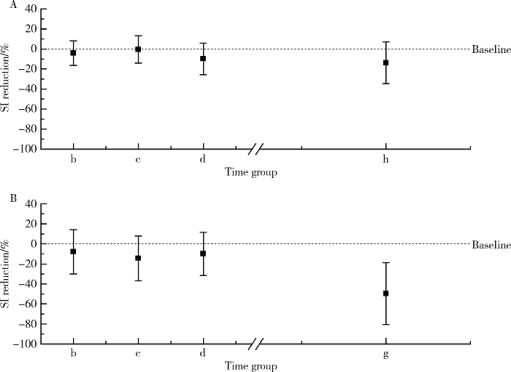
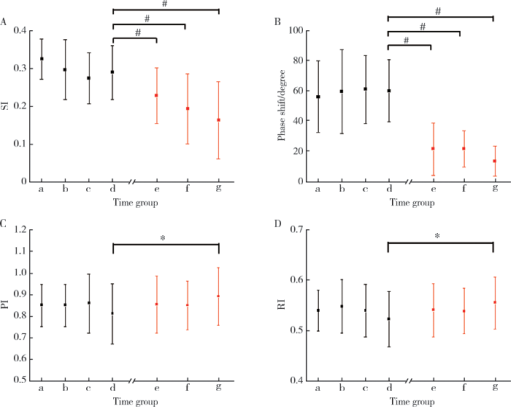
摘要: 目的 量化评价血管迷走性晕厥血压下降过程中的脑血流自动调节功能,用于在晕厥相关症状出现前预测其发生。方法 选取20位直立倾斜试验证实的血管迷走性晕厥患者,另选取20名正常对照者。所有被试在直立倾斜试验前都要平卧30 min,同时使用TCD 2 MHz Doppler监测探头监测双侧大脑中动脉血流速度,心电监护监测心率,使用连续每搏血压监测指端无创连续血压。在进行10 min基线数据采集后,被试继续进行70°直立倾斜试验,每位被试至少直立30 min,或在30 min内出现晕厥发作或晕厥前兆时或当被试出现突发血压下降≥20 mmHg时终止检查。利用多模态血流血压分析(multimodal pressure-flow analysis,MMPF)的非线性动力学方法对不同时相的脑血流自动调节功能进行分析。利用信号分析的方法将脑血流信号记录中的重搏切迹深度量化测量,定义新的预测参数晕厥指数(syncope index,SI)用于评估血压变化时的脑血管张力。结果 病例组在血管迷走性晕厥发生时的晕厥指数与倾斜试验开始时的基线数值相比存在明显下降(0.16±0.10 vs. 0.27±0.10,P<0.01), 而对照组在倾斜试验结束时的晕厥指数与倾斜试验开始时的基线数值相比差异无统计学意义。对于血管迷走性晕厥组的患者,在晕厥发生前3 min,搏动指数与基线数据相比未见明显变化(P>0.05),但晕厥指数已出现明显下降(0.23±0.07 vs.0.29±0.07,P<0.01)。结论 当血管迷走性晕厥发生时脑血流动态调节功能衰竭,小血管张力的丧失与脑血流自动调节功能的丧失是相关的;晕厥指数可以作为提前预测血管迷走性晕厥发生的一个有用的参数。
中图分类号:
- R725.4
| [1] | Peter N . Cerebral blood flow, heart rate, and blood pressure patterns during the tilt test in common orthostatic syndromes[J]. Neuroscience J, 2016,2016:6127340. |
| [2] | Shen WK, Sheldon RS, Benditt DG , et al. 2017 ACC/AHA/HRS Guideline for the evaluation and management of patients with syncope: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines and the Heart Rhythm Society[J]. Circulation, 2017,136(5):e60-e122. |
| [3] |
Brignole M , Moya A, de Lange FJ, et al. 2018 ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and management of syncope[J]. Eur Heart, 2018,39(21):1883-1948.
doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehy037 |
| [4] |
Victor C, Satish R . Confounders of vasovagal syncope: orthostatic hypotension[J]. Cardiol Clin, 2013,31(1):89-100.
doi: 10.1016/j.ccl.2012.09.003 |
| [5] |
Gommer ED, Shijaku E, Mess WH , et al. Dynamic cerebral autoregulation: different signal processing methods without influence on results and reproducibility[J]. Med Biol Eng Comput, 2010,48(12):1243-1250.
doi: 10.1007/s11517-010-0706-y |
| [6] |
Hu K, Peng CK, Huang NE , et al. Altered phase interactions between spontaneous BP and flow fluctuations in type 2 diabetes mellitus: nonlinear assessment of cerebral autoregulation[J]. Physica A, 2008,387(10):2279-2292.
doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2007.11.052 |
| [7] |
Lo MT, Novak V, Peng CK , et al. Nonlinear phase interaction between nonstationary signals: a comparison study of methods based on Hilbert-Huang and fourier transforms[J]. Phys Rev E Stat Nonlin Soft Matter Phys, 2009,79(6 Pt 1):61924.
doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.79.061924 |
| [8] |
Men-Tzung L, Kun H, Yanhui L , et al. Multimodal pressure-flow analysis: application of Hilbert-Huang transform in cerebral blood flow regulation[J]. EURASIP J Adv Signal Process, 2008,2008:785243.
doi: 10.1155/2008/785243 |
| [9] |
Tiecks FP, Lam AM, Aaslid R , et al. Comparison of static and dynamic cerebral autoregulation measurements[J]. Stroke, 1995,26:1014-1019.
doi: 10.1161/01.STR.26.6.1014 |
| [10] |
Grubb BP, Gerard G, Roush K , et al. Cerebral vasoconstriction during head-upright tilt-induced vasovagal syncope. A paradoxic and unexpected response[J]. Circulation 1991,84(3):1157-1164.
doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.84.3.1157 |
| [11] |
Albina G, Cisneros L F, Laiño R , et al. Transcranial Doppler monitoring during head upright tilt table testing in patients with suspected neurocardiogenic syncope[J]. Europace, 2004,6(1):63-69.
doi: 10.1016/j.eupc.2003.09.009 |
| [12] |
Furukawa T . Role of head-up tilt table testing in patients with syncope or transient loss of consciousness[J]. J Arrhythm, 2017,33(6):568-571.
doi: 10.1016/j.joa.2017.08.002 |
| [13] |
Carey BJ, Manktelow BN, Panerai R , et al. Cerebral autoregulatory responses to head-up tilt in normal subjects and patients with recurrent vasovagal syncope[J]. Circulation, 2001,104(8):898-902.
doi: 10.1161/hc3301.094908 |
| [14] |
Subudhi AW, Panerai RB, Roach RC . Acute hypoxia impairs dynamic cerebral autoregulation: results from two independent techniques[J]. J Appl Physiol, 2009,107(4):1165-1171.
doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00498.2009 |
| [15] |
Schondorf R, Stein R, Roberts R , et al. Dynamic cerebral autoregulation is preserved in neurally mediated syncope[J]. Eur J Appl Physiol, 2001,91(5):2493-2502.
doi: 10.1152/jappl.2001.91.6.2493 |
| [16] |
Krishnamurthy S, Wang X, Bhakta D , et al. Dynamic cardiorespiratory interaction during head-up tilt-mediated presyncope[J]. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol, 2004,287(6):2510-2517.
doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00485.2004 |
| [17] |
Wang KW, Chang HH, Hsu CC , et al. Extractions of steady-state auditory evoked fields in normal subjects and tinnitus patients using complementary ensemble empirical mode decomposition[J]. Biomed Eng Online, 2015,14:72.
doi: 10.1186/s12938-015-0062-0 |
| [18] |
Bondar RL, Kassam MS, Stein F , et al. Simultaneous cerebrovascular and cardiovascular responses during presyncope[J]. Stroke, 1995,26(10):1794-1800.
doi: 10.1161/01.STR.26.10.1794 |
| [19] |
Schondorf R, Benoit J, Wein T . Cerebrovascular and cardiovascular measurements during neurally mediated syncope induced by head-up tilt[J]. Stroke, 1997,28(8):1564-1568.
doi: 10.1161/01.STR.28.8.1564 |
| [20] |
Van Lieshout JJ, Wieling W, Karemaker JM , et al. Syncope, cerebral perfusion, and oxygenation[J]. J Appl Physiol, 2003,94(3):833-848
doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00260.2002 |
| [21] |
Bor-Seng-Shu E, Kita WS, Figueiredo EG , et al. Cerebral hemodynamics: concepts of clinical importance[J]. Arq Neuropsiquiatr, 2012,70(5):352-356.
doi: 10.1590/S0004-282X2012000500009 |
| [22] | Sweeney MD, Ayyadurai S, Zlokovic BV . Pericytes of the neurovascular unit: key functions and signaling pathways[J]. Nat Neurosci, 2016,19(6):771-783. |
| [1] | 闫辉,逄璐,李雪迎,杨文双,蒋世菊,刘平,闫存玲. 单中心就诊2~18岁儿童胆固醇水平异常发生率及病因分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(2): 217-221. |
| [2] | 陶春燕,李红霞,李雪迎,唐朝枢,金红芳,杜军保. 体位性心动过速综合征儿童及青少年在直立试验中血流动力学变化[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(3): 414-421. |
| [3] | 杜军保,陈咏冰. 川崎病丙种球蛋白无反应型的预测及治疗[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 0, (): 749-752. |
| [4] | 徐文瑞,廖莹,金红芳,张清友,唐朝枢,杜军保. 儿童晕厥诊断和治疗进展[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 0, (): 756-759. |
| [5] | 廖莹,张清友,李红霞,王瑜丽,刘平,杜军保. 儿童血管迷走性晕厥和体位性心动过速综合征共患过敏性疾病的临床特征分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 0, (): 783-788. |
| [6] | 杜军保, 陈咏冰. 川崎病丙种球蛋白无反应型的预测及治疗[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(5): 749-752. |
| [7] | 徐文瑞, 廖莹, 金红芳, 张清友, 唐朝枢, 杜军保. 儿童晕厥诊断和治疗进展[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(5): 756-759. |
| [8] | 廖莹, 张清友, 李红霞, 王瑜丽, 刘平, 杜军保. 儿童血管迷走性晕厥和体位性心动过速综合征共患过敏性疾病的临床特征分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(5): 783-788. |
| [9] | 曲艳吉, 刘小清, 麦劲壮, 聂志强, 欧艳秋, 高向民, 吴勇, 陈寄梅. 不同先天性心脏病类型的环境危险因素分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2015, 47(3): 420-430. |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 328
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 1057
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Cited |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shared | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Discussed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||