北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2020, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (1): 181-186. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2020.01.029
静脉给药镇静技术在2 582例口腔外科门诊手术中的临床应用
王菲1,赵阳阳2,关明3,王晶1,许向亮1,刘宇1,翟新利1,△( )
)
- 1. 北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院,口腔颌面外科 国家口腔疾病临床研究中心 口腔数字化医疗技术和材料国家工程试验室 口腔数字医学北京市重点实验室,北京 100081
2. 国家儿童医学中心,首都医科大学附属北京儿童医院口腔科, 北京 100045
3. 北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院第一门诊部, 北京 100081
Application of intravenous sedation in 2 582 cases of oral and maxillofacial surgery
Fei WANG1,Yang-yang ZHAO2,Ming GUAN3,Jing WANG1,Xiang-liang XU1,Yu LIU1,Xin-li ZHAI1,△( )
)
- 1. Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Laboratory for Digital and Material Technology of Stomatology & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
2. Department of Stomatology, Beijing Children’s Hospital, Capital Medical University, National Center for Children’s Health, Beijing 100045, China
3. First Clinical Division, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
摘要:
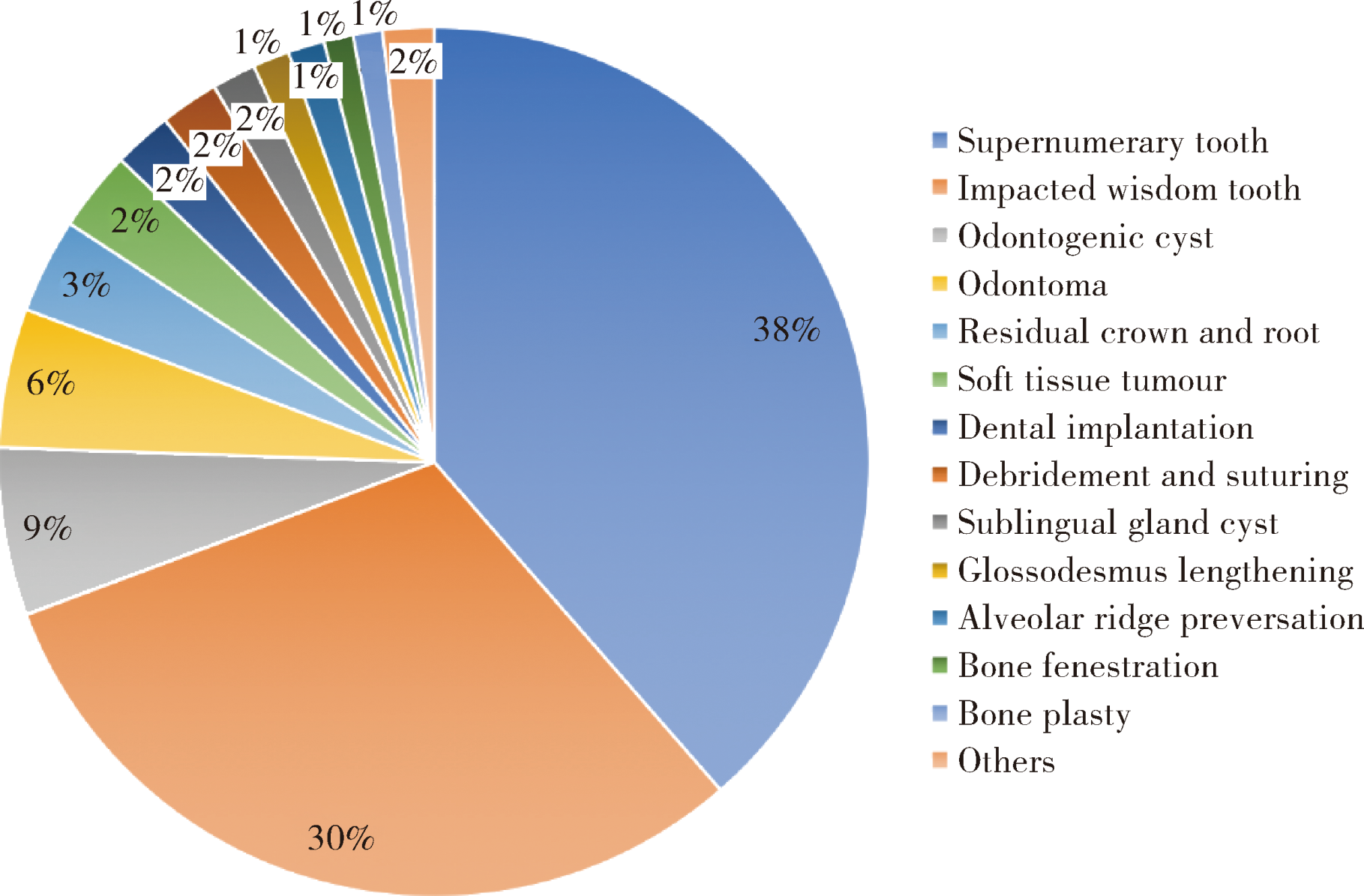
目的:分析镇静给药镇静技术用于口腔外科门诊手术患者基本资料,了解其流行病学特点,评价该技术用于口腔外科手术的效果及安全性,并总结相关经验。方法:统计北京大学口腔医院口腔颌面外科2010年1月至2018年12月间行静脉镇静下口腔颌面外科手术患者的病例资料,对其性别、年龄、疾病种类、围手术期的生命体征监测数值、镇静、镇痛用药情况、手术和镇静时长、术中镇静效果及术后顺行性遗忘情况进行总结分析。结果:9年间进行静脉镇静下口腔外科手术共2 582人次,患者年龄段集中于3.5岁至10岁及21~40岁。疾病种类最多的为多生牙,占38%(981/2 582), 阻生智牙占30%(775/2 582),其他疾病共占32%。围手术期患者心率(heart rate,HR)、平均动脉压(mean arterial pressure,MAP)、呼吸频率(respiratory rate,RR)、脑电双频指数(bispectral index,BIS)的数值在患者入室、局部麻醉、手术切开、手术开始10 min及术毕的差异有统计学意义。单独使用咪达唑仑静脉镇静占69%(1 781/2 582);单独使用丙泊酚占7%(181/2 582);咪达唑仑联合丙泊酚复合镇静占24%(620/2 582)。使用的静脉麻醉性镇痛药物主要为芬太尼、氟比洛芬酯、酮咯酸氨丁三醇,分别占33%(852/2 582)、 23%(594/2 582)、 6%(157/2 582), 未使用静脉镇痛药患者占35%(907/2 582)。手术总时长平均(31.2±20.8) min,镇静给药总时长平均(38.4±19.2) min;术中总体镇静效果较好,Ramsay镇静评分多为2~4分;术后患者对局部麻醉注射、手术切开、牙钻声音的顺行性遗忘率分别为94%(2 431/2 582)、 92%(2 375/2 582)、 75%(1 452/1 936)。结论:静脉镇静下口腔颌面外科门诊手术治疗安全有效,提高了手术的舒适性,应进一步推广应用。
中图分类号:
- R782.05
| [1] | 朱也森, 姜红 . 口腔麻醉学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2012: 632. |
| [2] | Ramsay MA, Savege TM, Simpson BR , et al. Controlled sedation with alphaxalone-alphadolone[J]. Br Med J, 1974,2(5920):656-659. |
| [3] | Allen SM, Madrio ME . Ramsay sedation scale project: Small, easy changes for a big effect on patient safety[J]. Crit Care Nurse, 2019,39(4):64-66 |
| [4] | 中华口腔医学会麻醉学专委会口腔镇静学组. 口腔门诊疼痛控制与镇静技术专家共识[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2014: 3-4. |
| [5] | Lin CS, Wu SY, Yi CA . Association between anxiety and pain in dental treatment: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. J Dent Res, 2017,96(2):153-162 |
| [6] | Wang YC, Lin IH, Huang CH , et al. Dental anesthesia for patients with special needs[J]. Acta Anaesthesiol Taiwan, 2012,50(3):122-125 |
| [7] | Gross JB, Bailey PL, Connis RT , et al. Practice guidelines for sedation and analgesia by non-anesthesiologists[J]. Anesthesiology, 2002,96(4):1004-1017 |
| [8] | Bell JK, Laasch HU, Wilbraham L , et al. Bispectral index monitoring for conscious sedation in intervention: better, safer, faster[J]. Clin Radiol, 2004,59(12):1106-1113 |
| [9] | Shah P, Manley G, Craig D . Bispectral index(BIS) monitoring of intravenous sedation for dental treatment[J]. SAAD Dig, 2014,30(1):7-11 |
| [10] | 关明, 王恩博, 刘宇 , 等. 咪达唑仑静脉注射对儿童埋伏多生牙拔除术中镇静效果的临床评价[J]. 北京大学学报 (医学版), 2012,44(1):120-124. |
| [11] | 关明, 王恩博, 刘宇 , 等. 丙泊酚靶控输注联合芬太尼静脉镇静拔除下颌阻生智齿的效果评价[J]. 北京大学学报 (医学版), 2014,46(1):107-110 |
| [12] | American Society of Anesthesiologists. Practice guidelines for moderate procedural sedation and analgesia 2018: A Report by the American Society of Anesthesiologists Task Force on Moderate Procedural Sedation and Analgesia, the American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons, American College of Radiology, American Dental Association, American Society of Dentist Anesthesiologists, and Society of Interventional Radiology[J]. Anesthesiology, 2018,128(3):437-479 |
| [13] | Southerland JH, Brown LR . Conscious intravenous sedation in dentistry: A review of current therapy[J]. Dent Clin North Am, 2016,60(2):309-346 |
| [14] | Hooghe JN, Eberl S, Bonta PI , et al. Propofol and remifentanil sedation for bronchial thermoplasty: A prospective cohort trial[J]. Respiration, 2017,93(1):58-64 |
| [15] | Bovaira M, Herrero Babiloni A, Peñarrocha-Oltra D , et al. Pre-operative anxiety and its influence on patient and surgeon satisfaction in patients receiving dental implant surgeries performed under intravenous conscious sedation.[J]. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants, 2017,32(4):912-918 |
| [16] | 王天骄, 刘宇, 关明 . 咪达唑仑联合丙泊酚靶控输注静脉镇静对拔除下颌第三磨牙患者焦虑水平的影响[J]. 北京大学学报 (医学版), 2017,49(6):1044-1049. |
| [17] | 谢锐捷, 刘少芬, 张松林 , 等. 咪唑安定联合腰硬联合麻醉对妇科手术患者镇静和术后遗忘效果观察[J]. 现代生物医学进展, 2013,13(21):4155-4158. |
| [18] | Hong YJ, Jang EH, Hwang J , et al. Effect of midazolam on memory during fiberoptic gastroscopy under conscious sedation[J]. Clin Neuropharmacol, 2015,38(2):47-51. |
| [19] | Hernández-Gancedo C, Pestaña D, Criado A , et al. Comparing entropy and the bispectral index with the Ramsay score in sedated ICU patients[J]. J Clin Monit Comput, 2007,21(5):295-302. |
| [20] | Hsu CW, Sun SF, Wong KF , et al. Monitoring sedation for bronchoscopy in mechanically ventilated patients by using the Ramsay sedation scale versus auditory-evoked potentials[J]. BMC Pulm Med, 2014,14:15. |
| [21] | Micheal M. Perterson口腔颌面外科学[M]. 蔡志刚, 译. 2版. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2011: 71. |
| [1] | 王军, 姚兰, 张宁, 索利斌, 李红培, 魏越, 查鹏, 梁正, 刘鲲鹏. 单侧胸椎旁阻滞对实施双腔气管插管患者血流动力学和意识水平的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 890-895. |
| [2] | 王江静,魏顺依,敖英芳,杨渝平. 前交叉韧带重建术后三种不同药物镇痛早期疗效的对比[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 293-298. |
| [3] | 史成梅,周阳,杨宁,李正迁,陶一帆,邓莹,郭向阳. 丙泊酚用于无痛胃肠镜检查对患者术后精神活动的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(2): 324-327. |
| [4] | 王洁初,姚优修,郭向阳. 严重低钾血症致麻醉后潜在致命性心律失常1例的术中管理[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(1): 186-189. |
| [5] | 康志宇,王磊磊,韩永正,郭向阳. 北京冬季奥林匹克运动会运动员手术的麻醉管理[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(4): 770-773. |
| [6] | 苏俊琪,宋扬,谢尚. 口腔鳞状细胞癌患者修复重建术后感染的病原学特征及感染风险预测模型的构建[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(1): 68-76. |
| [7] | 穆东亮,薛铖,安彬,王东信. 硬膜外阻滞与结直肠癌患者术后远期生存状态的关系:一项倾向性评分匹配的回顾性研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(6): 1152-1158. |
| [8] | 张庆芬,赵红,冯艺. 不同全身麻醉管理方式与早产儿眼底手术临床结局[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(1): 195-199. |
| [9] | 韩永正,井凤云,徐懋,郭向阳. 颈椎脊索瘤行肿瘤切除术的麻醉管理1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(5): 981-983. |
| [10] | 刘鲲鹏,王宝宁,申琰琰,李卫霞,李昭,姚兰. 胸部硬膜外给予利多卡因对双腔气管插管患者血流动力学和唤醒水平的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(4): 742-747. |
| [11] | 邓莹,李岩,姚瑶,冯丹丹,徐懋. 颈5-6神经根阻滞技术用于肩关节镜术后镇痛的随机对照研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(1): 177-181. |
| [12] | 李岩,王辉,邓莹,姚瑶,李民. 静脉输注右美托咪定对臂丛阻滞效果的随机对照研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(5): 845-849. |
| [13] | 李纯青,王东信,韦晓昱. 先天性纤维蛋白原缺乏症产妇的围术期管理:4例报道及文献回顾[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(5): 932-936. |
| [14] | 王楠,赵玉鸣. 62例残障儿童及青少年在全身麻醉下牙齿治疗的回顾性研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(2): 293-299. |
| [15] | 孟甜,张智勇,张晓,陈宇寰,李京琦,陈全,刘文曙,高巍. 口服洛索洛芬钠片在拔除阻生齿中的超前镇痛[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(1): 165-169. |
|
||