北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2020, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (1): 177-180. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2020.01.028
复合手术治疗无残端的症状性长段颈内动脉慢性闭塞
贾子昌1,李选1,郑梅2,栾景源1,王昌明1,韩金涛1,△( )
)
- 1. 北京大学第三医院 介入血管外科, 北京 100191
2. 北京大学第三医院 神经内科,北京 100191
Hybrid treatment for symptomatic long-segment chronic internal carotid artery occlusion without stump
Zi-chang JIA1,Xuan LI1,Mei ZHENG2,Jing-yuan LUAN1,Chang-ming WANG1,Jin-tao HAN1,△( )
)
- 1. Department of Interventional Radiology and Vascular Surgery, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
2. Department of Neurology, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
摘要:
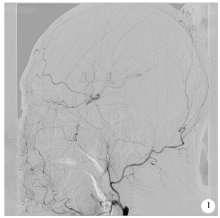
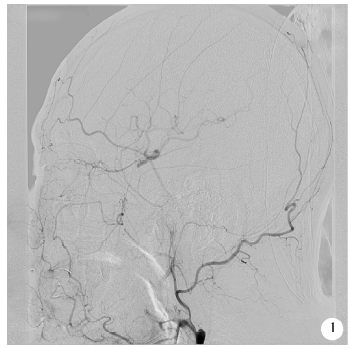
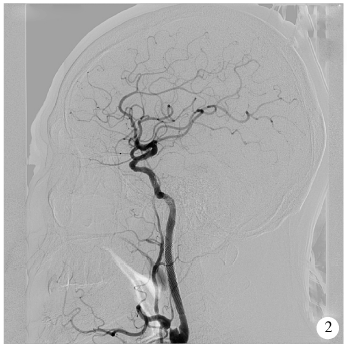
目的:总结采用复合手术方法治疗无残端症状性长段颈内动脉慢性闭塞(chronic internal carotid artery occlusion,CICAO)病变的初步经验。方法:回顾性总结分析2015年7月至2017年12月北京大学第三医院介入血管外科采取复合手术的方法进行治疗的12例无残端的症状性长段CICAO患者资料,初步分析手术的安全性及有效性。结果:11例患者获得技术成功,技术成功率91.7%(11/12),仅1例发生主要并发症,该患者术中出现颈内动脉海绵窦瘘,结扎颈内动脉近端后好转。全部12例患者无缺血性及出血性卒中,无死亡病例。10例患者获得随访,随访10~32个月,平均随访时间(19±9)个月,其中1例出现症状性支架内再狭窄,予再次手术治疗后好转。结论:对于经严格筛选的无残端的症状性长段CICAO患者,复合开通手术在技术上可行,有较高的手术安全性及技术成功率。
中图分类号:
- R543.4
| [1] | Iwata T, Mori T, Tajiri H , et al. Long-term angiographic and clinical outcome following stenting by flow reversal technique for chronic occlusions older than 3 months of the cervical carotid or vertebral artery[J]. Neurosurgery, 2012,70(1):82-90. |
| [2] | Sundaram S, Kannoth S, Thomas B , et al. Collateral assessment by CT angiography as a predictor of outcome in symptomatic cervical internal carotid artery occlusion[J]. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol, 2017,38(1):52-57. |
| [3] | Zirak P, Delgado-mederos R, Dinia L , et al. Microvascular versus macrovascular cerebral vasomotor reactivity in patients with severe internal carotid artery stenosis or occlusion[J]. Acad Radiol, 2014,21(2):168-174. |
| [4] | Paraskevas KI, Mikhailidis DP, Liapis CD . Internal carotid artery occlusion: association with atherosclerotic disease in other arterial beds and vascular risk factors[J]. Angiology, 2007,58(3):329-335. |
| [5] | Alexander JJ, Moawad J, Super D . Outcome analysis of carotid artery occlusion[J]. Vasc Endovascular Surg, 2007,41(5):409-416. |
| [6] | Powers WJ, Clarke WR, Grubb RL Jr . Extracranial-intracranial bypass surgery for stroke prevention in hemodynamic cerebral ischemia: the Carotid Occlusion Surgery Study randomized trial[J]. JAMA, 2011,306(18):1983-1992. |
| [7] | Jiao L, Song G, Hua Y , et al. Recanalization of extracranial internal carotid artery occlusion: A 12-year retrospective study[J]. Neural Regen Res, 2013,8(23):2204-2206. |
| [8] | Lee CW, Lin YH, Liu HM , et al. Predicting procedure successful rate and 1-year patency after endovascular recanalization for chro-nic carotid artery occlusion by CT angiography[J]. Int J Cardiol, 2016,221(15):772-776. |
| [9] | Chen YH, Leong WS, Lin MS , et al. Predictors for successful endovascular intervention in chronic carotid artery total occlusion[J]. JACC Cardiovasc Interv, 2016,9(17):1825-1832. |
| [10] | Park S, Park ES, Kwak JH , et al. Endovascular management of long segmental petrocavernous internal carotid artery (Carotid S) occlusion[J]. Stroke, 2015,17(3):336-343. |
| [11] | 中国医师协会介入医师分会神经介入专业委员会, 中华医学会放射学分会介入放射学组, 中国卒中学会复合介入神经外科分会, 国家脑卒中防治工程委员会缺血性卒中专业委员会. 慢性颈内动脉闭塞再通治疗中国专家共识[J]. 中华介入放射学电子杂志, 2019,7(1):1-6. |
| [12] | Namba K, Shojima M, Nemoto S . Wire-probing technique to revascularize subacute or chronic internal carotid artery occlusion[J]. Interv Neuroradiol, 2012,18(3):288-296. |
| [1] | 王明瑞, 王起, 胡浩, 赖金惠, 唐鑫伟, 万春艳, 许克新, 徐涛. 覆膜金属输尿管支架治疗盆腔脂肪增多症所致肾积水的疗效[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 919-922. |
| [2] | 杨文博,余磊,张维宇,徐涛,王强. 带线输尿管支架自排技术在肾移植受者中的效果及安全性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 656-660. |
| [3] | 赖金惠,王起,姬家祥,王明瑞,唐鑫伟,许克新,徐涛,胡浩. 新型冠状病毒肺炎疫情期间延迟拔除输尿管支架对泌尿系结石术后患者生活质量和心理状态的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 857-864. |
| [4] | 刘颖,霍然,徐慧敏,王筝,王涛,袁慧书. 磁共振血管壁成像评估颈动脉中重度狭窄患者斑块特征与脑血流灌注的相关性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 646-651. |
| [5] | 韩金涛,张宇翔,贾子昌,姜除寒,刘恋,栾景源,梁飞,赵彦清. Neuroform Atlas支架辅助弹簧圈栓塞未破裂性颅内宽颈动脉瘤[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(1): 139-143. |
| [6] | 李雨柯,王梅,唐琳,刘玉华,陈晓颖. 不同pH值对脱细胞小肠黏膜下层海绵支架螯合锶离子的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(1): 44-51. |
| [7] | 张春龙,王明瑞,王起,许克新,徐涛,胡浩. 覆膜金属输尿管支架维持性治疗输尿管镜碎石术后难治性输尿管狭窄的远期疗效评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(4): 674-679. |
| [8] | 邓艺,张一,李博文,王梅,唐琳,刘玉华. 不同交联剂处理对脱细胞小肠黏膜下层多孔支架的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(3): 557-564. |
| [9] | 白鹏,王涛,周阳,陶立元,李刚,李正迁,郭向阳. 不同转流标准对颈动脉内膜切除术后脑梗死的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(6): 1144-1151. |
| [10] | 朱正达,高岩,何汶秀,方鑫,刘洋,魏攀,闫志敏,华红. 红色诺卡氏菌细胞壁骨架治疗糜烂型口腔扁平苔藓的疗效及安全性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(5): 964-969. |
| [11] | 庄金满,李天润,李选,栾景源,王昌明,冯琦琛,韩金涛. Rotarex 旋切导管在下肢动脉硬化闭塞症支架内再狭窄中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(4): 740-743. |
| [12] | 董文敏,王明瑞,胡浩,王起,许克新,徐涛. Allium覆膜金属输尿管支架长期留置治疗输尿管-回肠吻合口狭窄的初期临床经验及随访结果[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(4): 637-641. |
| [13] | 曹春玲,杨聪翀,屈小中,韩冰,王晓燕. 可注射羟乙基壳聚糖基水凝胶理化性能及其对人牙髓细胞增殖和成牙本质向分化的作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(1): 10-17. |
| [14] | 赵海燕,樊东升,韩金涛. 重度颈内动脉狭窄伴未破裂动脉瘤的治疗策略[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(5): 829-834. |
| [15] | 贾子昌,卞焕菊,李选,栾景源,王昌明,刘启佳,韩金涛. Neuroform EZ支架在治疗复杂症状性颅内动脉重度狭窄中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(5): 835-839. |
|
||