北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2020, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (6): 1069-1074. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2020.06.013
腹膜后纤维化致肾盂积水的临床分析:附17例报道
刘世博1,高辉2,冯元春3,李静4,张彤5,万利6,刘燕鹰7,李胜光2,罗成华1,△( ),张学武7,△(
),张学武7,△( )
)
- 1. 北京大学国际医院 腹膜后肿瘤外科
2. 北京大学国际医院 风湿免疫科
3. 北京大学国际医院 放射科
4. 北京大学国际医院 检验科
5. 北京大学国际医院 病理科
6. 北京大学国际医院 肾内科,北京 102206
7. 北京大学人民医院风湿免疫科,北京 100044
Clinical features of hydronephrosis induced by retroperitoneal fibrosis: 17 cases reports
Shi-bo LIU1,Hui GAO2,Yuan-chun FENG3,Jing LI4,Tong ZHANG5,Li WAN6,Yan-ying LIU7,Sheng-guang LI2,Cheng-hua LUO1,△( ),Xue-wu ZHANG7,△(
),Xue-wu ZHANG7,△( )
)
- 1. Department of Retroperitoneal Tumor Surgery
2.Department of Rheumatology and Immunology
3. Department of Radiology
4. Department of Laboratory Medicine
5. Department of Pathology
6. Department of Nephrology, Peking University International Hospital, Beijing 102206, China
7. Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, Peking University People’s Hospital, Beijing 100044, China
摘要:
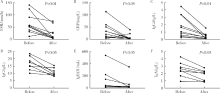
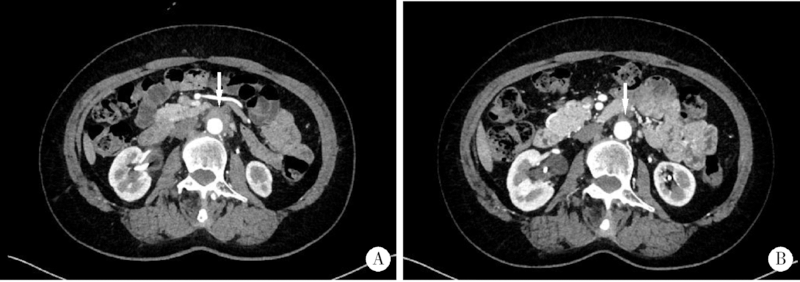
目的:分析腹膜后纤维化(retroperitoneal fibrosis,RPF)的临床特点,重点探讨通过药物联合外科干预治疗RPF及其所致肾盂积水的疗效及转归。方法:对北京大学国际医院2016年5月至2019年12月诊治的17例RPF合并肾盂积水患者的临床资料和转归进行回顾性分析。结果:17例患者中男12例,女5例,年龄38~71岁,中位年龄56(53,65)岁,中位病程4.00(0.83,8.00)个月。常见的临床表现为腰痛(9例)、腹痛(6例)、少尿(2例)以及下肢水肿(3例)。入组患者中,合并左侧肾盂积水8例、右侧1例、双侧8例。17例患者的血液样本检查发现,C反应蛋白(C-reactive protein,CRP)升高13例(76.5%), 红细胞沉降率(erythrocyte sedimentation rate,ESR)升高13例(76.5%),免疫球蛋白G亚型4(immunoglobin G4 subtype, IgG4)升高5例(29.4%);进行血免疫球蛋白(immunoglobin, Ig)亚型分析的13例患者中,IgG升高4例(30.8%), IgE升高4例(30.8%), IgA升高1例(7.7%)。有12例患者接受了病理活检,病理组织中的IgG4表达量高低不一,6例表达量<10/高倍视野(high power field,HPF)或不表达(50.0%), 2例为10~30/HPF(16.7%), 4例>30/HPF(33.3%),3例患者可诊断为IgG4相关性RPF。17例患者中,13例在接受药物治疗前放置输尿管支架,其中4例因药物治疗时间尚短,未到评估拔管时机,仍需继续随访;余9例患者平均置管时间(6.7±3.0)个月,包括6例在随访期间因药物治疗梗阻好转拔除支架,3例患者则因梗阻难以解除,拟行药物治疗前行输尿管松解术,术后顺利拔除支架。4例患者虽然存在单侧肾盂积水,但由于病变较小,梗阻轻,未放置输尿管支架,其中2例仅进行药物治疗后输尿管梗阻便得以解除,另外2例患者在接受药物治疗后失访。10例具有完整随访资料的患者中位随访时间为5(3,13)个月,ESR、CRP、IgG4、IgG、IgE、IgA治疗前分别为54.0(36.3,98.5) mm/h、26.8(8.7,53.0) mg/L、1.34(0.55,3.36) g/L、16.3(13.0,21.1) g/L、40.5(31.4,203.0) IU/mL、2.51(1.82,3.25) g/L,治疗后分别下降了38.5(23.5,54.3) mm/h(P<0.01)、23.0(5.5,52.0) mg/L(P<0.05)、0.92(0.40,2.85) g/L(P<0.01)、6.5(1.7,9.1) g/L(P<0.05)、23.7(4.8,162.0) IU/mL(P<0.05)、0.77(0.32,1.26) g/L(P<0.05)。对比治疗前后影像学资料发现RPF肿物较治疗前显著缩小,以上患者在治疗后输尿管梗阻均得以解除。结论:RPF起病隐匿,早期无特异性临床表现。以激素治疗为主并根据病情选择联用免疫抑制剂,同时积极通过外科手段解除输尿管梗阻的综合治疗方案可改善患者临床症状,取得确切疗效,改善预后。
中图分类号:
- R656.5
| [1] |
Uibu T, Oksa P, Auvinen A, et al. Asbestos exposure as a risk factor for retroperitoneal fibrosis[J]. Lancet, 2004,363(9419):1422-1426.
pmid: 15121404 |
| [2] |
Vaglio A, Palmisano A, Alberici F, et al. Prednisone versus tamoxifen in patients with idiopathic retroperitoneal fibrosis: An open-label randomised controlled trial[J]. Lancet, 2011,378(9788):338-346.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60934-3 pmid: 21733570 |
| [3] |
Scheel PJ Jr, Feeley N. Retroperitoneal fibrosis: the clinical, laboratory, and radiographic presentation[J]. Medicine (Baltimore), 2009,88(4):202-207.
doi: 10.1097/MD.0b013e3181afc439 |
| [4] |
Deshpande V, Zen Y, Chan JK, et al. Consensus statement on the pathology of IgG4-related disease[J]. Mod Pathol, 2012,25(9):1181-1192.
doi: 10.1038/modpathol.2012.72 pmid: 22596100 |
| [5] |
Ormond JK. Bilateral ureteral obstruction due to envelopment and compression by an inflammatory retroperitoneal process[J]. J Urol, 1948,59(6):1072-1079.
doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)69482-5 pmid: 18858051 |
| [6] |
Zen Y, Onodera M, Inoue D, et al. Retroperitoneal fibrosis: A clinicopathologic study with respect to immunoglobulin G4[J]. Am J Surg Pathol, 2009,33(12):1833-1839.
doi: 10.1097/pas.0b013e3181b72882 pmid: 19950407 |
| [7] |
Rossi GM, Rocco R, Accorsi Buttini E, et al. Idiopathic retroperitoneal fibrosis and its overlap with IgG4-related disease[J]. Intern Emerg Med, 2017,12(3):287-299.
doi: 10.1007/s11739-016-1599-z pmid: 28070877 |
| [8] | Yamashita K, Haga H, Mikami Y, et al. Degree of IgG4+ plasma cell infiltration in retroperitoneal fibrosis with or without multifocal fibrosclerosis[J]. 2010,52(3):404-409. |
| [9] |
Khosroshahi A, Carruthers MN, Stone JH, et al. Rethinking Ormond's disease: "idiopathic" retroperitoneal fibrosis in the era of IgG4-related disease[J]. Medicine (Baltimore), 2013,92(2):82-91.
doi: 10.1097/MD.0b013e318289610f |
| [10] |
Caiafa RO, Vinuesa AS, Izquierdo RS, et al. Retroperitoneal fibrosis: Role of imaging in diagnosis and follow-up[J]. Radiographics, 2013,33(2):535-552.
doi: 10.1148/rg.332125085 pmid: 23479712 |
| [11] |
George V, Tammisetti VS, Surabhi VR, et al. Chronic fibrosing conditions in abdominal imaging[J]. Radiographics, 2013,33(4):1053-1080.
doi: 10.1148/rg.334125081 pmid: 23842972 |
| [12] |
Pelkmans LG, Aarnoudse AJ, Hendriksz TR, et al. Value of acute-phase reactants in monitoring disease activity and treatment response in idiopathic retroperitoneal fibrosis[J]. Nephrol Dial Transplant, 2012,27(7):2819-2825.
doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfr779 pmid: 22273666 |
| [13] |
van Bommel EF, Siemes C, Hak LE, et al. Long-term renal and patient outcome in idiopathic retroperitoneal fibrosis treated with prednisone[J]. Am J Kidney Dis, 2007,49(5):615-625.
doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2007.02.268 pmid: 17472843 |
| [14] |
Fry AC, Singh S, Gunda SS, et al. Successful use of steroids and ureteric stents in 24 patients with idiopathic retroperitoneal fibrosis: A retrospective study[J]. Nephron Clin Pract, 2008,108(3):c213-220.
doi: 10.1159/000119715 pmid: 18332635 |
| [15] |
Alberici F, Palmisano A, Urban ML, et al. Methotrexate plus prednisone in patients with relapsing idiopathic retroperitoneal fibrosis[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2013,72(9):1584-1586.
doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-203545 pmid: 23696631 |
| [16] |
Scheel PJ Jr, Feeley N, Sozio SM. Combined prednisone and mycophenolate mofetil treatment for retroperitoneal fibrosis: a case series[J]. Ann Intern Med, 2011,154(1):31-36.
doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-154-1-201101040-00005 pmid: 21200036 |
| [17] |
Binder M, Uhl M, Wiech T, et al. Cyclophosphamide is a highly effective and safe induction therapy in chronic periaortitis: a long-term follow-up of 35 patients with chronic periaortitis[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2012,71(2):311-312.
doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2011-200148 pmid: 21859695 |
| [18] |
Li KP, Zhu J, Zhang JL, et al. Idiopathic retroperitoneal fibrosis (RPF): Clinical features of 61 cases and literature review[J]. Clin Rheumatol, 2011,30(5):601-605.
doi: 10.1007/s10067-010-1580-6 pmid: 20957401 |
| [19] |
Vaglio A, Maritati F. Idiopathic retroperitoneal fibrosis[J]. J Am Soc Nephrol, 2016,27(7):1880-1889.
doi: 10.1681/ASN.2015101110 pmid: 26860343 |
| [20] |
Mertens S, Zeegers AG, Wertheimer PA, et al. Efficacy and complications of urinary drainage procedures in idiopathic retroperitoneal fibrosis complicated by extrinsic ureteral obstruction[J]. Int J Urol, 2014,21(3):283-288.
doi: 10.1111/iju.12234 pmid: 24033464 |
| [21] |
Cristian S, Cristian M, Cristian P, et al. Management of idiopathic retroperitoneal fibrosis from the urologist's perspective[J]. Ther Adv Urol, 2015,7(2):85-99.
doi: 10.1177/1756287214565637 pmid: 25829952 |
| [1] | 欧俊永,倪坤明,马潞林,王国良,颜野,杨斌,李庚午,宋昊东,陆敏,叶剑飞,张树栋. 肌层浸润性膀胱癌合并中高危前列腺癌患者的预后因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 582-588. |
| [2] | 王明瑞,刘军,熊六林,于路平,胡浩,许克新,徐涛. 经皮微通道-微电子肾镜-微超声探针碎石术治疗1.5~2.5 cm肾结石的疗效和安全性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 605-609. |
| [3] | 刘帅,刘磊,刘茁,张帆,马潞林,田晓军,侯小飞,王国良,赵磊,张树栋. 伴静脉癌栓的肾上腺皮质癌的临床治疗及预后[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 624-630. |
| [4] | 应沂岑,杜毅聪,李志华,张一鸣,李新飞,王冰,张鹏,朱宏建,周利群,杨昆霖,李学松. 机器人辅助腹腔镜下颊黏膜补片输尿管成形术治疗复杂输尿管狭窄[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 640-645. |
| [5] | 虞乐,邓绍晖,张帆,颜野,叶剑飞,张树栋. 具有低度恶性潜能的多房囊性肾肿瘤的临床病理特征及预后[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 661-666. |
| [6] | 周泽臻,邓绍晖,颜野,张帆,郝一昌,葛力源,张洪宪,王国良,张树栋. 非转移性T3a肾细胞癌患者3年肿瘤特异性生存期预测[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 673-679. |
| [7] | 方杨毅,李强,黄志高,陆敏,洪锴,张树栋. 睾丸鞘膜高分化乳头状间皮肿瘤1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 741-744. |
| [8] | 曾媛媛,谢云,陈道南,王瑞兰. 脓毒症患者发生正常甲状腺性病态综合征的相关因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 526-532. |
| [9] | 苏俊琪,王晓颖,孙志强. 舌鳞状细胞癌根治性切除术后患者预后预测列线图的构建与验证[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 120-130. |
| [10] | 徐心雨,吴灵,宋凤岐,李自力,张益,刘筱菁. 基于下颌运动轨迹的正颌外科术中下颌骨髁突定位方法及初步精度验证[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 57-65. |
| [11] | 蔡安东,王晓霞,周文娟,柳忠豪. 下颌前突畸形患者上颌骨及髁突虚拟位置与术后现实位置的比较[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 74-80. |
| [12] | 李建斌,吕梦娜,池强,彭一琳,刘鹏程,吴锐. 干燥综合征患者发生重症新型冠状病毒肺炎的早期预测[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 1007-1012. |
| [13] | 刘欢锐,彭祥,李森林,苟欣. 基于HER-2相关基因构建风险模型用于膀胱癌生存预后评估[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 793-801. |
| [14] | 薛子璇,唐世英,邱敏,刘承,田晓军,陆敏,董靖晗,马潞林,张树栋. 青年肾肿瘤伴瘤栓的临床病理特征及预后分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 802-811. |
| [15] | 张心灵,林志禹,陈玉杰,董文芳,杨欣. 脊柱后路内固定术后切口愈合不良的整形外科治疗[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 910-914. |
|
||