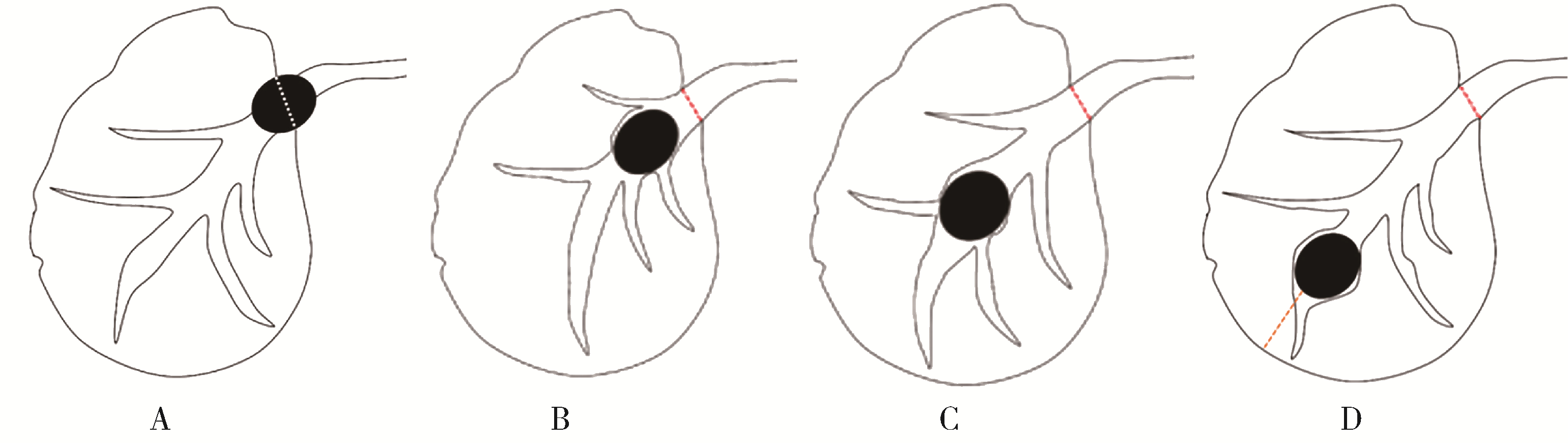
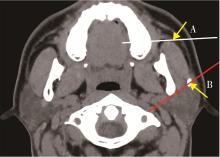
北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (1): 8-12. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2023.01.002
疑难唾液腺结石病的治疗研究
柳登高*( ),郑丹妮,赵雅宁,张亚琼,叶欣,张丽琪,谢晓艳,张雷,张祖燕,俞光岩
),郑丹妮,赵雅宁,张亚琼,叶欣,张丽琪,谢晓艳,张雷,张祖燕,俞光岩
- 北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院影像科,国家口腔医学中心,国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心,口腔生物材料和数字诊疗装备国家工程研究中心,口腔数字医学北京市重点实验室,国家卫生健康委员会口腔医学计算机应用工程技术研究中心,国家药品监督管理局口腔生物材料重点实验室,北京 100081
Recent progress in the treatment of intractable sialolithiasis
Deng-gao LIU*( ),Dan-ni ZHENG,Ya-ning ZHAO,Ya-qiong ZHANG,Xin YE,Li-qi ZHANG,Xiao-yan XIE,Lei ZHANG,Zu-yan ZHANG,Guang-yan YU
),Dan-ni ZHENG,Ya-ning ZHAO,Ya-qiong ZHANG,Xin YE,Li-qi ZHANG,Xiao-yan XIE,Lei ZHANG,Zu-yan ZHANG,Guang-yan YU
- Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Center of Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Research Center of Oral Biomaterials and Digital Medical Devices & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology & NHC Research Center of Engineering and Technology for Computerized Dentistry & NMPA Key Laboratory for Dental Materials, Beijing 100081, China
中图分类号:
- R781.75
| 1 |
姜岚, 张晔, 柳登高, 等. 涎腺内镜辅助颌下腺腺门结石取出术疗效分析[J]. 中华口腔医学杂志, 2012, 43 (3): 157- 159.
doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1002-0098.2012.03.007 |
| 2 |
叶欣, 谢晓艳, 柳登高, 等. 内镜辅助腮腺结石取出术67例疗效分析[J]. 中华口腔医学杂志, 2014, 49 (11): 645- 648.
doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1002-0098.2014.11.002 |
| 3 | Zhang YQ , Ye X , Meng Y , et al. Evaluation of parotid gland function before and after endoscopy-assisted stone removal[J]. J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2019, 77 (2): 327.e2- 328.e9. |
| 4 |
Liu DG , Jiang L , Xie XY , et al. Sialoendoscopy-assisted sialolithectomy for submandibular hilar calculi[J]. J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2013, 71 (2): 295- 301.
doi: 10.1016/j.joms.2012.02.016 |
| 5 |
赵雅宁, 张亚琼, 叶欣, 等. 内镜辅助下颌下腺腺门和腺内结石不同取石方法的探讨[J]. 中华口腔医学杂志, 2018, 53 (12): 826- 831.
doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1002-0098.2018.12.007 |
| 6 |
McGurk M , MacBean AD , Fan KFM , et al. Endoscopically assisted operative retrieval of parotid stones[J]. Br J Oral and Maxillofac Surg, 2006, 44 (2): 157- 160.
doi: 10.1016/j.bjoms.2005.03.026 |
| 7 |
Zhao YN , Zhang YQ , Zhang LQ , et al. Treatment strategy of hilar and intraglandular stones in Wharton's duct: 12-year experience[J]. Laryngoscope, 2020, 130 (10): 2360- 2365.
doi: 10.1002/lary.28361 |
| 8 |
Ye X , Zhang YQ , Xie XY , et al. Transoral and transcutaneous approach for removal of parotid gland calculi: A 10-year endosco-pic experience[J]. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pahtol Oral Radiol, 2017, 124 (2): 121- 127.
doi: 10.1016/j.oooo.2017.04.005 |
| 9 | Zhao Y, Zheng D, Zhang L, et al. Recovery of gland function after endoscopy-assisted removal of impacted hilo-parenchymal stones in the Wharton's duct[J/OL]. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg, (2022-10-07)[2022-11-05]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijom.2022.09.035. |
| 10 |
Schapher M , Mantsopoulos K , Messbacher ME , et al. Transoral submandibulotomy for deep hilar submandibular gland sialolithiasis[J]. Laryngoscope, 2017, 127 (9): 2038- 2044.
doi: 10.1002/lary.26459 |
| 11 |
Capaccio P , Gaffuri M , Rossi V , et al. Sialendoscope-assisted transoral removal of hilo-parenchymal sub-mandibular stones: Surgical results and subjective scores[J]. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital, 2017, 37 (2): 122- 127.
doi: 10.14639/0392-100X-1601 |
| 12 |
Xu H , Mao C , Liu J M , et al. Microanatomic study of the vascular and duct system of the submandibular gland[J]. Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2011, 69 (4): 1103- 1107.
doi: 10.1016/j.joms.2010.03.006 |
| 13 |
Xiao JQ , Sun HJ , Qiao QH , et al. Advantages of submandibular gland preservation surgery over submandibular gland resection for proximal submandibular stones[J]. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol, 2018, 125 (5): e113- e117.
doi: 10.1016/j.oooo.2017.12.009 |
| 14 |
Xie L , Pu Y , Yu C , et al. Transfacial lithotomy approach to intraparenchymal stones in the submandibular gland: Our primary exploration[J]. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2022, 60 (2): 201- 203.
doi: 10.1016/j.bjoms.2021.03.008 |
| 15 | Zheng DN, Zhao YN, Zhang LQ, et al. Comparison of two transcutaneous approaches for the removal of impacted parotid stones[J/OL]. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg, (2022-10-19)[2022-11-05]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijom.2022.10.007. |
| 16 | 叶欣, 张亚琼, 赵雅宁, 等. 内镜辅助腮腺结石口内途径取出术的适应证与疗效分析[J]. 中华口腔医学杂志, 2019, 54 (1): 17- 22. |
| 17 |
Koch M , Schapher M , Mantsopoulos K , et al. Intraductal lithotripsy in sialolithiasis using the calculase Ⅲ Ho ∶YAG laser: First experiences[J]. Lasers Surg Med, 2021, 53 (4): 488- 498.
doi: 10.1002/lsm.23325 |
| 18 |
Hills AJ , Holden AM , McGurk M . Sialendoscopy-assisted transfacial removal of parotid calculi[J]. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital, 2017, 37 (2): 128- 131.
doi: 10.14639/0392-100X-1602 |
| 19 |
Thomas G , Stephan H , Niels H , et al. Sialendoscopy plus laser lithotripsy in sialolithiasis of the submandibular gland in 64 patients: A simple and safe procedure[J]. Auris Nasus Larynx, 2019, 46 (5): 797- 802.
doi: 10.1016/j.anl.2019.01.009 |
| 20 |
Jason S , Lee MJ , Ben HC , et al. Optimal power settings for Holmium ∶YAG lithotripsy[J]. J Urol, 2012, 187 (3): 914- 919.
doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2011.10.147 |
| 21 |
Sionis S , Caria RA , Trucas M , et al. Sialoendoscopy with and without holmium ∶YAG laser-assisted lithotripsy in the management of obstructive sialadenitis of major salivary glands[J]. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2014, 52 (1): 58- 62.
doi: 10.1016/j.bjoms.2013.06.015 |
| 22 |
Catra F , Farneti P , Cantore S , et al. Sialendoscopy for salivary stones: Principles, technical skills and therapeutic experiences[J]. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital, 2017, 37 (2): 102- 112.
doi: 10.14639/0392-100X-1599 |
| 23 | Koch M , Hung SH , Iro H , et al. Intraductal lithotripsy in sialolithiasis with two different Ho ∶YAG lasers: Presetting parameters, effectiveness, success rates[J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 2019, 23 (13): 5548- 5557. |
| [1] | 杨玉淑, 齐晅, 丁萌, 王炜, 郭惠芳, 高丽霞. 抗唾液腺蛋白1抗体联合抗腮腺分泌蛋白抗体对干燥综合征的诊断价值[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 845-852. |
| [2] | 乔佳佳,田聪,黄晓波,刘军. 肾结石合并系统性红斑狼疮行经皮肾镜碎石取石术的安全性和有效性评估[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 745-749. |
| [3] | 田聪,刘军,杨波,乔佳佳,黄晓波,许清泉. 经皮肾镜取石术中异常肾盂黏膜活检结果分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 948-952. |
| [4] | 俞光岩,苏家增,柳登高,吴立玲,丛馨. 下颌下腺保存治疗新技术体系的建立与应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(5): 842-845. |
| [5] | 李炳雨,唐祖南,胡耒豪,章文博,于尧,俞光岩,彭歆. 腮腺微小肿瘤的临床病理研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(2): 335-339. |
| [6] | 俞光岩,柳登高,李巍,洪霞,张严妍,朱文瑄,张可夫,李潇,栗占国,刘燕鹰,陈艳,高岩,苏家增. 3类新型慢性唾液腺炎的诊断和治疗[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(1): 13-17. |
| [7] | 陈超伦,苏家增,俞光岩. 酸刺激对腮腺和下颌下腺唾液流率及成分的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(1): 89-94. |
| [8] | 戴翔,左美妮,张晓鹏,胡浩,徐涛. 经皮肾镜术中不同憩室颈部处理方式治疗肾盏憩室结石的长期预后[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(4): 704-709. |
| [9] | 朱忆颖,闵赛南,俞光岩. 局部注射环孢素A对非肥胖糖尿病小鼠下颌下腺分泌功能及炎症的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(4): 750-757. |
| [10] | 俞光岩. 多发性唾液腺肿大的鉴别诊断及处理[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(1): 1-4. |
| [11] | 王怡平,蔡志刚,彭歆,张杰,孙志鹏,李巍,张雷,俞光岩. 下颌下腺质量和体积的实体体外检测[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(1): 126-132. |
| [12] | 高健,胡立宝,陈尘,郅新,徐涛. 经皮肾镜去石术后出血的介入治疗[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(4): 667-671. |
| [13] | 王明瑞,王起,胡浩,赖金惠,贺永新,熊杰,刘献辉,刘士军,许克新,徐涛. 标准通道经皮肾镜取石术治疗孤立肾肾结石的长期安全性和有效性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(4): 663-666. |
| [14] | 李玉冰,孙丽莎,孙志鹏,谢晓艳,张建运,张祖燕,赵燕平,马绪臣. 腮腺CT影像报告与数据系统的初步研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(1): 83-89. |
| [15] | 丛馨,闵赛南,吴立玲,蔡志刚,俞光岩. 激活毒蕈碱乙酰胆碱受体调控下颌下腺分泌的机制研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(3): 390-396. |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 224
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 596
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Cited |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shared | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Discussed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||