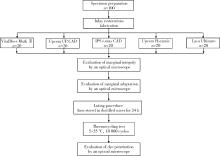
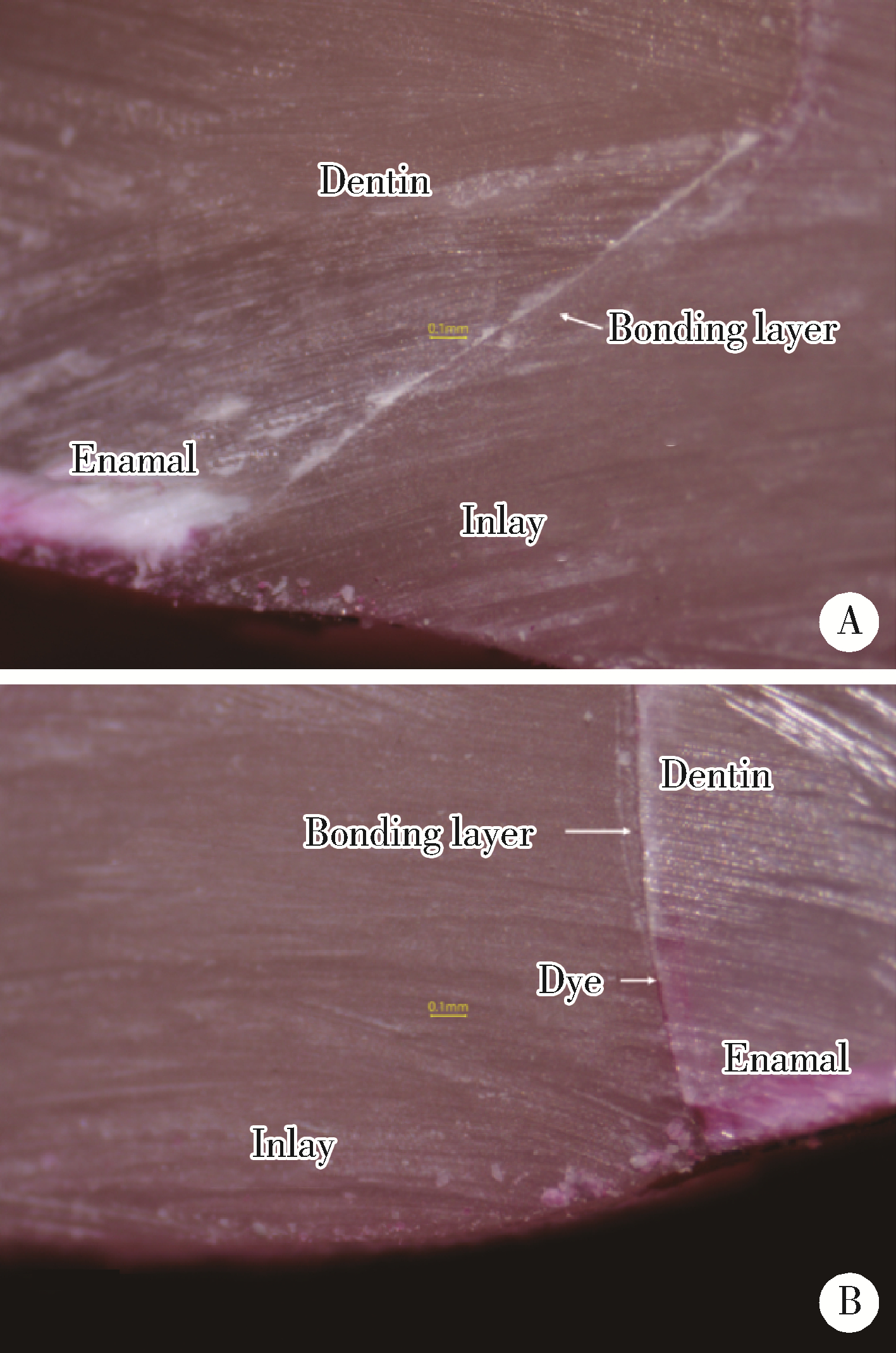
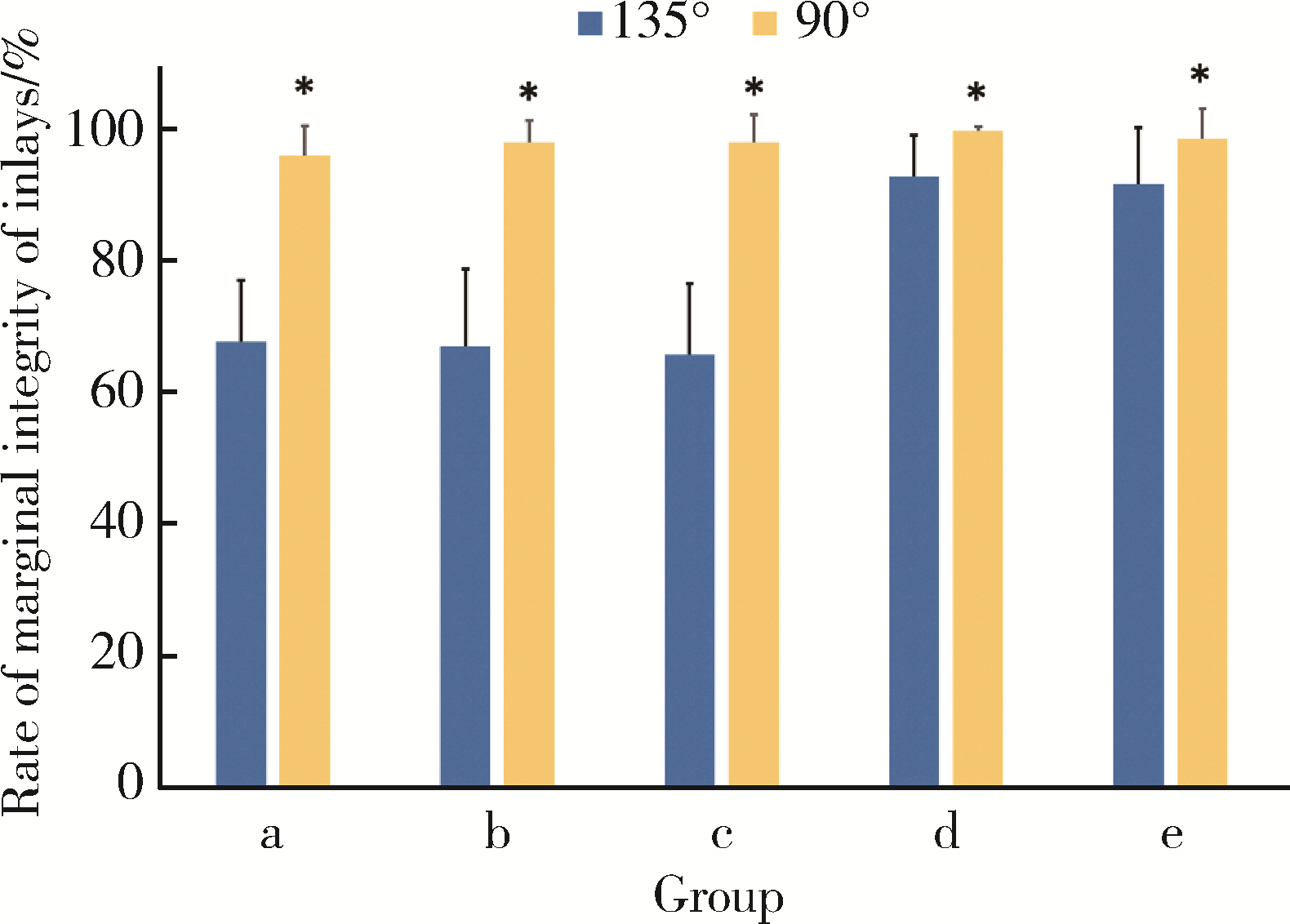
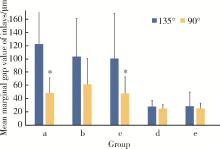
北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (6): 1105-1110. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2023.06.023
洞缘设计对CAD/CAM瓷嵌体边缘质量和边缘适应性及微渗漏的影响
- 北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院牙体牙髓科, 国家口腔医学中心, 国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心, 口腔生物材料和数字诊疗装备国家工程研究中心, 口腔数字医学北京市重点实验室, 国家卫生健康委员会口腔医学计算机应用工程技术研究中心, 国家药品监督管理局口腔生物材料重点实验室, 北京 100081
Influence of cavity design on quality of margin and marginal adaptation and microleakage of all-ceramic CAD/CAM inlays
- Department of Cariology and Endodontology, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Center of Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Research Center of Oral Biomaterials and Digital Medical Devices & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology & NHC Research Center of Engineering and Technology for Computerized Dentistry & NMPA Key Laboratory for Dental Materials, Beijing 100081, China
摘要:
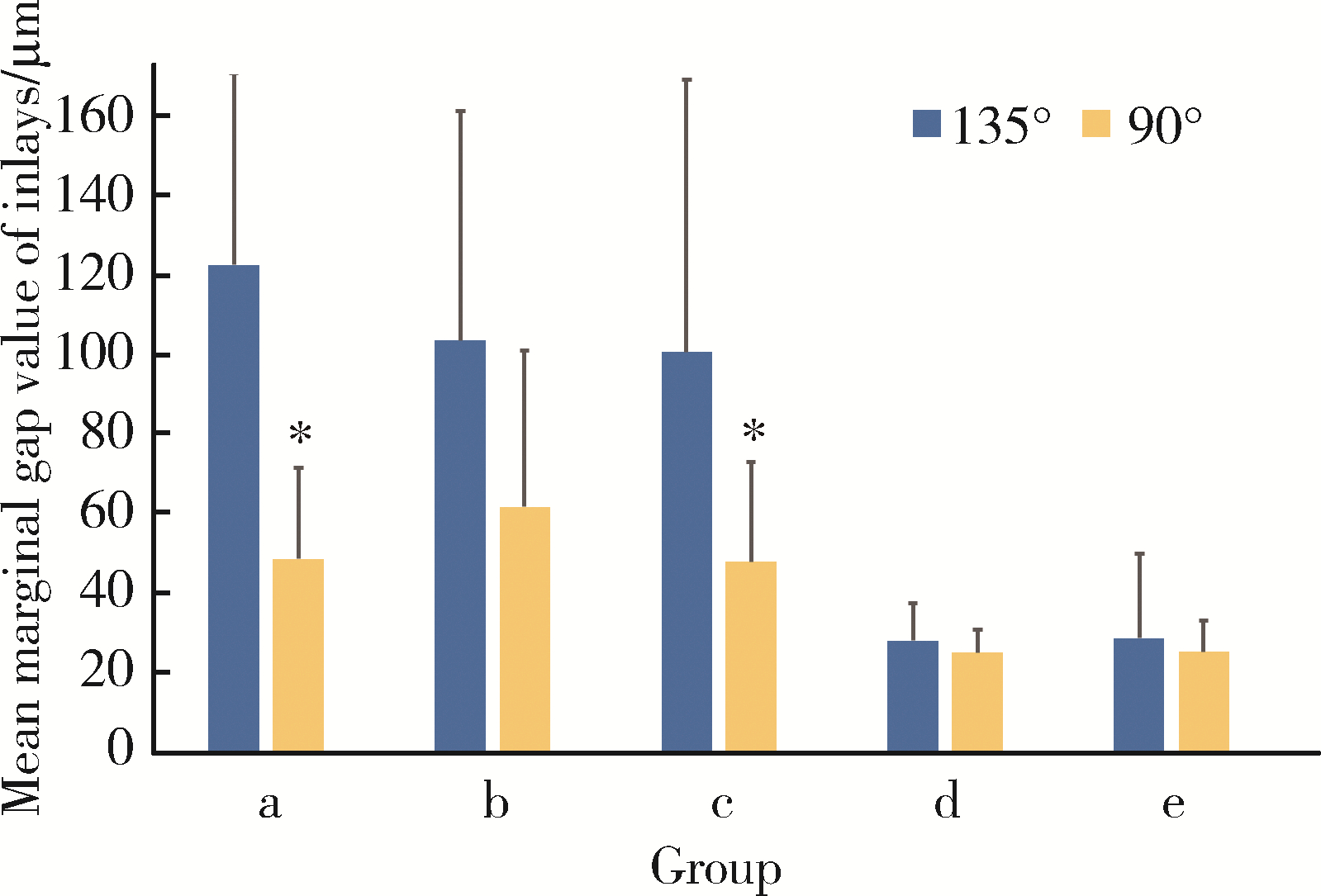
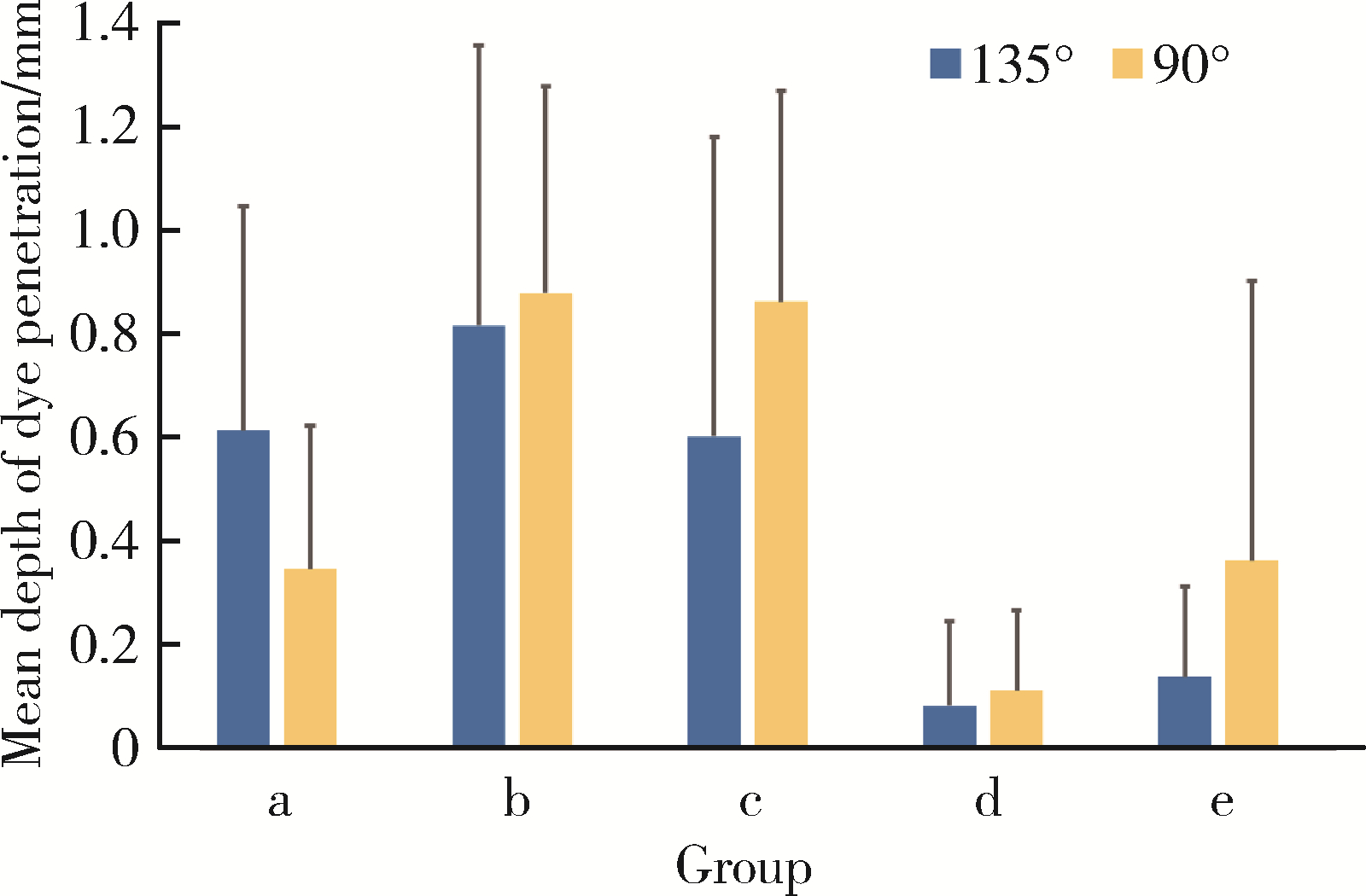
目的: 研究不同洞缘设计(135°洞缘斜面和90°洞缘)对不同材质计算机辅助设计/计算机辅助制造(computer aided design/computer aided manufacturing,CAD/CAM)瓷嵌体边缘质量、边缘适应性及微渗漏的影响。方法: 100颗人磨牙冠部进行颊
中图分类号:
- R783.1
| 1 | Azeem RA , Sureshbabu NM . Clinical performance of direct versus indirect composite restorations in posterior teeth: A systematic review[J]. J Conserv Dent, 2018, 21 (1): 2- 9. |
| 2 |
Schroeder M , Reis A , Luque-Martinez I , et al. Effect of enamel bevel on retention of cervical composite resin restorations: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. J Dent, 2015, 43 (7): 777- 788.
doi: 10.1016/j.jdent.2015.02.017 |
| 3 |
中华口腔医学会口腔美学专业委员会, 中华口腔医学会口腔材料专业委员会. 全瓷美学修复材料临床应用专家共识[J]. 中华口腔医学杂志, 2019, 54 (12): 825- 828.
doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1002-0098.2019.12.007 |
| 4 |
Taha D , Spintzyk S , Sabet A , et al. Assessment of marginal adaptation and fracture resistance of endocrown restorations utilizing different machinable blocks subjected to thermomechanical aging[J]. J Esthet Restor Dent, 2018, 30 (4): 319- 328.
doi: 10.1111/jerd.12396 |
| 5 |
Contrepois M , Soenen A , Bartala M , et al. Marginal adaptation of ceramic crowns: A systematic review[J]. J Prosthet Dent, 2013, 110 (6): 447- 454.
doi: 10.1016/j.prosdent.2013.08.003 |
| 6 |
Goujat A , Abouelleil H , Colon P , et al. Marginal and internal fit of CAD-CAM inlay/onlay restorations: A systematic review of in vitro studies[J]. J Prosthet Dent, 2019, 121 (4): 590- 597.
doi: 10.1016/j.prosdent.2018.06.006 |
| 7 |
Dioguardi M , Alovisi M , Troiano G , et al. Clinical outcome of bonded partial indirect posterior restorations on vital and non-vital teeth: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Clin Oral Investig, 2021, 25 (12): 6597- 6621.
doi: 10.1007/s00784-021-04187-x |
| 8 |
Oz FD , Bolay S , Canatan S . A clinical evaluation of resin nanoceramic CEREC omnicam restorations associated with several factors[J]. J Esthet Restor Dent, 2021, 33 (4): 583- 589.
doi: 10.1111/jerd.12691 |
| 9 | Frankenberger R , Hartmann VE , Krech M , et al. Adhesive luting of new CAD/CAM materials[J]. Int J Comput Dent, 2015, 18 (1): 9- 20. |
| 10 |
Gold SA , Ferracane JL , da Costa J . Effect of crystallization firing on marginal gap of CAD/CAM fabricated lithium disilicate crowns[J]. J Prosthodont, 2018, 27 (1): 63- 66.
doi: 10.1111/jopr.12638 |
| 11 |
Baldi A , Comba A , Michelotto Tempesta R , et al. External marginal gap variation and residual fracture resistance of composite and lithium-silicate CAD/CAM overlays after cyclic fatigue over endodontically-treated molars[J]. Polymers (Basel), 2021, 13 (17): 3002.
doi: 10.3390/polym13173002 |
| 12 |
Lima FF , Neto CF , Rubo JH , et al. Marginal adaptation of CAD-CAM onlays: Influence of preparation design and impression technique[J]. J Prosthet Dent, 2018, 120 (3): 396- 402.
doi: 10.1016/j.prosdent.2017.10.010 |
| 13 | Oliveira J , Dorado L , Koch D , et al. Marginal microleakage in cavities prepared with CVD tip and 245 bur[J]. Dent Implantol Update, 2009, 20 (3): 17- 23. |
| 14 |
Simi B , Suprabha B . Evaluation of microleakage in posterior nanocomposite restorations with adhesive liners[J]. J Conserv Dent, 2011, 14 (2): 178- 181.
doi: 10.4103/0972-0707.82631 |
| 15 | 傅柏平, 金光盛, MatthiasH. 自蚀粘接剂对复合树脂微渗漏的影响[J]. 浙江大学学报(医学版), 2002, 31 (5): 53- 56. |
| 16 | 周宪华, 牛文芝, 王鹏来, 等. 有无洞缘斜面对聚合瓷嵌体微渗漏影响的实验研究[J]. 现代口腔医学杂志, 2012, 26 (6): 392- 393. |
| [1] | 李秋菊,宫玮玉,董艳梅. 生物活性玻璃预处理对牙本质粘接界面耐久性的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(5): 931-937. |
| [2] | 李爽,张清. 玷污层对新型三氧化矿物凝聚体根尖封闭性的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(3): 560-563. |
| [3] | 谢窈, 张笋, 葛立宏. 乳牙应用Er:YAG激光备洞充填微渗漏效果的离体研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2014, 46(3): 474-477. |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 193
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 250
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Cited |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shared | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Discussed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||