北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (6): 1041-1046. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2024.06.015
系统性硬化症患者新型冠状病毒感染特点及疫苗接种效果:一项单中心队列研究
潘苇1,2, 李云1, 罗俊佳3, 李春1, 叶华1, 李雪1,*( ), 贾园1,*(
), 贾园1,*( )
)
- 1. 北京大学人民医院风湿免疫科,北京 100044
2. 中国人民解放军联勤保障部队第九二三医院检验科,南宁 530004
3. 深圳市龙华区人民医院风湿免疫科,广东深圳 518110
COVID-19 vaccines efficacy and infection features in patients with systemic sclerosis: A single-center cohort study
Wei PAN1,2, Yun LI1, Junjia LUO3, Chun LI1, Hua YE1, Xue LI1,*( ), Yuan JIA1,*(
), Yuan JIA1,*( )
)
- 1. Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, Peking University People' s Hospital, Beijing 100044, China
2. Department of Clinical Laboratory, 923 Hospital of the Chinese People' s Liberation Army Joint Logistic Support Force, Nanning 530021, China
3. Department of Rheumatism and Immunology, Longhua District People' s Hospital, Shenzhen 518110, Guangdong, China
摘要:
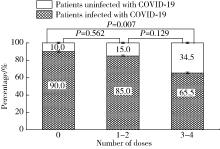
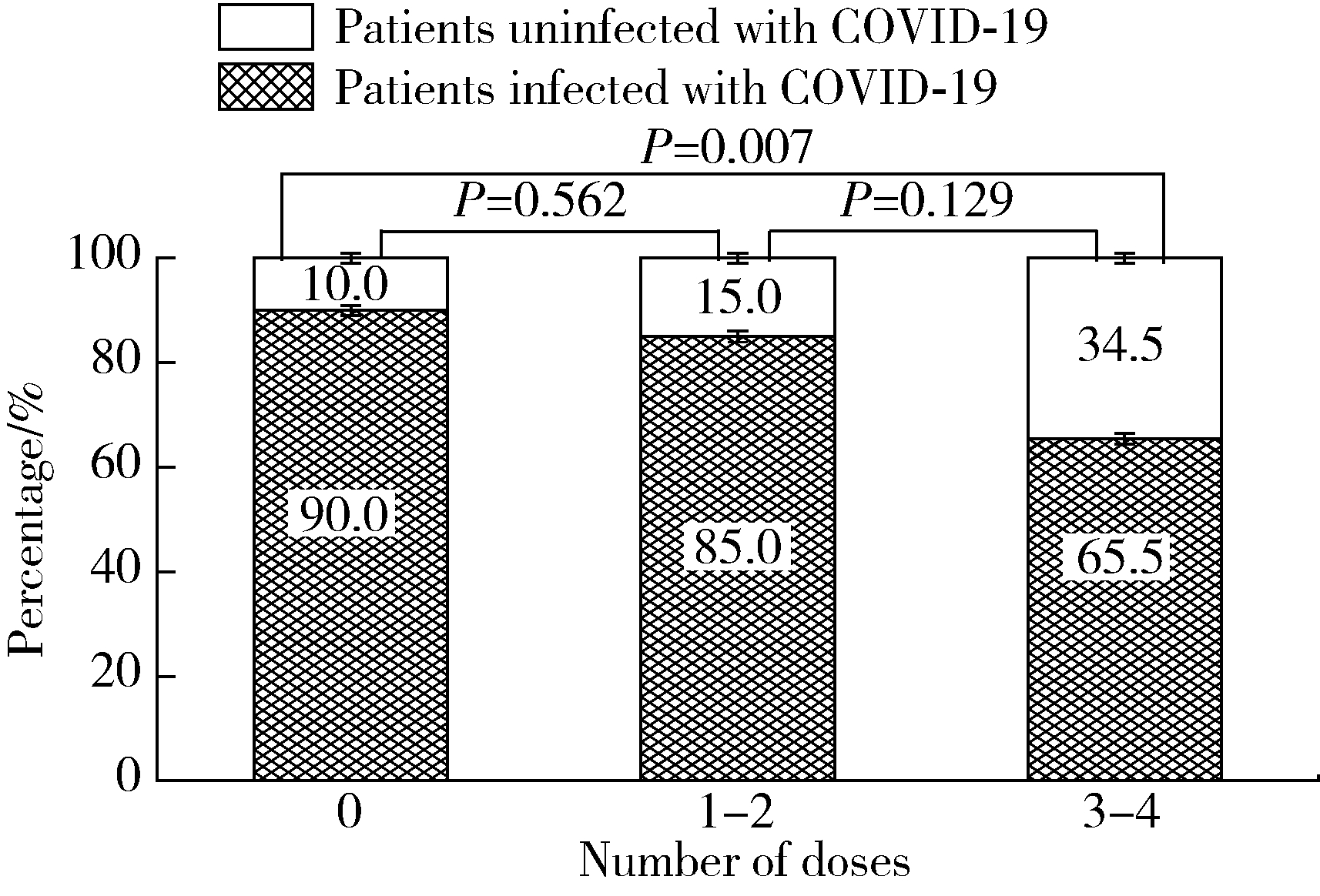
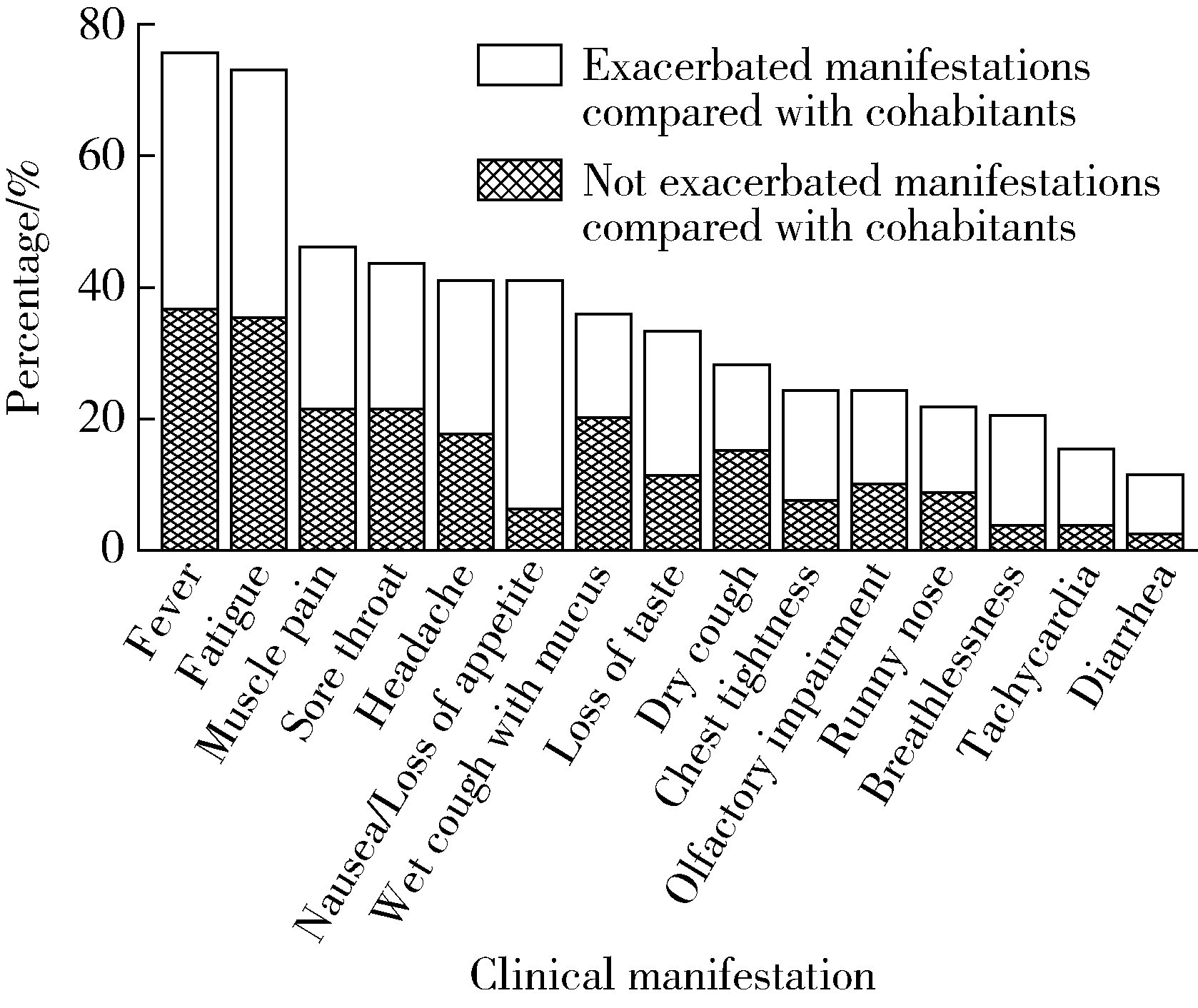
目的: 了解系统性硬化症(systemic sclerosis,SSc)患者COVID-19疫苗接种及新型冠状(简称新冠)病毒感染情况。方法: 选取2016年1月至2023年3月于北京大学人民医院风湿免疫科住院,明确诊断为SSc的患者,通过住院病历检索和电话随访的形式,收集患者的临床特征、COVID-19疫苗接种及新冠病毒感染情况。结果: 236例SSc患者中有99例接受了电话随访及问卷调查,其中局限型SSc 41例、弥漫型SSc 28例、重叠综合征30例;患者接受了糖皮质激素(57.58%)、免疫抑制剂(56.57%)、生物制剂(7.07%)和小分子靶向药(6.06%)治疗。共49例患者接种过COVID-19疫苗,2022年11月至2023年3月期间共81例患者感染新冠病毒,接种三针及以上疫苗患者的感染率(19/29,65.5%)较未接种患者(45/50,90.0%)明显降低(P=0.007)。14例患者因新冠病毒感染住院治疗,26例患者感染后SSc症状有所加重,包括雷诺现象(Raynaud phenomenon)、皮肤病变、指端溃疡、肺动脉高压和肺间质病变等。与健康同居者相比较,SSc患者新冠病毒感染后发热(36.71%)、乏力(35.44%)等症状更严重。多因素回归分析显示,皮下钙质沉积(OR=7.713,95%CI:1.142~45.051)和抗着丝点抗体阳性(OR=9.210,95%CI:1.211~70.028)是SSc患者因新冠病毒感染入院治疗的独立危险因素。结论: 对于SSc患者,接种COVID-19疫苗对预防新冠病毒感染有效且安全;SSc患者新冠病毒感染后原发病加重,且感染症状也较无基础病人群加重。预防和早期合理治疗新冠病毒感染,对SSc患者具有重要意义。
中图分类号:
- R593.2
| 1 | Lepri G , Di Battista M , Codullo V , et al.Systemic sclerosis: One year in review 2024[J].Clin Exp Rheumatol,2024,42(8):1517-1528. |
| 2 |
Teles MS , Brundage J , Chiang TP , et al.Prevalence and risk factors of post-acute sequela of COVID-19 in adults with systemic autoimmune rheumatic diseases[J].J Rheumatol,2024,51(9):928-933.
doi: 10.3899/jrheum.2023-1212 |
| 3 |
Perveen S , Samreen S , Gul H , et al.Effect of disease activity on the clinical outcome of SARS CoV-2 in patients with underlying rheumatic diseases; data from global rheumatology alliance[J].J Pak Med Assoc,2024,74(6):1055-1060.
doi: 10.47391/JPMA.9371 |
| 4 | 新型冠状病毒感染诊疗方案(试行第十版)[J]. 中国医药, 2023, 18(2): 161-166. |
| 5 | Pattanaik D , Brown M , Postlethwaite BC , et al.Pathogenesis of systemic sclerosis[J].Front Immunol,2015,6,272. |
| 6 |
Ding Z , Wei X , Pan H , et al.Unveiling the intricacies of COVID- 19: Autoimmunity, multi-organ manifestations and the role of autoantibodies[J].Scand J Immunol,2024,99(2):e13344.
doi: 10.1111/sji.13344 |
| 7 |
Denton CP , Campochiaro C , Bruni C , et al.COVID-19 and systemic sclerosis: Rising to the challenge of a pandemic[J].J Scleroderma Relat Disord,2021,6(1):58-65.
doi: 10.1177/2397198320963393 |
| 8 |
Liu Y , Sawalha AH , Lu Q .COVID-19 and autoimmune diseases[J].Curr Opin Rheumatol,2021,33(2):155-162.
doi: 10.1097/BOR.0000000000000776 |
| 9 |
Jung SW , Jeon JJ , Kim YH , et al.Long-term risk of autoimmune diseases after mRNA-based SARS-CoV2 vaccination in a Korean, nationwide, population-based cohort study[J].Nat Commun,2024,15(1):6181.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-50656-8 |
| 10 | 朱玥桢, 李雪, 钟雪.自身免疫性疾病与新型冠状病毒肺炎疫苗接种[J].中国新药杂志,2022,31(14):1395-1401. |
| 11 | Güler AA , Özçimen B , Aydoǧdu MS , et al.Clinical characteristics and disease course before and after SARS-CoV-2 infection in a large cohort of systemic sclerosis patients[J].Turk J Med Sci,2023,54(1):76-85. |
| 12 |
Panopoulos S , Tzilas V , Bournia VK , et al.COVID-19 and protection of vaccination in patients with systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease[J].J Scleroderma Relat Disord,2023,8(2):113-119.
doi: 10.1177/23971983221143252 |
| 13 | Update to living WHO guideline on drugs for COVID-19[J]. BMJ, 2023, 383: 2622. |
| 14 | Talarico R , Ramirez GA , Barreira SC , et al.ERN ReCONNET points to consider for treating patients living with autoimmune rheumatic diseases with antiviral therapies and anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibody products[J].Clin Exp Rheumatol,2023,41(3):543-553. |
| 15 |
Prajjwal P , Marsool MDM , Yadav V , et al.Neurological, car-diac, musculoskeletal, and renal manifestations of scleroderma along with insights into its genetics, pathophysiology, diagnostic, and therapeutic updates[J].Health Sci Rep,2024,7(4):e2072.
doi: 10.1002/hsr2.2072 |
| 16 | Ghosh S , Tanna D , Telang K , et al.Clinical and autoantibody profiles of systemic sclerosis patients: A cross-sectional study from North India[J].Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol,2023,1,1-7. |
| 17 | Hui M , Zhou J , Li M , et al.Digital gangrene in systemic sclerosis patients: Not only due to the microvascular disease[J].Clin Rheumatol,2024,43(3):1083-1092. |
| 18 | Ture HY , Lee NY , Kim NR , et al.Raynaud' s phenomenon: A current update on pathogenesis, diagnostic workup, and treatment[J].Vasc Specialist Int,2024,40,26. |
| 19 | Fairley JL , O' Rourke R , Puranik R , et al.Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging in systemic sclerosis: Heart involvement in high- resolution[J].Rheumatol Immunol Res,2024,5(2):83-92. |
| [1] | 赵柯林, 夏雪, 史乃旭, 周韩, 盖婧雯, 李萍. 铁死亡标志物4-HNE在系统性硬化症细胞模型中的表达及意义[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(6): 950-955. |
| [2] | 刘鑫,石雪迎,李军. 新型冠状病毒感染相关缺血性结肠炎1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 362-365. |
| [3] | 朱金荣,赵亚娜,黄巍,赵微微,王悦,王松,苏春燕. 感染新型冠状病毒的血液透析患者的临床特征[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 267-272. |
| [4] | 李文根,古晓东,翁锐强,刘苏东,陈超. 血浆外泌体miR-34-5p和miR-142-3p在系统性硬化症中的表达及临床意义[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 1022-1027. |
| [5] | 林卓华,蔡如意,孙洋,穆荣,崔立刚. 超微血流显像评价系统性硬化症指端血流的方法学与临床应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 636-640. |
| [6] | 罗靓,蔡青猛,刘香君,贠泽霖,李春,张晓盈. 以雷诺现象为首发表现的系统性硬化症临床特征及其相关因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1224-1228. |
| [7] | 马向波,张学武,贾汝琳,高颖,刘洪江,刘玉芳,李英妮. 外周血淋巴细胞亚群检测在系统性硬化症治疗中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(4): 721-727. |
| [8] | 赵静,孙峰,李云,赵晓珍,徐丹,李英妮,李玉慧,孙晓麟. 抗α-1C微管蛋白抗体在系统性硬化症中的表达及临床意义[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(6): 1009-1013. |
| [9] | 邢燕,张娟,韩彤妍,李在玲,李蕊,童笑梅. 新型冠状病毒感染肺炎疫情下综合医院儿科防控方式探索[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(3): 410-413. |
| [10] | 朱红林,杜倩,谌威霖,左晓霞,李全贞,刘思佳. 系统性硬化症血清细胞因子表达谱变化及调控机制[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(4): 716-722. |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 18
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 138
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Cited |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shared | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Discussed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||