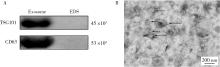
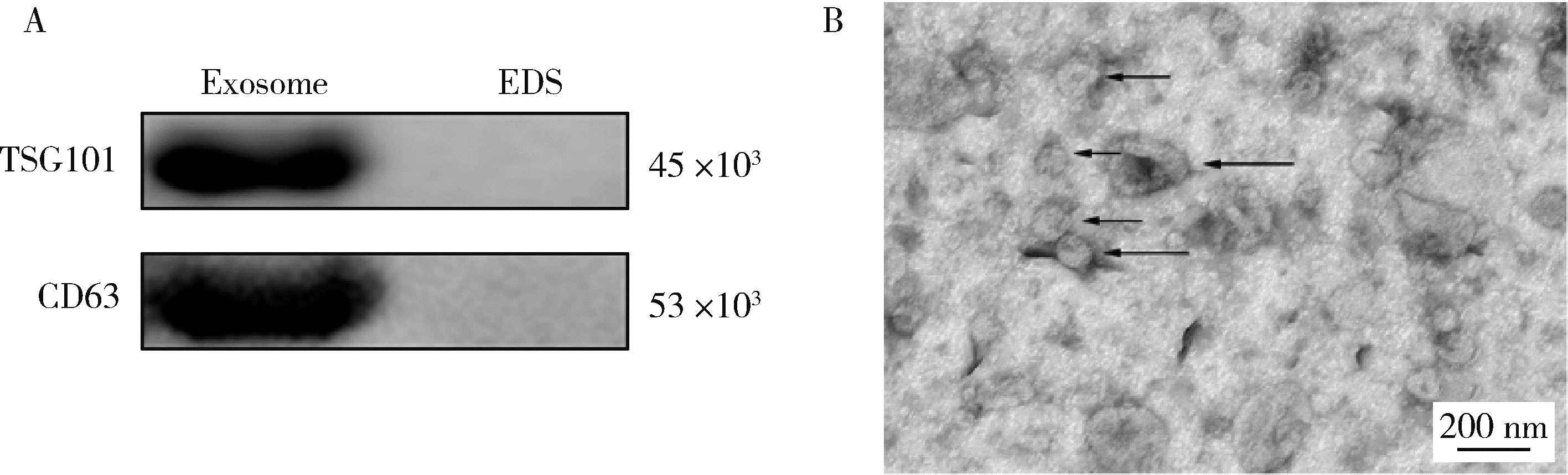
北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (6): 1022-1027. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2023.06.010
血浆外泌体miR-34-5p和miR-142-3p在系统性硬化症中的表达及临床意义
- 1. 梅州市人民医院(黄塘医院)风湿免疫科,广东梅州 514031
2. 梅州市人民医院(黄塘医院)科研实验中心,广东梅州 514031
Expression and clinical significance of plasma exosomal miR-34-5p and miR-142-3p in systemic sclerosis
Wen-gen LI1,*( ),Xiao-dong GU2,Rui-qiang WENG2,Su-dong LIU2,Chao CHEN1
),Xiao-dong GU2,Rui-qiang WENG2,Su-dong LIU2,Chao CHEN1
- 1. Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, Meizhou People's Hospital (Huangtang Hospital), Meizhou 514031, Guangdong, China
2. Scientific Research and Experimental Center, Meizhou People's Hospital (Huangtang Hospital), Meizhou 514031, Guangdong, China
摘要:
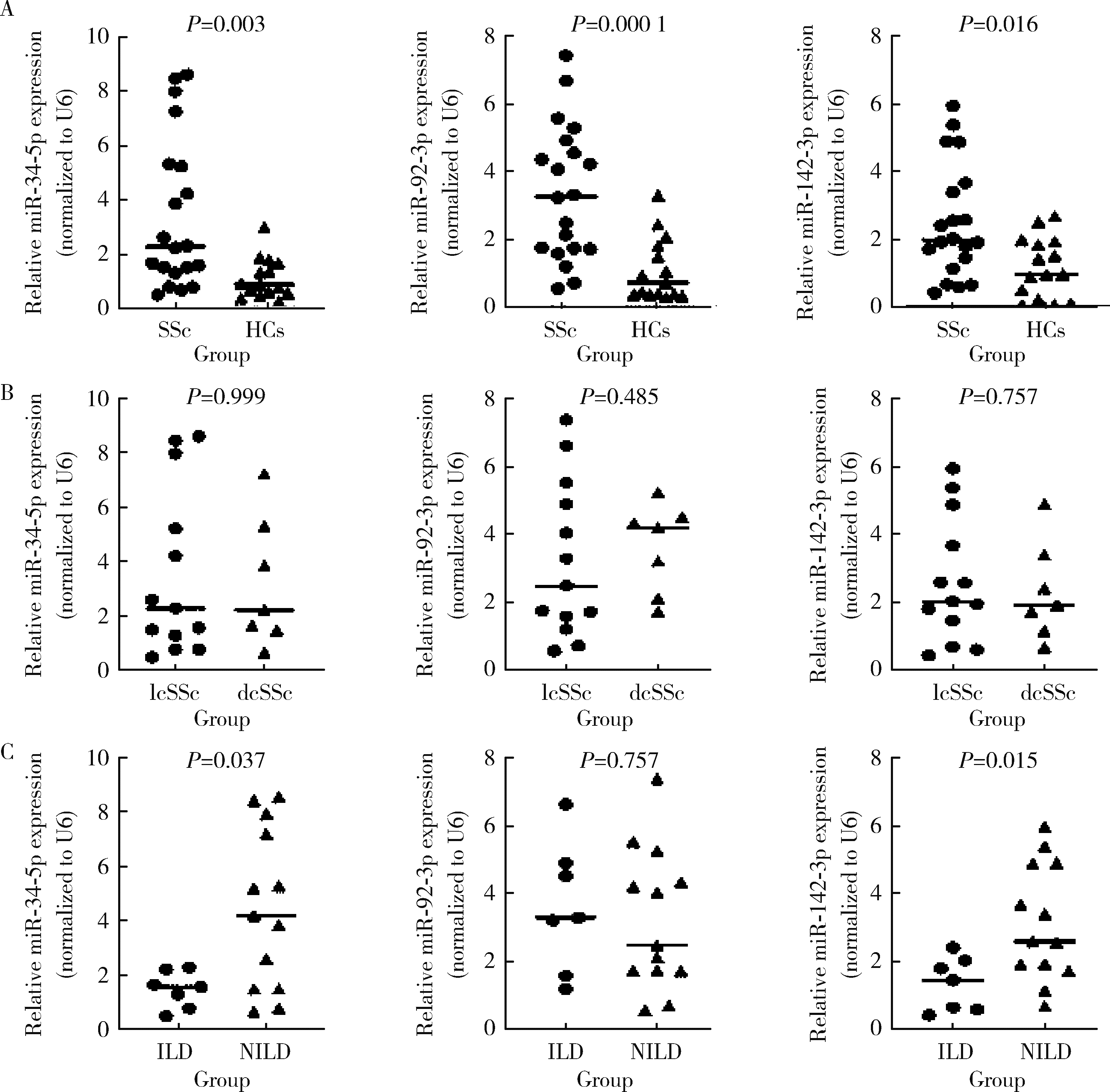
目的: 检测系统性硬化症(systemic sclerosis,SSc)患者血浆外泌体微小RNA(microRNA,miRNA)的表达,探讨其在SSc中的临床意义。方法: 选取20例梅州市人民医院风湿免疫科2020年1月至2022年1月未接受治疗的初诊SSc患者,同时以年龄及性别匹配的15例健康志愿者作为对照组。采用超速离心法获得血浆外泌体,采用实时荧光定量聚合酶链式反应(quantative real-time polymerase chain reaction, qRT-PCR)检测外泌体miR-34-5p、miR-92-3p和miR-142-3p的表达。采用Spearman秩相关系数检验分析miRNA表达水平与SSc临床特点的相关性。结果: 20例SSc患者的平均年龄为(52.6±12.6)岁,男性7例,女性13例。根据皮肤累及范围,13例为局限皮肤型SSc (limited cutaneous systemic sclerosis, lcSSc),7例为弥漫皮肤型SSc (diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis, dcSSc)。根据高分辨率胸部CT检查结果,7例确诊间质性肺病(interstitial lung disease, ILD),13例确诊非ILD。SSc患者血浆外泌体miR-34-5p、miR-92-3p和miR-142-3p的表达水平显著高于对照组(分别为P=0.003、P=0.000 1和P=0.016)。与未并发ILD的患者相比,并发ILD患者miR-34-5p和miR-142-3p的表达水平显著降低(分别为P=0.037和P=0.015)。miR-34-5p和miR-142-3p的表达水平与ILD(分别为r=-0.48、P=0.031和r=-0.55、P=0.011)、关节炎(分别为r=-0.46、P=0.040和r=-0.48、P=0.032)均呈负相关。miR-142-3p与红细胞沉降率呈负相关(r=-0.55、P=0.012)。结论: SSc的血浆外泌体miR-34-5p、miR-92-3p和miR-142-3p存在表达失调,表达异常的miR-34-5p和miR-142-3p与SSc相关ILD(SSc associated ILD, SSc-ILD)存在相关性。
中图分类号:
- R593.25
| 1 |
Denton CP , Khanna D . Systemic sclerosis[J]. Lancet, 2017, 390 (10103): 1685- 1699.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)30933-9 |
| 2 |
Szabo I , Muntean L , Crisan T , et al. Novel concepts in systemic sclerosis pathogenesis: Role for miRNAs[J]. Biomedicines, 2021, 9 (10): 1471.
doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9101471 |
| 3 |
Liu Y , Cheng L , Zhan H , et al. The roles of noncoding RNAs in systemic sclerosis[J]. Front Immunol, 2022, 13, 856036.
doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.856036 |
| 4 |
Henry TW , Mendoza FA , Jimenez SA . Role of microRNA in the pathogenesis of systemic sclerosis tissue fibrosis and vasculopathy[J]. Autoimmun Rev, 2019, 18 (11): 102396.
doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2019.102396 |
| 5 |
Zhao M , Qi Q , Liu S , et al. MicroRNA-34a: A novel therapeutic target in fibrosis[J]. Front Physiol, 2022, 13, 895242.
doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.895242 |
| 6 |
Wuttge DM , Carlsen AL , Teku G , et al. Specific autoantibody profiles and disease subgroups correlate with circulating micro-RNA in systemic sclerosis[J]. Rheumatology (Oxford), 2015, 54 (11): 2100- 2107.
doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kev234 |
| 7 |
Jafarinejad-Farsangi S , Gharibdoost F , Farazmand A , et al. MicroRNA-21 and microRNA-29a modulate the expression of collagen in dermal fibroblasts of patients with systemic sclerosis[J]. Autoimmunity, 2019, 52 (3): 108- 116.
doi: 10.1080/08916934.2019.1621856 |
| 8 | Shi J , Li F , Luo M , et al. Distinct roles of Wnt/β-catenin signaling in the pathogenesis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis[J]. Mediators Inflamm, 2017, 2017, 3520581. |
| 9 |
Cottin V , Brown KK . Interstitial lung disease associated with systemic sclerosis (SSc-ILD)[J]. Respir Res, 2019, 20 (1): 13.
doi: 10.1186/s12931-019-0980-7 |
| 10 |
Duan W , Zhang W , Jia J , et al. Exosomal microRNA in autoimmunity[J]. Cell Mol Immunol, 2019, 16 (12): 932- 934.
doi: 10.1038/s41423-019-0319-9 |
| 11 |
Mirzaei R , Zamani F , Hajibaba M , et al. The pathogenic, therapeutic and diagnostic role of exosomal microRNA in the autoimmune diseases[J]. J Neuroimmunol, 2021, 358, 577640.
doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2021.577640 |
| 12 | Wermuth PJ , Piera-Velazquez S , Jimenez SA . Exosomes isolated from serum of systemic sclerosis patients display alterations in their content of profibrotic and antifibrotic microRNA and induce a profibrotic phenotype in cultured normal dermal fibroblasts[J]. Clin Exp Rheumatol, 2017, 35 (Suppl 106): 21- 30. |
| 13 |
Cui H , Ge J , Xie N , et al. miR-34a inhibits lung fibrosis by inducing lung fibroblast senescence[J]. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol, 2017, 56 (2): 168- 178.
doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2016-0163OC |
| 14 |
Bulvik R , Biton M , Berkman N , et al. Forefront: MiR-34a-knockout mice with wild type hematopoietic cells, retain persistent fibrosis following lung injury[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21 (6): 2228.
doi: 10.3390/ijms21062228 |
| 15 |
Disayabutr S , Kim EK , Cha SI , et al. miR-34 miRNAs regulate cellular senescence in type Ⅱ alveolar epithelial cells of patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis[J]. PLoS One, 2016, 11 (6): e0158367.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0158367 |
| 16 |
Yang G , Yang L , Wang W , et al. Discovery and validation of extracellular/circulating microRNAs during idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis disease progression[J]. Gene, 2015, 562 (1): 138- 144.
doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2015.02.065 |
| 17 |
Blumer S , Fang L , Chen WC , et al. IPF-Fibroblast Erk1/2 acti-vity is independent from microRNA cluster 17-92 but can be inhibited by treprostinil through DUSP1[J]. Cells, 2021, 10 (11): 2836.
doi: 10.3390/cells10112836 |
| 18 |
Steen SO , Iversen LV , Carlsen AL , et al. The circulating cell-free microRNA profile in systemic sclerosis is distinct from both healthy controls and systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. J Rheumatol, 2015, 42 (2): 214- 221.
doi: 10.3899/jrheum.140502 |
| 19 | 黄赛赛, 王丹丹, 张卓亚, 等. 系统性硬化症患者血浆7种miRNA水平与脏器累及和临床指标的相关性[J]. 临床检验杂志, 2021, 39 (5): 358- 361. |
| 20 |
Sing T , Jinnin M , Yamane K , et al. microRNA-92a expression in the sera and dermal fibroblasts increases in patients with scleroderma[J]. Rheumatology (Oxford), 2012, 51 (9): 1550- 1556.
doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kes120 |
| 21 |
Guiot J , Cambier M , Boeckx A , et al. Macrophage-derived exosomes attenuate fibrosis in airway epithelial cells through delivery of antifibrotic miR-142-3p[J]. Thorax, 2020, 75 (10): 870- 881.
doi: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2019-214077 |
| 22 |
Njock MS , Guiot J , Henket MA , et al. Sputum exosomes: Promising biomarkers for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis[J]. Thorax, 2019, 74 (3): 309- 312.
doi: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2018-211897 |
| [1] | 林卓华,蔡如意,孙洋,穆荣,崔立刚. 超微血流显像评价系统性硬化症指端血流的方法学与临床应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 636-640. |
| [2] | 叶雨阳,岳林,邹晓英,王晓燕. 成牙本质方向分化牙髓干细胞外泌体形态及微小RNA表达谱特征[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 689-696. |
| [3] | 罗靓,蔡青猛,刘香君,贠泽霖,李春,张晓盈. 以雷诺现象为首发表现的系统性硬化症临床特征及其相关因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1224-1228. |
| [4] | 蒋青,张雨. 新形势下运动损伤特点及细胞生物治疗的应用前景和挑战[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(5): 828-831. |
| [5] | 马向波,张学武,贾汝琳,高颖,刘洪江,刘玉芳,李英妮. 外周血淋巴细胞亚群检测在系统性硬化症治疗中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(4): 721-727. |
| [6] | 夏芳芳,鲁芙爱,吕慧敏,杨国安,刘媛. 系统性红斑狼疮伴间质性肺炎的临床特点及相关因素分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(2): 266-272. |
| [7] | 赵静,孙峰,李云,赵晓珍,徐丹,李英妮,李玉慧,孙晓麟. 抗α-1C微管蛋白抗体在系统性硬化症中的表达及临床意义[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(6): 1009-1013. |
| [8] | 王晓,贺丹,李文婷,阿迪拉·斯依提,韩蕊,董颖. 144例维吾尔族与汉族女性子宫内膜癌微小RNA表达特点及临床意义[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(3): 570-577. |
| [9] | 高晓敏,邹晓英,岳林. 根尖牙乳头干细胞摄取外泌体的介导途径[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(1): 43-50. |
| [10] | 朱红林,杜倩,谌威霖,左晓霞,李全贞,刘思佳. 系统性硬化症血清细胞因子表达谱变化及调控机制[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(4): 716-722. |
| [11] | 张静,李素芳,陈红,宋俊贤. miR-106b-5p在调节内皮细胞基因表达谱中的作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(2): 221-227. |
| [12] | 康磊,霍焱,王荣福,张春丽,闫平,徐小洁. MicroRNA-155靶向的放射性标记探针对乳腺癌小鼠模型的活体显像[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(2): 326-330. |
| [13] | 蔡燚,郭浩,李汉忠,王文达,张玉石. 结节性硬化症细胞株TSC2-/- MEFs和正常细胞株TSC2+/+ MEFs微小RNA表达谱的差异分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(4): 580-584. |
| [14] | 贺大林,徐珊,郭鹏. 外泌体在泌尿系肿瘤精准诊断中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(4): 561-564. |
| [15] | 贾凌飞,甘业华,俞光岩. MicroRNA表达与舌鳞癌患者预后的关系及其调控舌鳞癌生物学行为的机制[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2016, 48(1): 5-9. |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 219
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 252
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Cited |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shared | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Discussed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||