北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (6): 1028-1032. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2023.06.011
IgG4相关性疾病患者就诊情况及其临床特征
- 1. 北京大学第三医院风湿免疫科, 北京 100191
2. 辽宁省健康产业集团本钢总医院风湿免疫科, 辽宁本溪 117000
Medical visit status and clinical features in patients with IgG4 related disease
Lu FENG1,2,Jia-yu ZHAI1,Jin-xia ZHAO1,*( )
)
- 1. Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
2. Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, Liaoning Health Industry Group Bengang General Hospital, Benxi 117000, Liaoning, China
摘要:
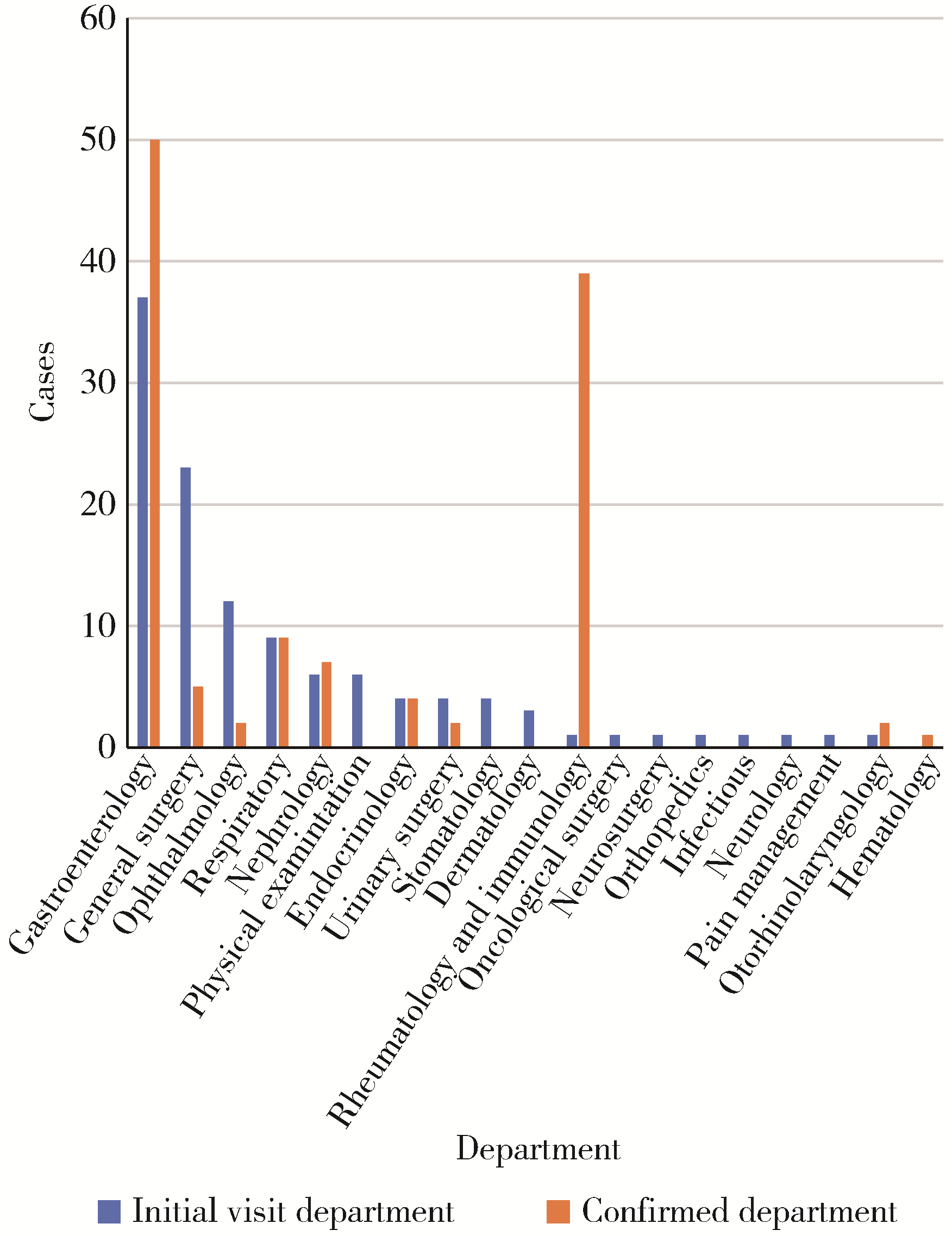
目的: 了解临床表现复杂且容易被误诊和漏诊的IgG4相关性疾病(IgG4-related disease,IgG4-RD)患者的就诊情况及临床特征,以提高相关科室医师对IgG4-RD的认识。方法: 选择2012年1月1日至2022年12月31日于北京大学第三医院住院且出院诊断为IgG4-RD患者的病例资料进行回顾性分析,总结患者就诊情况、临床表现、实验室检查、诊断及治疗情况。结果: 共纳入出院诊断为IgG4-RD的病例116例,男女比例为2.52∶ 1,平均年龄(61.83±10.80)岁。首诊科室以消化科、普外科、眼科为主,诊断科室主要为消化科、风湿免疫科、呼吸科,21例(18.10%)患者经过3个或者3个以上科室诊断后才最终确诊。从出现临床症状到首次就诊中位时间为2(1,7)个月,诊断中位时间为1(1,12)个月。24例(20.69%)患者在最终诊断前进行了受累部位的手术切除。依据IgG4-RD的分类标准,确定诊断68例(58.62%),可能诊断8例(6.90%),可疑诊断40例(34. 48%)。68例确定诊断的患者中,常见受累器官依次为颌下腺、胰腺、胆道、腮腺,血清IgG4水平的中位数为6.16(3.61,12.30) g/L,57例(83.82%)患者使用了糖皮质激素,14例(20.59%)患者使用了免疫抑制剂,使用免疫制剂者主要为风湿免疫科诊治患者(78.57%)。结论: IgG4-RD好发于老年男性,颌下腺、胰腺、胆道、腮腺易受累,首诊科室分布广泛,通过获取病理组织标本而确定诊断的比例较低,治疗上主要以激素为主,免疫抑制剂的使用率不高。
中图分类号:
- R593.2
| 1 |
Denton CP , Khanna D . Systemic sclerosis[J]. Lancet, 2017, 390 (10103): 1685- 1699.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)30933-9 |
| 2 |
Szabo I , Muntean L , Crisan T , et al. Novel concepts in systemic sclerosis pathogenesis: Role for miRNAs[J]. Biomedicines, 2021, 9 (10): 1471.
doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9101471 |
| 3 |
Liu Y , Cheng L , Zhan H , et al. The roles of noncoding RNAs in systemic sclerosis[J]. Front Immunol, 2022, 13, 856036.
doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.856036 |
| 4 |
Henry TW , Mendoza FA , Jimenez SA . Role of microRNA in the pathogenesis of systemic sclerosis tissue fibrosis and vasculopathy[J]. Autoimmun Rev, 2019, 18 (11): 102396.
doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2019.102396 |
| 5 |
Zhao M , Qi Q , Liu S , et al. MicroRNA-34a: A novel therapeutic target in fibrosis[J]. Front Physiol, 2022, 13, 895242.
doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.895242 |
| 6 |
Wuttge DM , Carlsen AL , Teku G , et al. Specific autoantibody profiles and disease subgroups correlate with circulating micro-RNA in systemic sclerosis[J]. Rheumatology (Oxford), 2015, 54 (11): 2100- 2107.
doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kev234 |
| 7 |
Jafarinejad-Farsangi S , Gharibdoost F , Farazmand A , et al. MicroRNA-21 and microRNA-29a modulate the expression of collagen in dermal fibroblasts of patients with systemic sclerosis[J]. Autoimmunity, 2019, 52 (3): 108- 116.
doi: 10.1080/08916934.2019.1621856 |
| 8 | Shi J , Li F , Luo M , et al. Distinct roles of Wnt/β-catenin signaling in the pathogenesis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis[J]. Mediators Inflamm, 2017, 2017, 3520581. |
| 9 |
Cottin V , Brown KK . Interstitial lung disease associated with systemic sclerosis (SSc-ILD)[J]. Respir Res, 2019, 20 (1): 13.
doi: 10.1186/s12931-019-0980-7 |
| 10 |
Duan W , Zhang W , Jia J , et al. Exosomal microRNA in autoimmunity[J]. Cell Mol Immunol, 2019, 16 (12): 932- 934.
doi: 10.1038/s41423-019-0319-9 |
| 11 |
Mirzaei R , Zamani F , Hajibaba M , et al. The pathogenic, therapeutic and diagnostic role of exosomal microRNA in the autoimmune diseases[J]. J Neuroimmunol, 2021, 358, 577640.
doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2021.577640 |
| 12 | Wermuth PJ , Piera-Velazquez S , Jimenez SA . Exosomes isolated from serum of systemic sclerosis patients display alterations in their content of profibrotic and antifibrotic microRNA and induce a profibrotic phenotype in cultured normal dermal fibroblasts[J]. Clin Exp Rheumatol, 2017, 35 (Suppl 106): 21- 30. |
| 13 |
Cui H , Ge J , Xie N , et al. miR-34a inhibits lung fibrosis by inducing lung fibroblast senescence[J]. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol, 2017, 56 (2): 168- 178.
doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2016-0163OC |
| 14 |
Bulvik R , Biton M , Berkman N , et al. Forefront: MiR-34a-knockout mice with wild type hematopoietic cells, retain persistent fibrosis following lung injury[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21 (6): 2228.
doi: 10.3390/ijms21062228 |
| 15 |
Disayabutr S , Kim EK , Cha SI , et al. miR-34 miRNAs regulate cellular senescence in type Ⅱ alveolar epithelial cells of patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis[J]. PLoS One, 2016, 11 (6): e0158367.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0158367 |
| 16 |
Yang G , Yang L , Wang W , et al. Discovery and validation of extracellular/circulating microRNAs during idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis disease progression[J]. Gene, 2015, 562 (1): 138- 144.
doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2015.02.065 |
| 17 |
Blumer S , Fang L , Chen WC , et al. IPF-Fibroblast Erk1/2 acti-vity is independent from microRNA cluster 17-92 but can be inhibited by treprostinil through DUSP1[J]. Cells, 2021, 10 (11): 2836.
doi: 10.3390/cells10112836 |
| 18 |
Steen SO , Iversen LV , Carlsen AL , et al. The circulating cell-free microRNA profile in systemic sclerosis is distinct from both healthy controls and systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. J Rheumatol, 2015, 42 (2): 214- 221.
doi: 10.3899/jrheum.140502 |
| 19 |
黄赛赛, 王丹丹, 张卓亚, 等. 系统性硬化症患者血浆7种miRNA水平与脏器累及和临床指标的相关性[J]. 临床检验杂志, 2021, 39 (5): 358- 361.
doi: 10.13602/j.cnki.jcls.2021.05.09 |
| 20 |
Sing T , Jinnin M , Yamane K , et al. microRNA-92a expression in the sera and dermal fibroblasts increases in patients with scleroderma[J]. Rheumatology (Oxford), 2012, 51 (9): 1550- 1556.
doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kes120 |
| 21 |
Guiot J , Cambier M , Boeckx A , et al. Macrophage-derived exosomes attenuate fibrosis in airway epithelial cells through delivery of antifibrotic miR-142-3p[J]. Thorax, 2020, 75 (10): 870- 881.
doi: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2019-214077 |
| 22 |
Njock MS , Guiot J , Henket MA , et al. Sputum exosomes: Promising biomarkers for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis[J]. Thorax, 2019, 74 (3): 309- 312.
doi: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2018-211897 |
| [1] | 冯敏,陈哲,程永静. 以十二指肠溃疡为突出表现的IgG4相关性疾病1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 1125-1129. |
| [2] | 李敏,侯林卿,金月波,何菁. 系统性红斑狼疮合并视网膜病变的临床及免疫学特点[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1106-1111. |
| [3] | 刘蕊,赵金霞,闫良. 类风湿关节炎合并下肢静脉血栓患者的临床特点[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1079-1085. |
| [4] | 孟广艳,张筠肖,张渝昕,刘燕鹰. IgG4相关性疾病中枢神经系统受累的临床特点分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(6): 1043-1048. |
| [5] | 夏芳芳,鲁芙爱,吕慧敏,杨国安,刘媛. 系统性红斑狼疮伴间质性肺炎的临床特点及相关因素分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(2): 266-272. |
| [6] | 魏士雄,黎苏佳,刘毅. 幼年特发性关节炎成人后的临床特点及生物制剂治疗[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(6): 1014-1022. |
| [7] | 张意兰,王智峰,陈宁. 血清IgG4在不同疾病患者中的表达[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(6): 961-964. |
| [8] | 高兰,樊勇,张卓莉. 强直性脊柱炎合并恶性肿瘤31例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2015, 47(6): 962-965. |
|
||