北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (2): 340-346. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2025.02.019
两种玷污层去除方法对牙本质表面性能的影响
朱灵丽1, 唐琳1, 李博文2, 王梅1, 刘玉华1,*( )
)
- 1. 北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院修复科,国家口腔医学中心,国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心,口腔数字化医疗技术和材料国家工程实验室,口腔数字医学北京市重点实验室,北京 100081
2. 北京医院口腔科,国家老年医学中心,中国医学科学院老年医学研究院,北京 100730
Influence of two methods of smear layer removal on the surface properties of dentin
Lingli ZHU1, Lin TANG1, Bowen LI2, Mei WANG1, Yuhua LIU1,*( )
)
- 1. Department of Prosthodontics, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Center for Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Laboratory for Digital and Material Technology of Stomatology & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
2. Department of Stomatology, Beijing Hospital; National Center of Gerontology; Institute of Geriatric Medicine, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Beijing 100730, China
摘要:
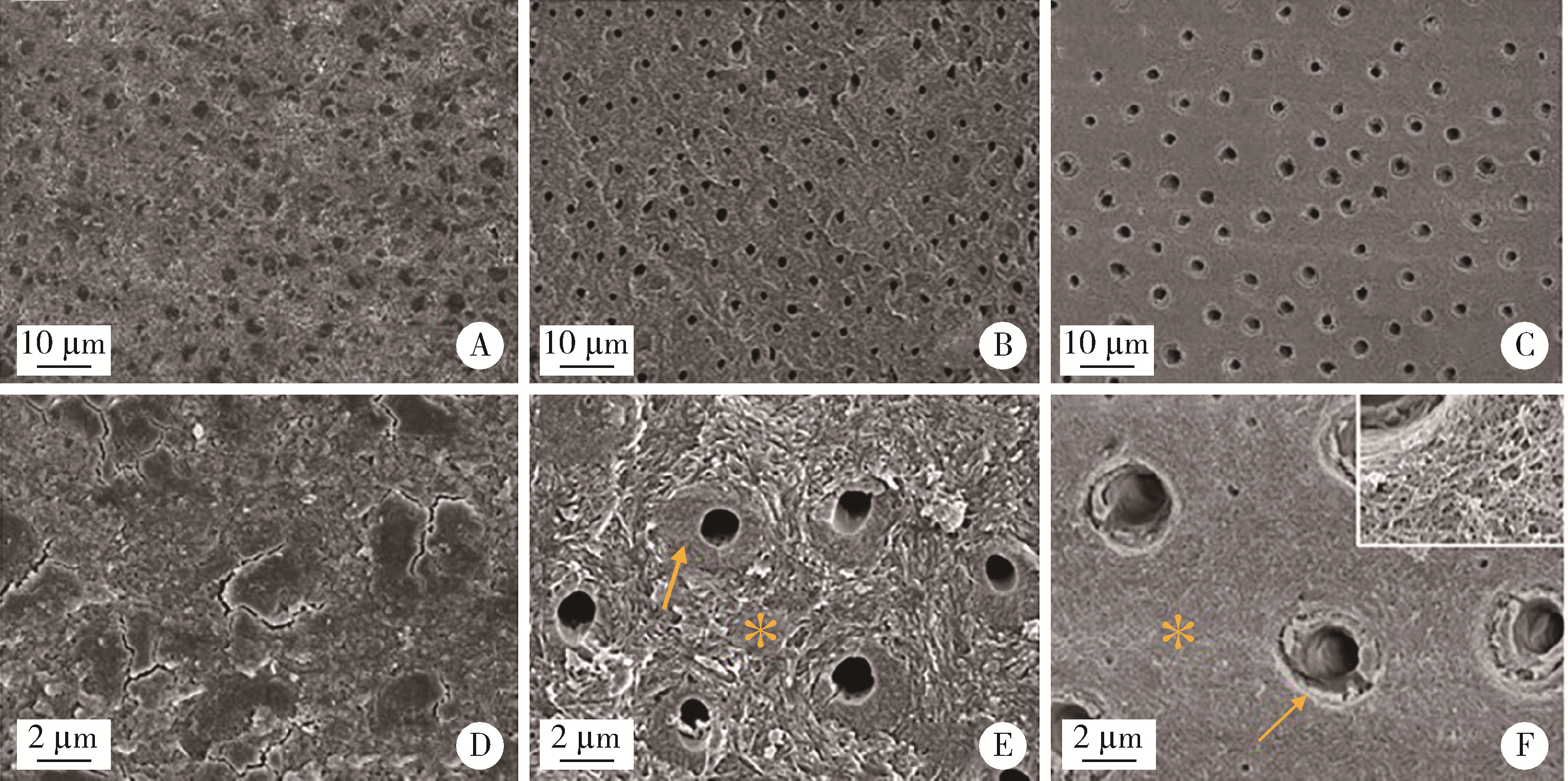
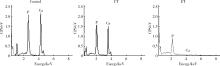
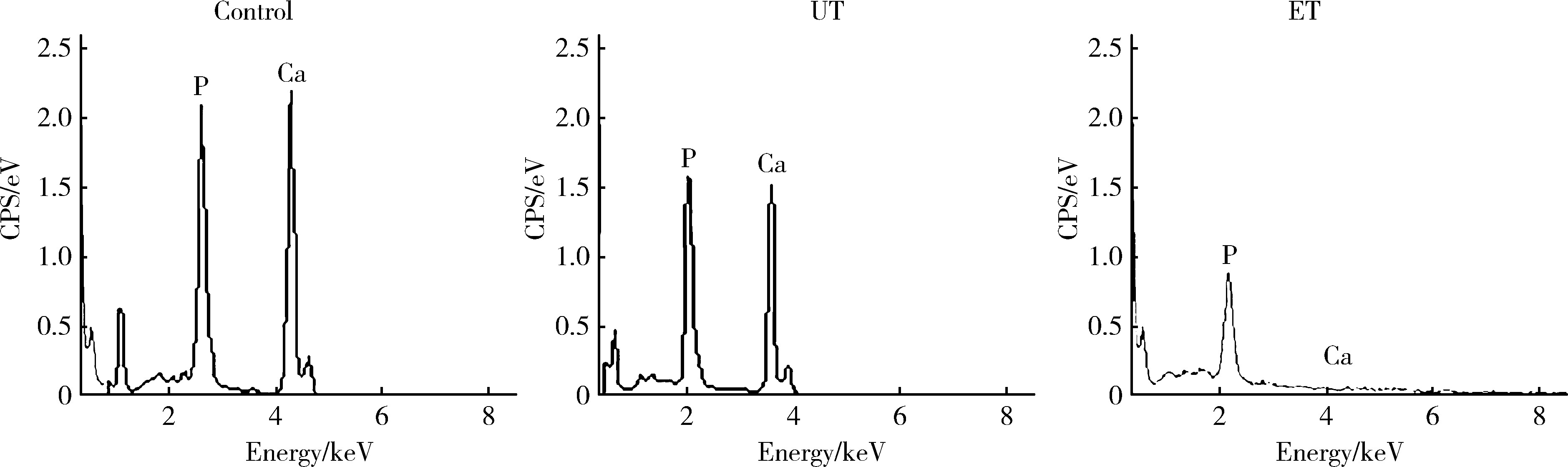
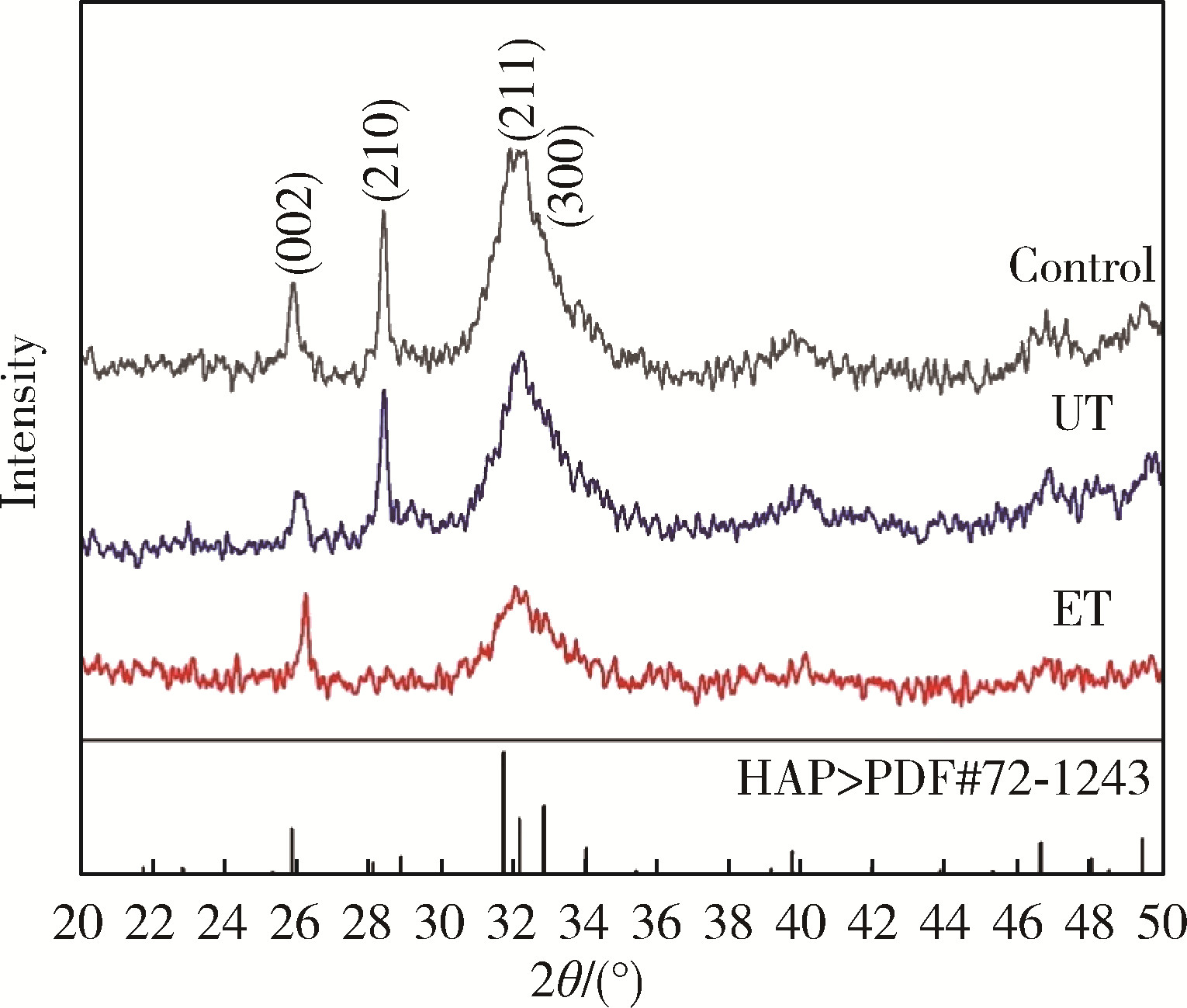
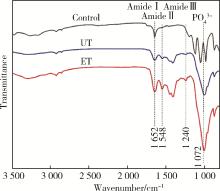
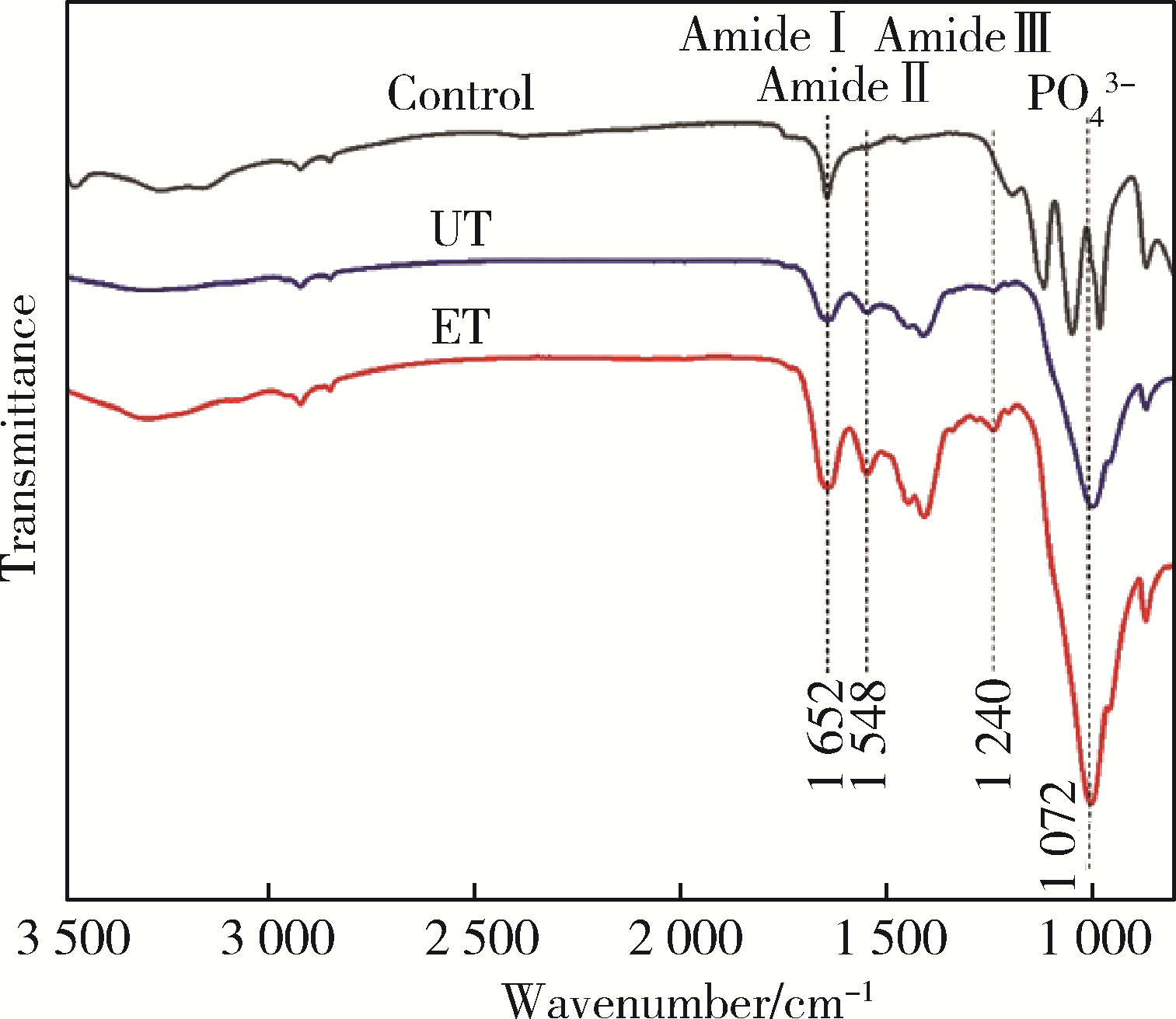
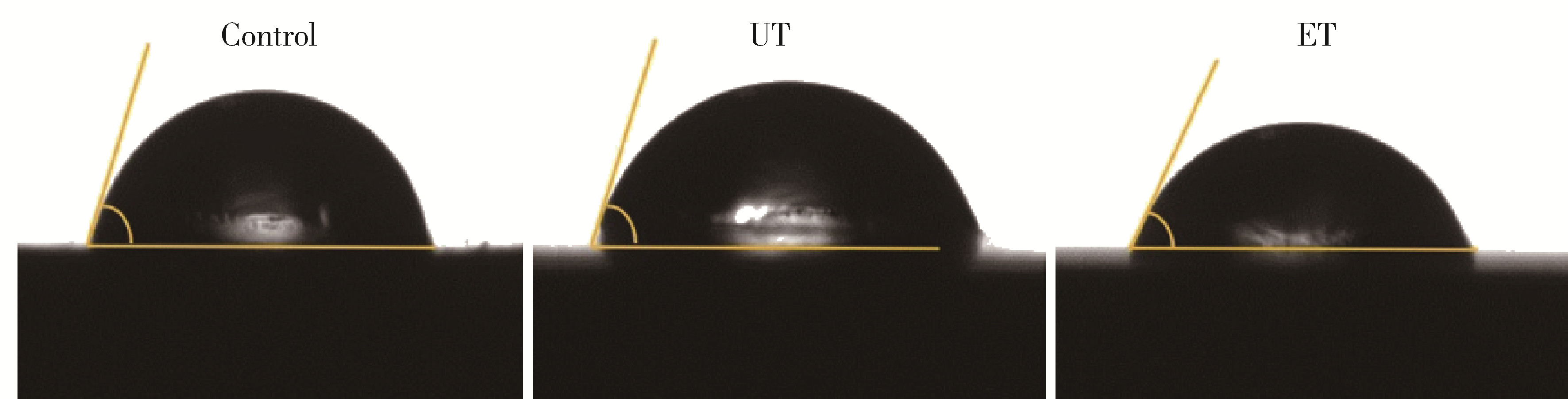
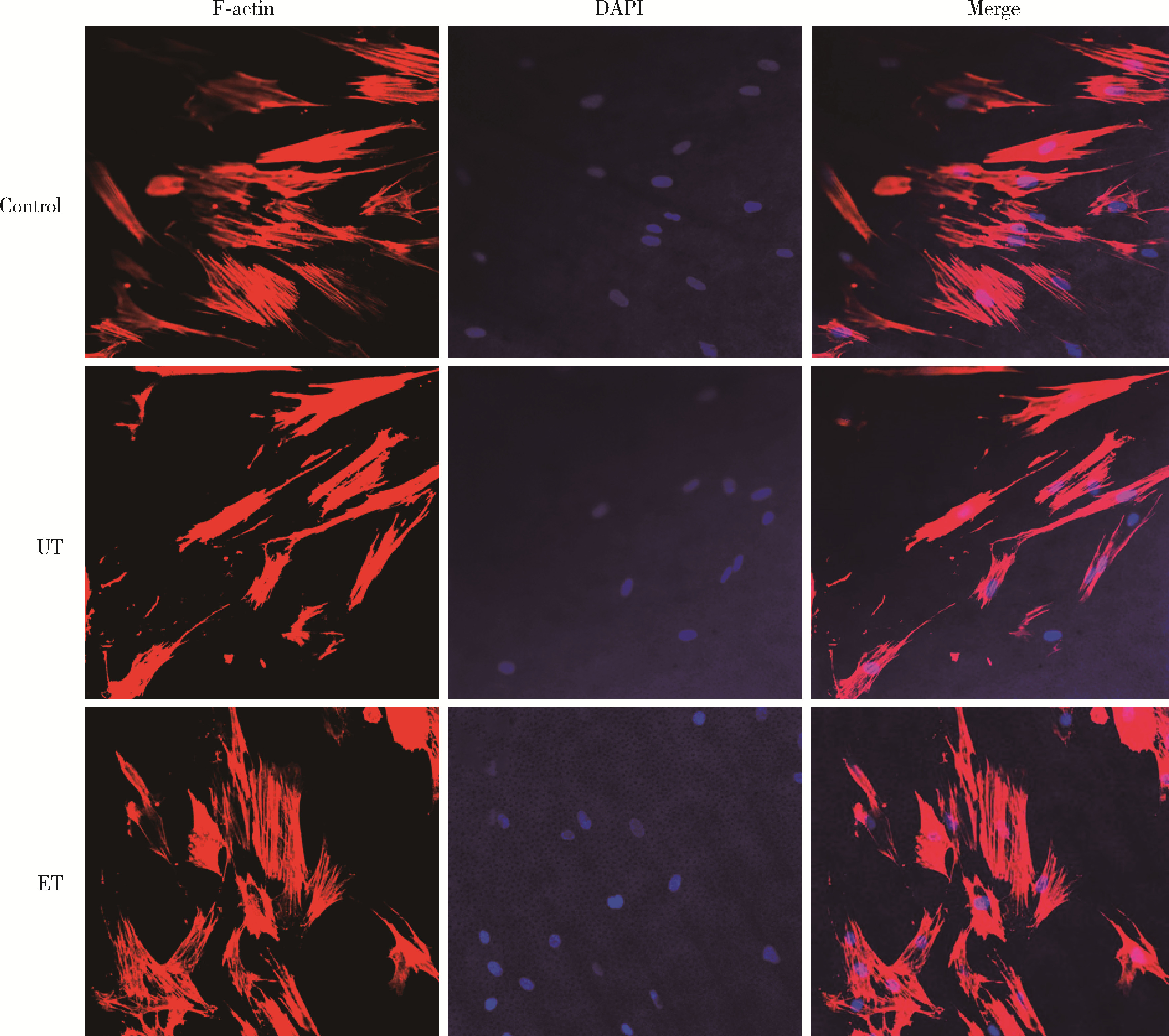
目的: 探究两种玷污层去除方法对牙本质表面性能的影响。方法: 选取60颗健康无龋第三磨牙,制备牙本质玷污层实验试件,随机分为3组:对照组、超声(ultrasonic treatment, UT)组、酸蚀(etched treatment,ET)组。采用扫描电镜观察各组的表面微观形貌,通过能量色散X射线光谱仪、X射线衍射仪、傅里叶变换红外光谱仪分别对表面元素、矿物相及官能团作分析,并进一步评价牙本质的机械性能、亲水性以及生物相容性。结果: 扫描电镜下UT组和ET组可见清晰的牙本质小管结构,对照组牙本质小管结构不清晰,可见大量牙本质碎屑;元素分析结果3组均可见钙磷峰,其中ET组的钙磷元素峰值最弱;矿物相分析表明3组均具有羟基磷灰石特征峰;官能团分析UT组和ET组可见胶原的酰胺Ⅰ、Ⅱ、Ⅲ带特征峰,而对照组酰胺带特征峰不明显;显微硬度显示ET组低于对照组以及UT组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);接触角实验证实ET组的亲水性优于对照组及UT组;荧光染色结果显示3组均具有良好的生物相容性。结论: UT和ET均可有效清除牙本质试件表面的玷污层,暴露出牙本质结构,且不影响其微观形貌和生物相容性,采用UT去除玷污层时对牙本质试件表面矿物质结构、亲水性和机械性能没有明显影响,ET虽能有效改善牙本质亲水性,但却会导致其表面钙磷含量下降,机械性能降低。
中图分类号:
- R783.3
| 1 |
Gu XH , Mao CY , Kern M . Effect of different irrigation on smear layer removal after post space preparation[J]. J Endodont, 2009, 35 (4): 583- 586.
doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2009.01.006 |
| 2 | 刘清, 杨玉琼, 聂蓉蓉, 等. 牙本质玷污层特性对自粘接树脂水门汀粘接强度的影响[J]. 华西口腔医学杂志, 2018, 36 (6): 619- 622. |
| 3 |
Tribst JPM , Dos-Santos AFC , da Cruz-Santos G , et al. Effect of cement layer thickness on the immediate and long-term bond strength and residual stress between lithium disilicate glass-ceramic and human dentin[J]. Materials (Basel), 2021, 14 (18): 5153.
doi: 10.3390/ma14185153 |
| 4 |
李秋菊, 宫玮玉, 董艳梅. 生物活性玻璃预处理对牙本质粘接界面耐久性的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52 (5): 931- 937.
doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2020.05.023 |
| 5 | 张健, 葛久禹. 微波对化学法根管预备中的玷污层的影响[J]. 口腔医学研究, 2008, 24 (2): 173- 176. |
| 6 | Ghasemi N , Torabi ZS . The effect of photodynamic therapy on the smear layer removal: A scanning electron microscopic study[J]. J Dent (Shiraz), 2021, 22 (3): 162- 168. |
| 7 |
Akter RS , Ahmed Z , Yamauti M , et al. Effects of remaining dentin thickness, smear layer and aging on the bond strengths of selfetch adhesives to dentin[J]. Dent Mater J, 2021, 40 (2): 538- 546.
doi: 10.4012/dmj.2019-436 |
| 8 | 李秋容, 韦小浪, 谢方方. 改性PAMAM促进脱矿牙本质再矿化的体外研究[J]. 牙体牙髓牙周病学杂志, 2014, 24 (3): 151- 154. |
| 9 |
Saikaew P , Matsumoto M , Sattabanasuk V , et al. Ultra-morphological characteristics of dentin surfaces after different preparations and treatments[J]. Eur J Oral Sci, 2020, 128 (3): 246- 254.
doi: 10.1111/eos.12698 |
| 10 |
Dai LL , Mei ML , Chu CH , et al. Remineralizing effect of a new strontium-doped bioactive glass and fluoride on demineralized enamel and dentine[J]. J Dent, 2021, 108, 103633.
doi: 10.1016/j.jdent.2021.103633 |
| 11 |
Feitosa VP , Ogliari FA , van Meerbeek B , et al. Can the hydrophilicity of functional monomers affect chemical interaction?[J]. J Dent Res, 2014, 93 (2): 201- 206.
doi: 10.1177/0022034513514587 |
| 12 |
Karade P , Sharma D , Hoshing UA , et al. Efficiency of different endodontic irrigation and activation systems, self-adjusting file instrumentation/irrigation system, and XP-Endo finisher in removal of the intracanal smear layer: An ex vivo scanning electron microscope study[J]. J Pharm Bioallied Sci, 2021, 13 (Suppl 1): 402- 407.
doi: 10.4103/jpbs.JPBS_775_20 |
| 13 |
Gungormus M , Tulumbaci F . Peptide-assisted pre-bonding remineralization of dentin to improve bonding[J]. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater, 2021, 113, 104119.
doi: 10.1016/j.jmbbm.2020.104119 |
| 14 |
Dai LL , Mei ML , Chu CH , et al. Effect of strontium-doped bioactive glass on preventing formation of demineralized lesion[J]. Materials (Basel), 2021, 14 (16): 4645.
doi: 10.3390/ma14164645 |
| 15 |
Jang JH , Lee MG , Ferracane JL , et al. Effect of bioactive glass-containing resin composite on dentin remineralization[J]. J Dent, 2018, 75, 58- 64.
doi: 10.1016/j.jdent.2018.05.017 |
| 16 |
Anastasiadis K , Verdelis K , Eliades G . The effect of universal adhesives on dentine collagen[J]. Dent Mater, 2021, 37 (8): 1316- 1324.
doi: 10.1016/j.dental.2021.05.004 |
| 17 |
Zhou Z , Ge X , Bian M , et al. Remineralization of dentin slices using casein phosphopeptide-amorphous calcium phosphate combined with sodium tripolyphosphate[J]. Biomed Eng Online, 2020, 19 (1): 18.
doi: 10.1186/s12938-020-0756-9 |
| 18 |
Sereda G , van Laecken A , Turner JA . Monitoring demineralization and remineralization of human dentin by characterization of its structure with resonance-enhanced AFM-IR chemical mapping, nanoindentation, and SEM[J]. Dent Mater, 2019, 35 (4): 617- 626.
doi: 10.1016/j.dental.2019.02.007 |
| 19 |
Ayad MF , Johnston WM , Rosenstiel SF . Influence of dental rotary instruments on the roughness and wettability of human dentin surfaces[J]. J Prosthet Dent, 2009, 102 (2): 81- 88.
doi: 10.1016/S0022-3913(09)60114-1 |
| 20 |
Jing X , Xie B , Li X , et al. Peptide decorated demineralized dentin matrix with enhanced bioactivity, osteogenic differentiation via carboxymethyl chitosan[J]. Dent Mater, 2021, 37 (1): 19- 29.
doi: 10.1016/j.dental.2020.09.019 |
| [1] | 原晋芳, 王新利, 崔蕴璞, 王雪梅. 尿促黄体生成素在女童中枢性性早熟预测中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 788-793. |
| [2] | 王明瑞,刘军,熊六林,于路平,胡浩,许克新,徐涛. 经皮微通道-微电子肾镜-微超声探针碎石术治疗1.5~2.5 cm肾结石的疗效和安全性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 605-609. |
| [3] | 杨捷,冯杰莉,张树栋,马潞林,郑清. 经食管超声心动图在肾切除术联合Mayo Ⅲ~Ⅳ级静脉瘤栓取栓术不同手术方式中的临床作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 631-635. |
| [4] | 陈延,李况蒙,洪锴,张树栋,程建星,郑仲杰,唐文豪,赵连明,张海涛,姜辉,林浩成. 阴茎海绵体注射试验对阴茎血管功能影响的回顾性研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 680-686. |
| [5] | 魏越,姚兰,陆希,王军,蔺莉,刘鲲鹏. 胃超声检查评估剖宫产产妇术前饮用碳水化合物后胃排空的效果[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 1082-1087. |
| [6] | 魏越,陆希,张静,刘鲲鹏,王永军,姚兰. 术前2 h口服碳水化合物对妇科腹腔镜特殊体位手术患者胃容量及反流误吸风险的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 893-898. |
| [7] | 傅强,高冠英,徐雁,林卓华,孙由静,崔立刚. 无症状髋关节前上盂唇撕裂超声与磁共振检查的对比研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 665-669. |
| [8] | 仲若情,朱梦倩,李应龙,潘洁. 低温等离子体对牙本质小管内粪肠球菌的抗菌效果[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(1): 38-43. |
| [9] | 郭若兰,黄桂彬,龙赟子,董艳梅. 新型生物活性玻璃促进人工牙本质龋再矿化的作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(1): 82-87. |
| [10] | 刘杨,程昉,王艳玲,艾香艳,朱振航,赵福涛. 唾液腺超声对干燥综合征的诊断价值[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1123-1127. |
| [11] | 王昱,张慧敏,邓雪蓉,刘伟伟,陈璐,赵宁,张晓慧,宋志博,耿研,季兰岚,王玉,张卓莉. 尿枸橼酸定量检测在原发性痛风患者肾结石诊断中的应用价值[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1134-1140. |
| [12] | 翟书珩,胡攀攀,刘晓光. 术中超声辅助下环形减压术治疗多节段胸椎后纵韧带骨化症[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(5): 1021-1027. |
| [13] | 邢海英,陈玉辉,许珂,黄点点,彭清,刘冉,孙葳,黄一宁. 三维超声血管斑块定量分析技术评估颈动脉粥样硬化斑块[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(5): 991-999. |
| [14] | 马欣蓉,朱晓鸣,李静,李德利,李和平,谭建国. 新型大气压冷等离子体射流处理对牙本质胶原纤维交联化的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(1): 83-88. |
| [15] | 邓雪蓉,孙晓莹,张卓莉. 类风湿关节炎患者足踝部体征和超声下病变的一致性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(6): 1037-1042. |
|
||