北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (2): 347-353. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2025.02.020
种植单冠修复后种植体周健康的相关分析
- 1. 北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院牙周科,北京 100081
2. 北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院第二门诊部,国家口腔医学中心,国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心,口腔生物材料和数字诊疗装备国家工程研究中心,口腔数字医学北京市重点实验室,国家卫生健康委员会口腔医学计算机应用工程技术研究中心,国家药品监督管理局口腔生物材料重点实验室,北京 100081
Correlation analysis of peri-implant health after single-tooth dental implant
- 1. Department of Periodontology, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
2. Second Clinical Division, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Center of Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Research Center of Oral Biomaterials and Digital Medical Devices & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology & NHC Research Center of Engineering and Technology for Computerized Dentistry & NMPA Key Laboratory for Dental Materials, Beijing 100081, China
摘要:
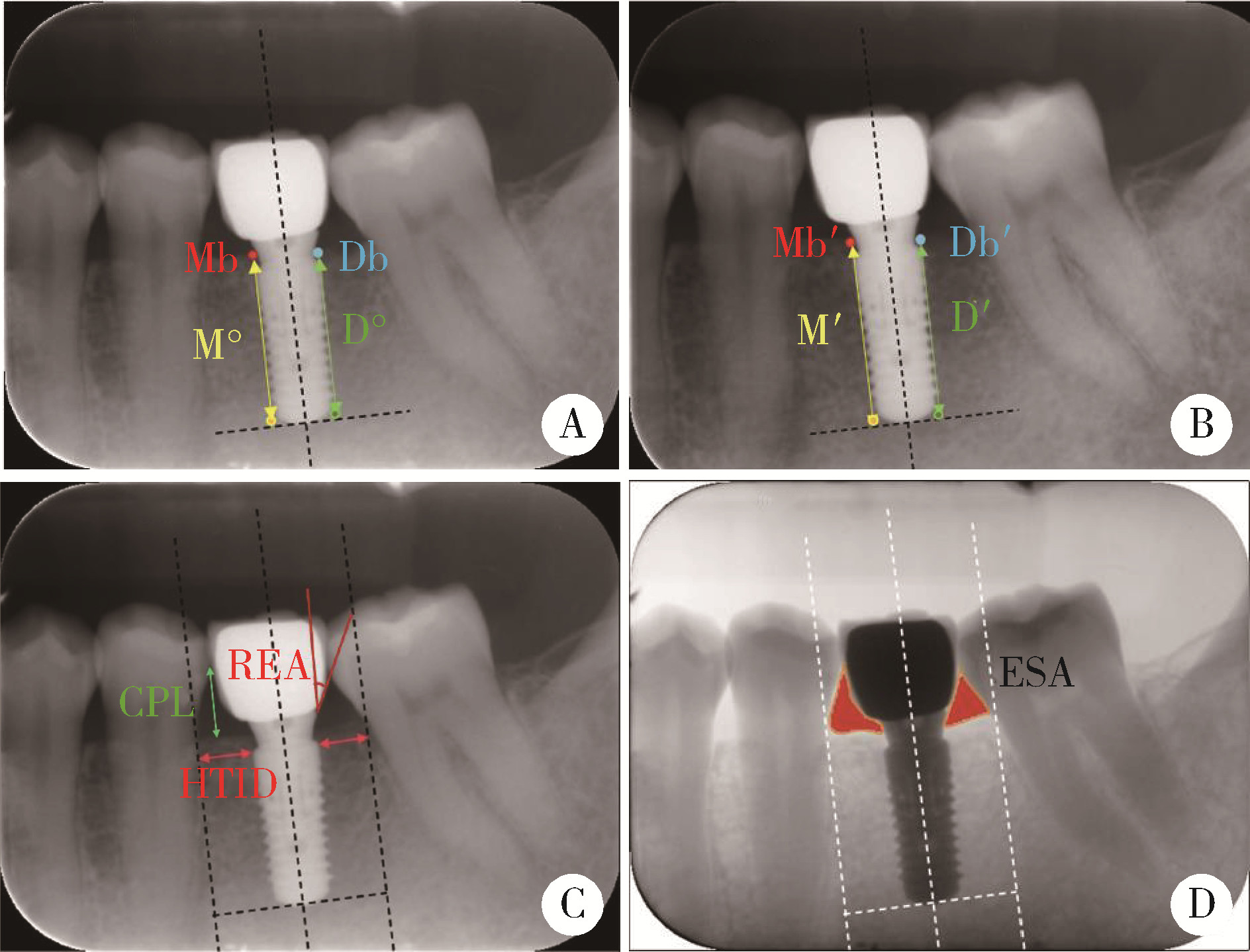
目的: 追踪观察第一磨牙种植单冠修复后种植体的健康情况,评估影响种植体周健康的相关因素。方法: 选择2008年1月至2020年12月就诊于北京大学口腔医院第二门诊部,行第一磨牙种植单冠修复的82位患者作为研究对象,共278个负重1年以上的种植体,记录种植体周的探诊深度(peri-implant probing depth, PPD)、改良出血指数(modified sulcus bleeding index, mSBI)、改良菌斑指数(modified plaque index, mPLI)、龈乳头指数(papilla index, PI),进行临床资料回顾及X线片的测量分析,X线片分析内容包括修复体穿龈角度(restoration emergence angle, REA)、种植牙临床冠根比(clinical crown-implant ratio, cC/I)、种植牙与邻牙牙根之间的水平距离(horizontal tooth-implant distance, HTID)、邻间隙高度(contact point level, CPL)、邻间隙面积(embrasure surface area, ESA)等。结果: 患者平均手术年龄为(40.2±9.5)岁(19~84岁),男性33例,女性49例,随访时间为(4.9±3.3)年(1~10年)。根据2018年的诊断标准,种植体周炎患病率在种植体水平为14.03%,患者水平为21.95%;种植体周健康率在种植体水平为19.06%,患者水平为18.29%;种植体周黏膜炎患病率在种植体水平为66.91%,患者水平为59.75%。种植体周健康组与种植体周炎组在负重1年时(基线)PPD、远中HTID、近中/远中CPL、cC/I,两组间差异具有统计学意义(P < 0.05),而mSBI、mPLI、PI、近中HTID、近中/远中REA、近中/远中ESA组间差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。在随访与基线之间的差值中,PPD、近中/远中HTID、近中/远中CPL、近中/远中ESA在两组间差异具有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。广义估计方程分析显示,PPD、近中/远中HTID、近中CPL以及近中ESA随访与基线的差值,与发生种植体周炎风险存在显著正相关。结论: 基于本研究结果,种植体周健康率仍不理想,种植体周探诊深度以及种植体与邻牙的关系(如HTID、CPL、ESA)与种植体周健康相关。
中图分类号:
- R783.6
| 1 | Raghoebar GM , Meijer HJ , Slot W , et al. A systematic review of implant-supported overdentures in the edentulous maxilla, compared to the mandible: How many implants?[J]. Eur J Oral Implantol, 2014, 7 (Suppl 2): S191- S201. |
| 2 | Sailer I , Mühlemann S , Zwahlen M , et al. Cemented and screw-retained implant reconstructions: A systematic review of the survival and complication rates[J]. Clin Oral Implants Res, 2012, 23 (Suppl 6): 163- 201. |
| 3 | Meyle J , Casado P , Fourmousis , et al. General genetic and acquired risk factors, and prevalence of peri-implant diseases: Consensus report of working group 1[J]. Int Dent J, 2019, 69 (Suppl 2): 3- 6. |
| 4 |
Vignoletti F , Di Domenico GL , Di Martino M , et al. Prevalence and risk indicators of peri-implantitis in a sample of university-based dental patients in Italy: A cross-sectional study[J]. J Clin Periodontol, 2019, 46 (5): 597- 605.
doi: 10.1111/jcpe.13111 |
| 5 | 余道信, 程梦, 金辉喜. 种植体周围病的发生率及其危险因素[J]. 武汉大学学报(医学版), 2019, 40 (5): 845- 849. |
| 6 | 张停停, 胡晓菁, 林璐. 种植体植入15年内种植体周围炎和种植周黏膜炎发生率调查[J]. 上海口腔医学, 2021, 30 (3): 292- 296. |
| 7 |
Schwendicke F , Tu YK , Stolpe M . Preventing and treating peri-implantitis: A cost-effectiveness analysis[J]. J Periodontol, 2015, 86 (9): 1020- 1029.
doi: 10.1902/jop.2015.150071 |
| 8 | Schwarz F , Alcoforado G , Guerrero A , et al. Peri-implantitis: Summary and consensus statements of group 3. The 6th EAO consensus conference 2021[J]. Clin Oral Implants Res, 2021, 32 (Suppl 21): 245- 253. |
| 9 |
Mombelli A , van Oosten MAC , Schürch Jr. E , et al. The microbiota associated with successful or failing osseointegrated titanium implants[J]. Oral Microbiol Immunol, 1987, 2 (4): 145- 151.
doi: 10.1111/j.1399-302X.1987.tb00298.x |
| 10 | Jemt T . Restoring the gingival contour by means of provisional resin crowns after single-implant treatment[J]. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent, 1999, 19 (1): 20- 29. |
| 11 |
Wada M , Mameno T , Onodera Y , et al. Prevalence of peri-implant disease and risk indicators in a Japanese population with at least 3 years in function: A multicentre retrospective study[J]. Clin Oral Implants Res, 2019, 30 (2): 111- 120.
doi: 10.1111/clr.13397 |
| 12 | Yotnuengnit B , Yotnuengnit P , Laohapand P , et al. Emergence angles in natural anterior teeth: Influence on periodontal status[J]. Quintessence Int, 2008, 39 (3): e126- e133. |
| 13 | Blanes RJ . To what extent does the crown-implant ratio affect the survival and complications of implant-supported reconstructions? A systematic review[J]. Clin Oral Implants Res, 2010, 20 (Suppl 4): 67- 72. |
| 14 |
Chanthasan S , Mattheos N , Pisarnturakit PP , et al. Influence of interproximal peri-implant tissue and prosthesis contours on food impaction, tissue health and patients' quality of life[J]. Clin Oral Implants Res, 2022, 33 (7): 768- 781.
doi: 10.1111/clr.13958 |
| 15 |
Jeong JS , Chang M . Food impaction and periodontal/peri-implant tissue conditions in relation to the embrasure dimensions between implant-supported fixed dental prostheses and adjacent teeth: A cross-sectional study[J]. J Periodontol, 2015, 86 (12): 1314- 1320.
doi: 10.1902/jop.2015.150322 |
| 16 | Berglundh T , Armitage G , Araujo MG , et al. Peri-implant diseases and conditions: Consensus report of workgroup 4 of the 2017 world workshop on the classification of periodontal and peri-implant diseases and conditions[J]. J Periodontol, 2018, 89 (Suppl 1): S313- S318. |
| 17 | Sanz M , Chapple IL . Working group 4 of the Ⅷ European workshop on periodontology. Clinical research on peri-implant diseases: Consensus report of working group 4[J]. J Clin Periodontol, 2012, 39 (Suppl 12): 202- 206. |
| 18 | Renvert S , Persson GR , Pirih FQ , et al. Peri-implant health, peri-implant mucositis, and peri-implantitis: Case definitions and diagnostic considerations[J]. J Periodontol, 2018, 89 (Suppl 1): S304- S312. |
| 19 |
Katafuchi M , Weinstein BF , Leroux BG , et al. Restoration contour is a risk indicator for peri-implantitis: A cross-sectional radiographic analysis[J]. J Clin Periodontol, 2018, 45 (2): 225- 232.
doi: 10.1111/jcpe.12829 |
| 20 |
Yi Y , Koo KT , Schwarz F , et al. Association of prosthetic features and peri-implantitis: A cross-sectional study[J]. J Clin Periodontol, 2020, 47 (3): 392- 403.
doi: 10.1111/jcpe.13251 |
| 21 | Wong AT , Wat PY , Pow EH , et al. Proximal contact loss between implant-supported prostheses and adjacent natural teeth: A retrospective study[J]. Clin Oral Implants Res, 2015, 26 (4): e68- 71. |
| 22 |
Wat PY , Wong AT , Leung KC . Proximal contact loss between implant-supported prostheses and adjacent natural teeth: A Clinical Report[J]. J Prosthet Dent, 2011, 105 (1): 1- 4.
doi: 10.1016/S0022-3913(10)00174-5 |
| 23 |
Saber A , Chakar C , Mokbel N , et al. Prevalence of interproximal contact loss between implant-supported fixed prostheses and adjacent teeth and its impact on marginal bone loss: A retrospective study[J]. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants, 2020, 35 (3): 625- 630.
doi: 10.11607/jomi.7926 |
| 24 |
Byun SJ , Heo SM , Ahn SG , et al. Analysis of proximal contact loss between implant-supported fixed dental prostheses and adjacent teeth in relation to influential factors and effects. A cross-sectional study[J]. Clin Oral Implants Res, 2015, 26 (6): 709- 714.
doi: 10.1111/clr.12373 |
| 25 | 罗强, 丁茜, 张磊, 等. 后牙种植冠桥修复邻接触丧失的临床回顾研究[J]. 中华口腔医学杂志, 2016, 51 (1): 15- 19. |
| 26 |
Pang NS , Suh CS , Kim KD , et al. Prevalence of proximal contact loss between implant-supported fixed prostheses and adjacent natural teeth and its associated factors: A 7-year prospective study[J]. Clin Oral Implants Res, 2017, 28 (12): 1501- 1508.
doi: 10.1111/clr.13018 |
| 27 | Wei H , Tomotake Y , Nagao K , et al. Implant prostheses and adjacent tooth migration: Preliminary retrospective survey using 3-dimensional occlusal analysis[J]. Int J Prosthodont, 2008, 21 (4): 302- 304. |
| 28 | Varthis S , Randi A , Tarnow DP . Prevalence of interproximal open contacts between single-implant restorations and adjacent teeth[J]. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants, 2016, 31 (5): 1089- 1092. |
| 29 | Koori H , Morimoto K , Tsukiyama Y , et al. Statistical analysis of the diachronic loss of interproximal contact between fixed implant prostheses and adjacent teeth[J]. Int J Prosthodont, 2010, 23 (6): 535- 540. |
| 30 | Ramanauskaite A , Roccuzzo A , Schwarz F . A systematic review on the influence of the horizontal distance between two adjacent implants inserted in the anterior maxilla on the inter-implant mucosa fill[J]. Clin Oral Implants Res, 2018, 29 (Suppl 15): 62- 70. |
| 31 | Jung RE , Heitz-Mayfield L , Schwarz F . Evidence-based knowledge on the aesthetics and maintenance of peri-implant soft tissues: Osteology foundation consensus report part 3: Aesthetics of peri-implant soft tissues[J]. Clin Oral Implants Res, 2018, 29 (Suppl 15): 14- 17. |
| 32 | Wu YJ , Tu YK , Huang SM , et al. The influence of the distance from the contact point to the crest of bone on the presence of the interproximal dental papilla[J]. Chang Gung Med J, 2003, 26 (11): 822- 828. |
| 33 |
Tarnow D , Elian N , Fletcher P , et al. Vertical distance from the crest of bone to the height of the interproximal papilla between adjacent implants[J]. J Periodontol, 2003, 74 (12): 1785- 1788.
doi: 10.1902/jop.2003.74.12.1785 |
| 34 |
Peng ZZ , Chen XM , Wang J , et al. Effect of proximal contact strength on the three-dimensional displacements of implant-supported cantilever fixed partial dentures under axial loading[J]. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B, 2013, 14 (6): 526- 532.
doi: 10.1631/jzus.B1200264 |
| 35 | Cosyn J , Sabzevar MM , Bruyn HD . Predictors of inter-proximal and midfacial recession following single implant treatment in the anterior maxilla: A multivariate analysis[J]. J Clin Periodontol, 2012, 39 (9): 895- 903. |
| [1] | 曾媛媛,谢云,陈道南,王瑞兰. 脓毒症患者发生正常甲状腺性病态综合征的相关因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 526-532. |
| [2] | 傅强,高冠英,徐雁,林卓华,孙由静,崔立刚. 无症状髋关节前上盂唇撕裂超声与磁共振检查的对比研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 665-669. |
| [3] | 林咏惟,周雅琳,赵润茏,许雅君,刘燕萍. 孕早期女性铁营养状况及其影响因素分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 600-605. |
| [4] | 孙菲,刘建,李思琪,危伊萍,胡文杰,王翠. 种植体黏膜下微生物在健康种植体和种植体周炎中的构成与差异:一项横断面研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(1): 30-37. |
| [5] | 孟令玮,李雪,高胜寒,李悦,曹瑞涛,张毅,潘韶霞. 三种方法建立大鼠种植体周炎模型的比较[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(1): 22-29. |
| [6] | 孙菲,李思琪,危伊萍,钟金晟,王翠,胡文杰. 种植体周病非手术治疗中联合应用甘氨酸粉喷砂的临床效果评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(1): 119-125. |
| [7] | 吴俊慧,陈泓伯,武轶群,吴瑶,王紫荆,吴涛,王梦莹,王斯悦,王小文,王伽婷,于欢,胡永华. 2015—2017年北京市2型糖尿病患者骨关节炎患病的相关因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(3): 518-522. |
| [8] | 耿研,宋志博,张晓慧,邓雪蓉,王昱,张卓莉. 银屑病关节炎抑郁和焦虑患病情况及相关因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(6): 1048-1055. |
| [9] | 邓思危,陈则亦,刘志科,王健,卓琳,高双庆,余家阔,詹思延. 基于城镇医保数据库骨关节伤病的流行病学研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(3): 527-534. |
| [10] | 许璐,陈璐,樊东升,冯菁楠,刘立立,詹思延,王胜锋. 基于15省城镇医疗保险数据测算我国成人进行性肌萎缩患病率[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(3): 521-526. |
| [11] | 石慧峰, 张敬旭, 张嵘, 王晓莉. 中国0~6岁儿童孤独症谱系障碍患病率的meta分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(5): 798-806. |
| [12] | 郁静茹, 金蕾, 肖利华, 靳蕾. 北京通州区神经管缺陷患病率及其与监测时限的关系[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2015, 47(6): 1042-1045. |
| [13] | 李恒, 黄悦勤, 马亚婷, 刘肇瑞. 中国归因于非痴呆器质性精神障碍残疾的描述性流行病学研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2014, 46(2): 247-253. |
| [14] | 李春, 王秀茹*, 唐熠达, 安媛, 周云杉, 郭时伟, 张晓盈, 段天骄, 朱佳鑫, 李晓峰, 王莉枝, 王彩虹, 王永福, 杨荣, 王国春, 卢昕, 朱平. 全国多中心类风湿关节炎冠心病危险因素的现况调查[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2012, 44(2): 176-181. |
| [15] | 王巍, 曾祥龙, 刘武. 中国夏代人的牙周疾病状况分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2007, 39(5): 511-514. |
|
||