北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (5): 903-910. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2025.05.014
丝氨酸蛋白酶23在系统性硬化病皮肤纤维化中的作用和机制
- 北京大学第三医院风湿免疫科,北京 100191
Pathogenesis and mechanism of serine protease 23 in skin fibrosis of systemic sclerosis
Xiandun YUAN, Zhaohua LI, Dan XU, Ting LI, Dan FANG, Rong MU*( )
)
- Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
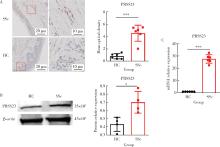
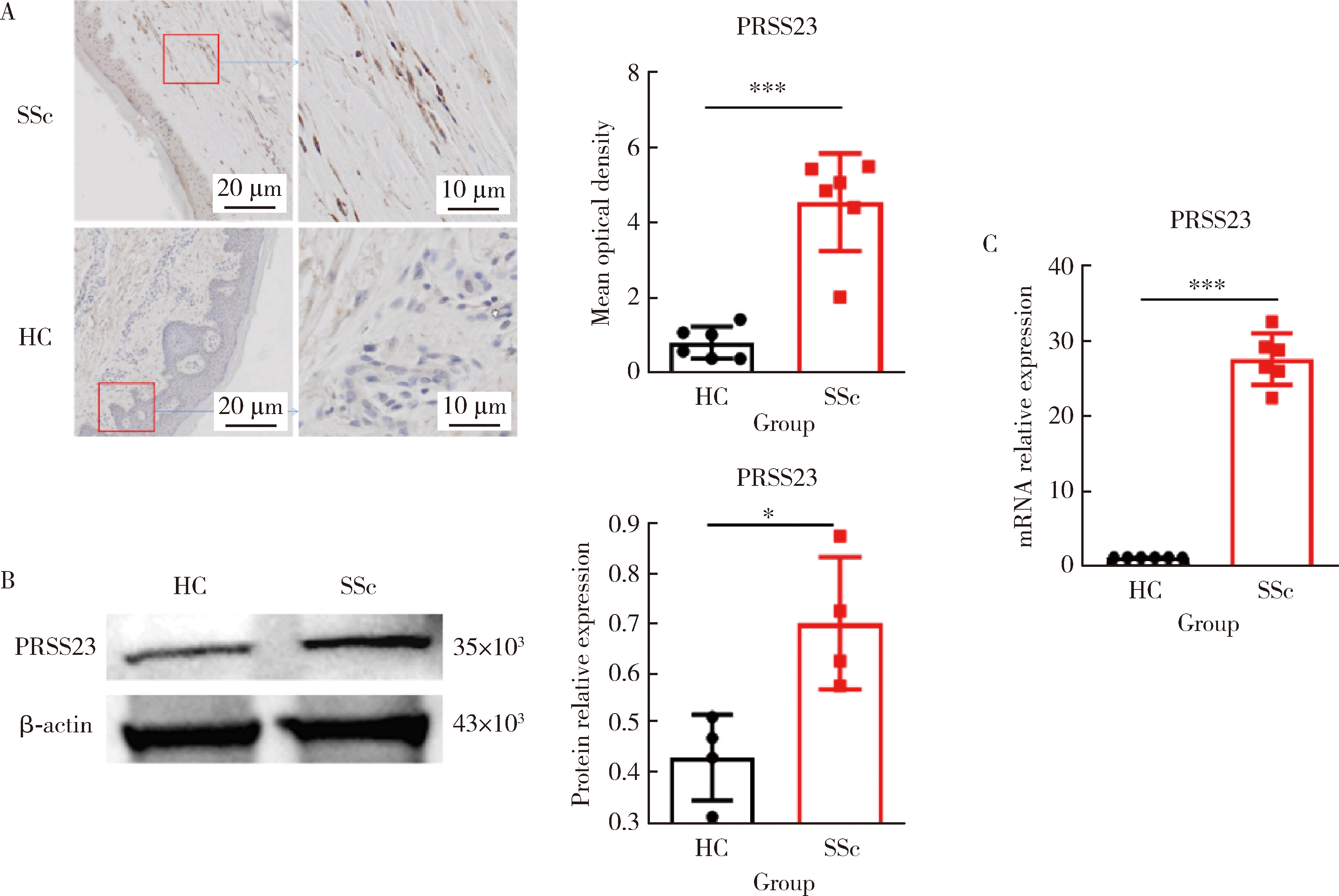
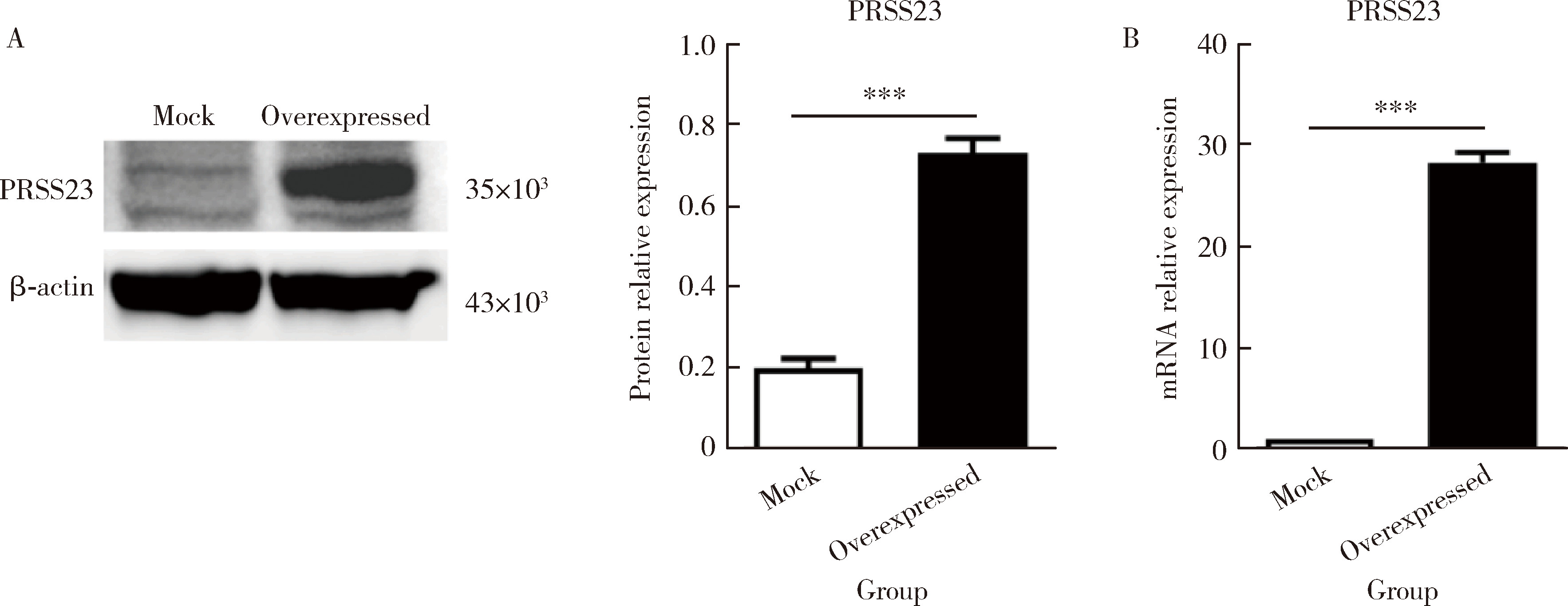
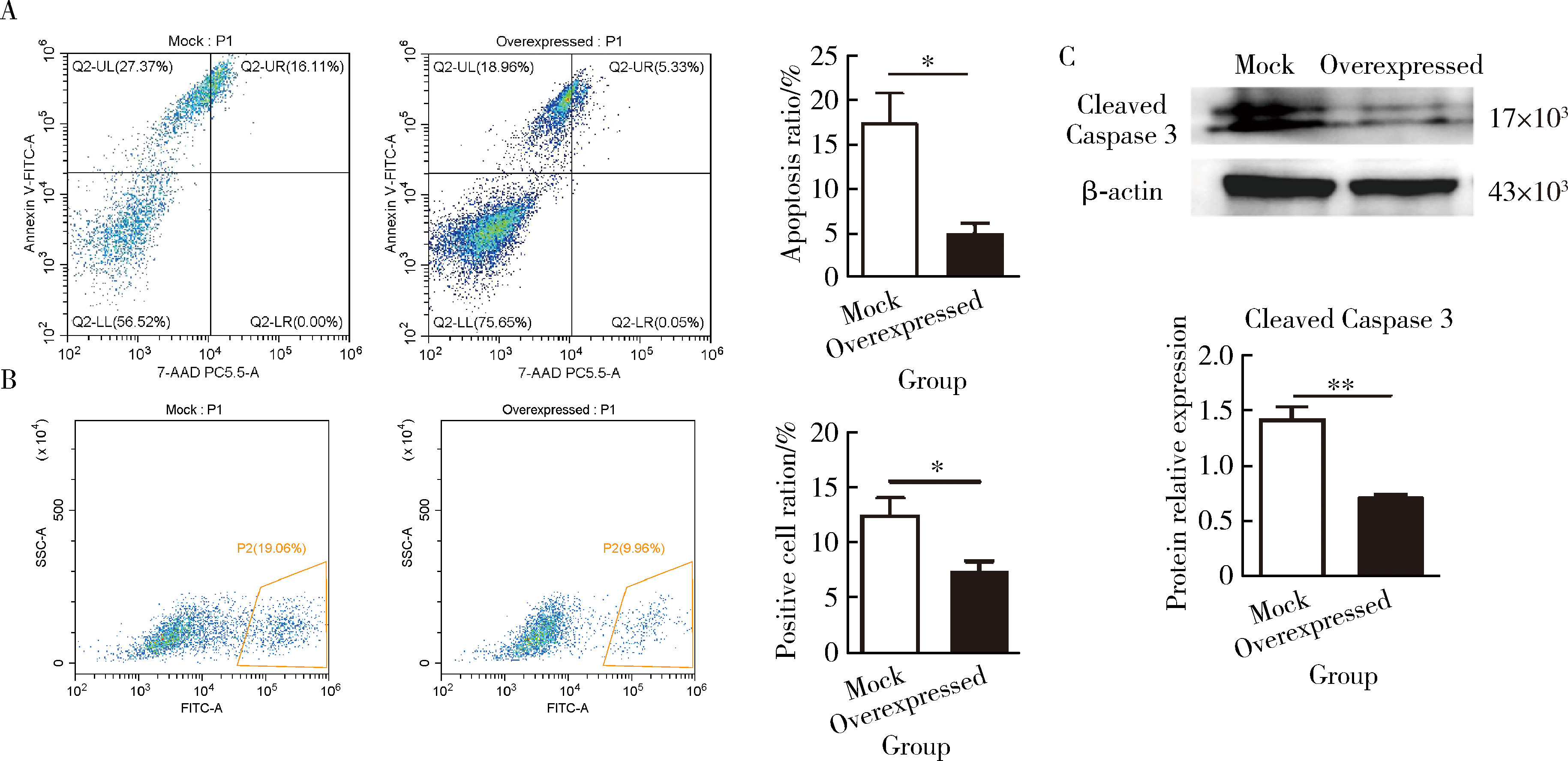
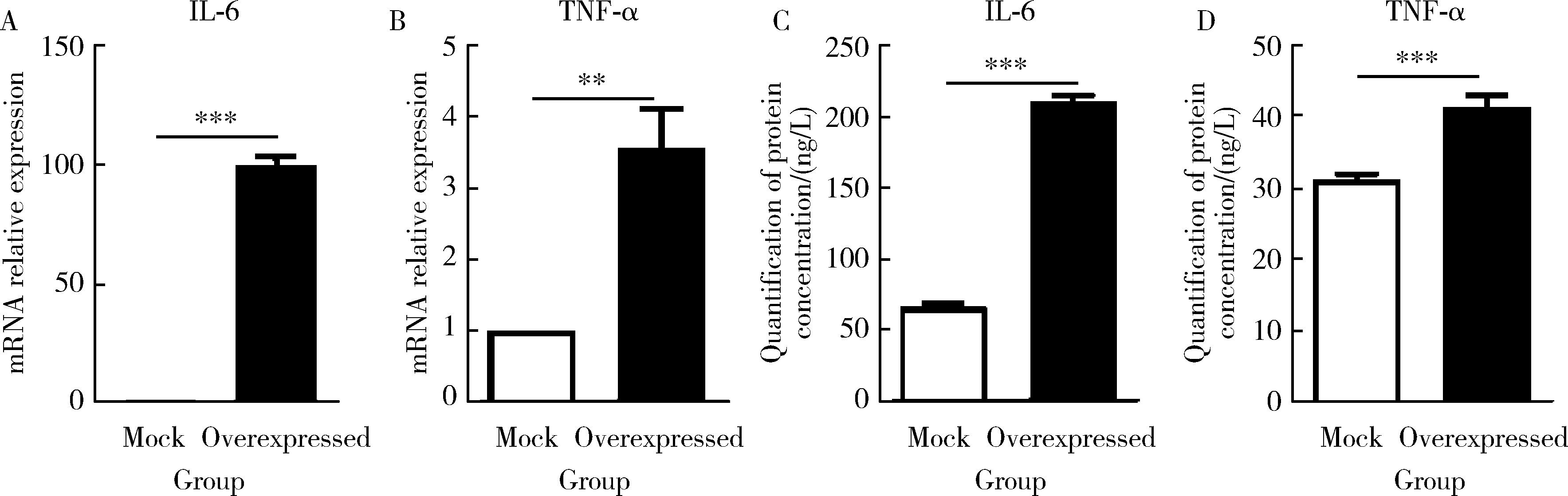
摘要: 目的: 系统性硬化病(systemic sclerosis, SSc)患者的皮肤成纤维细胞中丝氨酸蛋白酶23(serine protease 23,PRSS23)mRNA水平升高,本研究旨在探索PRSS23表达上调对SSc患者皮肤纤维化的作用及机制。方法: 采用免疫组织化学方法检测SSc患者和健康对照者皮肤组织石蜡切片中PRSS23蛋白的表达水平。分离新鲜皮肤组织的成纤维细胞,采用实时荧光定量PCR(real-time quantitative PCR,RT-qPCR)和蛋白免疫印迹法检测PRSS23在皮肤成纤维细胞中的mRNA和蛋白表达。采用慢病毒感染的方式构建过表达PRSS23的皮肤成纤维细胞BJ细胞系,以400 μmol/L过氧化氢刺激12 h后,采用膜联蛋白V/7-AAD染色检测凋亡成纤维细胞的比例,采用流式细胞仪和蛋白免疫印迹法检测凋亡相关蛋白激活型半胱氨酸-天冬氨酸蛋白酶-3(Caspase-3)的表达。采用RT-qPCR和酶联免疫吸附试验(enzyme linked immunosorbent assay, ELISA)法检测成纤维细胞分泌的白细胞介素-6(interleukin 6,IL-6)和肿瘤坏死因子-α(tumor necrosis factor alpha,TNF-α)水平。结果: 与健康对照组比较,SSc患者皮肤组织中的PRSS23蛋白表达显著升高[4.952 (3.806~5.439) vs. 0.806 (0.395~1.173),P<0.001]。PRSS23主要表达在成纤维细胞中,SSc患者分离的皮肤成纤维细胞中PRSS23的mRNA[27.59 (25.02~30.00) vs. 1.00,P<0.001]和蛋白表达水平[0.675 (0.587~0.837) vs. 0.451 (0.342~0.502),P=0.029]均显著上调。相较于对照组,过表达PRSS23的皮肤成纤维细胞抗凋亡能力增强,过氧化氢诱导后凋亡细胞的比例显著减少[(5.043±1.097)% vs. (17.480±3.212)%,P=0.022],凋亡相关蛋白激活型Caspase-3表达水平也显著降低[(0.718±0.022) vs. (1.422±0.105),P=0.003],而炎症因子IL-6的mRNA水平[(99.780±1.796) vs. (1.000±0.004),P<0.001]和蛋白分泌水平[(211.600±2.431) ng/L vs. (65.930±1.768) ng/L,P<0.001]显著上调,同时,TNF-α的mRNA水平[(3.555±0.555) vs. (1.000±0.004),P<0.001]和蛋白分泌水平[(41.190±0.949) ng/L vs. (31.150±0.360) ng/L,P<0.001]显著上调。结论: PRSS23在SSc患者皮肤成纤维细胞中的表达增加,可能通过抑制细胞凋亡,并促进炎症因子IL-6和TNF-α的分泌,调控皮肤成纤维细胞向促炎型转化,参与皮肤纤维化的发展。
中图分类号:
- R593.2
| 1 |
doi: 10.1136/ard.2009.127621 |
| 2 |
doi: 10.1038/s41584-019-0324-5 |
| 3 |
doi: 10.1186/s12931-018-0801-4 |
| 4 |
|
| 5 |
doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-24607-6 |
| 6 |
doi: 10.3390/ijms20030619 |
| 7 |
|
| 8 |
|
| 9 |
doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2019.02.008 |
| 10 |
|
| 11 |
doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-24110-y |
| 12 |
doi: 10.1038/s41401-023-01165-9 |
| 13 |
doi: 10.1186/ar4112 |
| 14 |
doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0560.2006.00584.x |
| 15 |
doi: 10.3390/biomedicines8050101 |
| 16 |
doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2012.09.014 |
| 17 |
doi: 10.7150/ijbs.75876 |
| 18 |
doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2011-200955 |
| 19 |
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)00232-4 |
| 20 |
doi: 10.1007/s10753-008-9067-1 |
| 21 |
|
| 22 |
|
| 23 |
doi: 10.7150/thno.60540 |
| 24 |
doi: 10.1038/s42003-020-0922-4 |
| 25 |
doi: 10.1242/dmm.044164 |
| 26 |
doi: 10.1186/s41232-017-0048-3 |
| [1] | 赵柯林, 夏雪, 史乃旭, 周韩, 盖婧雯, 李萍. 铁死亡标志物4-HNE在系统性硬化症细胞模型中的表达及意义[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(6): 950-955. |
| [2] | 何珊,陈炘,程琦,朱灵江,张培玉,童淑婷,薛静,杜燕. 托法替布通过JAK/STAT3通路抑制肺成纤维细胞向肌成纤维细胞转化[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 505-511. |
| [3] | 刘耘充,吴宗龙,葛力源,杜坦,吴雅倩,宋一萌,刘承,马潞林. 肾透明细胞癌中核蛋白1对阿昔替尼耐药的作用及机制[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 781-792. |
| [4] | 蔡天玉,朱振鹏,徐纯如,吉星,吕同德,郭振可,林健. 成纤维细胞生长因子受体2在肾透明细胞癌中的表达及意义[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(4): 628-635. |
| [5] | 郜洪宇,孟焕新,侯建霞,黄宝鑫,李玮. 钙结合蛋白在健康牙周组织和实验性牙周炎组织的表达分布[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(4): 744-749. |
| [6] | 耿良,吕静,范敬. 肺瘤平膏联合环磷酰胺化疗对肺癌的抑瘤作用和酸性微环境的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(2): 247-253. |
| [7] | 石冰清,袁晓静,赵玉鸣. 比较矿物三氧化物凝聚体及山东蜂胶乙醇提取物对牙髓成纤维细胞生物学性能的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(6): 1108-1114. |
| [8] | 郑苗,詹凌璐,刘志强,李和平,谭建国. 不同等离子体处理氧化锆对人牙龈成纤维细胞黏附能力的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(2): 315-320. |
| [9] | 王昊,陈亮,叶小云. 雷公藤甲素对TM4细胞氧化应激及PI3K/AKT通路的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(4): 607-612. |
| [10] | 李乾,常亮,苏冬梅,马旭. 粉防己碱对心肌成纤维细胞增殖、活化的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(2): 331-334. |
| [11] | 王玉洁,郭向阳,王军. 重复异丙酚麻醉对新生大鼠海马细胞凋亡及远期学习记忆能力的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(2): 310-314. |
| [12] | 杨光,程庆砾,李春霖,贾雅丽,岳文,裴雪涛,刘洋,赵佳慧,杜婧,敖强国. 高糖减弱肾组织干细胞条件培养液对缺氧损伤肾小管上皮细胞的修复作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(1): 125-130. |
| [13] | 曹珮,姜学军,席志军. 舒尼替尼通过抑制Akt/mTOR信号通路诱导肾癌细胞自噬[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2016, 48(4): 584-589. |
| [14] | 贾双双,李伟阳,刘欣,李丽英. 转化生长因子-β1 通过产生活性氧诱导骨髓间充质干细胞分化为肌成纤维细胞[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2015, 47(5): 737-742. |
| [15] | 李刚,张洪宪,王云鹏,张径,洪锴,田晓军,马潞林. 间苯三酚对大鼠肾缺血再灌注损伤的保护作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2015, 47(5): 743-748. |
|
||