北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2026, Vol. 58 ›› Issue (1): 107-114. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2026.01.014
上颌药物相关性颌骨坏死的不同分期手术治疗效果
FarinEbrahimi1, 冯志强2, FarazEbrahimi3, 韩玮华4, 于子杨4, 贾宽宽1, 安金刚1,*( )
)
- 1. 北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院口腔颌面外科, 国家口腔医学中心, 国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心, 口腔生物材料和数字诊疗装备国家工程研究中心, 北京 100081
2. 河北医科大学第三医院口腔颌面外科, 石家庄 050051
3. 北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院修复科, 北京 100081
4. 中国医学科学院北京协和医学院·北京协和医院口腔科, 北京 100730
Surgical treatment outcomes of different stages of maxillary medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw
Ebrahimi Farin1, Zhiqiang FENG2, Ebrahimi Faraz3, Weihua HAN4, Ziyang YU4, Kuankuan JIA1, Jingang AN1,*( )
)
- 1. Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Center for Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Research Center of Oral Biomaterials and Digital Medical Devices, Beijing 100081, China
2. Department of Stomatology, Hebei Medical University Third Hospital, Shijiazhuang 050051, China
3. Department of Prosthodontics, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
4. Department of Stomatology, Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College, Peking Union Medical College Hospital, Beijing 100730, China
摘要:
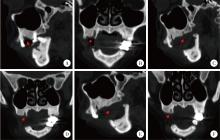
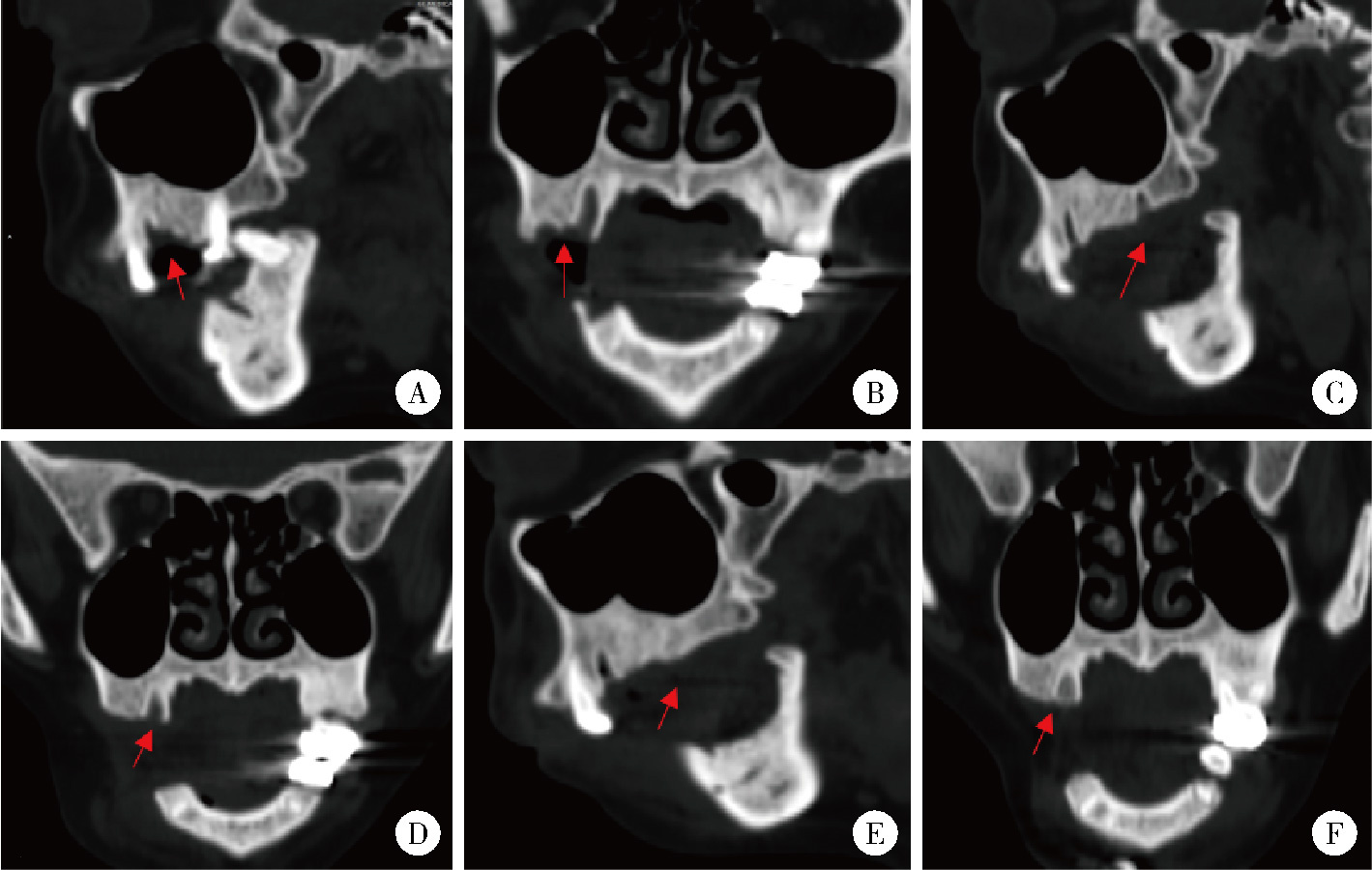
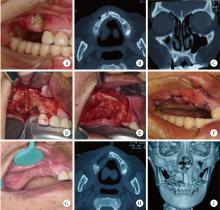
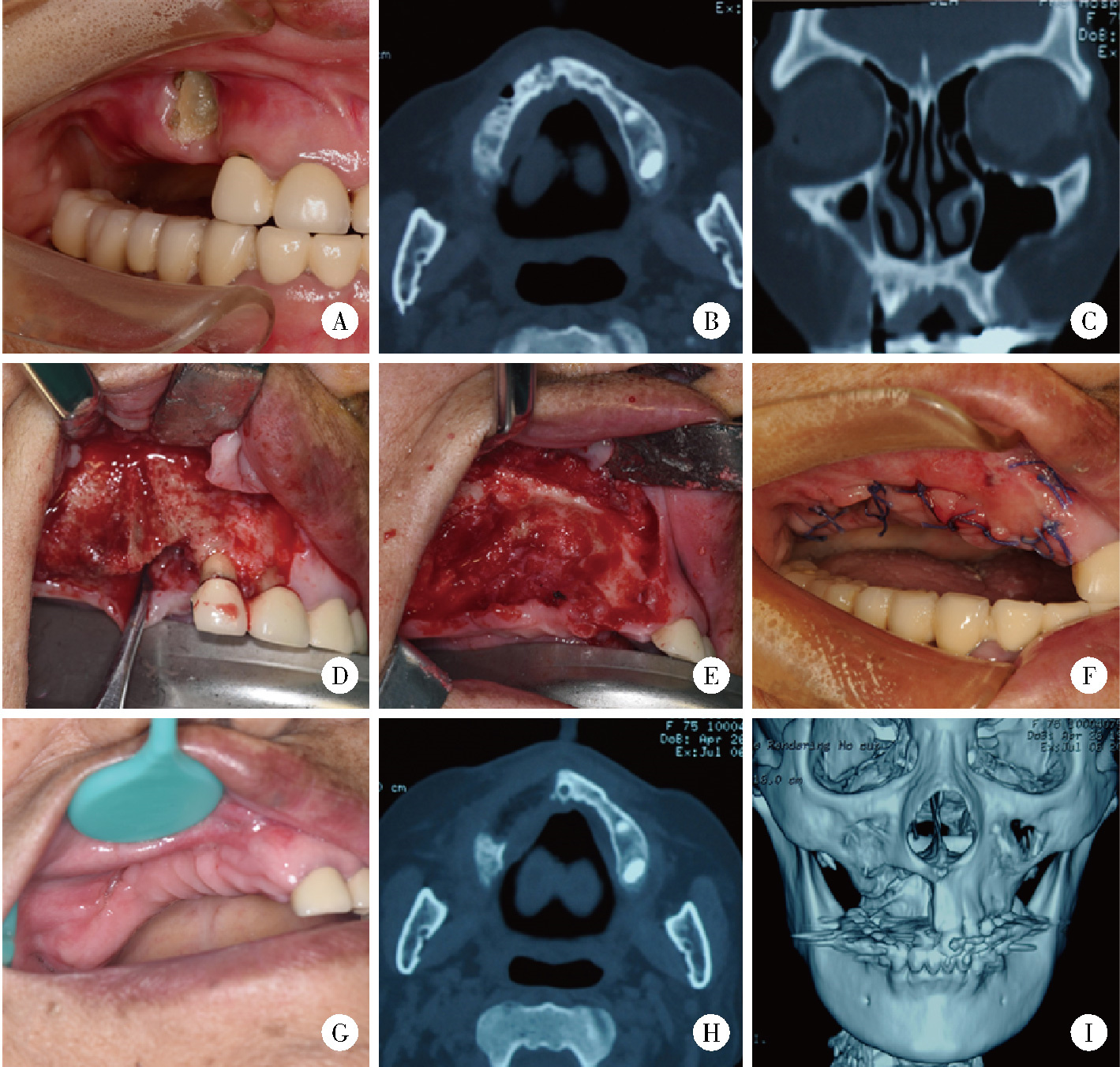
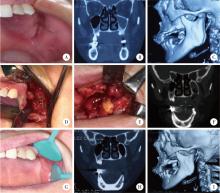
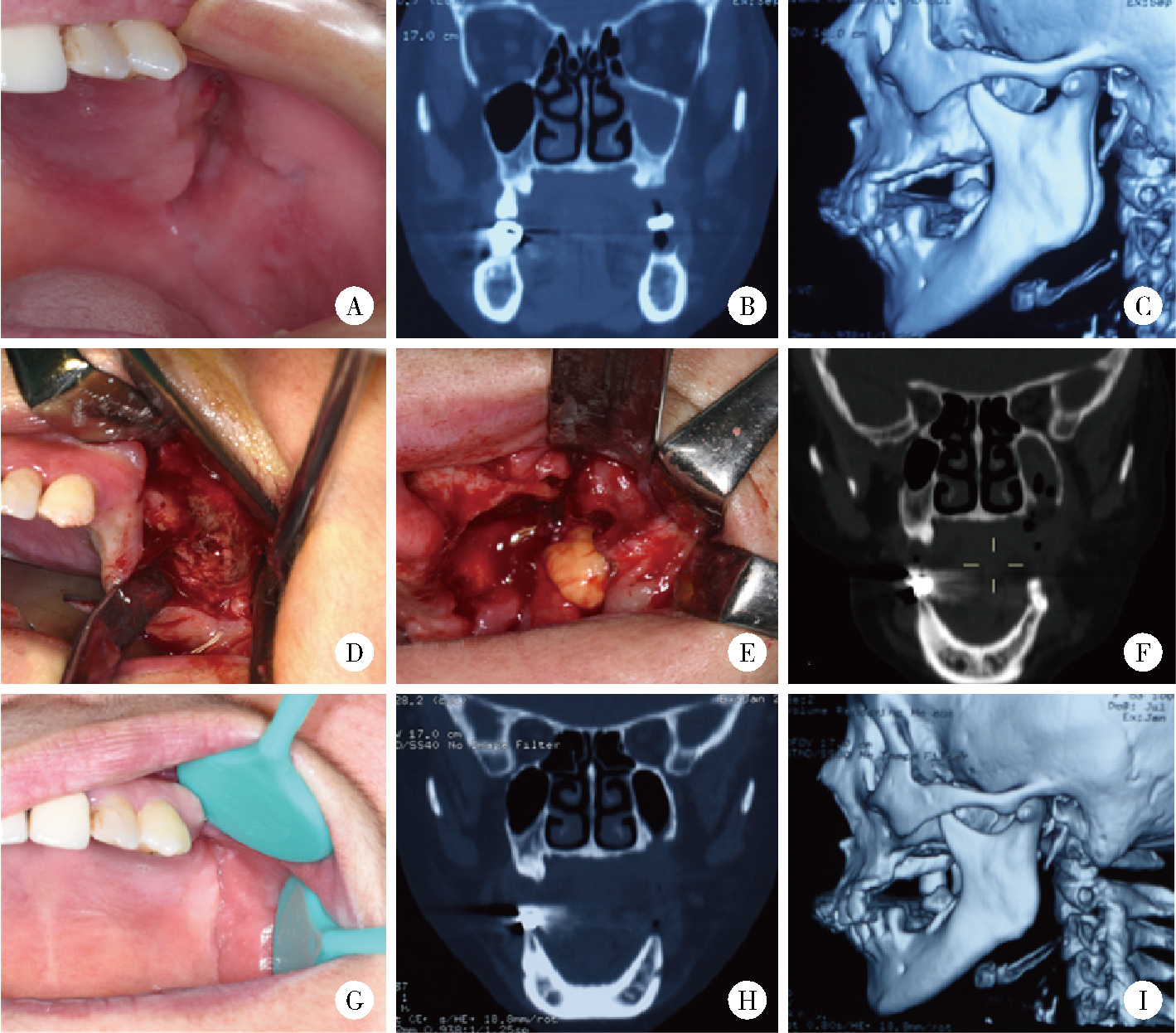
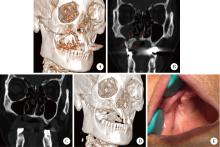
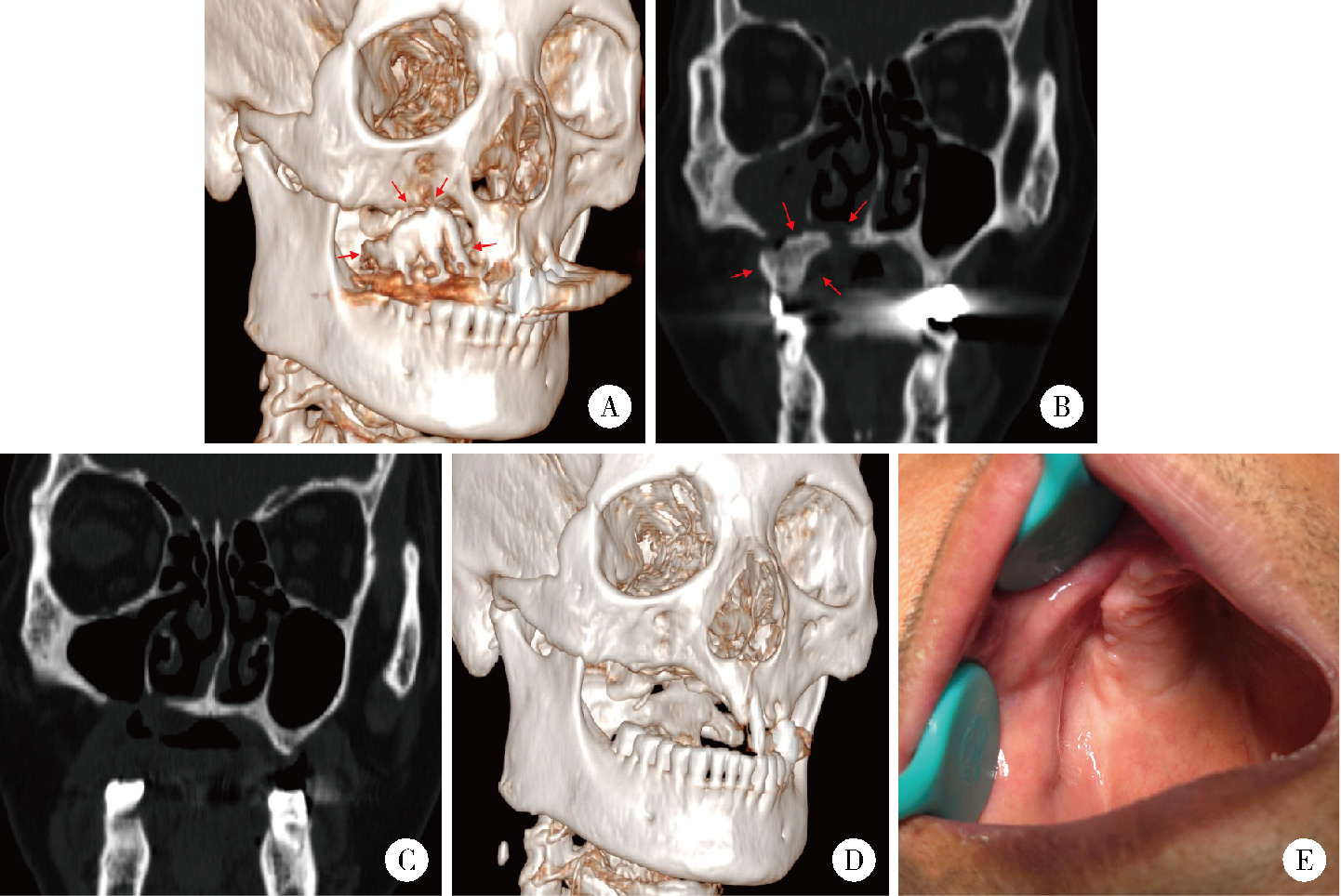
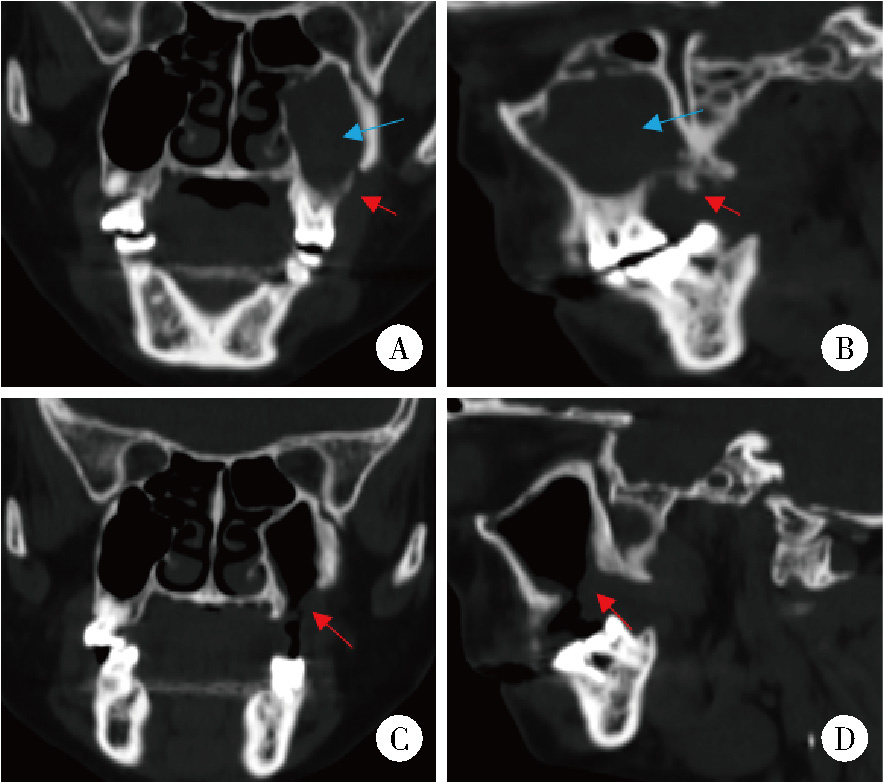
目的: 总结上颌药物相关性颌骨坏死(medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw, MRONJ)的手术治疗效果, 比较不同手术方式治疗Ⅲ期病变患者预后的差异。方法: 回顾性分析2014年4月至2024年2月于北京大学口腔医院颌面外科接受手术治疗的136例上颌MRONJ患者的临床资料。根据美国口腔颌面外科医师协会(American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons, AAOMS)2022年发布的分期标准, 将患者分为Ⅰ期(8例)、Ⅱ期(30例)和Ⅲ期(98例)三组。手术方式包括局部病变切除直接缝合、颊脂垫填塞及碘条填塞。患者术后随访1年, 评估黏膜愈合、疼痛、感染控制及上颌窦炎症改善情况。采用SPSS 20.0软件进行统计学分析。结果: 全部患者短期(3个月)总治愈率为91.2%(124/136), 长期(1年)总治愈率为94.9%(129/136)。Ⅲ期患者中, 颊脂垫填塞组在短期和长期随访中的口腔上颌窦瘘消除率均显著高于碘条填塞组(79.4% vs. 23.4%, P < 0.001;85.3% vs. 54.7%, P=0.002)。然而, 碘条填塞组在上颌窦炎症改善方面的表现更优, 其短期和长期炎症评分改善程度均显著高于颊脂垫填塞组(P=0.029, P=0.014)。结论: 手术治疗适宜于Ⅰ~Ⅲ期的上颌MRONJ患者, 对于Ⅲ期上颌MRONJ, 颊脂垫填塞更有利于口腔上颌窦瘘的闭合, 而碘条填塞在上颌窦炎症控制方面更具优势, 临床应根据患者具体情况选择个体化手术方案。
中图分类号:
- R782
| 1 |
doi: 10.1136/bcr-2018-224455 |
| 2 |
doi: 10.1016/j.joms.2020.05.037 |
| 3 |
|
| 4 |
doi: 10.1111/odi.12992 |
| 5 |
doi: 10.1111/odi.13615 |
| 6 |
doi: 10.1016/j.jds.2020.12.007 |
| 7 |
doi: 10.3390/ijerph19127430 |
| 8 |
田美, 王丹妮, 罗舒艳, 等. 上颌骨药物相关性颌骨坏死的手术治疗效果初探[J]. 中华口腔医学杂志, 2021, 56 (5): 447- 451.
|
| 9 |
何悦, 陈珩, 安金刚, 等. 药物相关性颌骨坏死临床诊疗专家共识[J]. 中国口腔颌面外科杂志, 2023, 21 (4): 313- 325.
|
| 10 |
doi: 10.2214/ajr.156.2.1898819 |
| 11 |
doi: 10.1111/idj.12186 |
| 12 |
doi: 10.1016/j.joms.2022.02.008 |
| 13 |
doi: 10.1016/j.jcms.2016.05.018 |
| 14 |
doi: 10.1016/j.jcms.2016.08.001 |
| 15 |
doi: 10.1016/j.jds.2024.03.006 |
| 16 |
doi: 10.1016/j.joms.2016.12.011 |
| 17 |
doi: 10.1016/j.jcms.2020.02.017 |
| 18 |
doi: 10.3390/jcm10194480 |
| 19 |
|
| 20 |
doi: 10.1016/j.joms.2017.09.021 |
| 21 |
doi: 10.3390/jcm12154909 |
| 22 |
doi: 10.3390/ijerph192114543 |
| 23 |
doi: 10.1007/s10006-021-00973-9 |
| 24 |
doi: 10.1016/j.jcms.2018.03.005 |
| [1] | 潘莲菲, 李文静, 王瑞洋, 焦剑, 曹战强, 高丽, 释栋. 口服抗生素辅助牙周机械治疗对重度牙周炎的短期疗效及影响因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2026, 58(1): 30-36. |
| [2] | 杨菊, 刘玥, 曲春娜, 孙健斌, 李天英, 石连杰. 双膦酸盐相关性颌骨坏死1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2025, 57(2): 388-392. |
| [3] | 康一帆, 葛严军, 吕晓鸣, 谢尚, 单小峰, 蔡志刚. 即刻种植体支持式义齿修复的血管化髂骨瓣重建下颌骨缺损[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2025, 57(1): 78-84. |
| [4] | 王明瑞,刘军,熊六林,于路平,胡浩,许克新,徐涛. 经皮微通道-微电子肾镜-微超声探针碎石术治疗1.5~2.5 cm肾结石的疗效和安全性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 605-609. |
| [5] | 应沂岑,杜毅聪,李志华,张一鸣,李新飞,王冰,张鹏,朱宏建,周利群,杨昆霖,李学松. 机器人辅助腹腔镜下颊黏膜补片输尿管成形术治疗复杂输尿管狭窄[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 640-645. |
| [6] | 李文菁,张保宙,李恒,赖良鹏,杜辉,孙宁,龚晓峰,李莹,王岩,武勇. 胫距跟融合治疗终末期踝和后足病变的中短期临床结果[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 299-306. |
| [7] | 周颖,赵宁,黄竑远,李庆祥,郭传瑸,郭玉兴. 左侧三叉神经第三支带状疱疹并发左侧下颌骨骨坏死1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 366-370. |
| [8] | 周颖,赵宁,黄竑远,李庆祥,郭传瑸,郭玉兴. 双层软组织缝合封闭技术在下颌骨中早期药物相关性颌骨骨坏死患者手术治疗中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 51-56. |
| [9] | 徐心雨,吴灵,宋凤岐,李自力,张益,刘筱菁. 基于下颌运动轨迹的正颌外科术中下颌骨髁突定位方法及初步精度验证[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 57-65. |
| [10] | 蔡安东,王晓霞,周文娟,柳忠豪. 下颌前突畸形患者上颌骨及髁突虚拟位置与术后现实位置的比较[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 74-80. |
| [11] | 邹雪,白小娟,张丽卿. 艾拉莫德联合托法替布治疗难治性中重度类风湿关节炎的疗效[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 1013-1021. |
| [12] | 薛蔚,董樑,钱宏阳,费笑晨. 前列腺癌新辅助治疗与辅助治疗的现状及进展[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 775-780. |
| [13] | 邱敏,宗有龙,王滨帅,杨斌,徐楚潇,孙争辉,陆敏,赵磊,卢剑,刘承,田晓军,马潞林. 腹腔镜肾部分切除术治疗中高复杂程度肾肿瘤的效果[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 833-837. |
| [14] | 张心灵,林志禹,陈玉杰,董文芳,杨欣. 脊柱后路内固定术后切口愈合不良的整形外科治疗[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 910-914. |
| [15] | 马建勋,夏有辰,李比,赵红梅,雷玉涛,布希. 乳腺癌改良根治术后即刻乳房重建的方式选择[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 612-618. |
|
||