北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2026, Vol. 58 ›› Issue (1): 139-144. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2026.01.018
基于非刚性配准构建三维颜面微笑仿真序列数据的方法
温奥楠1, 张晓会2, 杨咏涛3, 高梓翔1, 李文博3, 单珅瑶3, 商相宜3, 田淯文3, 郭殊玮1, 王艺蓁3, 王勇1,3,*( ), 赵一姣1,3,*(
), 赵一姣1,3,*( )
)
- 1. 北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院口腔医学数字化研究中心, 口腔修复教研室, 国家口腔医学中心, 国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心, 口腔生物材料和数字诊疗装备国家工程研究中心, 口腔数字医学北京市重点实验室, 国家卫生健康委员会口腔数字医学重点实验室, 北京 100081
2. 首都师范大学, 国家应用数学中心, 交叉科学研究院, 北京 100089
3. 北京大学医学部医学技术研究院, 北京 100191
Method of constructing 3D facial smile simulation sequence data based on non-rigid registration
Aonan WEN1, Xiaohui ZHANG2, Yongtao YANG3, Zixiang GAO1, Wenbo LI3, Shenyao SHAN3, Xiangyi SHANG3, Yuwen TIAN3, Shuwei GUO1, Yizhen WANG3, Yong WANG1,3,*( ), Yijiao ZHAO1,3,*(
), Yijiao ZHAO1,3,*( )
)
- 1. Center of Digital Dentistry, Department of Prosthodontics, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Center for Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Research Center of Oral Biomaterials and Digital Medical Devices & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology & NHC Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
2. National Center for Applied Mathematics, Academy for Multidisciplinary Studies, Capital Normal University, Beijing 100089, China
3. Institute of Medical Technology, Peking University Health Science Center, Beijing 100191, China
摘要:
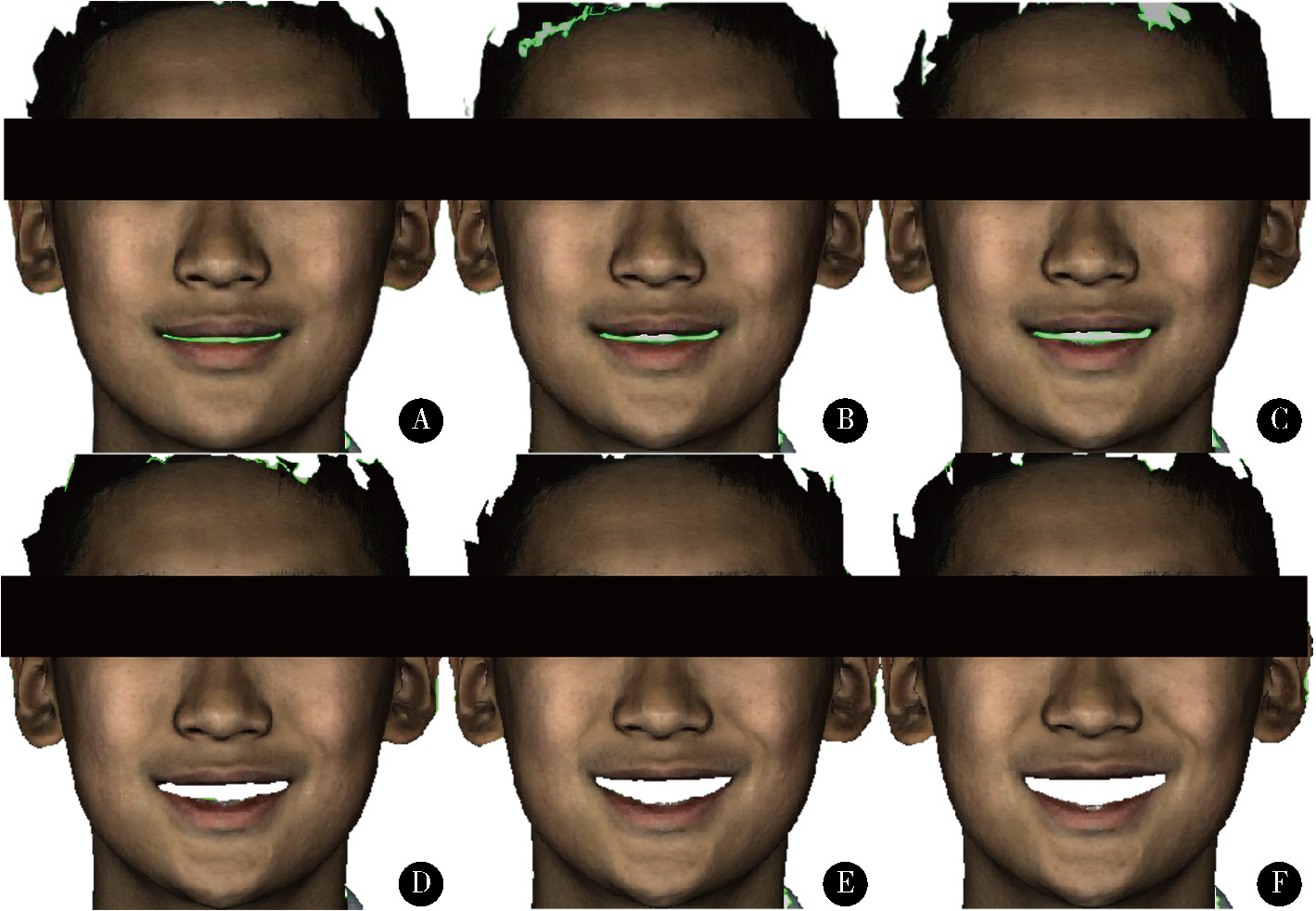
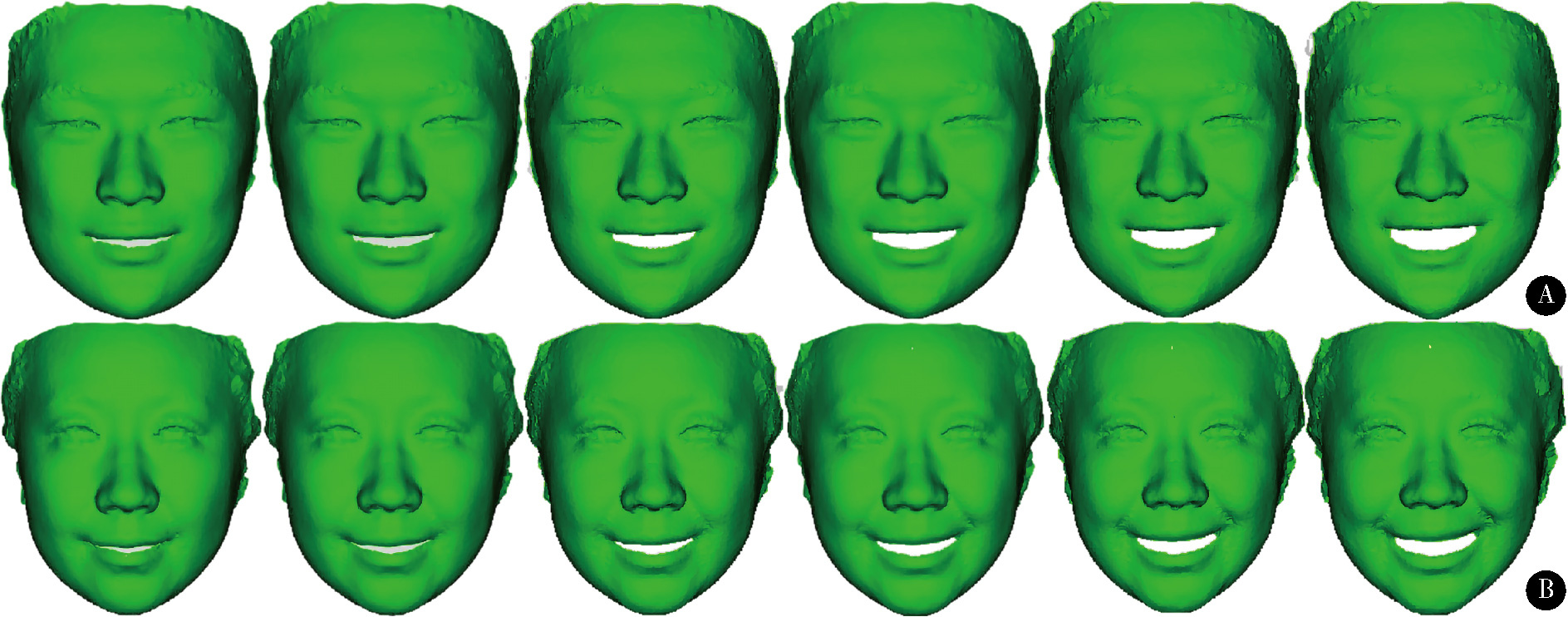
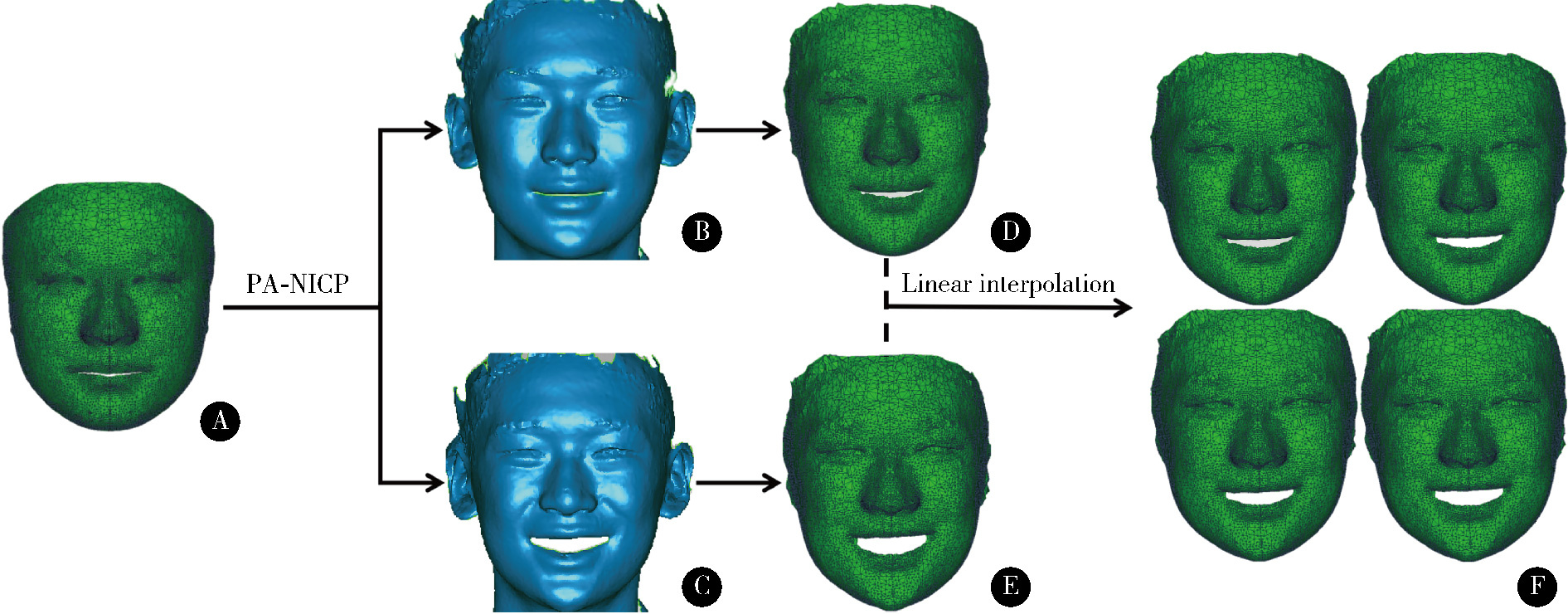
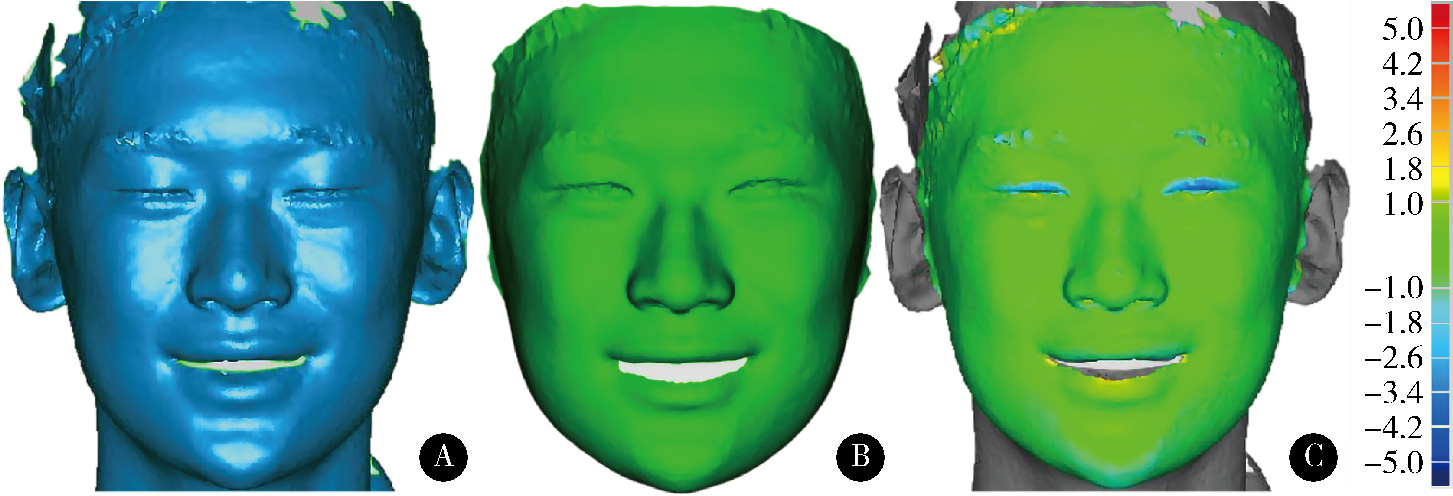
目的: 建立一种基于微笑静态起始和终止颜面数据构建颜面微笑仿真序列数据的方法, 初步评价该方法的准确性和可行性。方法: 使用动态颜面扫描设备3dMD采集受试者由中性表情进行微笑的颜面动态数据。使用本课题组提出的普氏分析非刚性迭代最近点算法(Procrustes analysis non-rigid iterative closest point, PA-NICP)将结构化的三维人脸模板分别变形配准至微笑起始颜面数据和微笑终止颜面数据上, 获得二者结构化的同源数据。在MATLAB软件中, 计算起始和终止两同源数据间的对应顶点位移量, 通过线性插值生成三角面片拓扑结构一致的中间过渡数据, 从而构建出颜面微笑仿真序列数据。以真实采集的颜面动态数据作为参考数据, 以本方法构建的仿真序列数据作为测试数据, 评价微笑过程中多个时间点的三维形态偏差, 评价本方法构建微笑仿真序列数据的准确性。结果: 本方法构建了男性和女性各1名受试者的三维颜面微笑仿真序列数据, 男性受试者仿真序列数据构建的平均三维形态偏差为(0.31±0.04) mm, 女性受试者仿真序列数据构建的平均三维形态偏差为(0.44±0.08) mm。结论: 基于PA-NICP配准算法, 可实现颜面微笑仿真序列数据的构建, 其中间过渡数据可基于插值函数进行参数化构建和调整, 为口腔美学修复设计、治疗效果评估和医患沟通等提供了一种新的动态颜面数据生成方法。
中图分类号:
- R783
| 1 |
doi: 10.1016/j.jobcr.2020.04.010 |
| 2 |
doi: 10.1016/j.sdentj.2023.12.014 |
| 3 |
doi: 10.1016/j.cden.2022.03.001 |
| 4 |
doi: 10.1111/jerd.12405 |
| 5 |
苏佳峰, 武峰, 罗晓晋. 数码微笑设计在前牙美学修复中的应用[J]. 中国实用口腔科杂志, 2016, 9 (10): 632- 634.
|
| 6 |
刘云松, 叶红强, 谷明, 等. 患者参与的数字化设计在前牙美学修复中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2014, 46 (1): 90- 94.
|
| 7 |
叶红强, 柳玉树, 王冠博, 等. 三维数字化仿真设计与实现技术在前牙美学修复中的应用[J]. 中华口腔医学杂志, 2020, 55 (10): 729- 736.
|
| 8 |
doi: 10.1016/j.prosdent.2019.04.007 |
| 9 |
Wright C, Benington P, Ju X, et al. The correlation between static and dynamic facial asymmetry in unilateral cleft lip and palate [J/OL]. Cleft Palate Craniofac J, 2024: 1055665624 1298143. [2024-11-14]. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/39539143/.
|
| 10 |
doi: 10.1007/s00784-023-05195-9 |
| 11 |
doi: 10.1016/j.prosdent.2025.02.056 |
| 12 |
温奥楠, 朱玉佳, 郑盛文, 等. 基于三维人脸模板的颜面解剖标志点自动定点方法初探[J]. 中华口腔医学杂志, 2022, 57 (4): 358- 365.
|
| 13 |
doi: 10.1016/j.job.2024.01.010 |
| 14 |
doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-15883-3 |
| 15 |
doi: 10.1016/j.biopsycho.2022.108453 |
| 16 |
doi: 10.1136/postgradmedj-2018-136286 |
| 17 |
doi: 10.4103/jpbs.jpbs_164_22 |
| 18 |
doi: 10.2196/22228 |
| 19 |
doi: 10.3390/bioengineering10050545 |
| 20 |
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0169402 |
| 21 |
温奥楠, 刘微, 柳大为, 等. 5种椅旁三维颜面扫描技术正确度的初步评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55 (2): 343- 350.
doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2023.02.021 |
| 22 |
doi: 10.1007/s00266-024-04121-y |
| 23 |
doi: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2025.03.009 |
| 24 |
doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-42533-y |
| 25 |
Deng Y, Yang J, Xu S, et al. Accurate 3D face reconstruction with weakly-supervised learning: From single image to image set [C]//2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW). Long Beach, CA: IEEE, 2019: 285-295.
|
| 26 |
Feng Y, Wu F, Shao X, et al. Joint 3D face reconstruction and dense alignment with position map regression network [C]//Computer Vision-ECCV 2018. Cham: Springer International Publi-shing, 2018: 557-574.
|
| 27 |
doi: 10.3390/s24196280 |
| 28 |
doi: 10.3390/jimaging7090169 |
| [1] | 肖宇嘉, 毛渤淳, 周彦恒. 姿势性微笑的三维形态学研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2025, 57(5): 989-995. |
| [2] | 凌晓彤,屈留洋,郑丹妮,杨静,闫雪冰,柳登高,高岩. 牙源性钙化囊肿与牙源性钙化上皮瘤的三维影像特点[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 131-137. |
| [3] | 张雯,刘筱菁,李自力,张益. 基于解剖标志的鼻翼基底缩窄缝合术对正颌患者术后鼻唇部形态的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 736-742. |
| [4] | 温奥楠,刘微,柳大为,朱玉佳,萧宁,王勇,赵一姣. 5种椅旁三维颜面扫描技术正确度的初步评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(2): 343-350. |
| [5] | 邱天成,刘筱菁,薛竹林,李自力. 基于三维动态照相机的正常人面部表情可重复性研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(6): 1107-1111. |
|
||