北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2019, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (4): 733-736. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2019.04.024
颈动脉支架成形术后脑高灌注综合征
贾子昌1,卞焕菊2,韩金涛1,赵海燕3,栾景源1,王昌明1,李选1,△( )
)
- 1. 北京大学第三医院介入血管外科, 北京 100191
2. 山东省冠县人民医院神经内科, 山东冠县 252500
3. 北京大学第三医院神经内科, 北京 100191
Cerebral hyper perfusion syndrome after carotid artery stenting
Zi-chang JIA1,Huan-ju BIAN2,Jin-tao HAN1,Hai-yan ZHAO3,Jing-yuan LUAN1,Chang-ming WANG1,Xuan LI1,△( )
)
- 1.Department of Interventional Radiology and Vascular Surgery, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
2. Department of Neurology,Guanxian Hospital,Guanxian 252500, Shandong, China
3.Department of Neurology, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
摘要:
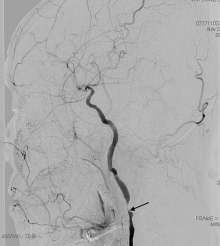
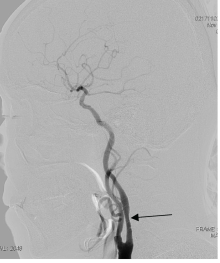
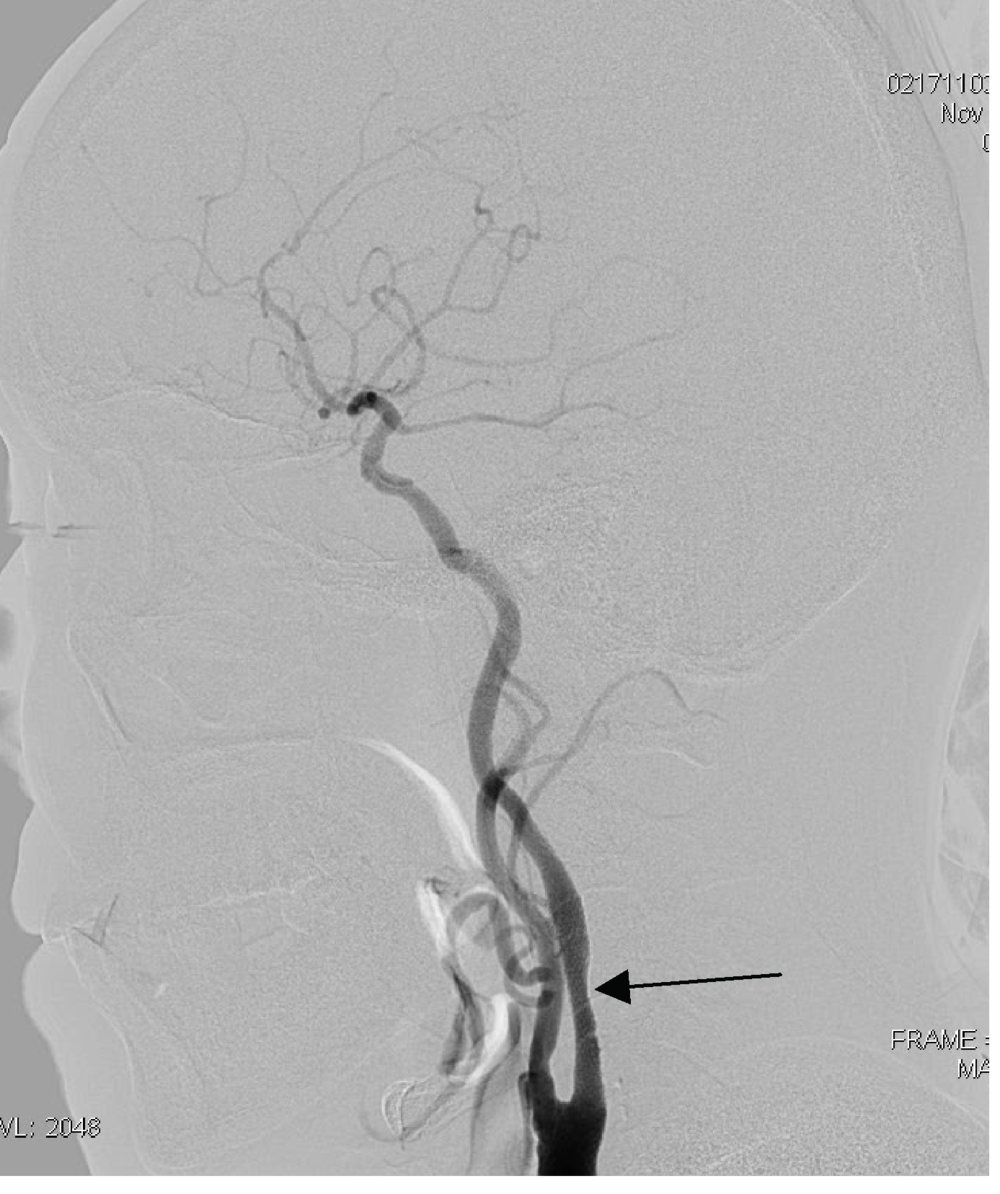
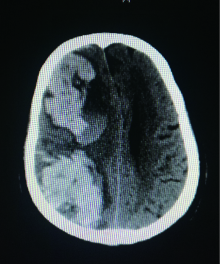
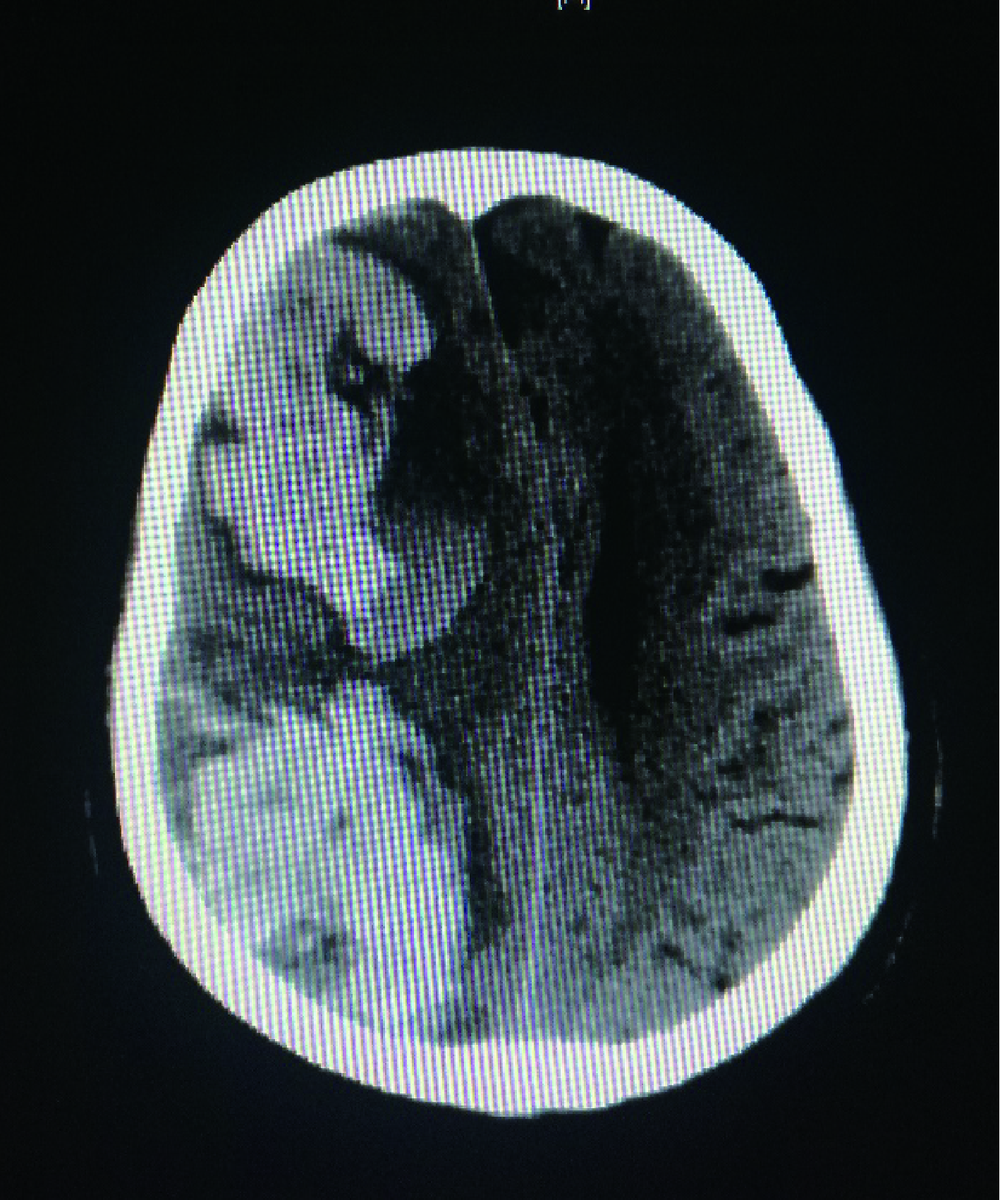
目的:探讨颈内动脉重度狭窄患者行颈动脉支架成形术(carotid artery stenting,CAS)后,发生脑高灌注综合征(hyper perfusion syndrome,HPS)的危险因素、临床特点以及防治方法。方法:选择2014年9月至2018年3月于北京大学第三医院介入血管外科接受CAS治疗的226例颈内动脉重度狭窄患者进行回顾性分析,总结其中发生HPS的5例患者的相关临床资料,分析其临床基线资料、影像学特点以及围手术期管理与HPS的关系。结果:226例行CAS手术的患者中5例发生了HPS(2.21%,5/226),其中2例为高灌注性脑出血(0.88%,2/226), 5例中男性4例,女性1例,年龄58~74岁。发生HPS时间在术后第4小时至术后第3天,症状为头痛2例,谵妄1例,左侧肢体偏瘫1例,昏迷(最终死亡)1例。结论:HPS是CAS术后少见但后果严重的并发症,应增强对其危险因素的认识,预防其发生,一旦发生则早诊断、早治疗尤为重要。
中图分类号:
- R619
| [1] | Fazekas G, Kasza G, Arató E , et al. Cerebral hyper perfusion syndrome and blood pressure control[J]. Orv Hetil, 2015,156(26):1049-1053. |
| [2] | Bouri S, Thapar A, Shalhoub J , et al. Hypertension and the post-carotid endarterectomy cerebral hyperperfusion syndrome[J]. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg, 2011,41(2):229-237. |
| [3] | North American Symptomatic Carotid Endarterectomy Trial. Methods,patient characteristics,and progress[J]. Stroke, 1991,22(6):711-720. |
| [4] | 黄家星, 林文华, 刘丽萍 , 等. 缺血性卒中侧支循环评估与干预中国专家共识[J]. 中国卒中杂志, 2013,8(4):285-293. |
| [5] | Ogasawara K, Sakai N, Kuroiwa T . Intracranial hemorrhage associated with cerebral hyperperfusion syndrome following carotid endarterectomy and carotid artery stenting: retrospective review of 4494 patients[J]. J Neurosurg, 2007,107(6):1130-1136. |
| [6] | Fujimura M, Niizuma K, Endo H , et al. Quantitative analysis of early postoperative cerebral blood flow contributes to the prediction and diagnosis of cerebral hyperperfusion syndrome after revas-cularization surgery for moyamoya disease[J]. Neurol Res, 2015,37(2):131-138. |
| [7] | Kitagawa K . Carotid stenosis, baroreceptor sensitivity and cerebral autoregulation: implication for cerebral hyperperfusion syndrome[J]. Circ J, 2010,74(10):2058-2059. |
| [8] | Macfarlane R, Moskowitz MA, Sakas DE , et al. The role of neuroeffector mechanisms in cerebral hyperperfusion syndromes[J]. J Neurosurg, 1991,75(6):845-855. |
| [9] | Moulakakis KG, Mylonas SN, Sfyroeras GS , et al. Hyper perfusion syndrome after carotid revascularization[J]. J Vasc Surg, 2009,49(4):1060-1068. |
| [10] | Mo DP, Luo G, Wang B , et al. Staged carotid artery angioplasty and stenting for patients with high-grade carotid stenosis with high risk of developing hyperperfusion injury: a retrospective analysis of 44 cases[J]. Stroke Vasc Neurol, 2016,1(4):147-153. |
| [11] | Wu F, Huang L, Lu G , et al. Two-stage cerebral hemodynamic changes in staged carotid angioplasty and stenting[J]. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis, 2016,25(12):2814-2820. |
| [1] | 周柏林,李危石,孙垂国,齐强,陈仲强,曾岩. 脊柱手术后深部切口感染患者多次清创的危险因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(2): 286-292. |
| [2] | 张玮,张培训. 老年髋部骨折患者围手术期血栓预防时限分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(3): 501-504. |
| [3] | 王博杰,郭超,李春晶,穆东亮. 围麻醉期过敏反应发生率及危险因素分析:一项2012—2017年回顾性调查[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(1): 193-199. |
| [4] | 王宇, 孟一森, 范宇, 谌诚, 虞巍, 郝瀚, 韩文科, 郝金瑞, 金杰, 周利群. 咀嚼口香糖对膀胱全切尿流改道术后肠道康复的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2016, 48(5): 822-824. |
| [5] | 刘坤,徐宗源,孟峻嵩,傅广波,顾硕,顾民. 术前营养风险对根治性全膀胱切除术后并发症发生率的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2015, 47(5): 800-803. |
| [6] | 李宏亮, 朱曦, 么改琦, 汪宗昱. 颈内静脉置管导致椎动脉损伤2例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2015, 47(2): 355-357. |
|
||