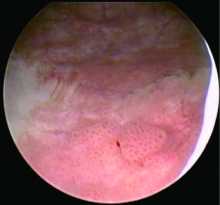
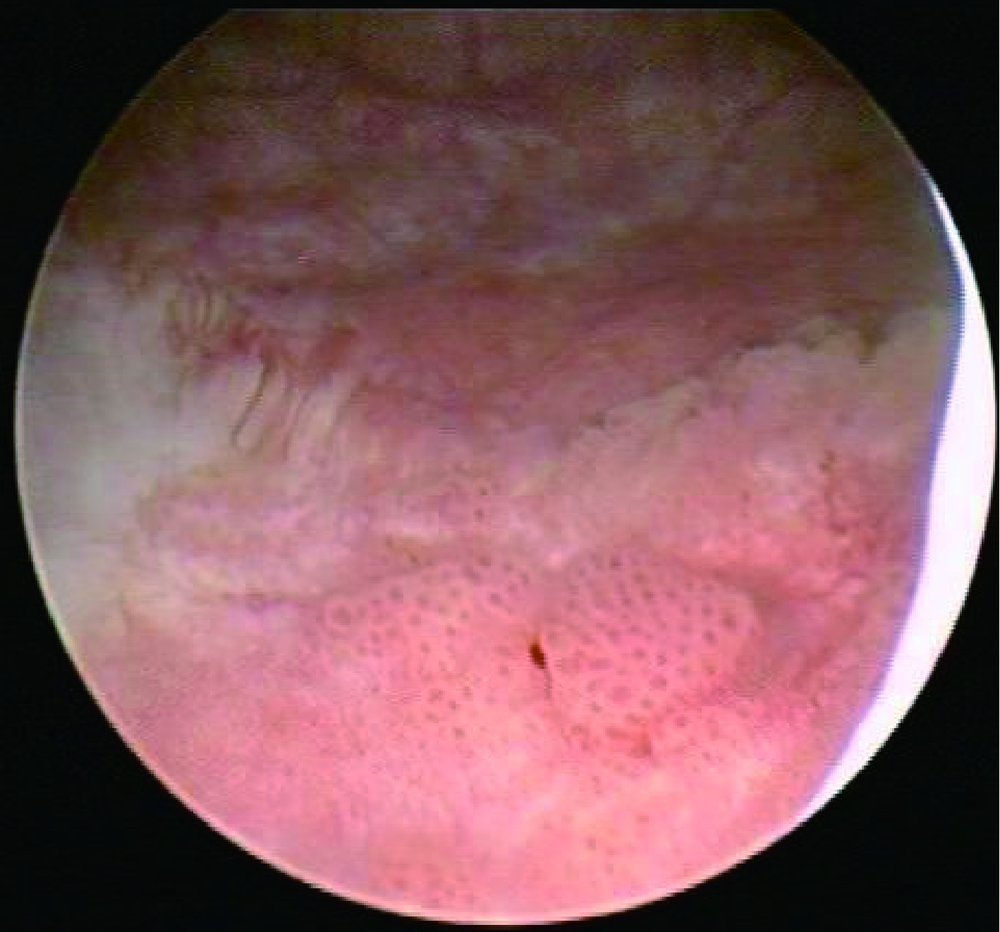
北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2020, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (4): 697-700. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2020.04.019
窄带成像与白光在经尿道膀胱肿瘤切除术中的自身对照分析
邱敏,徐楚潇,王滨帅,颜野,邓绍晖,肖春雷,刘承,卢剑,田晓军( ),马潞林
),马潞林
- 北京大学第三医院泌尿外科,北京 100191
Analysis of self-control trial results of narrow band imaging and white light in transurethral resection of bladder tumor
Min QIU,Chu-xiao XU,Bin-shuai WANG,Ye YAN,Shao-hui DENG,Chun-lei XIAO,Cheng LIU,Jian LU,Xiao-jun TIAN( ),Lu-lin MA
),Lu-lin MA
- Department of Urology,Peking University Third Hospital,Beijing 100191, China
摘要:
目的: 探讨窄带成像(narrow band imaging,NBI)辅助白光经尿道膀胱肿瘤切除术(transurethral resection of bladder tumor,TURBT)治疗膀胱尿路上皮癌的效果,总结NBI手术经验。方法: 选择2018年4月至2020年1月北京大学第三医院泌尿外科就诊膀胱尿路上皮癌的患者,麻醉后行TURBT。术中先在白光下寻找膀胱肿瘤并切除,完整取出病理标本。换成NBI,寻找可疑病灶并切除,将病理标本完整取出。两组术后标本区分开分别送病理科,记录白光下病灶的数目、位置及病理诊断结果,同时记录NBI下白光残留病灶的情况。计算白光下电切后膀胱肿瘤残留的比例,评估NBI的效果。后期病例按时间顺序平均分为3组,统计各组的临床数据,观察NBI辅助白光下TURBT的学习曲线。结果: 参加研究的患者共45例,其中男32例,女13例,年龄23~89岁,平均65.2岁。45例手术均顺利完成,术后未见明显并发症及发生。术中发现9例为单发,36例为多发,肿瘤最大径0.5~4.0 cm,平均2.2 cm。白光下切除标本病理诊断均为尿路上皮癌,另有19例白光切除后NBI辅助下再次切除标本病理诊断阳性(42.2%)。按时间顺序将45例分为3组,每组15例,白光下切除后3组NBI的真阳性率分别为33.3%、46.7%、46.7%,假阳性率分别为60.0%、46.7%、26.7%。结论: TURBT是治疗膀胱尿路上皮癌的有效方式,NBI是白光的有效补充,能增加膀胱肿瘤的检出率,减少术后复发。NBI光源有一定的学习曲线,随着病例的增加,NBI下假阳性率逐渐降低,而术者NBI经验丰富后,在白光下对扁平样肿瘤的辨识度也逐渐提高,白光下肿瘤切除后NBI辅助治疗肿瘤残留率降低。
中图分类号:
- R737.14
| [1] | Li K, Lin T, Xue W, et al. Current status of diagnosis and treatment of bladder cancer in China: analyses of Chinese bladder cancer consortium database[J]. Asian J Urol, 2015,2(2):63-69. |
| [2] |
Naselli A, Introini C, Timossi L, et al. A randomized prospective trial to assess the impact of transurethral resection in narrow band imaging modality on non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer recurrence[J]. Eur Urol, 2012,61(5):908-913.
pmid: 22280855 |
| [3] | 廖洪, 李汉忠, 张玉石, 等. 单中心尿路上皮癌2 115例临床特点分析[J]. 中华泌尿外科杂志, 2014,35(12):900-904. |
| [4] | Bryan RT, Billingham LJ, Wallace DM. Narrow-band imaging flexible cystoscopy in the detection of recurrent urothelial cancer of the bladder[J]. BJU Int, 2008,101(6):702-705. |
| [5] |
Cauberg ECC, Mamoulakis C, de la Rosette JJMC, et al. Narrow band imaging-assisted transurethral resection for non-muscle invasive bladder cancer significantly reduces residual tumour rate[J]. World J Urol, 2011,29(4):503-509.
pmid: 21350871 |
| [6] |
Malik K, Raja A, Mahalingam S, et al. Usefulness of narrow-band imaging in transurethral resection of bladder tumor: early experience from a tertiary center in India[J]. South Asian J Cancer, 2019,8(4):226.
pmid: 31807483 |
| [7] | 邱敏, 颜野, 田晓军, 等. 窄带成像技术辅助经尿道膀胱肿瘤切除术[J]. 中国微创外科杂志, 2018,18(10):888-890. |
| [8] |
Naito S, Algaba F, Babjuk M, et al. The clinical research office of the endourological society (CROES) multicentre randomised trial of narrow band imaging-assisted transurethral resection of bladder tumour (TURBT) versus conventional white light imaging-assisted TURBT in primary non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer patients: trial protocol and 1-year results[J]. Eur Urol, 2016,70(3):506-515.
pmid: 27117749 |
| [9] | Shadpour P, Emami M, Haghdani S. A Comparison of the progression and recurrence risk index in non-muscle-invasive bladder tumors detected by narrow-band imaging versus white light cystoscopy, based on the EORTC scoring system[J]. Nephro-Urol Mon, 2016,8(1):e33240. |
| [10] | 唐兴国, 颜野, 邱敏, 等. 单中心16年青年膀胱尿路上皮癌患者的诊治[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018,50(4):630-633. |
| [11] | Dalgaard LP, Zare R, Gaya JM, et al. Prospective evaluation of the performances of narrow-band imaging flexible videoscopy relative to white-light imaging flexible videoscopy, in patients scheduled for transurethral resection of a primary NMIBC[J]. World J Urol, 2018,37(8):1615-1621. |
| [1] | 欧俊永,倪坤明,马潞林,王国良,颜野,杨斌,李庚午,宋昊东,陆敏,叶剑飞,张树栋. 肌层浸润性膀胱癌合并中高危前列腺癌患者的预后因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 582-588. |
| [2] | 王田,洪欣,王晓峰. 等离子针状电极在经尿道近输尿管口膀胱肿瘤切除术中的临床应用(附16例报道)[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(4): 632-636. |
| [3] | 赵世明,杨铁军,许春苗,郭孝峰,马永康,陈学军,李祥,何朝宏. 3.0T磁共振成像在接受过经尿道膀胱肿瘤切除术膀胱癌中诊断肌层浸润的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(4): 701-704. |
| [4] | 黄厚锋,张玉石,范欣荣,严维刚,纪志刚,李汉忠. 膀胱平滑肌瘤临床特点分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(2): 372-373. |
| [5] | 周建华,王地,王焕瑞,侯晓利,郁卫东,许克新,胡浩. γδT细胞对膀胱癌细胞的细胞毒活性及MICA/B蛋白在膀胱癌中的表达[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(4): 595-601. |
| [6] | 王焕瑞,张维宇,刘献辉,胡浩,张晓鹏,许克新. 大部分膀胱切除生物补片膀胱扩大术在高龄浸润性膀胱癌患者中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(4): 626-629. |
| [7] | 林天歆. 膀胱癌的淋巴结清扫范围[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(4): 565-568. |
| [8] | 郝瀚,苏晓鸿,郑卫,葛鹏,何群,沈棋,杨新宇,张争,李学松,林健,周利群. 非肌层浸润性膀胱癌行膀胱根治性切除[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2016, 48(4): 627-631. |
| [9] | 刘余庆, 卢剑, 赵磊, 侯小飞, 马潞林. 肾移植受者上尿路尿路上皮癌术后膀胱复发的预后因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2015, 47(4): 605-610. |
| [10] | 郝瀚, 吴鑫, 郑卫, 虞巍, 范宇, 何群, 李学松, 周利群. 膀胱尿路上皮癌淋巴结转移特点:单中心522例膀胱根治性切除病例回顾[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2014, 46(4): 524-527. |
| [11] | 张治草,黄毅,王秀杰,王猛,马潞林. 膀胱尿路上皮癌患者血液中微小RNA的表达[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2013, 45(4): 532-. |
| [12] | 沈棋,孙莉华,王静华,刘漓波,何群,金杰. 32例肾源性腺瘤临床病理特点及免疫组织化学染色分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2013, 45(4): 522-. |
| [13] | 杨轩, 袁栋栋, 姜学军, 席志军. 顺铂通过诱导膀胱癌细胞自噬促进细胞凋亡[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2013, 45(2): 221-. |
| [14] | 郑卫, 吴鑫, 张雷, 宋刚, 张争, 龚侃, 宋毅, 李学松, 何志嵩, 周利群. 腹腔镜膀胱全切手术:单中心60例学习曲线结果分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2012, 44(4): 558-562. |
| [15] | 罗道升, 米其武, 孟祥军, 高勇, 戴宇平, 邓春华. 外磁场协同卟啉-葡聚糖磁性纳米微粒的光动力学对人膀胱癌细胞的杀伤作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2012, 44(4): 524-537. |
|
||