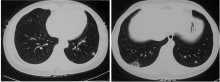
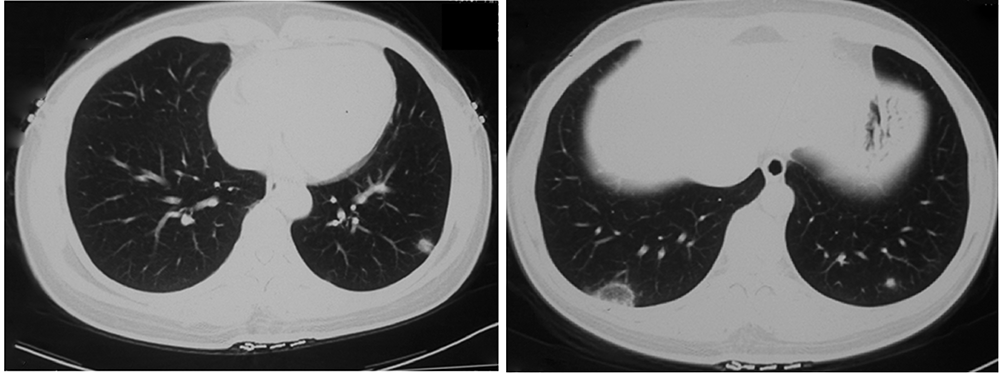
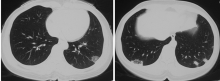
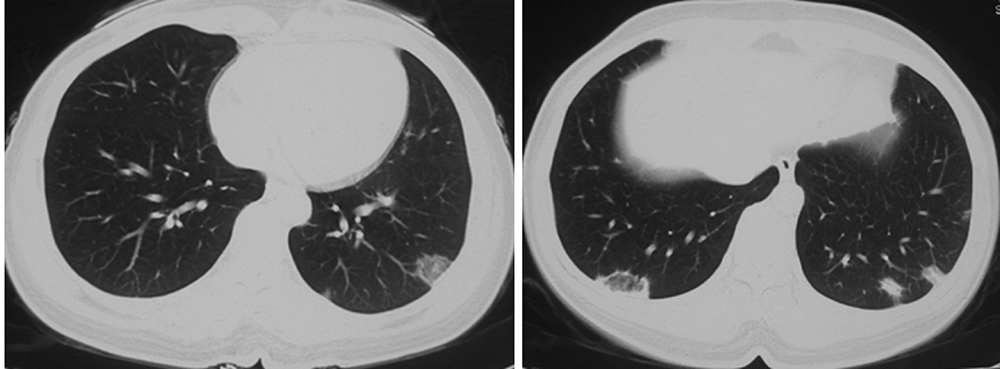
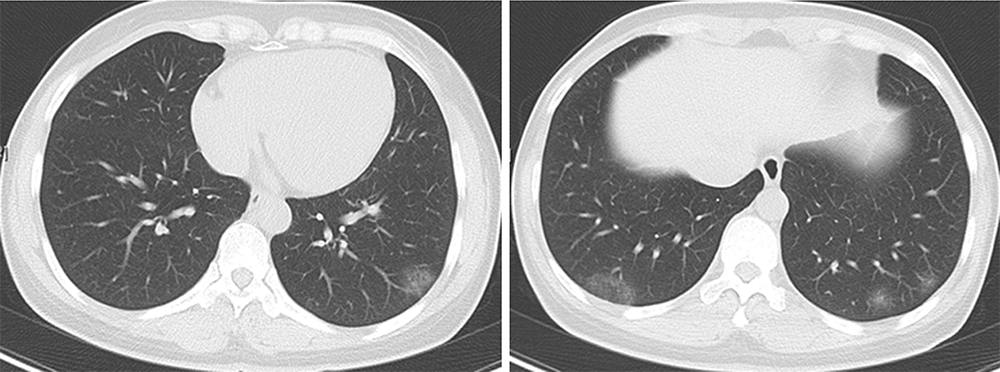
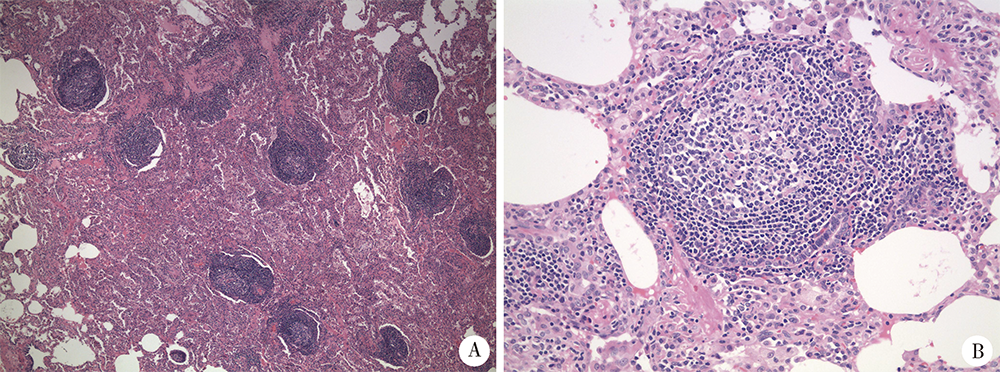
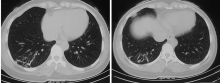
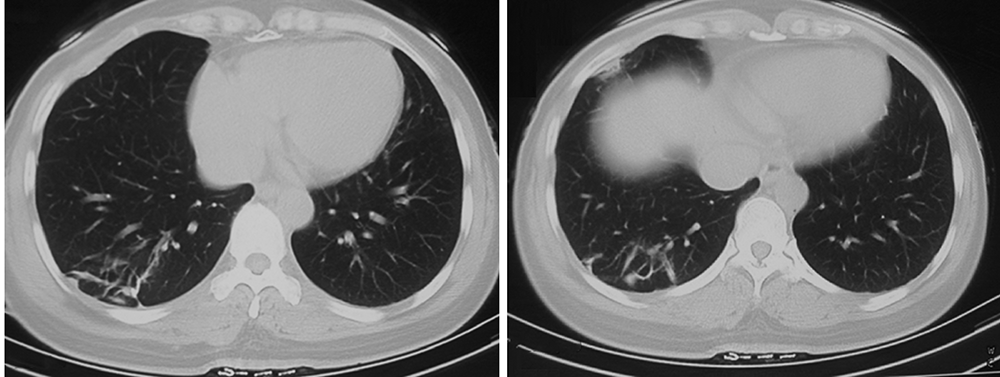
北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (6): 1196-1200. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2021.06.032
自发缓解的滤泡性细支气管炎伴非特异性间质性肺炎1例报道并文献复习
- 1.北京大学第三医院 呼吸与危重医学科,北京 100191
2.北京大学第三医院 病理科,北京 100191
Spontaneous remission of follicular bronchiolitis with nonspecific interstitial pneumonia: A case report and literature review
WANG Fei1,ZHU Xiang2,HE Bei1,ZHU Hong1,SHEN Ning1,△( )
)
- 1. Department of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
2. Department of Pathology, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
中图分类号:
- R562.21
| [1] |
Romero S, Barroso E, Gil J, et al. Follicular bronchiolitis: Clinical and pathologic findings in six patients[J]. Lung, 2003, 181(6):309-319.
pmid: 14749935 |
| [2] |
Burgel PR, Bergeron A, de Blic J, et al. Small airways diseases, excluding asthma and COPD: An overview[J]. Eur Respir Rev, 2013, 22(128):131-147.
doi: 10.1183/09059180.00001313 |
| [3] | 方芳, 王芳, 张伟, 等. 肺活检表现为滤泡性细支气管炎的干燥综合征一例[J]. 中华结核和呼吸杂志, 2013, 36(3):229-230. |
| [4] | 戴建, 蔡后荣, 李燕, 等. 滤泡性细支气管炎三例并文献复习[J]. 中华结核和呼吸杂志, 2017, 40(6):457-462. |
| [5] |
Lu J, Ma M, Zhao Q, et al. The clinical characteristics and outcomes of follicular bronchiolitis in chinese adult patients[J]. Sci Rep, 2018, 8(1):7300.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-25670-8 |
| [6] |
Aerni MR, Vassallo R, Myers JL, et al. Follicular bronchiolitis in surgical lung biopsies: Clinical implications in 12 patients[J]. Respir Med, 2008, 102(2):307-312.
doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2007.07.032 |
| [7] |
Exley CM, Suvarna SK, Matthews S. Follicular bronchiolitis as a presentation of HIV[J]. Clin Radiol, 2006, 61(8):710-713.
pmid: 16843757 |
| [8] | Mateos EA, Lópze FIA, Medel EB, et al. Follicular bronchiolitis. A review of 11 cases[J]. Virchows Arch, 2008, 452(Suppl 1):S56. |
| [9] |
Case records of the Massachusetts General Hospital. Weekly clinicopathological exercises. Case 17-2001. A 42-year-old man with multiple pulmonary cysts and recurrent respiratory infections[J]. N Engl J Med, 2001, 344(22):1701-1708.
doi: 10.1056/NEJM200105313442208 |
| [10] |
Vos R, Vanaudenaerde BM, De Vleeschauwer SI, et al. Follicular bronchiolitis. A rare cause of bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome after lung transplantation: A case report[J]. Am J Transplant, 2009, 9(3):644-650.
doi: 10.1111/j.1600-6143.2008.02518.x pmid: 19191770 |
| [11] |
Shimizu K, Konno S, Nasuhara Y, et al. A case of follicular bronchiolitis associated with asthma, eosinophilia, and increased immunoglobulin E[J]. J Asthma, 2010, 47(10):1161-1164.
doi: 10.3109/02770903.2010.515326 |
| [12] |
Goksel O, Nart D, Ergonul AG, et al. Successful colchicine the-rapy in a patient with follicular bronchiolitis presumed to be asthma[J]. Respir Care, 2015, 60(7):e122-e124.
doi: 10.4187/respcare.03610 |
| [13] |
Roddy E, Summers G, Chaudry Z, et al. Follicular bronchiolitis, an unusual cause of haemoptysis in giant cell arteritis[J]. Clin Rheumatol, 2006, 25(3):433-435.
doi: 10.1007/s10067-005-0009-0 |
| [14] | Terada T. Follicular bronchiolitis and lymphocytic interstitial pneumonia in a Japanese man[J]. Diagn Pathol, 2011(6):85. |
| [15] |
Hwangbo Y, Cha SI, Lee YH, et al. A case of multicentric castleman’s disease presenting with follicular bronchiolitis[J]. Tuberc Respir Dis (Seoul), 2013, 74(1):23-27.
doi: 10.4046/trd.2013.74.1.23 |
| [16] | Wakamatsu K, Nagata N, Taguchi K, et al. A case of follicular bronchiolitis as the histological counterpart to nodular opacities in bronchiectatic mycobacterium avium complex disease[J]. Case Rep Pulmonol, 2012, 2012:214601. |
| [17] | Thalanayar PM, Holguin F. Follicular bronchiolitis in primary ciliary dyskinesia[J]. Australas Med J, 2014, 7(7):294-297. |
| [18] | 牟向东, 廖纪萍, 贺丹眉, 等. 滤泡性细支气管炎一例[J]. 呼吸与危重监护杂志, 2018, 17(1):86-87. |
| [19] |
Hare SS, Souza CA, Bain G, et al. The radiological spectrum of pulmonary lymphoproliferative disease[J]. Br J Radiol, 2012, 85(1015):848-864.
doi: 10.1259/bjr/16420165 pmid: 22745203 |
| [20] | 何慕芝, 蔡闯, 王继业, 等. 反晕征的病因谱及临床意义研究进展[J]. 国际呼吸杂志, 2018, 38(19):1516-1520. |
| [21] |
Tansey D, Wells AU, Colby TV, et al. Variations in histological patterns of interstitial pneumonia between connective tissue disorders and their relationship to prognosis[J]. Histopathology, 2004, 44(6):585-596.
pmid: 15186274 |
| [22] |
Travis WD, Hoffman GS, Leavitt RY, et al. Surgical pathology of the lung in Wegener’s granulomatosis: Review of 87 open lung biopsies from 67 patients[J]. Am J Surg Pathol, 1991, 15(4):315-333.
pmid: 2006712 |
| [23] | Tashtoush B, Okafor NC, Ramirez JF, et al. Follicular bronchiolitis: A literature review [J]. J Clin Diagn Res, 2015, 9(9): OE01-OE05. |
| [24] |
Bates CA, Ellison MC, Lynch DA, et al. Granulomatous-lymphocytic lung disease shortens survival in common variable immunodeficiency[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2004, 114(2):415-421.
doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2004.05.057 |
| [1] | 刘家骏, 刘国康, 朱玉虎. 免疫相关性重症肺炎1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 932-937. |
| [2] | 黄教悌,胡菁,韩博. 治疗相关神经内分泌前列腺癌机制研究与靶向治疗新进展[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 557-561. |
| [3] | 欧俊永,倪坤明,马潞林,王国良,颜野,杨斌,李庚午,宋昊东,陆敏,叶剑飞,张树栋. 肌层浸润性膀胱癌合并中高危前列腺癌患者的预后因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 582-588. |
| [4] | 刘帅,刘磊,刘茁,张帆,马潞林,田晓军,侯小飞,王国良,赵磊,张树栋. 伴静脉癌栓的肾上腺皮质癌的临床治疗及预后[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 624-630. |
| [5] | 虞乐,邓绍晖,张帆,颜野,叶剑飞,张树栋. 具有低度恶性潜能的多房囊性肾肿瘤的临床病理特征及预后[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 661-666. |
| [6] | 周泽臻,邓绍晖,颜野,张帆,郝一昌,葛力源,张洪宪,王国良,张树栋. 非转移性T3a肾细胞癌患者3年肿瘤特异性生存期预测[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 673-679. |
| [7] | 方杨毅,李强,黄志高,陆敏,洪锴,张树栋. 睾丸鞘膜高分化乳头状间皮肿瘤1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 741-744. |
| [8] | 曾媛媛,谢云,陈道南,王瑞兰. 脓毒症患者发生正常甲状腺性病态综合征的相关因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 526-532. |
| [9] | 侯婉音,董捷. 腹膜透析患者获得性肾囊肿出血3例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 546-550. |
| [10] | 李文菁,张保宙,李恒,赖良鹏,杜辉,孙宁,龚晓峰,李莹,王岩,武勇. 胫距跟融合治疗终末期踝和后足病变的中短期临床结果[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 299-306. |
| [11] | 冯琦琛,盖铄,王昌明,李选. 经同侧大隐静脉入路髂静脉成型及支架植入术在日间治疗模式中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 322-325. |
| [12] | 彭圣嘉,祁雨,孙丽杰,李丹,王新宇,韩江莉,陈宝霞,张媛. 传入压力反射衰竭合并低钠血症1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 357-361. |
| [13] | 苏俊琪,王晓颖,孙志强. 舌鳞状细胞癌根治性切除术后患者预后预测列线图的构建与验证[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 120-130. |
| [14] | 陈晨,梁宇红. 复杂根管上颌磨牙的根管治疗3例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 190-195. |
| [15] | 任晓萌,李凯一,李春蕾. 基于转录组测序探索口腔扁平苔藓局部激素治疗敏感性相关分子特征[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 32-38. |
|
||