北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (6): 982-992. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2023.06.005
血脂异常与类风湿关节炎肺间质病变的相关性分析
- 1. 北京大学深圳医院风湿免疫科, 深圳市炎症与免疫性疾病重点实验室, 广东深圳 518000
2. 汕头大学医学院, 广东汕头 515000
3. 北京大学深圳医院呼吸与危重症医学科, 广东深圳 518000
Correlation between dyslipidemia and rheumatoid arthritis associated interstitial lung disease
Qi WU1,2,Yue-ming CAI1,Juan HE1,Wen-di HUANG3,Qing-wen WANG1,*( )
)
- 1. Department of Rheumatism and Immunology, Peking University Shenzhen Hospital; Shenzhen Key Laboratory of Immunity and Inflammatory Diseases, Shenzhen 518000, Guangdong, China
2. Shantou University Medical College, Shantou 515000, Guangdong, China
3. Department of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Peking University Shenzhen Hospital Shenzhen, Shenzhen 518000, Guangdong, China
摘要:
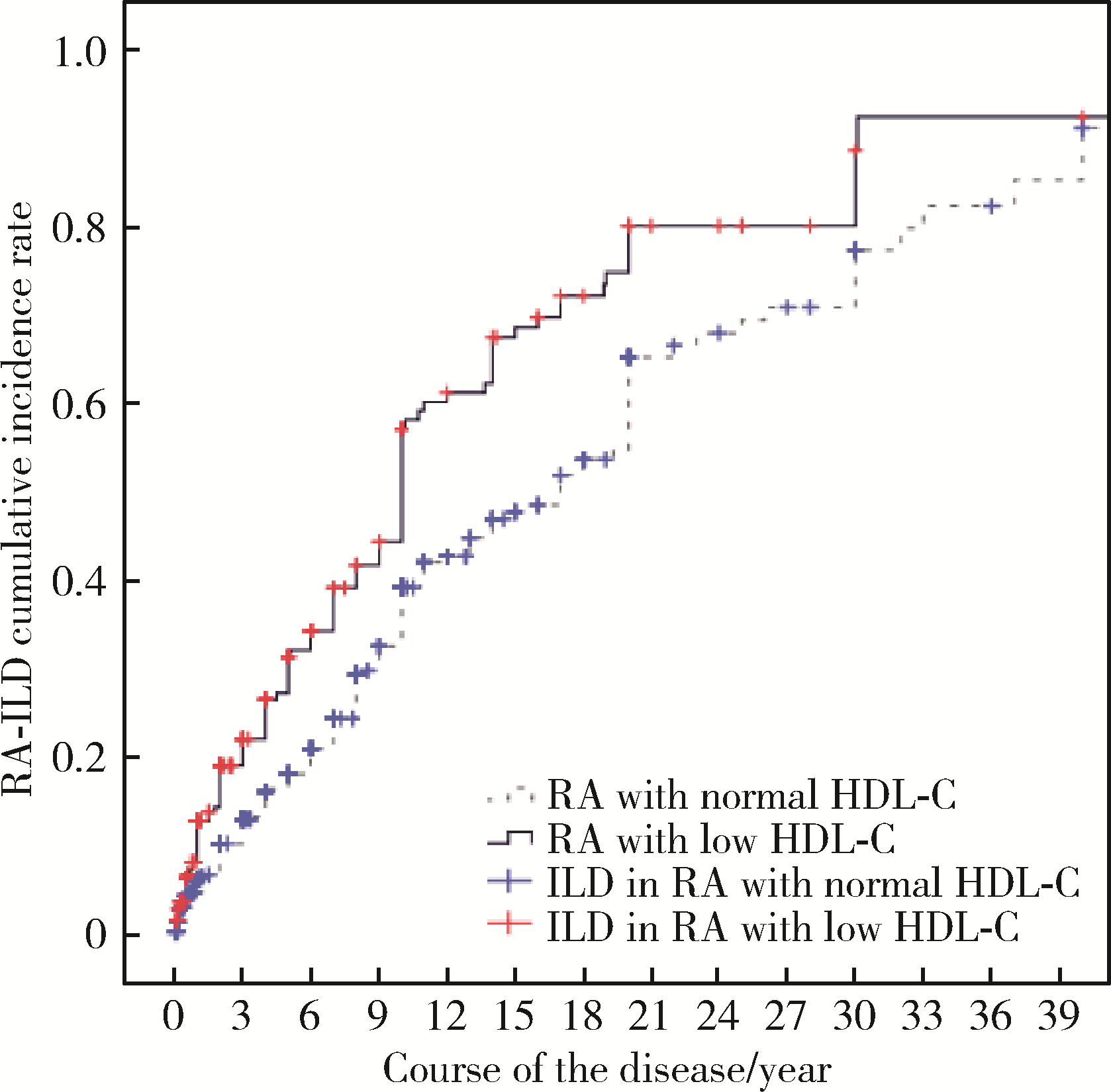
目的: 回顾性分析了解血脂异常与类风湿关节炎肺间质病变(rheumatoid arthritis associated interstitial lung disease, RA-ILD)的相关性。方法: 收集2015年1月至2020年7月期间在北京大学深圳医院风湿免疫科住院符合《2010年美国风湿病学会/欧洲风湿病防治联合会类风湿关节炎(rheumatoid arthritis, RA)分类标准》的患者病例资料,按照有无合并肺间质病变(interstitial lung disease, ILD)分组,对一般资料、临床特征及检验检查等数据单因素检验后将差异有意义的因素纳入Logistics多因素回归分析。根据有无血脂异常分组,分析血脂异常与RA-ILD的发生率、发生的中位时间及临床表现等相关性。结果: 共纳入737例RA患者,其中282例(38.26%)发生ILD,从开始出现RA相关的临床症状至发生ILD的中位时间为13(95%CI 11.33~14.67)年。多因素Logistic回归分析结果显示:低密度脂蛋白胆固醇(low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, LDL-C)是RA-ILD可能的危险因素(OR 1.452,95%CI 1.099~1.918,P=0.009),高密度脂蛋白胆固醇(high-density lipoprotein cholesterol,HDL-C)是RA-ILD可能的保护因素(OR 0.056,95%CI 0.025~0.125,P < 0.001)。在737例RA患者中,LDL-C升高及HDL-C降低的RA患者ILD的发生率均分别高于LDL-C正常及HDL-C正常的患者(分别为57.45% vs. 36.96%,P < 0.001;47.33% vs. 33.81%,P < 0.001)。HDL-C降低的RA患者出现ILD的中位时间明显短于HDL-C正常的RA患者[10.0(95%CI 9.33~10.67)年vs. 17.0(95%CI 14.58~19.42)年,P < 0.001]。RA患者的HDL-C水平与疾病活动呈负相关。RA-ILD患者中,HDL-C降低的患者胸部HRCT出现寻常型间质性肺炎(usual interstitial pneumonia, UIP)的比例高于HDL-C正常的患者(60.00% vs. 53.29%,P=0.002),LDL-C升高的RA-ILD患者出现用力肺活量(forced vital capacity,FVC)下降的发生率高于LDL-C正常的RA-ILD患者(50.00% vs.21.52%,P=0.015),HDL-C降低的RA-ILD患者出现FVC及一氧化碳弥散量(diffusing capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide, DLCO)下降的发生率高于HDL-C正常的RA-ILD患者(分别为26.92% vs.16.18%,P=0.003;80.76% vs. 50.00%,P=0.010)。结论: LDL-C可能是RA-ILD的潜在危险因素;HDL-C可能是RA-ILD的潜在保护因素;HDL-C水平与RA病情活动呈负相关;HDL-C降低的RA患者出现ILD的时间更早。
中图分类号:
- R593.2
| 1 |
Figus FA , Piga M , Azzolin I , et al. Rheumatoid arthritis: Extra-articular manifestations and comorbidities[J]. Autoimmun Rev, 2021, 20 (4): 102776.
doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2021.102776 |
| 2 | Suda T . UP-to-date information on rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease[J]. Clin Med Insights Circ Respir Pulm Med, 2015, 9, 155- 162. |
| 3 |
Hyldgaard C , Hilberg O , Pedersen AB , et al. A population-based cohort study of rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease: Comorbidity and mortality[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2017, 76, 1700- 1706.
doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2017-211138 |
| 4 |
Fazeli M S , Khaychuk V , Wittstock K , et al. Rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease: Epidemiology, risk/prognostic factors, and treatment landscape[J]. Clin Exp Rheumatol, 2021, 39 (5): 1108- 1118.
doi: 10.55563/clinexprheumatol/h9tc57 |
| 5 | Uzma E , Tasnim A , Danish K . Lipid abnormalities in patients with rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Pak J Med SCI, 2017, 33 (1): 227- 230. |
| 6 | 陈哲. 血清脂蛋白异常与IPF关系及其临床意义[D]. 广西: 广西医科大学, 2018. |
| 7 |
Aletaha D , Neogi T , Silman AJ , et al. 2010 rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: An American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative[J]. Arthritis Rheum, 2010, 62 (9): 2569- 2581.
doi: 10.1002/art.27584 |
| 8 |
Travis WD , Costabel U , Hansell DM , et al. An official American Thoracis Society/European Respiratory Society statement: Update of the international multisciplinary classification of the idiopathic interstitial pneumonias[J]. Am J Respir Crit Care Med, 2013, 188 (6): 733- 748.
doi: 10.1164/rccm.201308-1483ST |
| 9 | 中国成人血脂异常防治指南修订联合委员会. 中国成人血脂异常防治指南(2016年修订版)[J]. 中华全科医师杂志, 2017, 16 (1): 15- 35. |
| 10 |
Semb AG , Ikdahl E , Wibetoe G , et al. Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease prevention in rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Nat Rev Rheumatol, 2020, 16 (7): 361- 379.
doi: 10.1038/s41584-020-0428-y |
| 11 |
Hollan I , Ronda N , Dessein P , et al. Lipd management in rheumatoid arthritis: A position paper of the Working Group on Cardiovascular Pharmacotherapy of the European Society of Cardiology[J]. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Pharmacother, 2020, 6 (2): 104- 114.
doi: 10.1093/ehjcvp/pvz033 |
| 12 |
Charles-Schoeman C , Meriwether D , Lee YY , et al. High levels of oxidized fatty acids in HDL are associated with impaired HDL function in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Clin Rheumatol, 2018, 37 (3): 615- 622.
doi: 10.1007/s10067-017-3896-y |
| 13 | Gordon EM , Figueroa DM , Barochia AV , et al. High-density lipoproteins and apolipoprotein A-I: Potential new players in the prevention and treatment of lung disease[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2016, 7, 323. |
| 14 |
Hee LE , Eun-Ju L , Jeong KH , et al. Overexpression of apolipoprotein A1 in the lung abrogates fibrosis in experimental silicosis[J]. PloS One, 2013, 8 (2): e55827.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0055827 |
| 15 |
Belchamber K , Donnelly L E . Targeting defective pulmonary innate immunity: A new therapeutic option?[J]. Pharmacol Ther, 2020, 209, 107500.
doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2020.107500 |
| 16 | Tall AR , Yvan-Charvet L . Cholesterol, inflammation and innate immunity[J]. Nat Rev Immunol, 2015, 15 (2): 104- 116. |
| 17 | Laurent YC , Fabrizia B , Renè GR , et al. Immunometabolic function of cholesterol in cardiovascular disease and beyond[J]. Cardiovasc Res, 2019, 115 (9): 1393- 1407. |
| 18 | Chistiakov DA , ORekhov AN , Bobryshev YV . ApoA1 and ApoA1-specific self-antibodies in cardiovascular disease[J]. Lab Invest, 2016, 96 (7): 708- 718. |
| 19 | Vuilleumier N , Bratt J , Alizadeh R , et al. Anti-apoA-1 IgG and oxidized LDL are raised in rheumatoid arthritis (RA): Potential associations with cardiovascular disease and RA disease activity[J]. Scand J Rheumatol, 2010, 39 (6): 447- 453. |
| 20 | Salaffi F , Carotti M , di Carlo M , et al. High-resolution computed tomography of the lung in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: Prevalence of interstitial lung disease involvement and determinants of abnormalities[J]. Medicine (Baltimore), 2019, 98 (38): e17088. |
| 21 | Kelly CA , Saravanan V , Nisar M , et al. Rheumatoid arthritis-related interstitial lung disease: associations, prognostic factors and physiological and radiological characteristics: A large multicentre UK study[J]. Rheumatology (Oxford), 2014, 53 (9): 1676- 1682. |
| 22 | Ito Y , Arita M , Kumagai S , et al. Radiological fibrosis score is strongly associated with worse survival in rheumatoid arthritis-related interstitial lung disease[J]. Mod Rheumatol, 2019, 29 (1): 98- 104. |
| [1] | 刘东武, 陈杰, 高明利, 于静. 类风湿关节炎伴发淋巴结Castleman样病理改变1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 928-931. |
| [2] | 黄会娜,赵静,赵祥格,白自然,李霞,王冠. 乳酸对类风湿关节炎患者外周血CD4+T细胞亚群的调控作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 519-525. |
| [3] | 汤晓菲,李永红,丁秋玲,孙卓,张阳,王育梅,田美伊,刘坚. 类风湿关节炎患者下肢深静脉血栓发病率及危险因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 279-283. |
| [4] | 邹雪,白小娟,张丽卿. 艾拉莫德联合托法替布治疗难治性中重度类风湿关节炎的疗效[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 1013-1021. |
| [5] | 张警丰,金银姬,魏慧,姚中强,赵金霞. 体重指数与类风湿关节炎临床特征的相关性分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 993-999. |
| [6] | 金银姬,孙琳,赵金霞,刘湘源. 血清IgA型抗鼠科肉瘤病毒癌基因同源物B1抗体在类风湿关节炎中的意义[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 631-635. |
| [7] | 蔡文心,李仕成,刘一鸣,梁如玉,李静,郭建萍,胡凡磊,孙晓麟,李春,刘栩,叶华,邓立宗,李茹,栗占国. 类风湿关节炎临床分层及其特征的横断面研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1068-1073. |
| [8] | 程昉,杨邵英,房星星,王璇,赵福涛. CCL28-CCR10通路在类风湿关节炎单核细胞迁移中的作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1074-1078. |
| [9] | 刘蕊,赵金霞,闫良. 类风湿关节炎合并下肢静脉血栓患者的临床特点[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1079-1085. |
| [10] | 张警丰,金银姬,魏慧,姚中强,赵金霞. 类风湿关节炎患者生活质量与疾病活动度的横断面研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1086-1093. |
| [11] | 闫辉,逄璐,李雪迎,杨文双,蒋世菊,刘平,闫存玲. 单中心就诊2~18岁儿童胆固醇水平异常发生率及病因分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(2): 217-221. |
| [12] | 高超,陈立红,王莉,姚鸿,黄晓玮,贾语博,刘田. 类风湿关节炎合并纤维肌痛简易分类标准的临床验证[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(2): 278-282. |
| [13] | 娄雪,廖莉,李兴珺,王楠,刘爽,崔若玫,徐健. 类风湿关节炎患者外周血TWEAK基因启动子区甲基化状态及其表达[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(6): 1020-1025. |
| [14] | 钟华,徐丽玲,白明欣,苏茵. 类风湿关节炎患者趋化因子CXCL9和CXCL10在骨侵蚀中的作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(6): 1026-1031. |
| [15] | 罗靓,霍文岗,张钦,李春. 类风湿关节炎合并角膜溃疡的临床特点和相关因素分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(6): 1032-1036. |
|
||