北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (1): 25-31. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2024.01.005
血管化骨瓣重建颌骨种植体周软组织病理学特点
- 北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院牙周科,国家口腔医学中心,国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心,口腔生物材料和数字诊疗装备国家工程研究中心,北京 100081
Histopathological characteristics of peri-implant soft tissue in reconstructed jaws with vascularized bone flaps
Jiayun DONG,Xuefen LI,Ruifang LU*( ),Wenjie HU,Huanxin MENG
),Wenjie HU,Huanxin MENG
- Department of Periodontology, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Center for Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Research Center of Oral Biomaterials and Digi-tal Medical Devices, Beijing 100081, China
摘要:
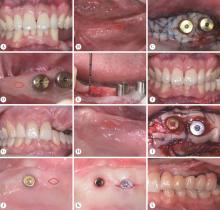
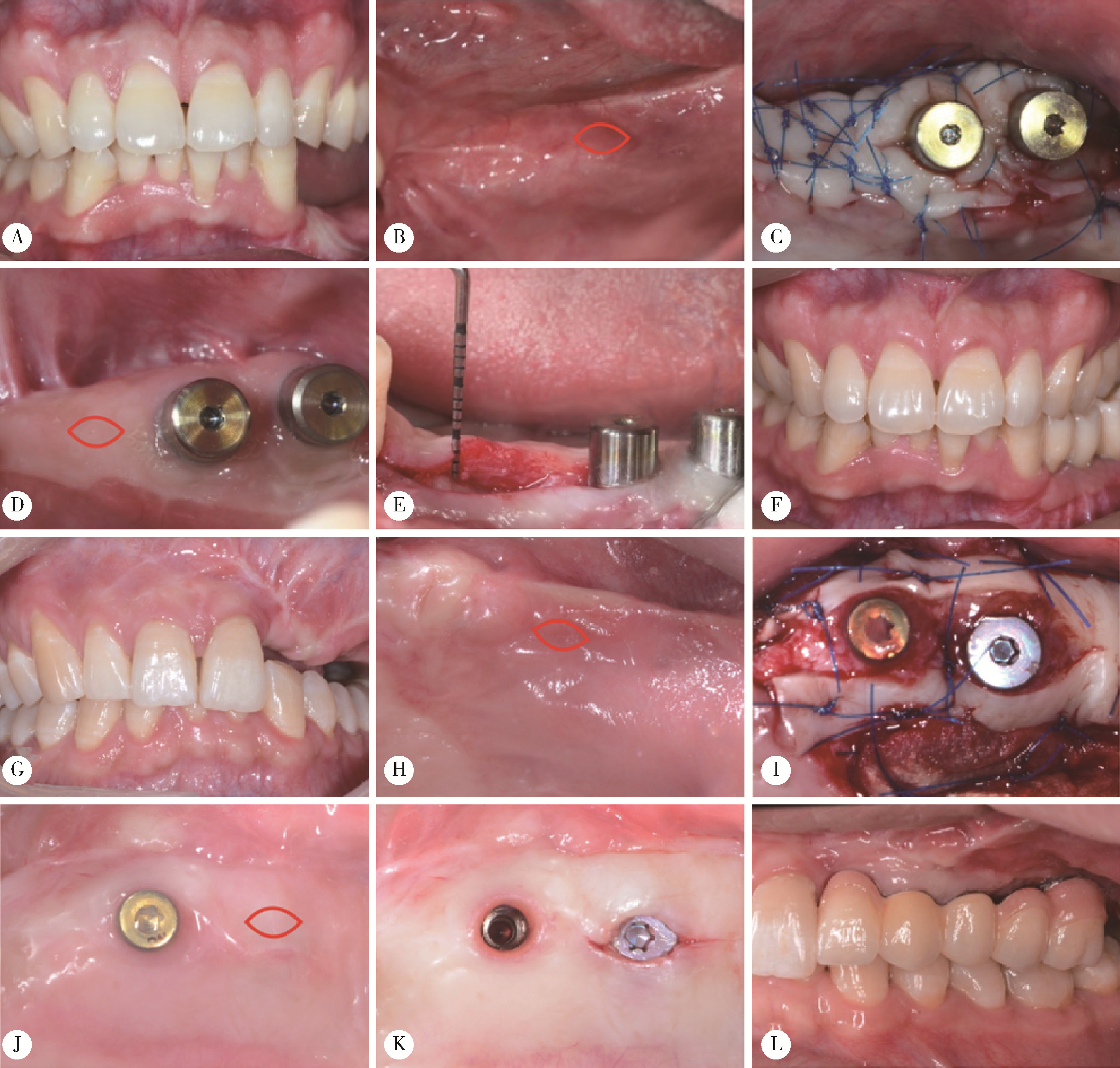
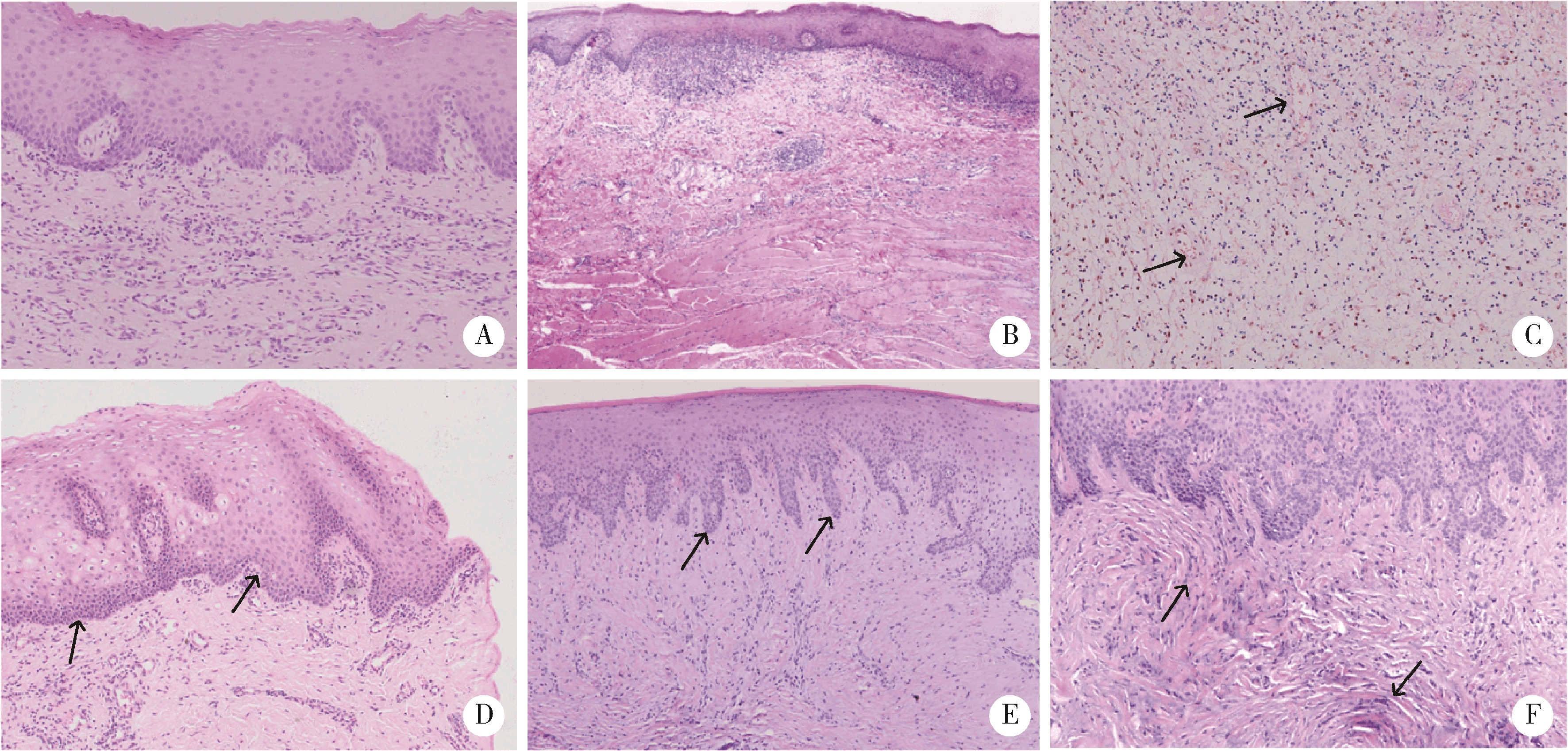
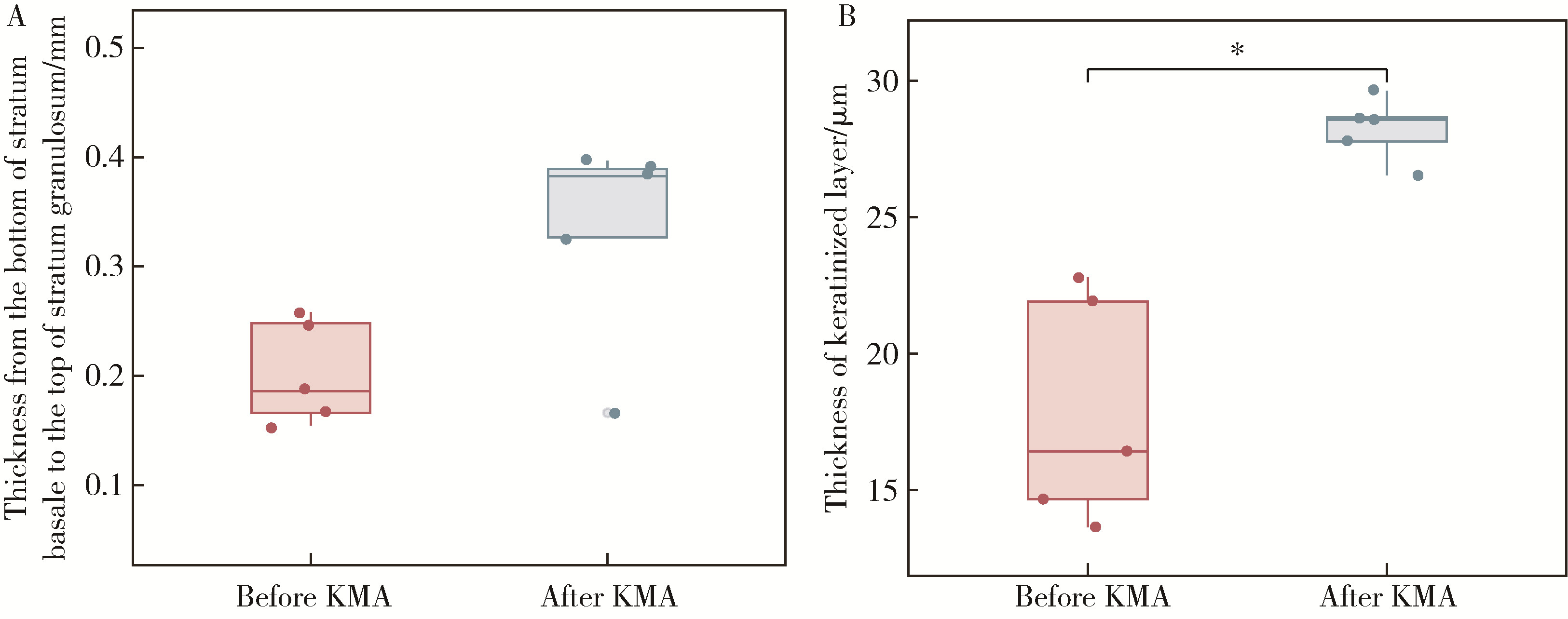
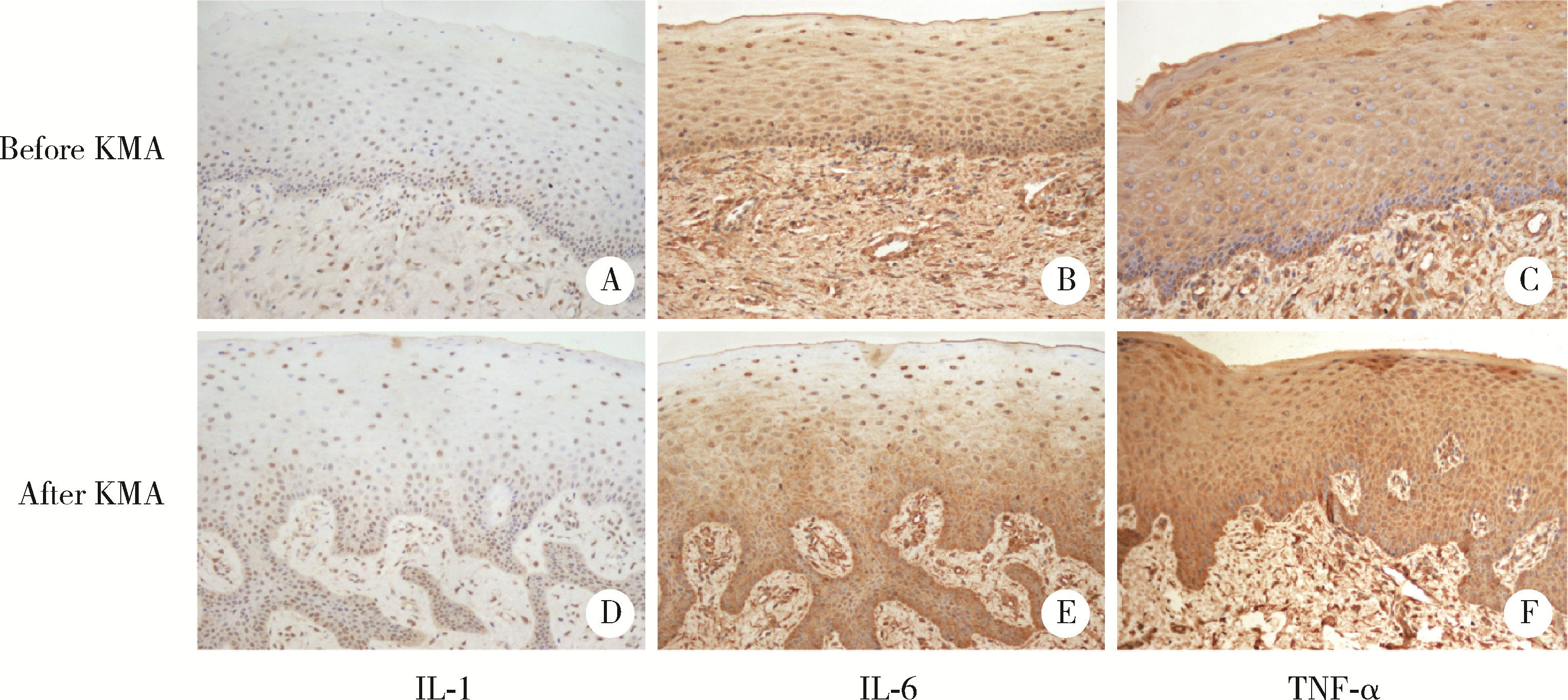
目的: 分析血管化骨瓣重建颌骨区域种植体周软组织结构特点,以及游离龈移植术后种植体周软组织结构改变,为临床治疗提供指导。方法: 共纳入2020年10月至2022年12月就诊于北京大学口腔医院牙周科的患者20例,其中5例作为健康对照,全身及牙周健康,行牙冠延长术,收集牙冠延长术中切除的部分健康天然角化龈;15例在颌骨重建区域行游离龈移植术,有10例为腓骨瓣重建,5例为髂骨瓣重建,均在术前采集嵴顶软组织,其中5例患者(3例为腓骨瓣重建,2例为髂骨瓣重建)在术后8周时再次采集种植体周软组织。所有软组织采用苏木精-伊红染色观察组织结构特点,测量上皮钉突处基底层底端至颗粒层顶端的厚度及角化层厚度,采用免疫组织化学染色方法检测白细胞介素-1(interlukin-1, IL-1)、白细胞介素-6(interlukin-6, IL-6)、肿瘤坏死因子-α(tumor necrosis factor-α, TNF-α)的分布和表达水平。结果: 与健康天然角化龈相比,颌骨重建患者种植体周黏膜缺乏正常复层鳞状上皮的组织结构,上皮钉突处基底层底端至颗粒层顶端的厚度及角化层厚度更小[0.36 (0.35, 0.47) mm vs. 0.27 (0.20, 0.30) mm, P<0.05; 26.37 (24.12, 31.53) μm vs. 16.49 (14.90, 23.37) μm, P<0.05]。游离龈移植术后,上皮钉突处基底层底端至颗粒层顶端的厚度较治疗前呈现增加的趋势[0.38 (0.25, 0.39) mm vs. 0.19 (0.16, 0.25) mm, P=0.059],角化层厚度较治疗前增加,差异有统计学意义[28.57 (27.16, 29.14) μm vs. 16.42 (14.16, 22.35) μm, P<0.05],形成了与健康天然角化龈类似的上皮结构;IL-1、IL-6、TNF-α的阳性细胞个数较术前更多,差异有统计学意义[11.00 (9.16, 18.00) vs. 0.67 (0.17, 8.93), P<0.05; 21.89 (15.00, 28.12) vs. 13.00 (8.50, 14.14), P<0.05; 2.83 (1.68, 5.00) vs. 0.22 (0.04, 0.63), P<0.05];术后平均光密度值升高,差异有统计学意义[0.18 (0.17, 0.21) vs. 0.15 (0.14, 0.17), P<0.05; 0.36 (0.33, 0.37) vs. 0.28 (0.26, 0.33), P<0.05; 0.30 (0.28, 0.42) vs. 0.23 (0.22, 0.29), P<0.05],且与健康天然角化龈之间的差异无统计学意义。结论: 颌骨重建区域种植体周角化黏膜缺失或不足的患者,通过游离龈移植行角化黏膜增量有利于改善种植体周黏膜的组织结构,维护种植体周黏膜的稳定性。
中图分类号:
- R781.4
| 1 |
Goker F , Baj A , Bolzoni AR , et al. Dental implant-based oral rehabilitation in patients reconstructed with free fibula flaps: Clinical study with a follow-up 3 to 6 years[J]. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res, 2020, 22 (4): 514- 522.
doi: 10.1111/cid.12928 |
| 2 |
Pellegrino G , Tarsitano A , Ferri A , et al. Long-term results of osseointegrated implant-based dental rehabilitation in oncology patients reconstructed with a fibula free flap[J]. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res, 2018, 20 (5): 852- 859.
doi: 10.1111/cid.12658 |
| 3 |
Sonmez TT , Prescher A , Salama A , et al. Comparative clinico-anatomical study of ilium and fibula as two commonly used bony donor sites for maxillofacial reconstruction[J]. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2013, 51 (8): 736- 741.
doi: 10.1016/j.bjoms.2013.07.010 |
| 4 | 林野, 邱立新, 胡秀莲, 等. 硬腭游离黏膜移植在种植体周软组织结构重建中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2007, 39 (1): 21- 25. |
| 5 | Shan X , Han D , Ge Y , et al. Clinical outcomes of keratinized mucosa augmentation in jaws reconstructed with fibula or iliac bone flaps[J]. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2021, 51 (7): 949- 956. |
| 6 |
Han J , Ulevitch RJ . Limiting inflammatory responses during activation of innate immunity[J]. Nat Immunol, 2005, 6 (12): 1198- 1205.
doi: 10.1038/ni1274 |
| 7 |
Vignoletti F , Nunez J , de Sanctis F , et al. Healing of a xenoge-neic collagen matrix for keratinized tissue augmentation[J]. Clin Oral Implants Res, 2015, 26 (5): 545- 552.
doi: 10.1111/clr.12441 |
| 8 |
Wu T , Xiong X , Zhang W , et al. Morphogenesis of rete ridges in human oral mucosa: A pioneering morphological and immunohistochemical study[J]. Cells Tissues Organs, 2013, 197 (3): 239- 248.
doi: 10.1159/000342926 |
| 9 |
Sa GL , Liu ZK , Ren JG , et al. Keratinocyte growth factor (KGF) induces podosome formation via integrin-Erk1/2 signaling in human immortalized oral epithelial cells[J]. Cell Signal, 2019, 61, 39- 47.
doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2019.05.007 |
| 10 |
Sa GL , Xiong XP , Ren JG , et al. KGF enhances oral epithelial adhesion and rete peg elongation via integrins[J]. J Dent Res, 2017, 96 (13): 1546- 1554.
doi: 10.1177/0022034517720360 |
| 11 | Squier C , Brogden KA . Human oral mucosa: Development, structure and function[M]. Chichester: John Wiley & Sons, 2011: 55- 57. |
| 12 |
Lawlor K , Kaur P . Dermal contributions to human interfollicular epidermal architecture and self-renewal[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2015, 16 (12): 28098- 28107.
doi: 10.3390/ijms161226078 |
| 13 |
de Luca M , Albanese E , Megna M , et al. Evidence that human oral epithelium reconstituted in vitro and transplanted onto patients with defects in the oral mucosa retains properties of the original donor site[J]. Transplantation, 1990, 50 (3): 454- 459.
doi: 10.1097/00007890-199009000-00019 |
| 14 | Henry J , Toulza E , Hsu CY , et al. Update on the epidermal differentiation complex[J]. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed), 2012, 17 (4): 1517- 1532. |
| 15 |
Nemes Z , Steinert PM . Bricks and mortar of the epidermal barrier[J]. Exp Mol Med, 1999, 31 (1): 5- 19.
doi: 10.1038/emm.1999.2 |
| 16 |
孙凯, 刘丽骏, 张倩倩, 等. Wistar大鼠自然衰老过程中口腔颊黏膜上皮厚度的改变[J]. 中华老年口腔医学杂志, 2018, 16 (6): 333- 335.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2973.2018.06.004 |
| 17 | Sabine E , Groeger JM . Epithelial barrier and oral bacterial infection[J]. Periodontology 2000, 2015, 69 (1): 46- 67. |
| 18 | Jandinski JJ . Osteoclast activating factor is now interleukin-1 beta: Historical perspective and biological implications[J]. J Oral Pathol, 1988, 17 (4): 145- 152. |
| 19 | Kondo S , Sauder DN . Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor type 1 (p55) is a main mediator for TNF-alpha-induced skin inflammation[J]. Eur J Immunol, 1997, 27 (7): 1713- 1718. |
| [1] | 王聪伟,高敏,于尧,章文博,彭歆. 游离腓骨瓣修复下颌骨缺损术后义齿修复的临床分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 66-73. |
| [2] | 周颖,赵宁,黄竑远,李庆祥,郭传瑸,郭玉兴. 双层软组织缝合封闭技术在下颌骨中早期药物相关性颌骨骨坏死患者手术治疗中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 51-56. |
| [3] | 赵然,刘延青,田华. 应用累积和控制图分析全膝关节置换术中电子压力垫片指导软组织平衡的学习曲线[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 658-664. |
| [4] | 张众,孟焕新,韩劼,张立,释栋. 软组织垂直厚度对牙周炎患者种植修复临床效果的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(2): 332-338. |
| [5] | 张添文,王晓霞,李自力,伊彪,梁成,王兴. 上颌前突患者鼻唇区软组织三维形态测量方法的建立[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(5): 944-948. |
| [6] | 赵丽萍, 詹雅琳, 胡文杰, 王浩杰, 危伊萍, 甄敏, 徐涛, 刘云松. 磨牙位点保存后进行种植修复及软组织增量的1例报告[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2016, 48(6): 1090-1094. |
| [7] | 王寿宇*, 张振*, 吴青松, 吕德成. 负压封闭引流术在下肢自体植皮术中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2012, 44(6): 966-969. |
| [8] | 蔡雷, 高子芬, 黄啸原. 软组织间叶性软骨肉瘤临床病理分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2006, 38(5): 501-505. |
| [9] | 许天民, 刘妍, 黄微, 林久祥. 临界病例拔牙与不拔牙矫治对颅颌面软组织形态的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2004, 36(6): 650-654. |
| [10] | 米川, 马忠泰, 施学东, 付占立. 18F-2-脱氧葡萄糖显像在骨及软组织恶性肿瘤中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2003, 35(3): 336-336. |
| [11] | 郑旭, 林久祥, 谢以岳. (牙合)型、骨型、软组织面型的相关表型研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2003, 35(1): 61-64. |
| [12] | 柳萍, 那加, 李峻, 徐元洪. 软组织恶性纤维组织细胞瘤临床病理特点和预后相关因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2001, 33(4): 373-376. |
|
||