北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (5): 845-852. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2024.05.015
抗唾液腺蛋白1抗体联合抗腮腺分泌蛋白抗体对干燥综合征的诊断价值
- 河北医科大学第二医院风湿免疫科,石家庄 050011
Diagnostic values of anti-salivary gland protein-1 antibody combined with anti-parotid secretory protein antibody for Sjögren's syndrome
Yushu YANG, Xuan QI, Meng DING, Wei WANG, Huifang GUO, Lixia GAO*( )
)
- Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, the Second Hospital of Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang 050011, China
摘要:
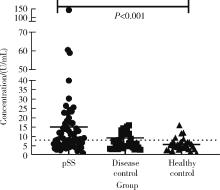
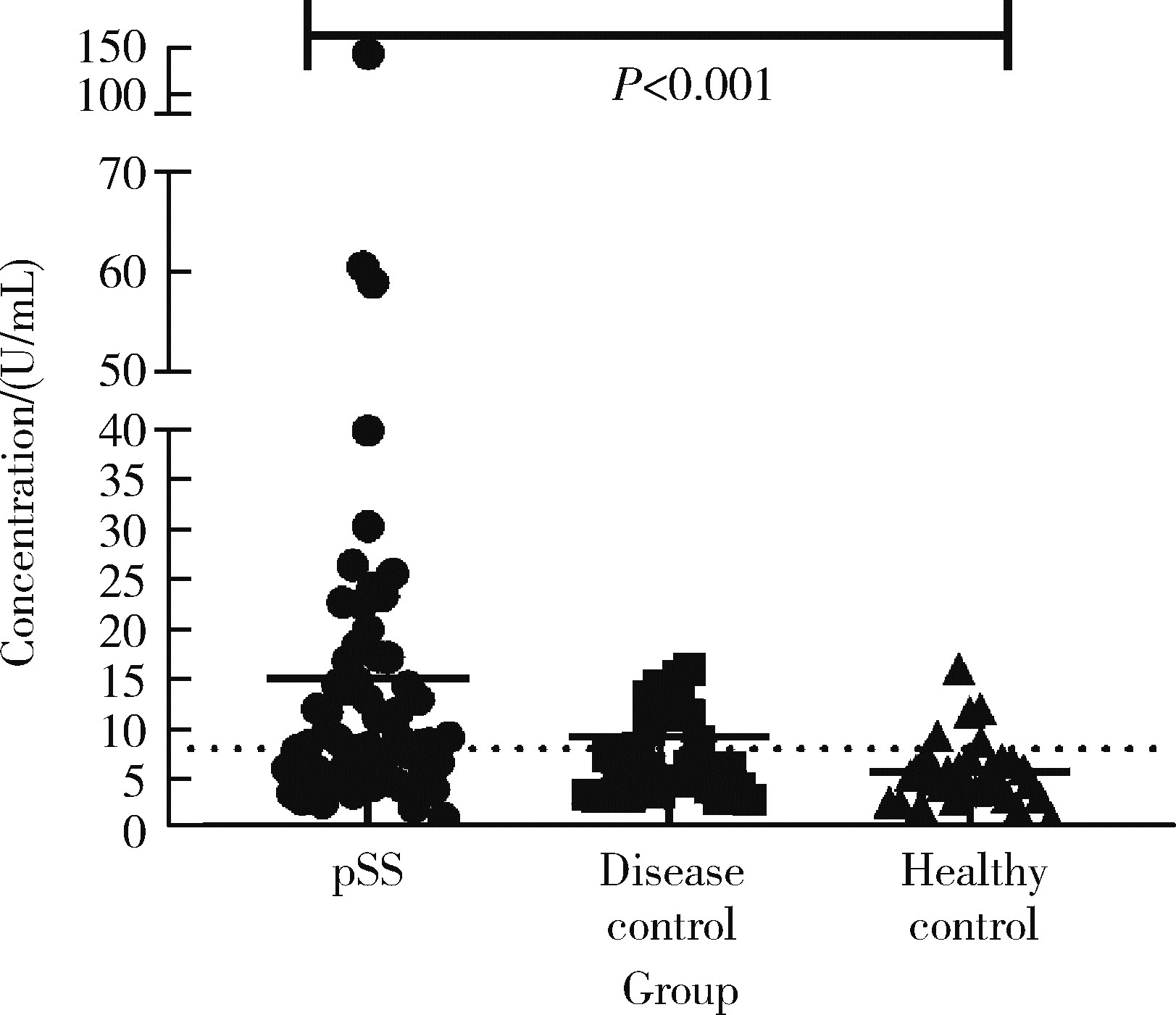
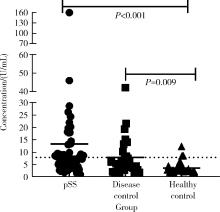
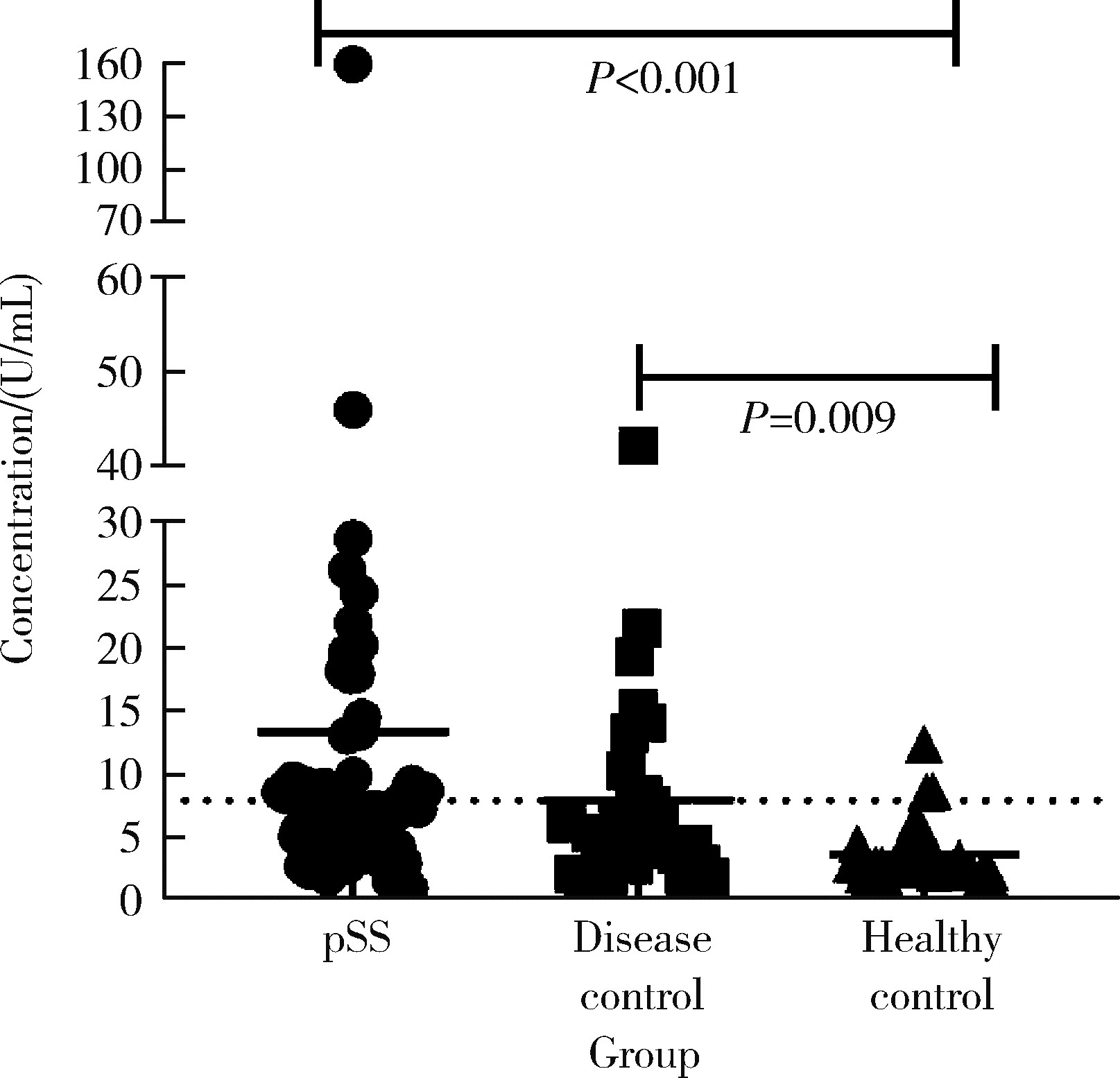
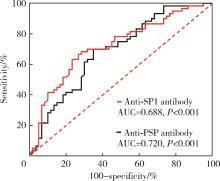
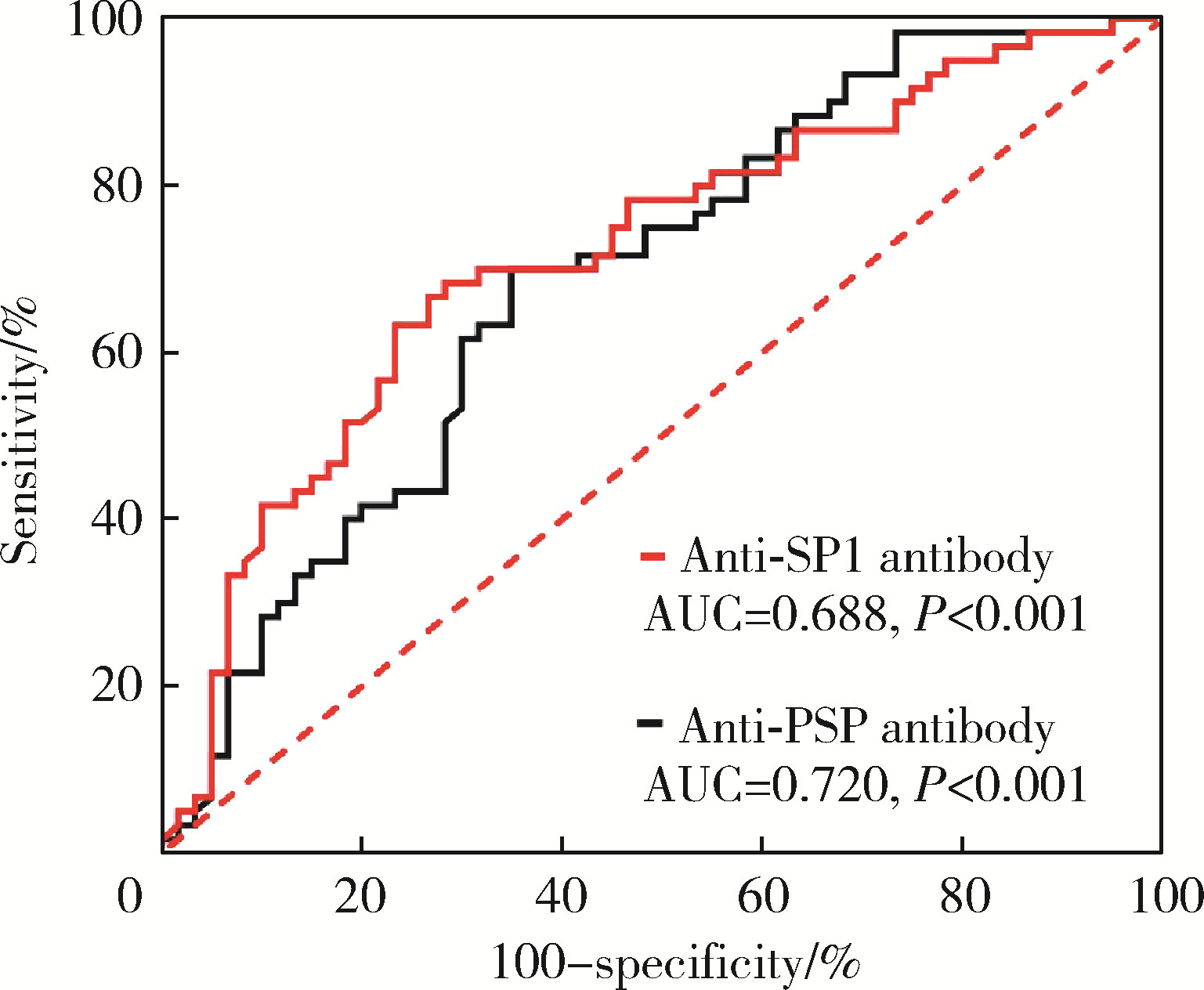
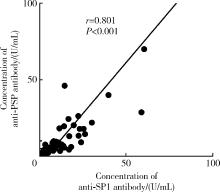
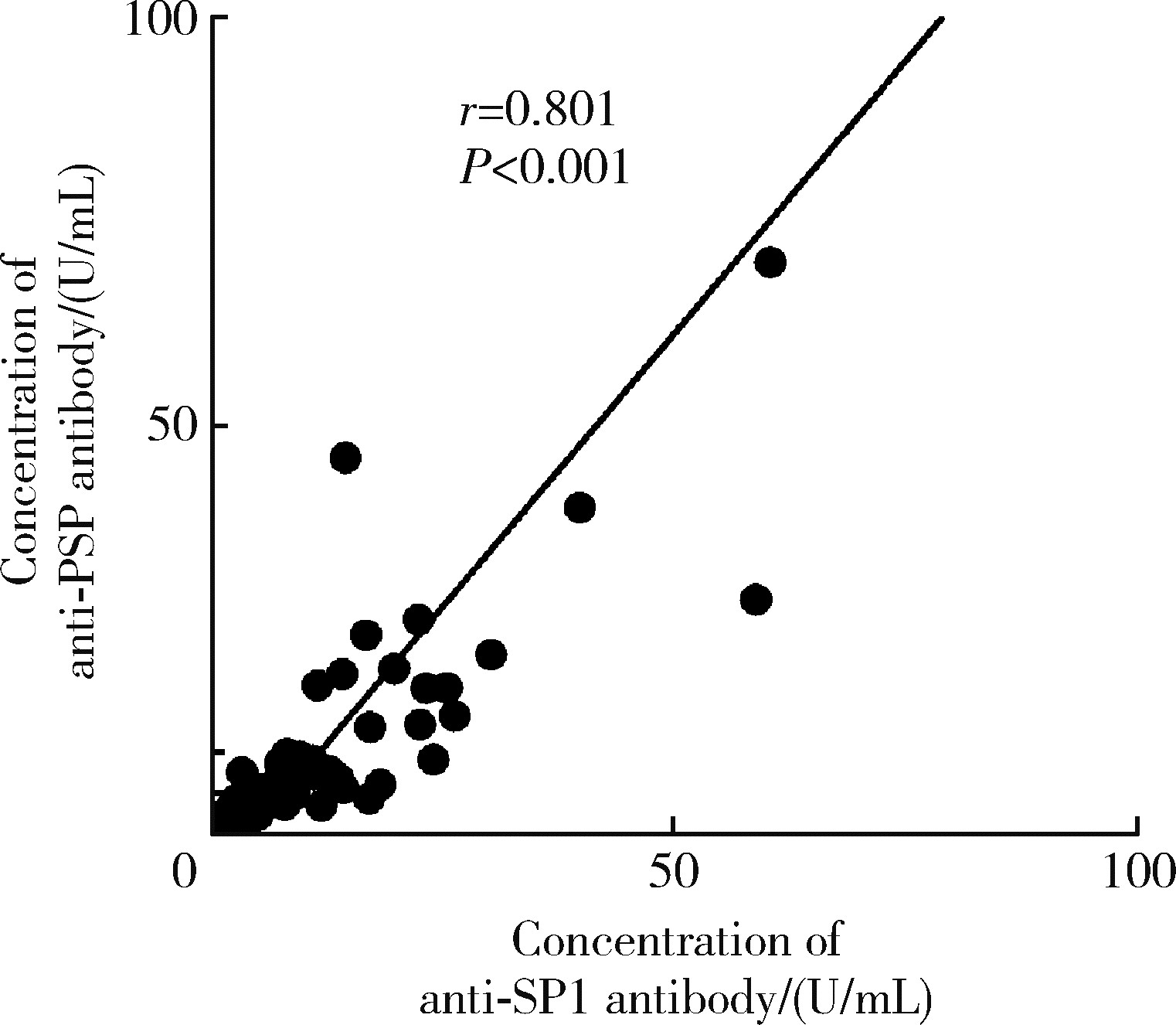
目的: 探讨抗唾液腺蛋白1(salivary protein 1, SP1)抗体联合抗腮腺分泌蛋白(parotid secretory protein, PSP)抗体在干燥综合征(Sjögren’s syndrome,SS)诊断中的价值。方法: 收集2020年1月至2022年12月就诊于河北医科大学第二医院风湿免疫科门诊及住院部的原发性SS(primary SS, pSS)患者60例, 其他自身免疫病伴有口干和(或)眼干症状的患者30例为疾病对照组,体检中心的健康体检者30例为健康对照组,留取血清备用,同时记录一般资料、临床表现、实验室指标及其它辅助检查。采用2016年美国风湿病学会(American College of Rheumatology,ACR)/欧洲抗风湿病联盟(European League against Rheumatism,EULAR)干燥综合征分类标准作为pSS诊断金标准。采用化学发光免疫分析法检测免疫球蛋白G(immunoglobulin G,IgG)型抗SP1抗体和抗PSP抗体。用受试者工作特征(receiver operating characteristic, ROC)曲线评估抗SP1抗体和抗PSP抗体诊断pSS的准确性,并比较pSS组中抗SP1抗体和抗PSP抗体阳性患者与阴性患者的临床特征。采用t检验及Mann-Whitney U检验、方差分析、Kruskal-Wallis检验、卡方检验或Fisher确切概率法、Spearman相关分析进行统计学分析。结果: 3组之间年龄(F=1.406,P=0.495)、性别(χ2=2.105,P=0.349)差异无统计学意义。抗SP1抗体(H=16.73, P < 0.001)和抗PSP抗体(H=26.09, P < 0.001)在3组之间表达水平差异有统计学意义。组间比较发现,抗SP1抗体和抗PSP抗体表达水平在pSS和健康对照组之间差异均有统计学意义(P < 0.001),抗PSP抗体表达水平在疾病对照组和健康对照组之间差异有统计学意义(P=0.009)。在pSS组、疾病对照组、健康对照组中,抗SP1抗体阳性率分别为58.33% vs. 40.00% vs.13.33%,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.001);抗PSP抗体阳性率分别为75.00% vs. 56.17% vs.16.67%,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.001)。抗SP1抗体、抗PSP抗体的曲线下面积分别为0.688(P < 0.001)、0.720 (P < 0.001),敏感性分别为58.33%(35/60)和75.00%(45/60),特异性分别为70.00%(42/60)和63.33%(38/60),阳性预测值分别为66.04%(35/53)和67.16%(45/67),阴性预测值分别为54.55%(42/77)和71.70%(38/53)。13例pSS患者中抗干燥综合征A (Sjögren’s syndrome A, SSA, 包括SSA52和SSA60)抗体和抗干燥综合征B (Sjögren’s syndrome B, SSB) 抗体均阴性,其中11例抗SP1抗体和抗PSP抗体均阳性,1例抗SP1抗体单独阳性,1例抗PSP抗体单独阳性。在pSS患者中,分别对抗SP1抗体和抗PSP抗体阳性与阴性组临床特征进行比较,抗SP1抗体阳性较阴性患者病程短(Z=-2.277,P=0.023);抗PSP抗体阳性较阴性患者比较:年龄相对较轻(t=2.598,P < 0.05),类风湿因子(rheumatoid factor,RF)阳性率较高(P=0.002),IgG水平相对较高(t=3.806,P=0.003);对pSS患者抗SP1抗体和抗PSP抗体的相关性进行分析,发现二者之间存在明显的相关性(r=0.801,P < 0.001)。结论: 抗SP1抗体和抗PSP抗体在SS诊断中价值均较高,其中抗SP1抗体有助于pSS的早期诊断;两种抗体联合检测有助于抗SSA抗体和抗SSB抗体阴性pSS患者的早期诊断。
中图分类号:
- R593.2
| 1 | Goules AV , Argyropoulou OD , Pezoulas VC , et al. Primary Sjögren's syndrome of early and late onset: Distinct clinical phenotypes and lymphoma development[J]. Front Immunol, 2020, 11, 594096. |
| 2 | Vitali C , Bombardieri S , Jonsson R , et al. Classification criteria for Sjögren's syndrome: A revised version of the European criteria proposed by the American-European Consensus Group[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2002, 61 (6): 554- 558. |
| 3 | Shiboski SC , Shiboski CH , Criswell L , et al. American College of Rheumatology classification criteria for Sjögren's syndrome: A data-driven, expert consensus approach in the Sjögren's International Collaborative Clinical Alliance cohort[J]. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken), 2012, 64 (4): 475- 487. |
| 4 | Shiboski CH , Shiboski SC , Seror R , et al. 2016 American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism classification criteria for primary Sjögren's syndrome: A consensus and data-driven methodology involving three international patient cohorts[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2017, 76 (1): 9- 16. |
| 5 | Hoshina Y , Wong KH , Galli J , et al. Neurologic involvement in seronegative primary Sjögren's syndrome with positive minor salivary gland biopsy: A single-center experience[J]. Front Neurol, 2023, 14, 1174116. |
| 6 | Chen J , He Q , Yang J , et al. Anti-SSA/SSB-negative primary Sjögren's syndrome showing different clinical phenotypes: A retrospective study of 934 cases[J]. Adv Rheumatol, 2023, 63 (1): 21. |
| 7 | Bodeutsch C , de Wilde PC , Kater L , et al. Labial salivary gland biopsy in Sjögren's syndrome[J]. Neth J Med, 1992, 40 (3/4): 148- 157. |
| 8 | Theander E , Jonsson R , Sjöström B , et al. Prediction of Sjögren's syndrome years before diagnosis and identification of patients with early onset and severe disease course by autoantibody profiling[J]. Arthritis Rheumatol, 2015, 67 (9): 2427- 2436. |
| 9 | Jonsson R , Theander E , Sjöström B , et al. Autoantibodies present before symptom onset in primary Sjögren syndrome[J]. JAMA, 2013, 310 (17): 1854- 1855. |
| 10 | Lee AYS , Lin MW . Serological intermolecular epitope spreading in a patient with primary Sjögren's syndrome[J]. BMJ Case Rep, 2023, 16 (5): e254632. |
| 11 | Mona M , Mondello S , Hyon JY , et al. Clinical usefulness of anti-muscarinic type 3 receptor autoantibodies in patients with primary Sjögren's syndrome[J]. Clin Exp Rheumatol, 2021, 39 (4): 795- 803. |
| 12 | Alam J , Koh JH , Kwok SK , et al. Functional epitopes for anti-aquaporin 5 antibodies in Sjögren syndrome[J]. J Dent Res, 2017, 96 (12): 1414- 1421. |
| 13 | Alam J , Koh JH , Kim N , et al. Detection of autoantibodies against aquaporin-5 in the sera of patients with primary Sjögren's syndrome[J]. Immunol Res, 2016, 64 (4): 848- 856. |
| 14 | Tjensvoll AB , Lauvsnes MB , Zetterberg H , et al. Neurofilament light is a biomarker of brain involvement in lupus and primary Sjögren's syndrome[J]. Journal of Neurology, 2021, 268 (4): 1385- 1394. |
| 15 | Shen L , Gao C , Suresh L , et al. Central role for marginal zone B cells in an animal model of Sjögren's syndrome[J]. Clin Immunol, 2016, 168, 30- 36. |
| 16 | Jin Y , Li J , Chen J , et al. Tissue-specific autoantibodies improve diagnosis of primary Sjögren's syndrome in the early stage and indicate localized salivary injury[J]. J Immunol Res, 2019, 2019, 3642937. |
| 17 | Shen L , Suresh L , Lindemann M , et al. Novel autoantibodies in Sjögren's syndrome[J]. Clin Immunol, 2012, 145 (3): 251- 255. |
| 18 | Xuan J , Wang Y , Xiong Y , et al. Investigation of autoantibodies to SP-1 in chinese patients with primary Sjögren's syndrome[J]. Clin Immunol, 2018, 188, 58- 63. |
| 19 | Xian Z , Fu D , Liu S , et al. Association between B cell growth factors and primary Sjögren's syndrome-related autoantibodies in patients with non-Hodgkin's lymphoma[J]. J Immunol Res, 2019, 2019, 7627384. |
| 20 | Bunya VY , Massaro-Giordano M , Vivino FB , et al. Prevalence of novel candidate Sjögren syndrome autoantibodies in the penn Sjögren's International Collaborative Clinical Alliance Cohort[J]. Cornea, 2019, 38 (12): 1500- 1505. |
| 21 | Shen L , Kapsogeorgou EK , Yu M , et al. Evaluation of salivary gland protein 1 antibodies in patients with primary and secondary Sjögren's syndrome[J]. Clin Immunol, 2014, 155 (1): 42- 46. |
| 22 | Applbaum E , Lichtbroun A . Novel Sjögren's autoantibodies found in fibromyalgia patients with sicca and/or xerostomia[J]. Autoimmun Rev, 2019, 18 (2): 199- 202. |
| 23 | de Langhe E , Bossuyt X , Shen L , et al. Evaluation of autoantibodies in patients with primary and secondary Sjögren's syndrome[J]. Open Rheumatol J, 2017, 11, 10- 15. |
| 24 | Hubschman S , Rojas M , Kalavar M , et al. Association between early Sjögren markers and symptoms and signs of dry eye[J]. Cornea, 2020, 39 (3): 311- 315. |
| 25 | Geetha C , Venkatesh SG , Dunn BH , et al. Expression and anti-bacterial activity of human parotid secretory protein (PSP)[J]. Biochem Soc Trans, 2003, 31 (Pt 4): 815- 818. |
| 26 | Karakus S , Baer AN , Akpek EK . Clinical correlations of novel autoantibodies in patients with dry eye[J]. J Immunol Res, 2019, 2019, 7935451. |
| 27 | Burbelo PD , Ferré E , Chaturvedi A , et al. Profiling autoanti-bodies against salivary proteins in sicca conditions[J]. J Dent Res, 2019, 98 (7): 772- 778. |
| 28 | Thatayatikom A , Jun I , Bhattacharyya I , et al. The diagnostic performance of early Sjögren's syndrome autoantibodies in juvenile Sjögren's syndrome: The university of florida pediatric cohort study[J]. Front Immunol, 2021, 12, 704193. |
| 29 | Lee KA , Kim KW , Kim BM , et al. Clinical and diagnostic signi-ficance of serum immunoglobulin A rheumatoid factor in primary Sjögren's syndrome[J]. Clin Oral Investig, 2019, 23 (3): 1415- 1423. |
| 30 | Zhong H , Wang Y , Yang P , et al. Hyperglobulinemia predicts increased risk of mortality in primary Sjögren's syndrome: Based on a Chinese multicentre registry[J]. Mod Rheumatol, 2023, 34 (1): 137- 143. |
| 31 | Kota SK , Pernicone E , Leaf DE , et al. BPI fold-containing family a member 2/parotid secretory protein is an early biomarker of AKI[J]. J Am Soc Nephrol, 2017, 28 (12): 3473- 3478. |
| [1] | 韩艺钧,李常虹,陈秀英,赵金霞. 抗SSB抗体阳性和阴性的原发性干燥综合征患者临床及免疫学特征的比较[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 1000-1006. |
| [2] | 李建斌,吕梦娜,池强,彭一琳,刘鹏程,吴锐. 干燥综合征患者发生重症新型冠状病毒肺炎的早期预测[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 1007-1012. |
| [3] | 孟彦宏,陈怡帆,周培茹. CENP-B抗体阳性的原发性干燥综合征患者的临床和免疫学特征[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 1088-1096. |
| [4] | 吴洁,张雯,梁舒,秦艺璐,范文强. 妊娠期原发性干燥综合征合并视神经脊髓炎谱系疾病危重症1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 1118-1124. |
| [5] | 王丽芳,石连杰,宁武,高乃姝,王宽婷. 干燥综合征合并冷凝集素病1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 1130-1134. |
| [6] | 邢海霞,王琳,乔迪,刘畅,潘洁. 干燥综合征口腔疾病的治疗特点[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 929-933. |
| [7] | 刘杨,程昉,王艳玲,艾香艳,朱振航,赵福涛. 唾液腺超声对干燥综合征的诊断价值[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1123-1127. |
| [8] | 李红霞,周雅馨,王亚飞,王鹏宇,吴振彪. 唇腺病理阴性干燥综合征患者的临床特点[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1229-1233. |
| [9] | 于昊哲,曾唯珍,吴文雨,姚中强,冯云. 原发性干燥综合征合并甲状腺功能减退眼表状态评估[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(4): 705-711. |
| [10] | 杨群智,张舸,费雅楠,付爽,闫冰. 沙利度胺治疗原发性干燥综合征合并轻中度非特异性间质性肺炎疗效观察[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(2): 413-416. |
| [11] | 俞光岩. 多发性唾液腺肿大的鉴别诊断及处理[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(1): 1-4. |
| [12] | 池彦廷,张延平,张秋露,刘翠苓,李斌斌. 唾液腺干燥综合征继发黏膜相关淋巴组织淋巴瘤的临床病理分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(1): 40-45. |
| [13] | 张警丰,叶修玲,段萌,周小利,姚中强,赵金霞. 抗核抗体阳性类风湿关节炎的临床和实验室检查特点[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(6): 1023-1028. |
| [14] | 王一帆,范稹,成姚斌,金月波,霍阳,何菁. 原发性干燥综合征患者睡眠障碍的相关影响因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(6): 1063-1068. |
| [15] | 陈伟钱,戴小娜,余叶,王沁,梁钧昱,柯旖旎,易彩虹,林进. 原发性干燥综合征合并自身免疫性肝病的临床特点及预后分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(5): 886-891. |
|
||