北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (4): 633-643. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2025.04.002
氧化应激相关基因与前列腺癌关系的多组学分析
宁家昕1,2,*, 王浩然1,2,*, 罗书航1,2, 敬吉波1,2, 王建业1,2, 侯惠民1,*( ), 刘明1,2,*(
), 刘明1,2,*( )
)
- 1. 北京医院泌尿外科, 国家老年医学中心, 老年医学研究所, 北京 100005
2. 北京协和医学院, 中国医学科学院, 北京 100730
Multi-omics analysis of the relationship between oxidative stress-related gene and prostate cancer
Jiaxin NING1,2, Haoran WANG1,2, Shuhang LUO1,2, Jibo JING1,2, Jianye WANG1,2, Huimin HOU1,*( ), Ming LIU1,2,*(
), Ming LIU1,2,*( )
)
- 1. Department of Urology, Beijing Hospital, National Center of Gerontology, Institute of Geriatric Medicine, Beijing 100005, China
2. Peking Union Medical College & Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Beijing 100730, China
摘要:
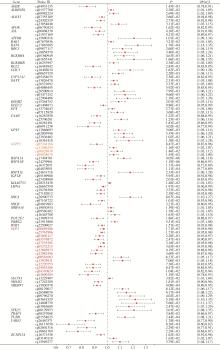
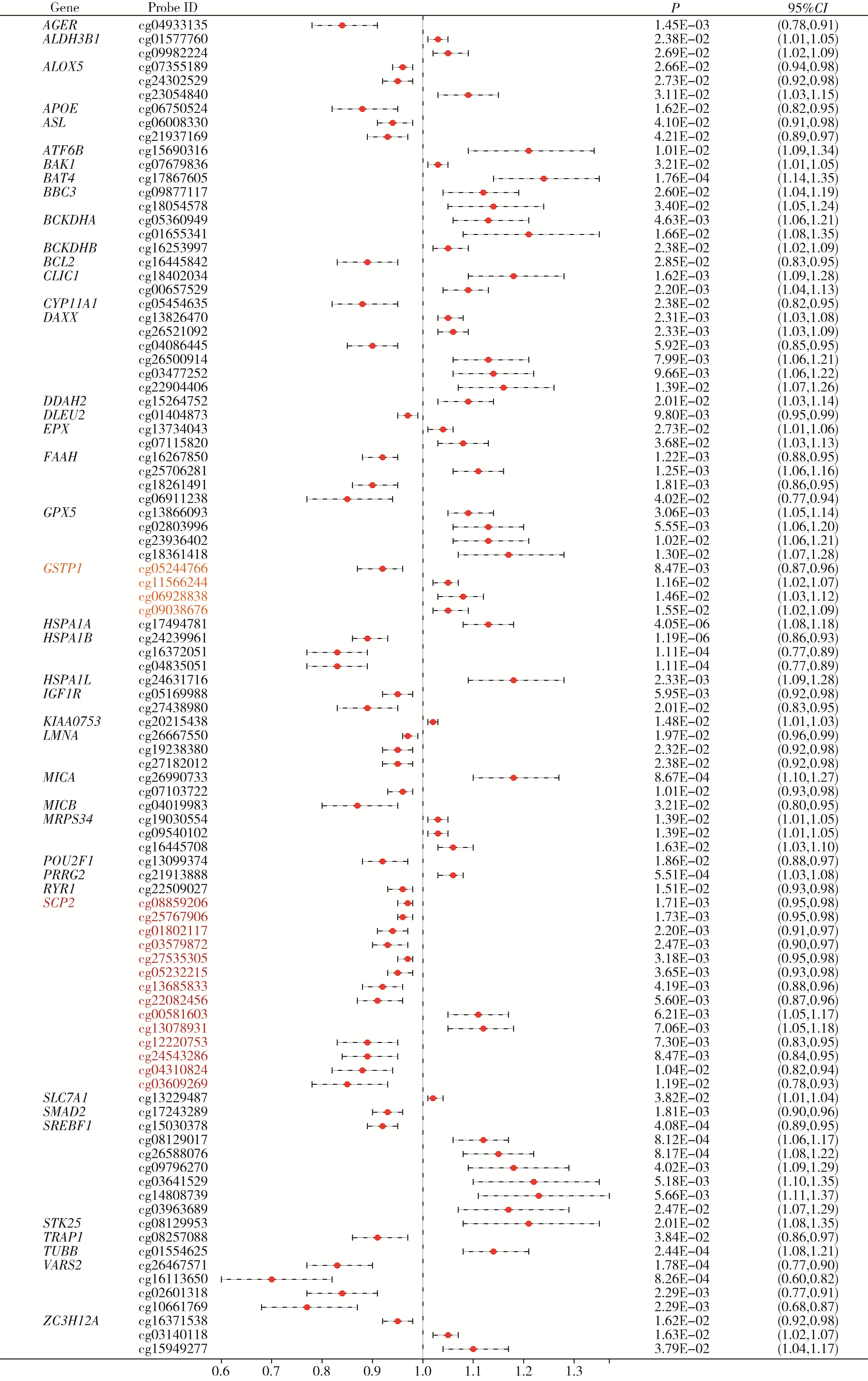
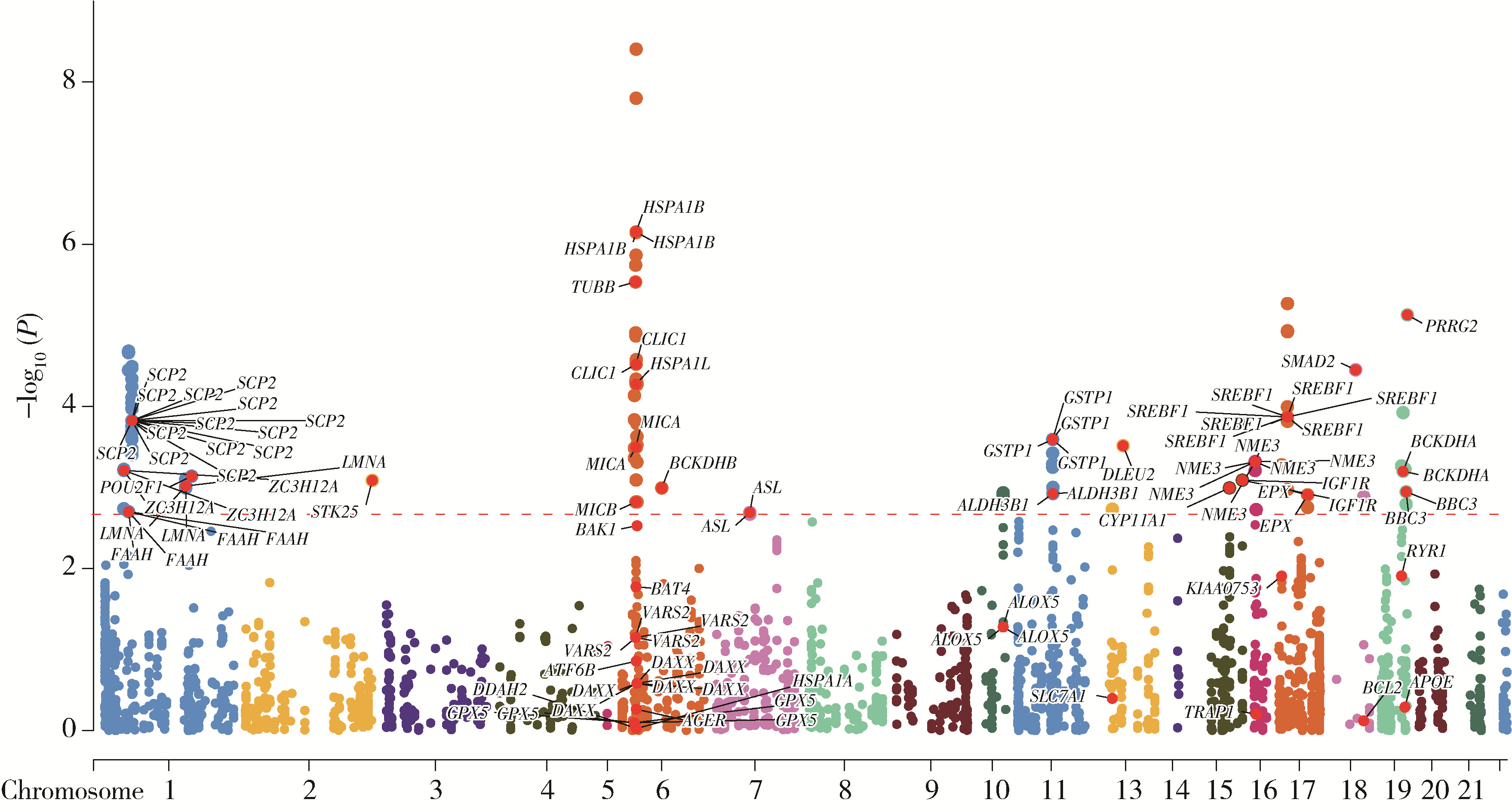
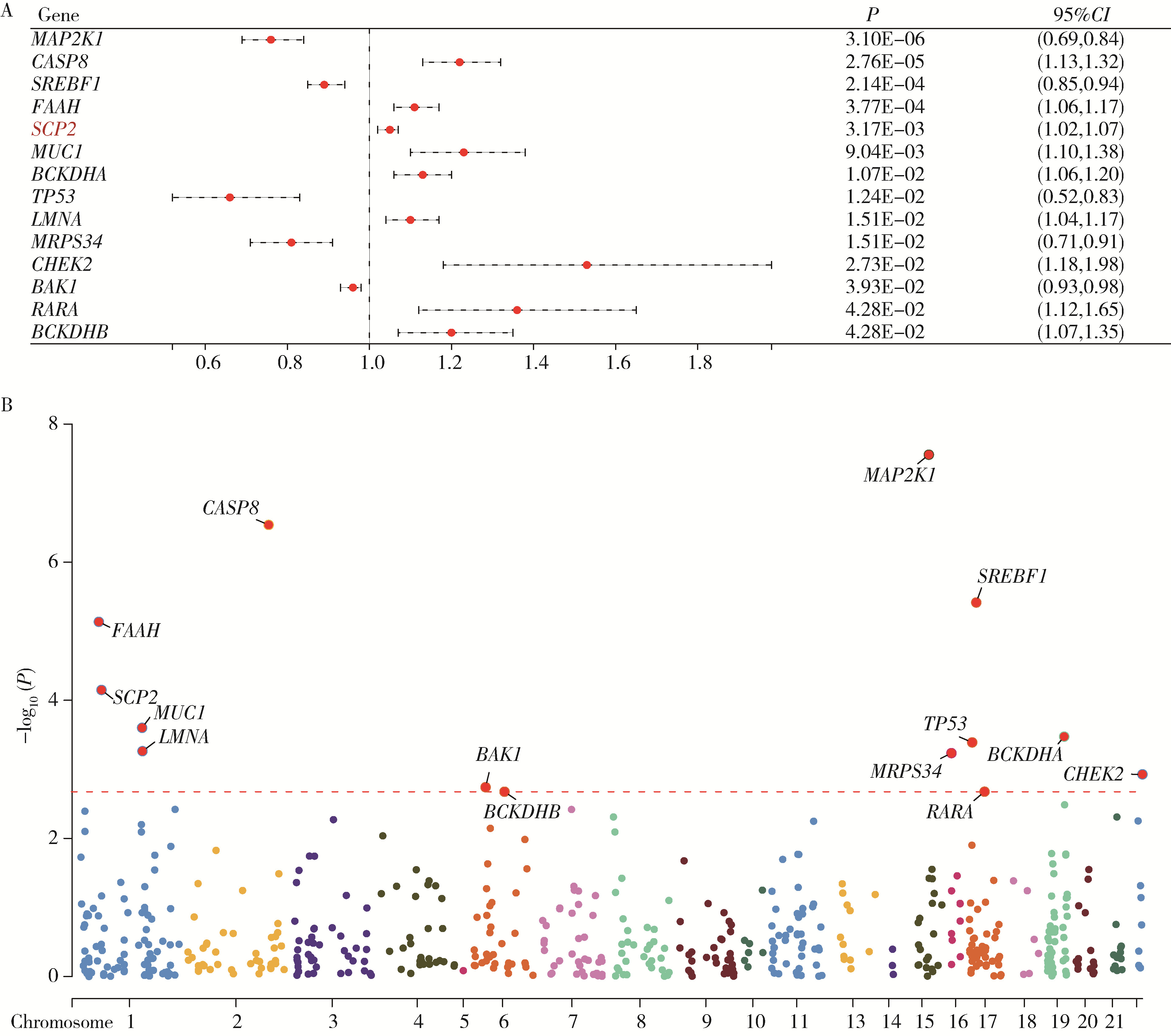
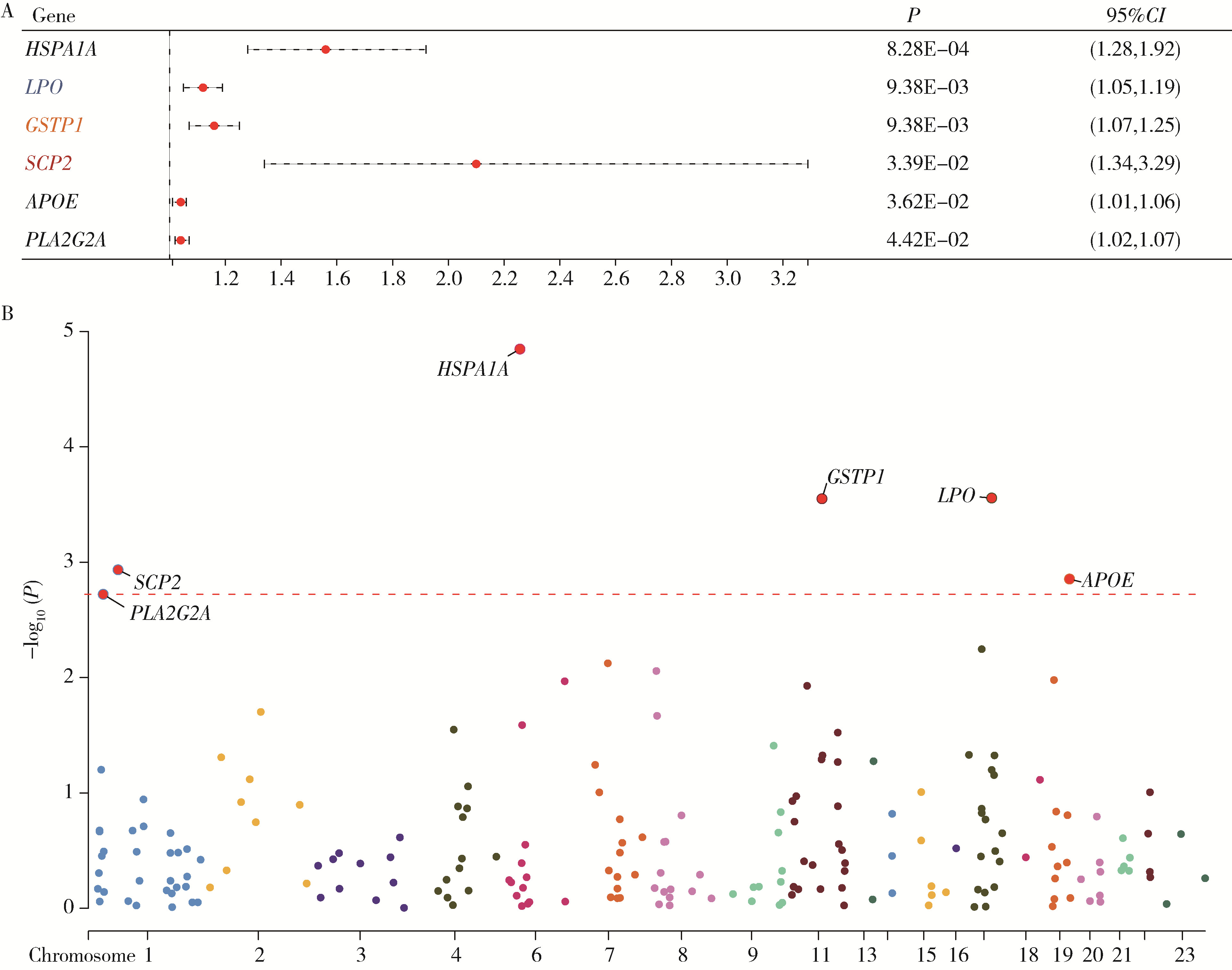
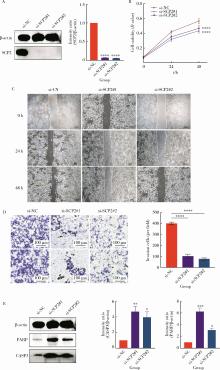
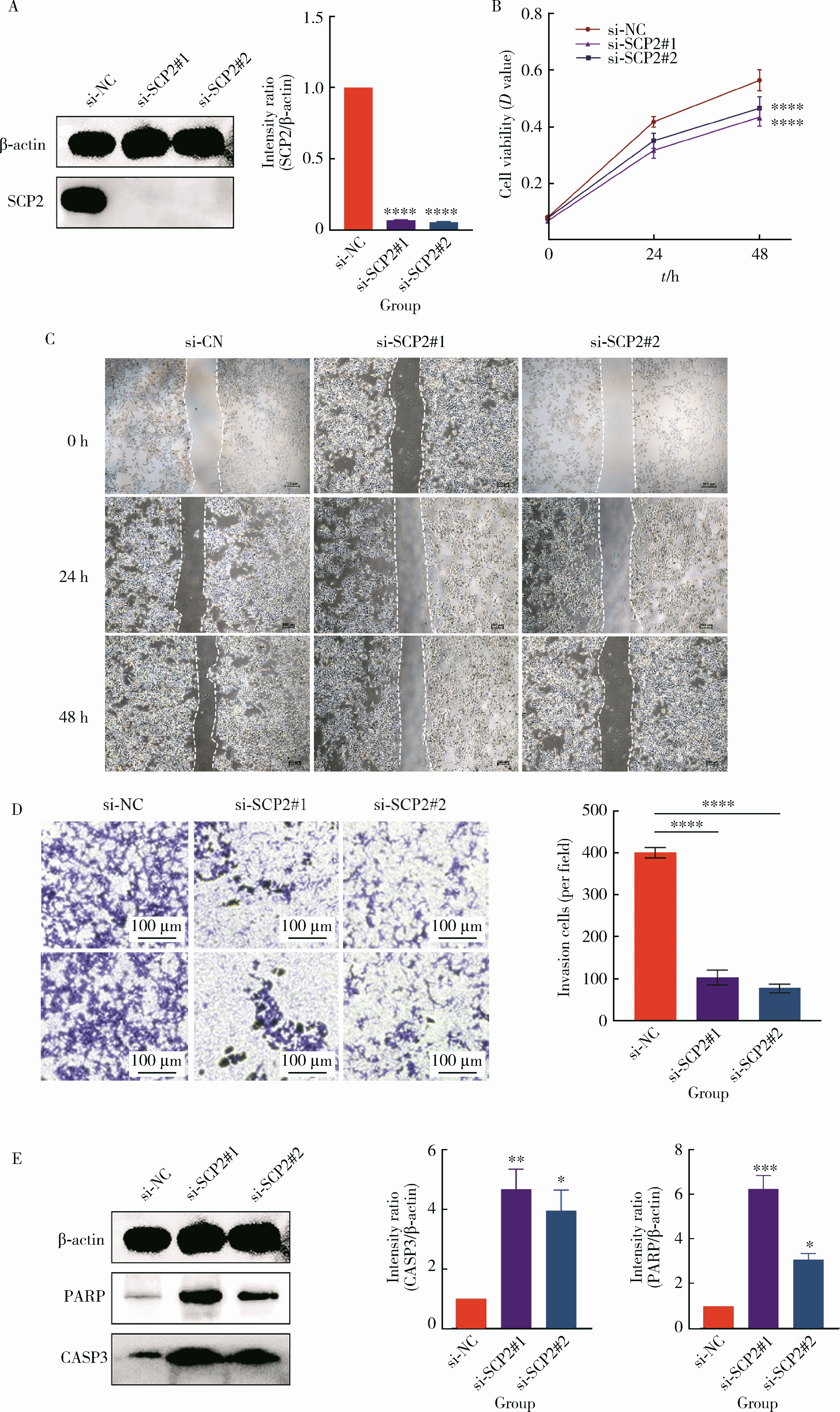
目的: 利用基于汇总数据的孟德尔随机化(summary-data-based Mendelian randomization, SMR)、共定位分析和细胞实验, 从多组学角度研究氧化应激相关基因与前列腺癌(prostate cancer, PCa)之间的关系。方法: 对基因甲基化、基因表达和循环蛋白质的汇总级数据在下载后进行筛选, 将PRACTICAL队列作为观察队列, deCODE数据库作为验证队列, 使用SMR分析和依赖性工具异质性(heterogeneity in dependent instruments, HEIDI)检验评估氧化应激相关基因与PCa的关联性和异质性, 采用共定位分析确定氧化应激相关基因与PCa之间是否存在共享突变。进一步对筛选出的基因采用CCK-8、细胞划痕实验、Transwell侵袭实验、蛋白免疫印迹实验探究其对PCa细胞系C4-2生物学行为的影响。结果: 经过多组学分析, SCP2在基因甲基化、基因表达和循环蛋白质层面均被确定为与PCa风险增加存在显著关联性, 而GSTP1在基因甲基化和循环蛋白质层面, LPO在循环蛋白质层面被认为与PCa风险增加存在显著关联。在基因甲基化层面, SCP2的cg00581603(OR=1.11, 95%CI: 1.05~1.17)和cg13078931(OR=1.12, 95%CI: 1.05~1.18)甲基化被认为是PCa的致病因素; GSTP1的cg05244766(OR=0.89, 95%CI: 0.84~0.95)甲基化被认为是PCa的保护因素。在基因表达层面, SCP2(OR=1.05, 95%CI: 1.02~1.07)同样被确定为PCa的致病因素。在循环蛋白质层面, SCP2(OR=2.10, 95%CI: 1.34~3.29)显示出了与基因甲基化和基因表达层面一致的PCa致病趋势, 此外, GSTP1(OR=1.16, 95%CI: 1.07~1.25)和LPO(OR=1.12, 95%CI: 1.05~1.19)都与PCa风险增加显著相关。进一步的细胞实验表明, 敲除SCP2能显著降低PCa细胞的致癌表型。结论: 通过多组学分析和细胞实验验证, 本研究证实了SCP2与PCa发生风险增加之间存在显著关联性, 这一发现加深了对PCa发病机制的了解, 并为PCa治疗提供了新的靶点和治疗方向。
中图分类号:
- R737.25
| 1 |
|
| 2 |
|
| 3 |
|
| 4 |
|
| 5 |
|
| 6 |
|
| 7 |
|
| 8 |
|
| 9 |
|
| 10 |
|
| 11 |
|
| 12 |
|
| 13 |
|
| 14 |
|
| 15 |
|
| 16 |
|
| 17 |
|
| 18 |
|
| 19 |
|
| 20 |
|
| 21 |
|
| 22 |
|
| 23 |
|
| 24 |
|
| 25 |
|
| 26 |
|
| 27 |
|
| 28 |
|
| 29 |
|
| 30 |
|
| 31 |
|
| 32 |
|
| 33 |
|
| 34 |
|
| 35 |
|
| 36 |
|
| 37 |
|
| 38 |
|
| 39 |
|
| 40 |
|
| 41 |
|
| 42 |
|
| 43 |
|
| 44 |
|
| 45 |
|
| 46 |
|
| 47 |
|
| 48 |
|
| 49 |
|
| [1] | 王泽远, 于栓宝, 郑浩轲, 陶金, 范雅峰, 张雪培. 基于临床特征和多参数MRI的前列腺癌盆腔淋巴结转移的术前预测模型[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2025, 57(4): 684-691. |
| [2] | 李志存, 吴天俣, 梁磊, 范宇, 孟一森, 张骞. 穿刺活检单针阳性前列腺癌术后病理升级的危险因素分析及列线图模型构建[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 896-901. |
| [3] | 田宇轩,阮明健,刘毅,李德润,吴静云,沈棋,范宇,金杰. 双参数MRI改良PI-RADS评分4分和5分病灶的最大径对临床有意义前列腺癌的预测效果[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 567-574. |
| [4] | 姚凯烽,阮明健,李德润,田宇轩,陈宇珂,范宇,刘毅. 靶向穿刺联合区域系统穿刺对PI-RADS 4~5分患者的前列腺癌诊断效能[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 575-581. |
| [5] | 欧俊永,倪坤明,马潞林,王国良,颜野,杨斌,李庚午,宋昊东,陆敏,叶剑飞,张树栋. 肌层浸润性膀胱癌合并中高危前列腺癌患者的预后因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 582-588. |
| [6] | 马雨佳,卢燃藜,周泽宸,李晓怡,闫泽玉,武轶群,陈大方. 基于两样本孟德尔随机化的失眠与2型糖尿病关联研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 174-178. |
| [7] | 薛蔚,董樑,钱宏阳,费笑晨. 前列腺癌新辅助治疗与辅助治疗的现状及进展[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 775-780. |
| [8] | 刘毅,袁昌巍,吴静云,沈棋,肖江喜,赵峥,王霄英,李学松,何志嵩,周利群. 靶向穿刺+6针系统穿刺对PI-RADS 5分患者的前列腺癌诊断效能[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 812-817. |
| [9] | 毛海,张帆,张展奕,颜野,郝一昌,黄毅,马潞林,褚红玲,张树栋. 基于MRI前列腺腺体相关参数构建腹腔镜前列腺癌术后尿失禁的预测模型[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 818-824. |
| [10] | 袁昌巍,李德润,李志华,刘毅,山刚志,李学松,周利群. 多参数磁共振成像中动态对比增强状态在诊断PI-RADS 4分前列腺癌中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 838-842. |
| [11] | 刘志伟,刘鹏,孟凡星,李天水,王颖,高嘉琪,周佐邑,王聪,赵斌. 内源性二氧化硫对脓毒症大鼠心肌氧化应激的调节[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 582-586. |
| [12] | 白枫,何倚帆,牛亚楠,杨若娟,曹静. 超细颗粒物对大鼠离体灌注心脏功能的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(2): 240-245. |
| [13] | 刘毅,刘志坚,沈棋,吴静云,范宇,李德润,虞巍,何志嵩. 14例恶性潜能未定的前列腺间质肿瘤病例分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(4): 621-624. |
| [14] | 郝一昌,颜野,张帆,邱敏,周朗,刘可,卢剑,肖春雷,黄毅,刘承,马潞林. 穿刺活检单针阳性的前列腺癌手术策略选择及经验总结[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(4): 625-631. |
| [15] | 轩艳,蔡宇,王啸轩,石巧,邱立新,栾庆先. 牙龈卟啉单胞菌感染对载脂蛋白e基因敲除小鼠动脉粥样硬化的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(4): 743-749. |
|
||