北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (6): 1188-1192. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2025.06.026
中枢神经系统感染模拟神经精神狼疮1例
- 内蒙古科技大学包头医学院第一附属医院风湿免疫科, 内蒙古自体免疫学重点实验室, 内蒙古包头 014010
Central nervous system infection mimicking neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus: A case report
Kai ZHAO, Fu'ai LU, Yongfu WANG*( )
)
- Department of Rheumatism and Immunology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Baotou Medical College, Inner Mongolia University of Science and Technology; Inner Mongolia Autoimmunology Key Laboratory, Baotou 014010, Inner Mongolia, China
摘要:
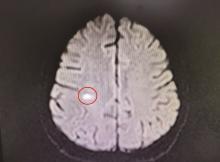
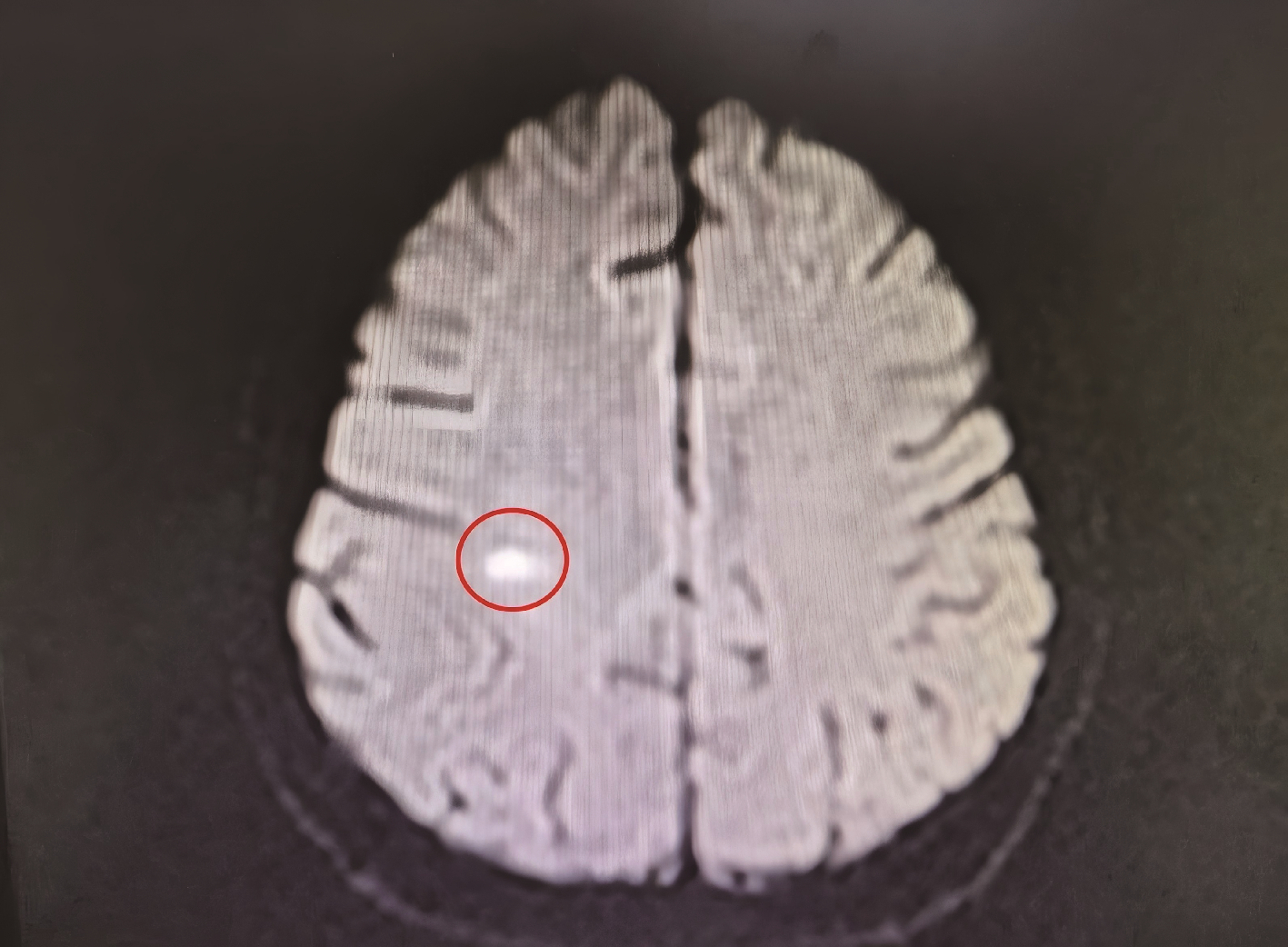
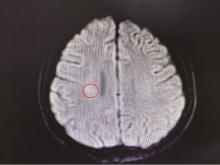
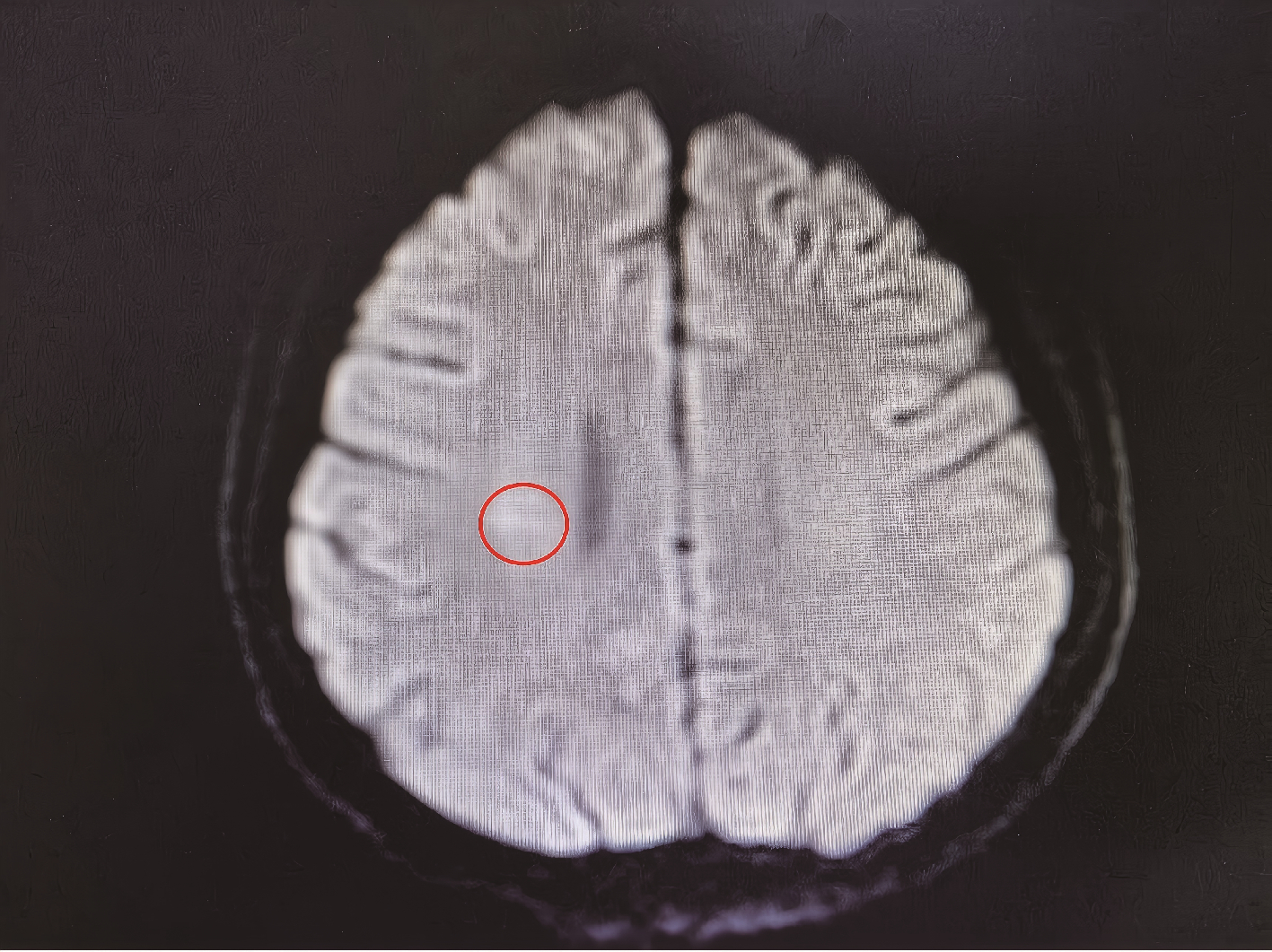
报道一例青年女性系统性红斑狼疮(systemic lupus erythematosus, SLE)患者, 在接受糖皮质激素联合环孢素长期免疫抑制治疗期间出现神经精神症状。头颅磁共振成像(magnetic resonance imaging, MRI)提示右侧顶叶急性炎症性病变, 初期拟诊为神经精神狼疮(neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus, NPSLE), 但调整免疫抑制方案后病情仍持续进展, 出现意识障碍及脑膜刺激征。进一步实验室检查显示, 血培养检出单核细胞增生李斯特菌(Listeria), 脑脊液新一代测序(next-generation sequencing, NGS)技术检测到水痘-带状疱疹病毒(varicella-zoster virus, VZV)。经美罗培南联合利奈唑胺靶向抗感染及丙种球蛋白支持治疗后, 患者神经症状及影像学异常显著改善, 最终确诊为中枢神经系统(central nervous system, CNS)混合感染而非NPSLE。本研究提示, 对免疫抑制治疗中的SLE患者出现神经精神表现时, 需重点鉴别CNS感染与NPSLE。CNS感染常伴显著发热、脑膜刺激征及炎症标志物升高, 脑脊液可见细胞数增多、蛋白升高及葡萄糖降低, 而NPSLE相关脑脊液改变多较轻微, 影像学动态随访及治疗反应有助于判别, CNS感染病灶在有效抗感染后短期内可吸收。脑脊液NGS技术可快速识别混合病原体, 对精准诊断具有重要价值, 临床需避免误诊为NPSLE而盲目强化免疫抑制, 导致感染加重。建议多学科协作, 结合病原学、影像与治疗反应综合评估, 以指导早期抗感染治疗, 改善预后。
中图分类号:
- R593.24
| 1 |
|
| 2 |
doi: 10.1097/BOR.0000000000000682 |
| 3 |
doi: 10.1038/s41584-018-0156-8 |
| 4 |
国家皮肤与免疫疾病临床医学研究中心, 中华医学会风湿病学分会, 风湿免疫病学教育部重点实验室, 等. 中国成人中枢神经精神狼疮临床实践专家共识(2024版)[J]. 中华风湿病学杂志, 2024, 28 (9): 613- 625.
|
| 5 |
doi: 10.1186/s12879-020-05327-6 |
| 6 |
doi: 10.1080/1040841X.2021.1911930 |
| 7 |
蒋钟吉, 许智坤, 吴劲松, 等. 深圳单核细胞增生李斯特菌感染10例临床分析[J]. 中国抗生素杂志, 2022, 47 (11): 1202- 1206.
|
| 8 |
doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2018.11.007 |
| 9 |
年李想, 葛沈瑞, 帅垠琦. 系统性红斑狼疮合并李斯特菌脓毒症1例[J]. 临床医学进展, 2024, 14 (4): 718- 723.
|
| 10 |
doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2020.102592 |
| 11 |
罗芷筠, 吴佳佳, 宋优, 等. 伴神经精神系统病变的系统性红斑狼疮相关巨噬细胞活化综合征2例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55 (6): 1111- 1117.
doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2023.06.024 |
| [1] | 李欣艺, 赵金霞, 穆荣. 阿司匹林对系统性红斑狼疮妊娠者结局的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2025, 57(6): 1074-1080. |
| [2] | 王晓林, 郭邵逸, 陈大召, 温锡杰, 华勇, 张亮, 张秦. 全髋关节置换术治疗系统性红斑狼疮继发股骨头缺血性坏死的随访研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2025, 57(6): 1081-1088. |
| [3] | 卫春, 杨月, 赵新菊, 刘栩, 贾园. 系统性红斑狼疮合并自身免疫性郎飞结病1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2025, 57(6): 1174-1179. |
| [4] | 王小梦, 曾晓君, 李娟. 黎族与汉族系统性红斑狼疮患者的主要临床特征[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2025, 57(6): 1213-1218. |
| [5] | 王文琼, 侯玉珂, 李春, 张学武. 系统性红斑狼疮患者不良妊娠结局的预测因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2025, 57(3): 599-603. |
| [6] | 王红彦, 李鑫铭, 房柯池, 朱华群, 贾汝琳, 王晶. 系统性红斑狼疮疾病活动度相关特征分析及评估模型的构建[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(6): 1017-1022. |
| [7] | 陈丹丹, 李云, 卢情怡, 相晓红, 孙峰, 李英妮, 赵静, 王红彦, 李春. 育龄期系统性红斑狼疮患者卵巢功能的评价及其影响因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(6): 1023-1028. |
| [8] | 王莉, 高超, 任欢欢, 沈艳平, 黄晓玮, 姚鸿, 韩丹丹. 系统性红斑狼疮患者自我管理能力现状及相关因素分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(6): 1029-1035. |
| [9] | 柴静, 王钥, 穆荣, 赵金霞. 系统性红斑狼疮累及穹窿柱导致低钠血症1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(6): 1115-1118. |
| [10] | 王明霞, 丁菱, 王敏, 邹婵娟, 颜丝语, 梁颖文, 王伟佳, 何善智. 双靶点嵌合抗原受体T细胞治疗系统性红斑狼疮患者停药后安全孕产1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(6): 1119-1125. |
| [11] | 武志慧, 胡明智, 赵巧英, 吕凤凤, 张晶莹, 张伟, 王永福, 孙晓林, 王慧. miR-125b-5p修饰脐带间充质干细胞对系统性红斑狼疮的免疫调控机制[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 860-867. |
| [12] | 乔佳佳,田聪,黄晓波,刘军. 肾结石合并系统性红斑狼疮行经皮肾镜碎石取石术的安全性和有效性评估[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 745-749. |
| [13] | 任立敏,赵楚楚,赵义,周惠琼,张莉芸,王友莲,沈凌汛,范文强,李洋,厉小梅,王吉波,程永静,彭嘉婧,赵晓珍,邵苗,李茹. 系统性红斑狼疮低疾病活动度及缓解状况的真实世界研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 273-278. |
| [14] | 罗芷筠,吴佳佳,宋优,梅春丽,杜戎. 伴神经精神系统病变的系统性红斑狼疮相关巨噬细胞活化综合征2例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 1111-1117. |
| [15] | 姚海红,杨帆,唐素玫,张霞,何菁,贾园. 系统性红斑狼疮及成人Still病合并巨噬细胞活化综合征的临床特点及诊断指标[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 966-974. |
|
||