北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2019, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (2): 239-244. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2019.02.007
二氧化硫对大鼠肢体缺血再灌注致急性肺损伤中肺泡巨噬细胞凋亡的影响
- 首都医科大学附属北京朝阳医院骨科, 北京 100020
Effects of sulfur dioxide on alveolar macrophage apoptosis in acute lung injury induced by limb ischemia/reperfusion in rats
Yan-rui ZHAO,Yang LIU,Dong WANG,Wen-rui LV,Jun-lin ZHOU( )
)
- Department of Orthopedics, Beijing Chao-yang Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100020, China
摘要:
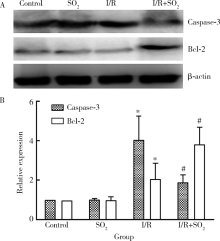
目的: 探讨二氧化硫(sulfur dioxide,SO2)在肢体缺血再灌注(ischemia/reperfusion,I/R)致急性肺损伤(acute lung injury,ALI)保护作用中对肺泡巨噬细胞(alveolar macrophage,AM)凋亡的影响,为控制炎症反应寻找新的靶点。方法: 分离培养AM,应用肢体缺血再灌注致ALI大鼠血清制备细胞模型,给予外源性SO2,然后检测线粒体膜电位以及线粒体通透性转换孔(mitochondrial permeability transition pore,mPTP)开放情况,AM凋亡情况及凋亡相关Bcl-2、Caspase-3分子蛋白表达情况。结果: 与对照组相比,I/R组红、绿荧光的比值下降,吸光度显著降低,AM凋亡率增加到43.81%±2.40%,Caspase-3蛋白表达升高,Bcl-2蛋白表达下降;而与I/R组比较,I/R+SO2组红、绿荧光的比值升高,吸光度增高,AM凋亡率减少37.01%±1.93%,Caspase-3蛋白表达降低,Bcl-2蛋白表达升高。结论: 外源性SO2可通过抑制线粒体途径改善巨噬细胞的凋亡。
中图分类号:
- R364.12
| [1] |
Steiger AK, Yang Y, Royzen M , et al. Bio-orthogonal “click-and-release” donation of caged carbonyl sulfide (COS) and hydrogen sulfide (H2S)[J]. Chem Commun (Camb), 2017,53(8):1378-1380.
doi: 10.1039/C6CC09547J |
| [2] |
Steiger AK, Pardue S, Kevil CG , et al. Self-immolative thiocarbamates provide access to triggered H2S donors and analyte replacement fluorescent probes[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 2016,138(23):7256-7259.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.6b03780 |
| [3] |
Aggarwal NR, D’Alessio FR, Tsushima K , et al. Moderate oxygen augments lipopolysaccharide-induced lung injury in mice[J]. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol, 2010,298(3):L371-L381.
doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00308.2009 |
| [4] |
Howard KM . Differential expression of platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase in lung macrophages[J]. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol, 2009,297(6):L1141-L1150.
doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00022.2009 |
| [5] | Z’Graggen BR, Tornic J, Muller-Edenborn B , et al. Acute lung injury: apoptosis in effector and target cells of the upper and lower airway compartment[J]. Clin Exp Immunol, 2010,161(2):324-331. |
| [6] |
Meng Z, Liu Y . Cell morphological ultrastructural changes in va-rious organs from mice exposed by inhalation to sulfur dioxide[J]. Inhal Toxicol, 2007,19(6-7):543-551.
doi: 10.1080/08958370701271373 |
| [7] | Ubuka T, Yuasa S, Ohta J , et al. Formation of sulfate from L-cysteine in rat liver mitochondria[J]. Acta Med Okayama, 1990,44(2):55-64. |
| [8] | 赵彦瑞, 刘洋, 王东 , 等. PI3KAkt和JAK2STAT3信号转导通路在SO2抗大鼠肢体缺血再灌注致急性肺损伤中的作用[J]. 中华病理生理杂志, 2015,31(11):2076-2082. |
| [9] |
Huang XL, Liu Y, Zhou JL , et a1. Role of sulfur dioxide in acute lung injury following limb ischemia/reperfusion in rats[J]. J Biochem Mol Toxicol, 2013,27(8):389-397.
doi: 10.1002/jbt.2013.27.issue-8 |
| [10] |
Zhao YR, Wang D, Liu Y , et al. The PI3K/Akt, p38MAPK, and JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathways mediate the protection of SO2 against acute lung injury induced by limb ischemia/reperfusion in rats[J]. J Physiol Sci, 2016,66(3):229-239.
doi: 10.1007/s12576-015-0418-z |
| [11] |
Cohen SM, Siddiqi FA, Darakchiev B , et al. Attenuation of acute lung injury caused by hind-limb ischemia-reperfusion injury by butyrolactone anti-inflammatory agent FLl003[J]. J Trauma, 1997,43(2):247-252.
doi: 10.1097/00005373-199708000-00007 |
| [12] | Javadov S, Choi A, Rajapurohitam V , et al. NHE-1 inhibition-induced cardioprotection against ischaemia/reperfusion is associa-ted with attenuation of the mitochondrial permeability transition[J]. Cardiovasc Res, 2008,77(2):416-424. |
| [13] | Kaltenbach JP, Jennings RB . Metabolism of ischemic cardiac muscle[J]. Circ Res, 1960(8):207-213. |
| [14] |
Ward PA . Editorial commentary: New strategies for treatment of humans with acute lung injury/acute respiratory distress syndrome[J]. Clin Infect Dis, 2015,60(4):596-597.
doi: 10.1093/cid/ciu892 |
| [15] |
Tauber AI . Metchnikoff and the phagocytosis theory[J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2003,4(11):897-901.
doi: 10.1038/nrm1244 |
| [16] |
Ovchinnikov, Dmitry A . Macrophages in the embryo and beyond: Much more than just giant phagocytes[J]. Genesis, 2008,46(9):447-462.
doi: 10.1002/dvg.v46:9 |
| [17] | Yong Y, Matthew S, Wittwer J , et al. Dichamanetin inhibits cancer cell growth by affecting ROS-related signaling components through mitochondrial-mediated apoptosis[J]. Anticancer Res, 2013,33(12):5349-5355. |
| [1] | 罗芷筠,吴佳佳,宋优,梅春丽,杜戎. 伴神经精神系统病变的系统性红斑狼疮相关巨噬细胞活化综合征2例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 1111-1117. |
| [2] | 姚海红,杨帆,唐素玫,张霞,何菁,贾园. 系统性红斑狼疮及成人Still病合并巨噬细胞活化综合征的临床特点及诊断指标[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 966-974. |
| [3] | 刘志伟,刘鹏,孟凡星,李天水,王颖,高嘉琪,周佐邑,王聪,赵斌. 内源性二氧化硫对脓毒症大鼠心肌氧化应激的调节[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 582-586. |
| [4] | 邢晓燕,张筠肖,朱冯赟智,王一帆,周新尧,李玉慧. 皮肌炎合并巨噬细胞活化综合征5例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1214-1218. |
| [5] | 贾园,栗占国. 成人巨噬细胞活化综合征诊断困境和个体化治疗[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(6): 991-994. |
| [6] | 陈颖怡,胡紫琪,惠甜倩,刘鹤. Zeste同源蛋白2增强子通过调节巨噬细胞趋化影响牙髓炎症反应[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(1): 18-23. |
| [7] | 姚海红,王旖旎,张霞,赵金霞,贾园,王昭,栗占国. 67例成人巨噬细胞活化综合征的临床特征及治疗转归[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(6): 996-1002. |
| [8] | 王莹,李明慧,张岩,胡晓燕,马瑞霞. 狼疮性肾炎患者足细胞损伤与肾组织巨噬细胞浸润的关系[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(4): 723-727. |
| [9] | 吴小静,李敏,詹庆元. 以高热为表现的外源性脂质性肺炎1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(5): 921-923. |
| [10] | 余建峰, 金月波, 何菁, 安媛, 栗占国. 皮肌炎继发干燥综合征伴肺间质病变的血清人Ⅱ型肺泡细胞表面抗原变化1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(5): 910-914. |
| [11] | 高翔,陈香梅,张婷,张静,陈茉,郭正阳,石岩岩,鲁凤民,丁士刚. 巨噬细胞加帽蛋白与胃癌细胞增殖及迁移能力的关系[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(3): 489-494. |
| [12] | 涂静宜, 朱莹, 尚淑玲, 张茜, 唐慧, 王瑞敏. Keap1-tat小肽降低缺血后大鼠海马CA1区神经元氧化应激损伤和空间学习记忆缺陷[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2016, 48(1): 154-159. |
| [13] | 李刚,张洪宪,王云鹏,张径,洪锴,田晓军,马潞林. 间苯三酚对大鼠肾缺血再灌注损伤的保护作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2015, 47(5): 743-748. |
| [14] | 王宁, 王贵松, 于海奕, 米琳, 郭丽君, 高炜. 远隔缺血后适应在急性ST段抬高型心肌梗死直接经皮冠状动脉介入治疗术中的心肌保护作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2014, 46(6): 838-843. |
| [15] | 王艳飞, 贾新未, 赵文萍, 王凤娟, 刘亚宁, 张芳, 张丽敏, 王鸿超. 辛伐他汀后适应对缺血再灌注损伤大鼠TNF-α及NF-κB的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2014, 46(6): 990-992. |
|
||