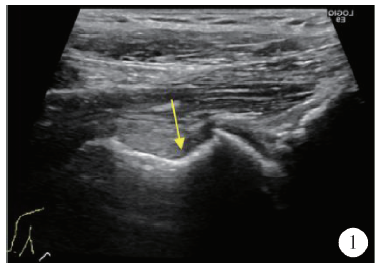
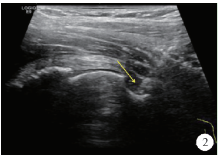
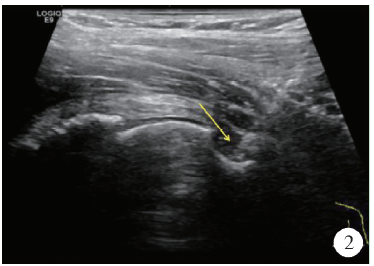
北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2019, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (2): 265-267. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2019.02.012
超声引导下髋关节药物注射在关节镜盂唇修复术后康复中的应用
张翠平1,刘佩佩1,傅强1,高冠英2,崔立刚1,∆( ),徐雁2,∆(
),徐雁2,∆( ),王健全2
),王健全2
- 1. 北京大学第三医院 超声科, 北京 100191
2. 北京大学第三医院 运动医学研究所, 北京 100191
Application of ultrasound-guided hip joint drug injection in the postoperative rehabilitation of arthroscopie repair of acetabular labral tears
Cui-ping ZHANG1,Pei-pei LIU1,Qiang FU1,Guan-ying GAO2,Li-gang CUI1,∆( ),Yan XU2,∆(
),Yan XU2,∆( ),Jian-quan WANG2
),Jian-quan WANG2
- 1. Department of Ultrasound, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
2. Institute of Sports Medicine, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
摘要:
目的: 探讨超声引导下髋关节药物注射在髋关节镜盂唇修复术后促进康复中的临床应用。方法: 纳入2015年6月至2017年5月于北京大学第三医院行髋关节镜盂唇修复术,术后1~6个月[平均(2.3±0.6)个月]仍有髋部疼痛导致康复期康复训练受限,但影像学检查显示盂唇愈合良好的36例患者,其中2例患者为双侧,共计38侧髋关节,行超声引导下髋关节疼痛阻滞治疗。对注射治疗前及治疗后满4周时患者髋部疼痛程度进行评分,应用SPSS 21.0统计学软件进行数据分析,同时随访患者髋关节功能状况,计算髋关节药物注射治疗的有效率[有效率=(“优良”+“好转”)例数/总例数×100%]。髋部疼痛程度评估采用视觉模拟评分法(visual analogue score, VAS)评估,疼痛程度分为0~10分,0分为无疼痛感,10分为难以忍受的剧烈疼痛。髋关节功能状况通过髋关节活动度进行评估。疗效“优良”指髋部无疼痛或偶有轻微疼痛,Patrick试验转阴性,运动功能不受限;“好转”指疼痛明显减轻,运动功能稍受限;“无效”指治疗前后疼痛和运动功能无明显改善,Patrick试验阳性。结果: 在接受髋关节药物注射治疗前,患者髋部疼痛程度VAS评分为(5.46±1.46)分,注射治疗后满4周时VAS评分为(2.01±0.53)分,VAS值明显减低,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);药物注射治疗后,髋关节活动度有明显提高,治疗有效率为84.2%。结论: 对髋关节镜盂唇修复术后仍存在疼痛、功能受限的患者,行超声引导下髋关节药物注射可有效减轻髋部疼痛,改善髋关节活动度,促进髋关节功能重建。
中图分类号:
- R684
| [1] | 郑博文, 任杰, 曹君 , 等. 超声引导下髋关节穿刺注药的临床应用研究[J]. 中国超声医学杂志, 2013,29(1):65-68. |
| [2] | 陈孝平 . 8年制外科学 [M]. 2版. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2010: 886-887. |
| [3] |
Ha YC, Kim KC, Shin YE . Patient satisfaction after arthroscopie repair of acetabular labral tears[J]. Clin Orthop Surg, 2014,6(2):159-164.
doi: 10.4055/cios.2014.6.2.159 |
| [4] | 左辉, 赵树恩, 姚军 , 等. 得宝松的药理作用、临床应用及不良反应的评价[J]. 实用疼痛学杂志, 2004,12(2):40-42. |
| [5] |
Shankar H . Ultrasound guided hip joint injections: a new scanning routine for easy methodical training[J]. Pain Practice, 2012,12(1):80-81.
doi: 10.1111/ppr.2011.12.issue-1 |
| [6] |
Smith J, Handle MF, Weingarten TN . Accuracy of sonographicauy guided intra-article injections in the native adult hip[J]. Ultrasound Med, 2009,28(3):329-335.
doi: 10.7863/jum.2009.28.3.329 |
| [7] |
Sotka CM, Saboeim G, Adler RS . Ultrasound-guilded adult hip injections[J]. Vasc Interv Radiol, 2005,16(8):1121-1123.
doi: 10.1097/01.RVI.0000167855.43900.74 |
| [1] | 原晋芳, 王新利, 崔蕴璞, 王雪梅. 尿促黄体生成素在女童中枢性性早熟预测中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 788-793. |
| [2] | 汪琪伟, 包鹏宇, 洪士皓, 杨昕, 王宇, 曹永平. 改良股骨颈截骨术在伴严重屈曲畸形强直性脊柱炎患者手术治疗过程中的疗效[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 884-889. |
| [3] | 王明瑞,刘军,熊六林,于路平,胡浩,许克新,徐涛. 经皮微通道-微电子肾镜-微超声探针碎石术治疗1.5~2.5 cm肾结石的疗效和安全性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 605-609. |
| [4] | 杨捷,冯杰莉,张树栋,马潞林,郑清. 经食管超声心动图在肾切除术联合Mayo Ⅲ~Ⅳ级静脉瘤栓取栓术不同手术方式中的临床作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 631-635. |
| [5] | 陈延,李况蒙,洪锴,张树栋,程建星,郑仲杰,唐文豪,赵连明,张海涛,姜辉,林浩成. 阴茎海绵体注射试验对阴茎血管功能影响的回顾性研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 680-686. |
| [6] | 魏越,姚兰,陆希,王军,蔺莉,刘鲲鹏. 胃超声检查评估剖宫产产妇术前饮用碳水化合物后胃排空的效果[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 1082-1087. |
| [7] | 魏越,陆希,张静,刘鲲鹏,王永军,姚兰. 术前2 h口服碳水化合物对妇科腹腔镜特殊体位手术患者胃容量及反流误吸风险的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 893-898. |
| [8] | 傅强,高冠英,徐雁,林卓华,孙由静,崔立刚. 无症状髋关节前上盂唇撕裂超声与磁共振检查的对比研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 665-669. |
| [9] | 刘杨,程昉,王艳玲,艾香艳,朱振航,赵福涛. 唾液腺超声对干燥综合征的诊断价值[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1123-1127. |
| [10] | 王昱,张慧敏,邓雪蓉,刘伟伟,陈璐,赵宁,张晓慧,宋志博,耿研,季兰岚,王玉,张卓莉. 尿枸橼酸定量检测在原发性痛风患者肾结石诊断中的应用价值[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1134-1140. |
| [11] | 翟书珩,胡攀攀,刘晓光. 术中超声辅助下环形减压术治疗多节段胸椎后纵韧带骨化症[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(5): 1021-1027. |
| [12] | 邢海英,陈玉辉,许珂,黄点点,彭清,刘冉,孙葳,黄一宁. 三维超声血管斑块定量分析技术评估颈动脉粥样硬化斑块[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(5): 991-999. |
| [13] | 邓雪蓉,孙晓莹,张卓莉. 类风湿关节炎患者足踝部体征和超声下病变的一致性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(6): 1037-1042. |
| [14] | 宋志博,耿研,邓雪蓉,张晓慧,张卓莉. 肌肉骨骼超声在指导银屑病关节炎临床分型中的价值[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(6): 1061-1066. |
| [15] | 彭喆,丁亚敏,裴林,姚海红,张学武,唐素玫. 痛风患者发生关节及肌腱内晶体沉积的临床特点[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(6): 1067-1071. |
|
||