北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2019, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (4): 665-672. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2019.04.012
输尿管镜活体组织检查对上尿路尿路上皮癌根治性手术的影响
马闰卓1,夏海缀1,陆敏2,张智荧1,张启鸣1,卢剑1,王国良1,△( ),马潞林1,△(
),马潞林1,△( )
)
- 1. 北京大学第三医院泌尿外科, 北京 100191
2. 北京大学第三医院病理科, 北京 100191
Impact of diagnostic ureteroscopy and biopsy on radical nephroureterectomy of upper tract urothelial carcinoma
Run-zhuo MA1,Hai-zhui XIA1,Min LU2,Zhi-ying ZHANG1,Qi-ming ZHANG1,Jian LU1,Guo-liang WANG1,△( ),Lu-lin MA1,△(
),Lu-lin MA1,△( )
)
- 1. Department of Urology, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
2. Department of Pathology, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
摘要:
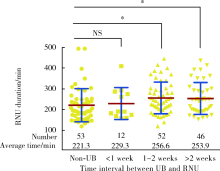
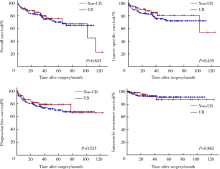
目的:探讨术前输尿管镜活体组织检查(ureteroscopy and biopsy, UB)对上尿路尿路上皮癌(upper tract urothelial carcinoma, UTUC)肾输尿管全长膀胱袖状切除术(radical nephroureterectomy, RNU)及肿瘤学预后的影响。方法:回顾性分析北京大学第三医院2007年1月至2016年12月行RNU手术的UTUC患者资料,中位随访时间40个月,比较行UB和未行UB两组患者RNU手术时长及手术出血量的差异,按UB术至RNU术的间隔时间和输尿管末端手术方式进行亚组分析,采用线性回归模型对常见手术难度的影响因素进行校正。结果:纳入UTUC患者163例,输尿管下段行开放切除者91例(55.9%),行后腹腔镜切除者72例(44.1%),110例(67.5%)术前行UB。与未行UB组相比,行UB组的平均手术时间显著延长[(221.3±79.8) min vs. (252.5±79.8) min, P=0.019],而中位出血量(50 mL vs. 50 mL, P=0.143)差异无统计学意义。亚组分析显示,UB术1周后行RNU手术的患者平均手术时间显著延长(P=0.023),等待2周以上的患者中位失血量(100 mL)显著多于未行BU的患者(50 mL,P=0.012)。多因素分析中,术前行UB(P=0.049)、≥pT3(P=0.039)、pN+(P=0.018)及输尿管下段切除术式(P=0.005)与手术时间的延长显著相关。本组患者3年肿瘤特异性生存率(cancer specific survival, CSS)为87.2%,UB对其无显著影响(P=0.435)。结论:术前UB是RNU手术时间延长的独立危险因素,但对肿瘤特异性生存无显著影响。
中图分类号:
- R737.1
| [1] | Roupret M, Babjuk M, Comperat E , et al. European Association of Urology Guidelines onupper urinary tract urothelial carcinoma: 2017 update[J]. Eur Urol, 2018,73(1):111-122. |
| [2] | Soria F, Shariat SF, Lerner SP , et al. Epidemiology, diagnosis, preoperative evaluation and prognostic assessment of upper-tract urothelial carcinoma (UTUC)[J]. World J Urol, 2017,35(3):379-387. |
| [3] | Marchioni M, Primiceri G, Cindolo L , et al. Impact of diagnostic ureteroscopy on intravesical recurrence in patients undergoing radical nephroureterectomy for upper tract urothelial cancer: a syste-matic review and meta-analysis[J]. BJU Int, 2017,120(3):313-319. |
| [4] | Guo RQ, Hong P, Xiong GY , et al. Impact of ureteroscopy before radical nephroureterectomy for upper tract urothelial carcinomas ononcological outcomes: a meta-analysis[J]. BJU Int, 2018,121(2):184-193. |
| [5] | Ma YC, Zuo L, Chen JH , et al. Modified glomerular filtration rate estimating equation for Chinese patients with chronic kidney disease[J]. J Am Soc Nephrol, 2006,17(10):2937-2944. |
| [6] | Brierley JD . TNM classification of malignant tumors[M]. 8th ed. Wiley-Blackwell: UICC International Union Against Cancer, 2017. |
| [7] | Eble J, Sauter G, Epstein J , et al. Pathology and genetics of tumours of the urinary system and male genital organs[J]. Histopathology, 2010,46(5):586. |
| [8] | Moch H, Humphrey PA, Ulbright TM , et al. WHO classification of tumours of the urinary system and male genital organs[M]. 4th ed. France: Lyon, 2016. |
| [9] | Tan P, Xie N, Yang L , et al. Diagnosticureteroscopy prior to radical nephroureterectomy for upper tract urothelial carcinoma increased the risk of intravesical recurrence[J]. Urol Int, 2018,100(1):92-99. |
| [10] | Liu Z, Zheng S, Li X , et al. Oncologic outcomes of patients undergoing diagnostic ureteroscopy before radical nephroureterectomy for upper urinary tract urothelial carcinomas: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A, 2018,28(11):1316-1325. |
| [11] | Lee HY, Yeh HC, Wu WJ , et al. The diagnostic ureteroscopy before radical nephroureterectomy in upper urinary tract urothelial carcinoma is not associated with higher intravesical recurrence[J]. World J Surg Oncol, 2018,16(1):135. |
| [12] | Xylinas E, Kluth L, Passoni N , et al. Prediction of intravesical recurrence after radical nephroureterectomy: development of a clinical decision-making tool[J]. Eur Urol, 2014,65(3):650-658. |
| [13] | Luo HL, Kang CH, Chen YT , et al. Diagnostic ureteroscopy independently correlates with intravesical recurrence after nephroureterectomy for upper urinary tracturothelial carcinoma[J]. Ann Surg Oncol, 2013,20(9):3121-3126. |
| [14] | Lee JK, Kim KB, Park YH , et al. Correlation between the timing of diagnostic ureteroscopy and intravesical recurrence in upper tract urothelial cancer[J]. Clin Genitourin Cancer, 2016,14(1):e37-e41. |
| [15] | Horuz R, Goktas C, Cetinel CA , et al. Simple preoperative parameters to assess technical difficulty during a radicalperineal prostatectomy[J]. Int Urol Nephrol, 2013,45(1):129-133. |
| [16] | Liu P, Su XH, Xiong GY , et al. Diagnosticureteroscopy for upper tract urothelial carcinoma is independently associated with intrave-sical recurrence after radical nephroureterectomy[J]. Int Braz J Urol, 2016,42(6):1129-1135. |
| [17] | Sankin A, Tin AL, Mano R , et al. Impact ofureteroscopy before nephroureterectomy for upper tract urothelial carcinoma on oncolo-gic outcomes[J]. Urology, 2016,94:148-153. |
| [18] | Lee JN, Kwon SY, Choi GS , et al. Impact of surgical wait time on oncologic outcomes in upper urinary tracturothelial carcinoma[J]. J Surg Oncol, 2014,110(4):468-475. |
| [19] | Waldert M, Karakiewicz PI, Raman JD , et al. A delay in radical nephroureterectomy can lead to upstaging[J]. BJU Int, 2010,105(6):812-817. |
| [20] | Boorjian S, Ng C, Munver R , et al. Impact of delay to nephroureterectomy for patients undergoing ureteroscopic biopsy and laser tumor ablation of upper tract transitional cell carcinoma[J]. Uro-logy, 2005,66(2):283-287. |
| [21] | Nison L, Roupret M, Bozzini G , et al. The oncologic impact of a delay between diagnosis and radicalnephroureterectomy due to diagnostic ureteroscopy in upper urinary tract urothelial carcinomas: results from a large collaborative database[J]. World J Urol, 2013,31(1):69-76. |
| [22] | Shibing Y, Liangren L, Qiang W , et al. Impact of tumour size on prognosis of upper urinary tract urothelial carcinoma after radical nephroureterectomy: a multi-institutional analysis of 795 cases[J]. BJU Int, 2016,118(6):902-910. |
| [23] | Simone G, Papalia R, Loreto A , et al. Independent prognostic value of tumour diameter and tumour necrosis in upper urinary tracturothelial carcinoma[J]. BJU Int, 2009,103(8):1052-1057. |
| [24] | Espiritu PN, Sverrisson EF, Sexton WJ , et al. Effect of tumor size on recurrence-free survival of upper tract urothelial carcinoma following surgical resection[J]. Urol Oncol, 2014,32(5):619-624. |
| [25] | Pieras E, Frontera G, Ruiz X , et al. Concomitant carcinoma in situ and tumour size are prognostic factors for bladder recurrence after nephroureterectomy for upper tract transitional cell carcinoma[J]. BJU Int, 2010,106(9):1319-1323. |
| [26] | Milenkovic-Petronic D, Milojevic B, Djokic M , et al. The impact of tumor size on outcomes in patients with upper urinary tracturothelial carcinoma[J]. Int Urol Nephrol, 2014,46(3):563-569. |
| [27] | Su X, Fang D, Li X , et al. Theinfluence of tumor size on oncolo-gic outcomes for patients with upper tract urothelial carcinoma after radical nephroureterectomy[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2016,2016:4368943. |
| [1] | 张崔建,何志嵩,周利群. 上尿路尿路上皮癌的淋巴清扫[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(4): 592-594. |
| [2] | 戴翔,王飞,杜依青,宋宇轩,徐涛. 上尿路尿路上皮癌组织中脂肪因子表达与临床病理特征及预后的相关性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(4): 605-614. |
| [3] | 李志华,徐纯如,刘颖,贯华,张萌,车新艳,唐琦,黄燕波,李学松,周利群. 饮水习惯与上尿路尿路上皮癌病理特征的相关性分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(4): 621-627. |
| [4] | 张春龙,王明瑞,王起,许克新,徐涛,胡浩. 覆膜金属输尿管支架维持性治疗输尿管镜碎石术后难治性输尿管狭窄的远期疗效评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(4): 674-679. |
| [5] | 陈怀安,刘硕,李秀君,王哲,张潮,李凤岐,苗文隆. 炎症生物标志物对输尿管尿路上皮癌患者预后预测的临床价值[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(2): 302-307. |
| [6] | 关豹,翁迈,凡航,彭鼎,方冬,熊耕砚,李学松,周利群. 术前贫血对上尿路尿路上皮癌预后的影响: 单中心686例患者回顾性研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(6): 1056-1061. |
| [7] | 郝一昌,陈昆,刘余庆,卢剑,肖春雷,马潞林. 输尿管软镜下钬激光切除术治疗肾盂癌6例报道及文献复习[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(5): 816-821. |
| [8] | 王冰,叶剑飞,赵磊,毕海,卢剑,马潞林. 经皮肾通道多镜联合顺行治疗回肠膀胱术后上尿路结石1例并文献复习[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(4): 733-735. |
| [9] | 马闰卓,邱敏,何为,杨斌,夏海缀,邹达,陆敏,马潞林,卢剑. 输尿管镜活检可协助上尿路尿路上皮癌危险分层[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(4): 632-637. |
| [10] | 叶海云,许清泉,马凯,黄晓波. 内镜治疗的输尿管结石患者治疗前结石位置和输尿管扩张特点分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(4): 622-625. |
| [11] | 叶雄俊,刘军,阿不都克依木·阿不力米提,熊六林,刘士军,徐涛,黄晓波. 后腹腔镜联合经腰小切口“杂交”手术在复杂肾肿瘤保留肾单位手术中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(4): 613-616. |
| [12] | 关豹,曹振朋,彭鼎,李一帆,詹永豪,刘漓波,何世明,熊耕砚,李学松,周利群. T2N0M0期上尿路尿路上皮癌患者预后相关因素分析:单中心235例患者回顾性研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(4): 603-607. |
| [13] | 刘可, 肖春雷, 刘余庆, 郝一昌, 张树栋, 田雨, 马潞林. 输尿管软镜下钬激光憩室颈部切开及碎石治疗微小出口肾盏憩室结石[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2015, 47(4): 618-621. |
| [14] | 马凯, 黄晓波, 熊六林, 许清泉, 徐涛, 叶海云, 于路平, 王晓峰. 国产新型可拆卸式输尿管软镜在治疗上尿路结石中的应用(附36例报告)[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2015, 47(4): 615-617. |
| [15] | 张力杰, 叶雄俊, 黄晓波, 熊六林, 马凯, 李建兴, 王晓峰. 无管化经皮肾镜和输尿管镜碎石术处理最大径线1.5 cm以上输尿管上段结石的比较[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2015, 47(1): 170-174. |
|
||