北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2020, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (2): 332-338. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2020.02.022
软组织垂直厚度对牙周炎患者种植修复临床效果的影响
- 北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院,牙周科 国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心 口腔数字化医疗技术和材料国家工程实验室 口腔数字医学北京市重点实验室,北京 100081
Effect of vertical soft tissue thickness on clinical manifestation of peri-implant tissue in patients with periodontitis
Zhong ZHANG,Huan-xin MENG( ),Jie HAN(
),Jie HAN( ),Li ZHANG,Dong SHI
),Li ZHANG,Dong SHI
- Department of Periodontology, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Laboratory for Digital and Material Technology of Stomatology & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
摘要:
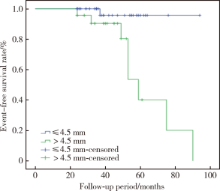
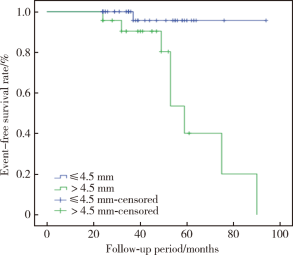
目的 观察牙周炎病史患者种植后的中,长期临床效果,探讨软组织垂直厚度对植体周组织健康及植体周病发生的影响.方法: 根据种植术中测量的植入位点软组织垂直厚度,将66名患者的66颗植体分为正常组(normal,软组织垂直厚度 ≤4.5 mm)及过厚组(thick,软组织垂直厚度 >4.5 mm)两组.随访至少2年后进行复查,记录植体留存情况,植体周探诊深度,出血指数,菌斑指数,植体周边缘骨吸收量及植体周病发生情况,并进行统计分析,比较两组之间的差异.结果: 植体留存率为100%.复查时过厚组植体的植体周探诊深度最大值(max PDi),植体周探诊深度平均值(mean PDi),植体周出血指数最大值(max BIi),植体周出血指数平均值(mean BIi),植体近中边缘骨吸收量平均值,植体远中边缘骨吸收量平均值,植体周边缘骨吸收量平均值,植体周菌斑指数平均值(mean PLIi)均显著高于正常组(P<0.05).此外,正常组复查时植体周炎发病率2.3%,过厚组复查时植体周炎发病率34.8%,两组植体周炎发病率的差异有统计学意义(P<0.05).结论: 牙周炎患者种植位点的软组织垂直厚度对植体周软硬组织健康存在显著影响;过厚的软组织垂直厚度与植体周探诊深度及植体周边缘骨吸收量增多有关,最终可能增加植体周病的发病风险.
中图分类号:
- R783.3
| [1] | Hämmerle CHF, Dennis T.The etiology of hard- and soft-tissue deficiencies at dental implants: a narrative review[J]. J Periodontol, 2018, 89(Suppl 1): S291-S303 |
| [2] | Karoussis I, Salvi G, Heitzmayfield L, et al.Long-term implant prognosis in patients with and without a history of chronic periodontitis: a 10-year prospective cohort study of the ITI® dental implant system[J]. Clin Oral Implants Res, 2003, 14(3): 329-339. |
| [3] | Xie Y, Meng H, Han J, et al.A retrospective cohort study of peri-implant condition in Chinese patients with different periodontal condition and maintenance frequency[J]. Clin Oral Implants Res, 2018, 29(11): 1135-1142. |
| [4] | Linkevicius T, Apse P, Grybauskas S, et al.The influence of soft tissue thickness on crestal bone changes around implants: a 1-year prospective controlled clinical trial[J]. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants, 2009, 24(4): 712-719. |
| [5] | Lee CT, Huang YW, Zhu L, et al.Prevalence of peri-implantitis and peri-implant mucositis: systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. J Dent, 2017, 62: 1-12. |
| [6] | Berglundh T, Lindhe J.Dimension of the periimplant mucosa: biological width revisited[J]. J Clin Periodontol, 1996, 23(10): 971-973. |
| [7] | Linkevicius T, Puisys A, Linkeviciene L, et al.Crestal bone stability around implants with horizontally matching connection after soft tissue thickening: a prospective clinical trial[J]. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res, 2015, 17(3): 497-508. |
| [8] | Puisys A, Linkevicius T.The influence of mucosal tissue thickening on crestal bone stability around bone-level implants: a prospective controlled clinical trial[J]. Clin Oral Implants Res, 2015, 26(2): 123-129. |
| [9] | Linkevicius T, Puisys A, Steigmann M, et al.Influence of vertical soft tissue thickness on crestal bone changes around implants with platform switching: a comparative clinical study[J]. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res, 2015, 17(6): 1228-1236. |
| [10] | Suárez-López del Amo F, Lin GH, Monje A, et al. Influence of soft tissue thickness upon peri-implant marginal bone loss: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. J Periodontol, 2016, 87(6): 690-699. |
| [11] | Berglundh T, Lindhe J, Ericsson I, et al.The soft tissue barrier at implants and teeth[J]. Clin Oral Implants Res, 1991, 2(2): 81-90. |
| [12] | Cochran DL, Hermann JS, Schenk RK, et al.Biologic width around titanium implants. A histometric analysis of the implanto-gingival junction around unloaded and loaded nonsubmerged implants in the canine mandible[J]. J Periodontol, 1997, 68(2):186-197. |
| [13] | Schwarz F, Derks J, Monje A, et al.Peri-implantitis[J]. J Periodontol, 2018, 89(6): S267-S290. |
| [14] | Papaioannou W, Quirynen M, Steenberghe DV.The influence of periodontitis on the subgingival flora around implants in partially edentulous patients[J]. Clin Oral Implants Res, 1997, 7(4): 405-409. |
| [15] | 闫夏. 牙周炎患者种植植骨的影像学分析和种植体及邻牙的微生物研究[D]. 北京: 北京大学医学部, 2016: 1-82. |
| [16] | Kassebaum NJ, Bernabé E, Dahiya M, et al.Global burden of severe periodontitis in 1990-2010: a systematic review and meta-regression[J]. J Dent Res, 2014, 93(11): 1045-1053. |
| [17] | Roccuzzo M, De AN, Bonino L, et al.Ten-year results of a three-arm prospective cohort study on implants in periodontally compromised patients. Part 1: implant loss and radiographic bone loss[J]. Clin Oral Implants Res, 2010, 21(5): 490-496. |
| [18] | Roccuzzo M, Bonino F, Aglietta M, et al.Ten-year results of a three arms prospective cohort study on implants in periodontally compromised patients. Part 2: clinical results[J]. Clin Oral Implants Res, 2012, 23(4): 389-395. |
| [19] | Koldsland OC, Scheie AA, Aass AM.Prevalence of peri-implantitis related to severity of the disease with different degrees of bone loss[J]. J Periodontol, 2010, 81(2): 231-238. |
| [20] | Ladeira CP, Constante PM, Leite DME, et al.History of chronic periodontitis is a high risk indicator for peri-implant disease[J]. Braz Dent J, 2013, 24(2): 136-141. |
| [21] | Han J, Zhang X, Tang Z, et al.A prospective, multicenter study assessing the DENTSPLY Implants, OsseoSpeedTM TX, length 6 mm in the posterior maxilla and mandible: a 1-year follow-up study[J]. Clin Oral Implants Res, 2016, 27(4): 452-457. |
| [22] | Fuchigami K, Munakata M, Kitazume T, et al.A diversity of peri-implant mucosal thickness by site[J]. Clin Oral Implants Res, 2017, 28(2): 171-176. |
| [23] | Zhang H, Li W, Zhang L, et al.A nomogram prediction of peri-implantitis in treated severe periodontitis patients: a 1-5-year prospective cohort study[J]. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res, 2018, 20(6): 962-968. |
| [1] | 孙菲,刘建,李思琪,危伊萍,胡文杰,王翠. 种植体黏膜下微生物在健康种植体和种植体周炎中的构成与差异:一项横断面研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(1): 30-37. |
| [2] | 孟令玮,李雪,高胜寒,李悦,曹瑞涛,张毅,潘韶霞. 三种方法建立大鼠种植体周炎模型的比较[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(1): 22-29. |
| [3] | 孙菲,李思琪,危伊萍,钟金晟,王翠,胡文杰. 种植体周病非手术治疗中联合应用甘氨酸粉喷砂的临床效果评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(1): 119-125. |
| [4] | 释栋,曹婕,戴世爱,孟焕新. 植体周炎再生治疗短期疗效观察[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(1): 58-63. |
|
||