北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2020, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (3): 425-431. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2020.03.005
成年双生子空腹血糖、糖化血红蛋白与全基因组DNA甲基化的相关性研究
王兆年1,高文静1,△( ),王碧琦1,曹卫华1,吕筠1,余灿清1,逄增昌2,丛黎明3,汪华4,吴先萍5,刘彧6,李立明1
),王碧琦1,曹卫华1,吕筠1,余灿清1,逄增昌2,丛黎明3,汪华4,吴先萍5,刘彧6,李立明1
- 1. 北京大学公共卫生学院流行病与卫生统计学系,北京 100191
2. 青岛市疾病预防控制中心,山东青岛 266033
3. 浙江省疾病预防控制中心,杭州 310051
4. 江苏省疾病预防控制中心,南京 210009
5. 四川省疾病预防控制中心,成都 610041
6. 黑龙江省农垦总局疾病预防控制中心,哈尔滨 150090
Correlation between fasting plasma glucose, HbA1c and DNA methylation in adult twins
Zhao-nian WANG1,Wen-jing GAO1,△( ),Bi-qi WANG1,Wei-hua CAO1,Jun LV1,Can-qing YU1,Zeng-chang PANG2,Li-ming CONG3,Hua WANG4,Xian-ping WU5,Yu LIU6,Li-ming LI1
),Bi-qi WANG1,Wei-hua CAO1,Jun LV1,Can-qing YU1,Zeng-chang PANG2,Li-ming CONG3,Hua WANG4,Xian-ping WU5,Yu LIU6,Li-ming LI1
- 1. Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, Peking University School of Public Health, Beijing 100191, China
2. Qingdao Municipal Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Qingdao 266033, Shandong, China
3. Zhejiang Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Hangzhou 310051, China
4. Jiangsu Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Nanjing 210009, China
5. Sichuan Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Chengdu 610041, China
6. Center for Disease Control and prevention, Heilongjiang Agricultural Reclamation Bureau, Harbin 150090, China
摘要:
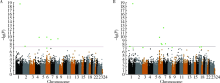
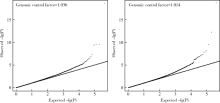
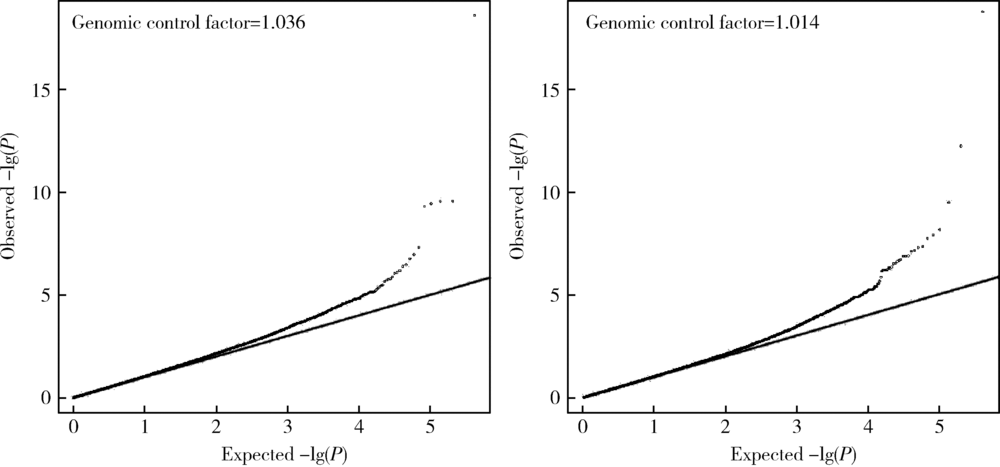
目的 利用双生子人群分别探索与空腹血糖(fasting plasma glucose,FPG)或糖化血红蛋白(glycated haemoglobin, HbA1c)存在相关性的胞嘧啶-磷酸-鸟嘌呤(cytidine-phosphate-guanosine site,CpG)位点。方法 研究对象来自中国双生子登记系统2013年6月至12月和2017年6月至2018年10月于山东青岛、浙江、江苏、四川及黑龙江五地募集的338人(169对)同卵双生子。甲基化检测分别为Illumina Infinium HumanMethylation450 BeadChip和Illumina Infinium MethylationEPIC BeadChip两种芯片,采用混合效应模型,分别将空腹血糖及HbA1c作为主效应,将甲基化水平(β值)作为因变量,将年龄、体重指数(body mass index, BMI)、血压、血细胞组成成分、用SVA包生成的代理变量等连续变量,及性别、吸烟、饮酒、是否服用降糖药等分类变量作为协变量纳入固定效应模型,将双生子对编号纳入随机效应模型,将截距设置为随机,进行回归分析,找出分别与空腹血糖或HbA1c相关的CpG位点。结果 本研究最终纳入同卵双生子338人(169对),CpG位点412 459个,其中男性同卵双生子114对、女性55对,平均年龄(48.2±11.9)岁。在调整年龄、性别、BMI、血压、吸烟、饮酒、血细胞成分等协变量及多重比较校正后,发现7个与空腹血糖相关的CpG位点(cg19693031、cg01538969、cg08501915、cg04816311、ch.8.1820050F、cg06721411、cg26608667), 其中3个位点(cg08501915、ch.8.1820050F、cg26608667)为本研究新发现的位点;发现10个与HbA1c相关的CpG位点(cg19693031、cg04816311、cg01538969、cg01339781、cg01676795、cg24667115、cg09029192、cg20697417、ch.4.1528651F、cg16097041),其中4个位点(cg01339781、cg24667115、cg20697417、ch.4.1528651F)为本研究新发现的位点。本研究发现,位于TXNIP基因上的cg19693031位点在DNA甲基化与空腹血糖及HbA1c相关分析中均是P值最小的位点(PFPG=2.42×10-19, FD
中图分类号:
- R179
| [1] | Cho NH, Shaw JE, Karuranga S, et al. IDF diabetes atlas: Glo-bal estimates of diabetes prevalence for 2017 and projections for 2045[J]. Diabetes Res Clin Pract, 2018,138:271-281. |
| [2] |
Wang L, Gao P, Zhang M, et al. Prevalence and ethnic pattern of diabetes and prediabetes in China in 2013[J]. JAMA, 2017,317(24):2515-2523.
doi: 10.1001/jama.2017.7596 pmid: 28655017 |
| [3] | Zheng Y, Ley SH, Hu FB. Global aetiology and epidemiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its complications[J]. Nat Rev Endocrinol, 2018,14(2):88-98. |
| [4] | American Diabetes Association. Classification and diagnosis of diabetes: Standards of medical care in diabetes-2018[J]. Diabetes Care, 2018,41(Suppl 1):13-27. |
| [5] | World Health Organization. Use of glycated haemoglobin (HbA1c) in the diagnosis of diabetes mellitus: Abbreviated report of a who consultation[R/OL]. (2011-01-12)[2020-01-05]. https://www.who.int/diabetes/publications/report-hba1c_2011.pdf. |
| [6] |
Singh GM, Danaei G, Farzadfar F, et al. The age-specific quantitative effects of metabolic risk factors on cardiovascular diseases and diabetes: A pooled analysis[J]. PLoS One, 2013,8(7):e65174.
pmid: 23935815 |
| [7] | 高文静, 李立明. 以分开抚养双生子为基础的研究进展[J]. 中华医学遗传学杂志, 2014,31(3):327-329. |
| [8] |
Tan Q, Christiansen L, von Bornemann Hjelmborg J, et al. Twin methodology in epigenetic studies[J]. J Exp Biol, 2015,218(Pt 1):134-139.
pmid: 25568460 |
| [9] |
Hwang JY, Lee HJ, Go MJ, et al. Genome-wide methylation ana-lysis identifies ELOVL5 as an epigenetic biomarker for the risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. Sci Rep, 2018,8(1):14862.
pmid: 30291282 |
| [10] |
Liu F, Sun Q, Wang L, et al. Bioinformatics analysis of abnormal DNA methylation in muscle samples from monozygotic twins discordant for type 2 diabetes[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2015,12(1):351-356.
pmid: 25760736 |
| [11] | Yuan W, Xia Y, Bell CG, et al. An integrated epigenomic analysis for type 2 diabetes susceptibility loci in monozygotic twins[J]. Nat Commun, 2014,5:5719. |
| [12] |
Fortin JP, Triche TJ Jr., Hansen KD. Preprocessing, normalization and integration of the Illumina HumanMethylationEPIC array with minfi[J]. Bioinformatics, 2017,33(4):558-560.
pmid: 28035024 |
| [13] | Pidsley R, Cc YW, Volta M, et al. A data-driven approach to preprocessing Illumina 450K methylation array data[J]. BMC Genomics, 2013,14:293. |
| [14] |
Wang B, Gao W, Yu C, et al. Determination of zygosity in adult Chinese twins using the 450K methylation array versus questionnaire data[J]. PLoS One, 2015,10(4):e0123992.
pmid: 25927701 |
| [15] |
Houseman EA, Accomando WP, Koestler DC, et al. DNA methylation arrays as surrogate measures of cell mixture distribution[J]. BMC Bioinformatics, 2012,13:86.
doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-13-86 pmid: 22568884 |
| [16] |
Leek JT, Storey JD. Capturing heterogeneity in gene expression studies by surrogate variable analysis[J]. PLoS Genet, 2007,3(9):1724-1735.
pmid: 17907809 |
| [17] | Michels KB, Binder AM. Considerations for design and analysis of DNA methylation studies[J]. Methods Mol Biol, 2018,1708:31-46. |
| [18] |
Carlin JB, Gurrin LC, Sterne JA, et al. Regression models for twin studies: A critical review[J]. Int J Epidemiol, 2005,34(5):1089-1099.
pmid: 16087687 |
| [19] | Soriano-Tarraga C, Jimenez-Conde J, Giralt-Steinhauer E, et al. Epigenome-wide association study identifies TXNIP gene associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus and sustained hyperglycemia[J]. Hum Mol Genet, 2016,25(3):609-619. |
| [20] | Meeks KAC, Henneman P, Venema A, et al. Epigenome-wide association study in whole blood on type 2 diabetes among sub-Saharan African individuals: Findings from the RODAM study[J]. Int J Epidemiol, 2019,48(1):58-70. |
| [21] | Pena GG, Dutra MS, Gazzinelli A, et al. Heritability of phenotypes associated with glucose homeostasis and adiposity in a rural area of Brazil[J]. Ann Hum Genet, 2014,78(1):40-49. |
| [22] | Cardona A, Day FR, Perry JRB, et al. Epigenome-wide association study of incident type 2 diabetes in a british population: EPIC-Norfolk study[J]. Diabetes, 2019,68(12):2315-2326. |
| [23] | Al Muftah WA, Al-Shafai M, Zaghlool SB, et al. Epigenetic associations of type 2 diabetes and BMI in an Arab population[J]. Clin Epigenetics, 2016,8:13. |
| [24] | Kulkarni H, Kos MZ, Neary J, et al. Novel epigenetic determinants of type 2 diabetes in Mexican-American families[J]. Hum Mol Genet, 2015,24(18):5330-5344. |
| [25] | Galmozzi A, Kok BP, Kim AS, et al. PGRMC2 is an intracellular haem chaperone critical for adipocyte function[J]. Nature, 2019,576(7785):138-142. |
| [26] | Alhawiti NM, Al Mahri S, Aziz MA, et al. TXNIP in metabolic regulation: Physiological role and therapeutic outlook[J]. Curr Drug Targets, 2017,18(9):1095-1103. |
| [27] | Waldhart AN, Dykstra H, Peck AS, et al. Phosphorylation of TXNIP by AKT mediates acute influx of glucose in response to insulin[J]. Cell Rep, 2017,19(10):2005-2013. |
| [28] |
Gencheva M, Kato M, Newo AN, et al. Contribution of deah-box protein DHX16 in human pre-mRNA splicing[J]. Biochem J, 2010,429(1):25-32.
pmid: 20423332 |
| [1] | 王薇,王佳宁,虞巍,朱赛楠,高莹,张俊清. 肾上腺性库欣综合征与无功能腺瘤患者的凝血功能比较及其影响因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 1062-1067. |
| [2] | 汪雨欣,邓宇含,谭银亮,刘宝花. 应激性血糖升高对重症监护病房患者28 d全因死亡风险的预测价值[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 442-449. |
| [3] | 娄雪,廖莉,李兴珺,王楠,刘爽,崔若玫,徐健. 类风湿关节炎患者外周血TWEAK基因启动子区甲基化状态及其表达[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(6): 1020-1025. |
| [4] | 尹雪倩, 张晓玄, 文婧, 刘思奇, 刘欣然, 周若宇, 王军波. 荞麦、燕麦、豌豆复配对糖尿病大鼠血糖的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(3): 447-452. |
| [5] | 郭洪萍,赵艾,薛勇,马良坤,张玉梅,王培玉. 孕期营养素摄入与妊娠期糖尿病孕妇血糖控制效果的相关性研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(3): 467-472. |
| [6] | 吴震天,高文静,王碧琦,曹卫华,吕筠,余灿清,逄增昌,丛黎明,汪华,吴先萍,李立明. 成年双生子血压水平与DNA甲基化相关性研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(3): 387-394. |
| [7] | 何海珍,张婷,周景,王东平,王浩杰,宋阳,朱珠,王培玉,刘爱萍. 乌海市成人含糖饮料饮用与糖尿病的关系[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(3): 469-473. |
| [8] | 朱振杰,许清泉,黄晓波,洪扬,杨庆亚,王澍,安立哲,徐涛. 糖尿病患者经皮肾镜取石术后发生全身炎症反应综合征的危险因素分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2016, 48(4): 643-649. |
| [9] | 李志霞,武珊珊,杨智荣,詹思延,孙凤. 胰高血糖素样肽1受体激动剂类降糖药致2型糖尿病患者鼻咽炎和上呼吸道感染的网状meta分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2016, 48(3): 454-459. |
| [10] | 孙可欣, 刘志, 曹亚英, 隽娟, 项骁, 杨成, 黄少平, 刘晓芬, 李娜, 唐迅, 李劲, 吴涛, 陈大方, 胡永华 . 北京某社区2型糖尿病患者血糖控制情况与肱踝脉搏波传导速度的相关性研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2015, 47(3): 431-436. |
| [11] | 徐可, 刘雪芹, 张春雨, 王颖, 李星, 吴晔, 杨艳玲, 肖慧捷. 果糖-1,6-二磷酸酶缺乏症基因诊断1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2014, 46(5): 681-685. |
| [12] | 胡倩, 于丽, 廖秦平. 基质金属蛋白酶2基因启动子的甲基化状态对子宫内膜癌侵袭力调控的分子机制[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2012, 44(6): 911-915. |
| [13] | 王先火, 赵秀娟, 邱立华, 王华庆, 王玺, . 肿瘤发生的表观遗传学:进展与临床意义[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2012, 44(5): 701-707. |
| [14] | 于卓人*, 刘丽笙, 栾庆先, 王兴宇, 李蓬, 沙月琴, 刘曦. 北京石景山区老年人群牙周炎与代谢综合征的相关性探讨[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2012, 44(4): 633-638. |
| [15] | 李立明, 高文静, 胡永华, 曹卫华, 詹思延, 吕筠, 余灿清. 方兴未艾的双生子研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2012, 44(3): 331-333. |
|
||