北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2020, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (3): 464-469. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2020.03.011
孕晚期妇女与新生儿血浆维生素A水平的相关性分析
李秀翠1,2,周玉博1,2,△( ),司可艺1,2,李宏田1,2,张乐1,2,张亚黎1,2,刘菊芬1,2,刘建蒙1,2,△(
),司可艺1,2,李宏田1,2,张乐1,2,张亚黎1,2,刘菊芬1,2,刘建蒙1,2,△( )
)
- 1. 北京大学公共卫生学院流行病与卫生统计学系,北京 100191
2. 北京大学生育健康研究所,国家卫生健康委员会生育健康重点实验室,北京 100191
Relationship of plasma vitamin A levels between neonates and pregnant women in third trimester
Xiu-cui LI1,2,Yu-bo ZHOU1,2,△( ),Ke-yi SI1,2,Hong-tian LI1,2,Le ZHANG1,2,Ya-li ZHANG1,2,Ju-fen LIU1,2,Jian-meng LIU1,2,△(
),Ke-yi SI1,2,Hong-tian LI1,2,Le ZHANG1,2,Ya-li ZHANG1,2,Ju-fen LIU1,2,Jian-meng LIU1,2,△( )
)
- 1. Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, Peking University School of Public Health, Beijing 100191, China
2. Institute of Reproductive and Child Health, National Health Commission Key Laboratory of Reproductive Health, Peking University, Beijing 100191, China
摘要:
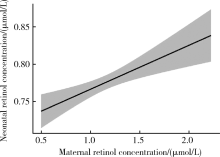
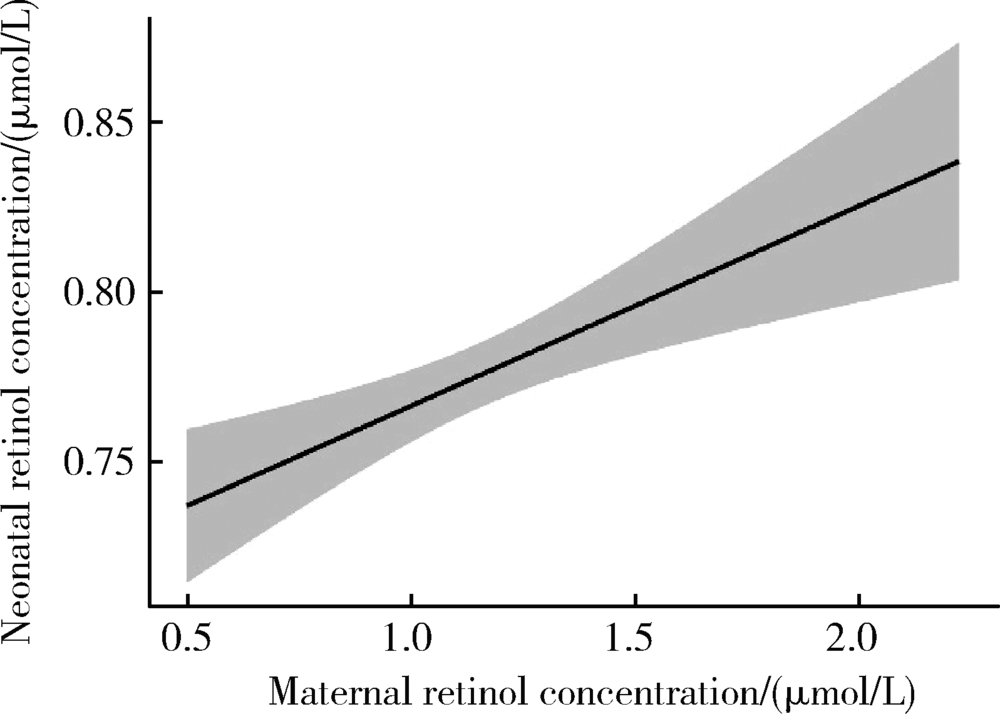
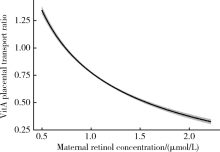
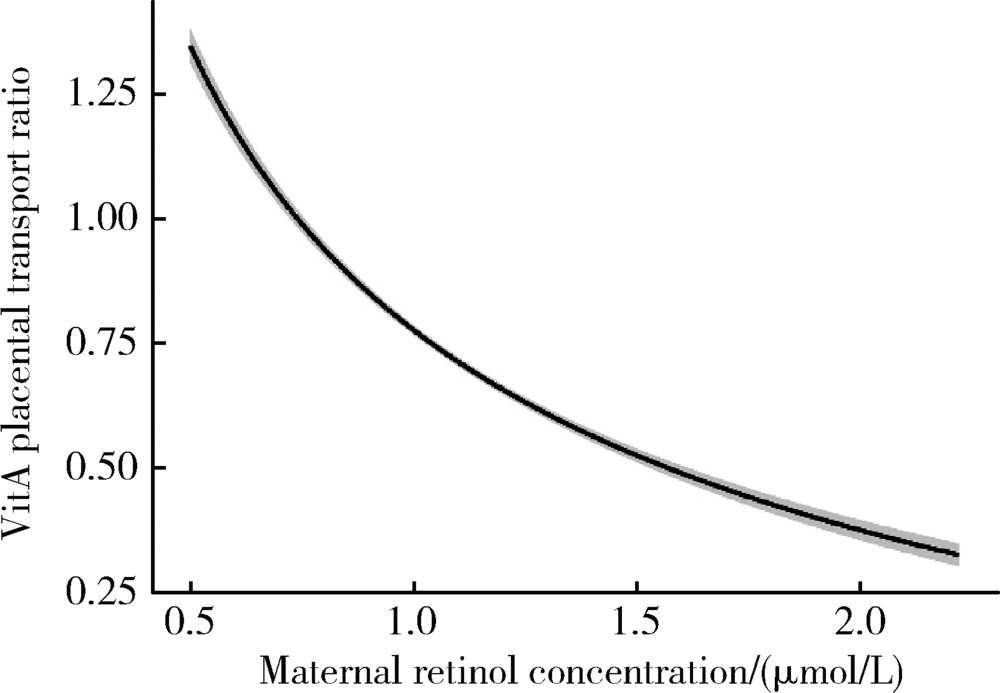
目的 探讨孕晚期妇女静脉血与新生儿脐带血血浆维生素A(vitamin A,VitA)水平的相关性。方法 2009年5月至6月在河北省元氏县和乐亭县募集孕妇688例,采集产前静脉血和新生儿脐带血,采用高效液相色谱法检测血浆视黄醇浓度,用以反映VitA水平。根据产前静脉血血浆视黄醇浓度,孕妇VitA营养状态分为缺乏(<0.70 μmol/L)、边缘性缺乏(0.70~<1.05 μmol/L)、充足(≥1.05 μmol/L)。根据脐带血血浆视黄醇浓度,新生儿VitA营养状态分为缺乏(<0.35 μmol/L)、边缘性缺乏(0.35~<0.70 μmol/L)、充足(≥0.70 μmol/L);将脐带血血浆视黄醇浓度低于第10百分位数定义为新生儿VitA相对缺乏。新生儿与孕妇血浆视黄醇浓度比值定义为VitA胎盘转运系数。采用多元分式多项式(multivariable fractional polynomials,MFP)模型和Pearson相关探讨孕妇与新生儿血浆VitA水平的关系,采用Logistic回归模型探讨孕妇VitA营养状态对新生儿VitA缺乏的影响,采用MFP模型和Spearman相关探讨孕妇VitA水平与胎盘转运系数的关系。结果 孕晚期妇女视黄醇平均浓度为(1.15±0.30)μmol/L,VitA缺乏率和边缘性缺乏率分别为4.5%和37.8%;新生儿视黄醇平均浓度为(0.78±0.13)μmol/L,无VitA缺乏,边缘性缺乏率为28.2%。调整孕妇年龄、体重指数等因素后,孕妇与新生儿VitA水平间呈线性正向剂量-反应关系(幂参数=1,P<0.05), Pearson相关系数为0.13(P<0.01)。与VitA充足组孕妇相比,缺乏组(crude OR=2.20,95%CI:1.04~4.66)和边缘性缺乏组(crude OR=1.43,95%CI:1.01~2.02)分娩VitA边缘性缺乏新生儿的风险显著升高,但多因素调整后,上述效应不再有统计学意义;VitA缺乏组孕妇分娩VitA相对缺乏新生儿的风险在调整多因素前后均显著增加(crude OR=3.02,95%CI:1.21~7.50;adjusted OR=2.76,95%CI:1.05~7.22)。孕妇VitA水平与VitA胎盘转运系数间呈非线性负向剂量-反应关系(幂参数=-0.5,P<0.05),调整后Spearman相关系数为-0.82(P<0.001)。结论 孕晚期妇女与新生儿血浆VitA水平呈正向线性剂量-反应关系,提示孕妇VitA营养状态影响新生儿VitA储存水平。
中图分类号:
- R172
| [1] | Murguia-Peniche T. Vitamin D, vitamin A, maternal-perinatal considerations: old concepts, new insights, new questions[J]. J Pediatr, 2013,162(Suppl 3):26-30. |
| [2] | Ahmad SM, Alam MJ, Afsana K, et al. Vitamin A supplementation during pregnancy enhances pandemic H1N1 vaccine response in mothers, but enhancement of transplacental antibody transfer may depend on when mothers are vaccinated during pregnancy[J]. J Nutr, 2018,148(12):1968-1975. |
| [3] |
Neves PAR, Castro MC, Oliveira CVR, et al. Effect of vitamin A status during pregnancy on maternal anemia and newborn birth weight: results from a cohort study in the Western Brazilian Amazon[J]. Eur J Nutr, 2018,59(1):45-56.
pmid: 30560301 |
| [4] |
Handel MN, Moon RJ, Titcombe P, et al. Maternal serum retinol and beta-carotene concentrations and neonatal bone mineralization: results from the Southampton women’s survey cohort[J]. Am J Clin Nutr, 2016,104(4):1183-1188.
doi: 10.3945/ajcn.116.130146 pmid: 27629051 |
| [5] | Hanson C, Lyden E, Anderson-Berry A, et al. Status of retinoids and carotenoids and associations with clinical outcomes in maternal-infant pairs in Nigeria[J]. Nutrients, 2018,10(9):1286. |
| [6] | 黄娜, 刘颖. 维生素A与呼吸系统疾病关系的研究进展[J]. 国际儿科学杂志, 2019,46(7):512-515. |
| [7] |
Ali H, Hamadani J, Mehra S, et al. Effect of maternal antenatal and newborn supplementation with vitamin A on cognitive development of school-aged children in rural Bangladesh: a follow-up of a placebo-controlled, randomized trial[J]. Am J Clin Nutr, 2017,106(1):77-87.
pmid: 28490513 |
| [8] |
West KP, Sommer A. Neonatal vitamin A: time to move on?[J]. Lancet, 2015,386(9989):131-132.
pmid: 26194387 |
| [9] | 刘欢, 苗静琨, 余林超, 等. 新生儿与母亲孕晚期维生素A水平的相关研究[J]. 重庆医科大学学报, 2018 ( 6):818-823. |
| [10] | Ramalho RA, dos Anjos LA, Flores H. Nutritional status of vitamin A in mother/newborn pairs from 2 hospital nurseries in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil[J]. Arch Latinoam Nutr, 1999,49(4):318-321. |
| [11] | Wassef L, Quadro L. Uptake of dietary retinoids at the maternal-fetal barrier: in vivo evidence for the role of lipoprotein lipase and alternative pathways[J]. J Biol Chem, 2011,286(37):32198-32207. |
| [12] | World Health Organization. Global prevalence of vitamin A deficiency in populations at risk 1995—2005: WHO global database on vitamin A deficiency[R]. Geneva: WHO, 2005. |
| [13] | 中国疾病预防控制中心营养与健康所. 人群维生素A缺乏筛查方法: WS/T 553—2017[S/OL]. 北京: 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会, 2017, 8 ( 2017- 08- 01)[2020-02-20]. http://www.nhc.gov.cn/wjw/yingyang/201708/da44da0299504b9da360b4da7ebeb2a6.shtml. |
| [14] |
Berggren SM, Fex GA, Nilsson-Ehle P. Concentrations of reti-noids in early pregnancy and in newborns and their mothers[J]. Am J Clin Nutr, 2005,81(3):633-636.
pmid: 15755833 |
| [15] | 胡贻椿, 李敏, 陈竞, 等. 2010—2012年中国农村孕妇贫血及维生素A、维生素D营养状况[J]. 卫生研究, 2017,46(3):361-366, 372. |
| [16] | Mills JP, Terasawa E, Tanumihardjo SA. Ingestion of excessive preformed vitamin A by mothers amplifies storage of retinyl esters in early fetal livers of captive old world monkeys[J]. Comp Med, 2007,57(5):505-511. |
| [17] | Godel JC, Basil TK, Pabst HF, et al. Perinatal vitamin A (retinol) status of northern Canadian mothers and their infants[J]. Neonatology, 1996,69(3):133-139. |
| [18] | Gomes MM, Saunders C, Ramalho A, et al. Serum vitamin A in mothers and newborns in the city of Rio de Janeiro[J]. Int J Food Sci Nutr, 2009,60(4):282-292. |
| [19] | Agarwal K, Dabke AT, Phuljhele NL, et al. Factors affecting serum vitamin A levels in matched maternal-cord pairs[J]. Indian J Pediatr, 2008,75(5):443-446. |
| [20] | Hanson C, Schumacher M, Lyden E, et al. Status of vitamin A and related compounds and clinical outcomes in maternal-infant pairs in the Midwestern United States[J]. Ann Nutr Metab, 2017,71(3/4):175-182. |
| [21] |
Ismadi SD, Olson JA. Dynamics of the fetal distribution and transfer of vitamin A between rat fetuses and their mother[J]. Int J Vitam Nutr Res, 1982,52(2):112-119.
pmid: 7129792 |
| [22] | Inorganic Toxicology and Nutrition Branch Division of Laboratory Sciences National Center for Environmental Health, The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Fat soluble micronutrients (vitamins A, E and carotenoids) UV-visible detection[EB/OL]. ( 2005-06-01) [2020-02-20]. https://wwwcdcgov/nchs/data/nhanes/nhanes_05_06/vitaec_d_met_aecarpdf. |
| [1] | 秦婧, 周玉博, 李宏田, 孟莹, 刘建蒙. 中国三地乳母乳汁维生素A营养状况及影响因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 794-801. |
| [2] | 李宁宁,季丽娜,晁爽,袁珂,孟洪,黄振宇,张华斌. 新生儿先天性肾脏和泌尿道畸形的超声筛查及随访[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(6): 1062-1066. |
| [3] | 赵丽君,李宏田,张亚黎,周玉博,刘建蒙. 基于移动终端开展中国新生儿出生特征研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(5): 813-818. |
| [4] | 郁静茹, 金蕾, 肖利华, 靳蕾. 北京通州区神经管缺陷患病率及其与监测时限的关系[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2015, 47(6): 1042-1045. |
| [5] | 彭容, 魏小平, 梁小华, 陈洁, 刘友学, 张霆, 李廷玉 . 重庆市巴南区学龄前儿童膳食维生素A摄入量与血浆维生素A的关系[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2014, 46(3): 366-372. |
| [6] | 崔好胜, 李宏田, 朱丽萍 , 李智文, 周玉博, 刘建蒙, . 1993~2005年中国南方部分地区经产妇剖宫产和孕妇要求剖宫产率变化趋势[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2013, 45(03): 422-426. |
| [7] | 徐佳露, 杨茹莱, 毛华庆, 赵正言. 浙江省不同地域新生儿先天性甲状腺功能低下症筛查分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2012, 44(5): 816-818. |
| [8] | 陈智滨, 和璐, 康军, 黄振, 沙月琴, 朱万孚, 闫玲 . 早产低体重儿与母亲唾液中牙周致病菌的关系[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2012, 44(1): 29-33. |
| [9] | 沙月琴, 黄振, 陈智滨, 康军, 和璐, 于晓潜. 孕妇牙周炎与新生儿早产低体重的关联[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2009, 41(1): 117-120. |
| [10] | Chun-li YU, 顾学范. 串联质谱仪在新生儿遗传代谢病筛查中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2006, 38(1): 103-106. |
| [11] | 伍细言, 王华, 黄定梅, 雷花香, 胡蓉, 马力, 邹珊静, 禹虹. 湖南省106 224例新生儿先天性甲状腺功能减低症筛查[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2005, 37(1): 42-44. |
| [12] | 李银涛, 李世荫, 潘得海. 维A酸对银屑病皮损中角朊细胞凋亡的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2001, 33(2): 184-185. |
|
||