北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2020, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (3): 457-463. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2020.03.010
纳米二氧化钛经口暴露90天对大鼠粪便代谢组的影响
- 北京大学公共卫生学院劳动卫生与环境卫生学系,北京 100191
Effects of titanium dioxide nanoparticles on fecal metabolome in rats after oral administration for 90 days
Shuo HAN,Zhang-jian CHEN,Di ZHOU,Pai ZHENG,Jia-he ZHANG,Guang JIA( )
)
- Department of Occupational and Environmental Health Sciences, Peking University School of Public Health, Beijing 100191, China
摘要:
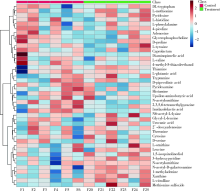
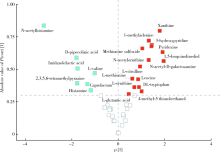
目的 通过粪便代谢组学,探索纳米二氧化钛(titanium dioxide nanoparticles,TiO2 NPs)经口染毒90 d对大鼠肠道及肠道菌群代谢的影响及其相关机制。方法 12只清洁级雄性Sprague Dawley(SD)大鼠按体质量随机分成两组,分别以0和50 mg/kg体质量的TiO2 NPs持续灌胃90 d,对TiO2 NPs的粒径、晶型、纯度、比表面积进行表征,并在第90天收集大鼠的新鲜粪便。经过冻干、亲水相萃取等前处理后,使用超高效液相色谱-轨道阱高分辨质谱仪联用系统(ultra performance liquid chromatography-Q-exactive orbitrap-high-resolution mass spectrometry system,UPLC-QEMS)对粪便代谢物进行非靶向测定,鉴定标注检测得到的代谢物,并进行代谢组学分析。结果 与对照组相比,TiO2 NPs染毒组大鼠体质量显著降低(P<0.05)。粪便代谢组学共发现22种代谢物浓度发生显著改变,其中黄嘌呤、甲基腺嘌呤、羟基吡啶、蛋氨酸亚砜等15种代谢物浓度显著上升,乙酰组胺、派可林酸、咪唑乳酸、缬氨酸等7种代谢物浓度显著下降。N-乙酰组胺、缬氨酸和蛋氨酸亚砜的改变倍数大于16倍。京都基因与基因组百科全书(Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes,KEGG)通路分析发现,精氨酸生物合成通路和氨酰基-tRNA生物合成通路这两个代谢通路发生显著改变(错误发现率<0.05,通路受影响程度>0.10)。结论 TiO2 NPs经口染毒90 d可扰乱肠道及肠道菌群代谢,并导致大鼠粪便中代谢物及代谢通路发生显著改变,提示TiO2 NPs经口暴露对大鼠的毒性作用可能与肠道及肠道菌群代谢改变密切相关。
中图分类号:
- R994.4
| [1] | Ropers MH, Terrisse H, Mercier-Bonin M, et al. Titanium dio-xide as food additive[M]. Magdalena Janus: InTech Rijeka, 2017. |
| [2] |
Baranowska-Wójcik E, Szwajgier D, Oleszczuk P, et al. Effects of titanium dioxide nanoparticles exposure on human health: A review[J]. Biol Trace Elem Res, 2020,193(1):118-129.
doi: 10.1007/s12011-019-01706-6 pmid: 30982201 |
| [3] |
Weir A, Westerhoff P, Fabricius L, et al. Titanium dioxide nanoparticles in food and personal care products[J]. Environ Sci Technol, 2012,46(4):2242-2250.
pmid: 22260395 |
| [4] | Yang Y, Doudrick K, Bi X, et al. Characterization of food-grade titanium dioxide: the presence of nanosized particles[J]. Environ Sci Technol, 2014,48(11):6391-6400. |
| [5] |
Winkler HC, Notter T, Meyer U, et al. Critical review of the safety assessment of titanium dioxide additives in food[J]. J Nanobiotechnology, 2018,16(1):51.
pmid: 29859103 |
| [6] |
Wang J, Zhou G, Chen C, et al. Acute toxicity and biodistribution of different sized titanium dioxide particles in mice after oral administration[J]. Toxicol Lett, 2007,168(2):176-185.
pmid: 17197136 |
| [7] | Shukla RK, Kumar A, Gurbani D, et al. TiO2 nanoparticles induce oxidative DNA damage and apoptosis in human liver cells[J]. Nanotoxicology, 2013,7(1):48-60. |
| [8] |
Bachler G, von Goetz N, Hungerbuhler K. Using physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) modeling for dietary risk assessment of titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticles[J]. Nanotoxicology, 2015,9(3):373-380.
pmid: 25058655 |
| [9] | Karu N, Deng L, Slae M, et al. A review on human fecal metabolomics: Methods, applications and the human fecal metabolome database[J]. Anal Chim Acta, 2018(1030):1-24. |
| [10] |
Johnson CH, Ivanisevic J, Siuzdak G. Metabolomics: Beyond biomarkers and towards mechanisms[J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2016,17(7):451-459.
doi: 10.1038/nrm.2016.25 pmid: 26979502 |
| [11] | 周迪, 陈章健, 胡贵平, 等. 纳米二氧化钛亚急性经口暴露对大鼠氧化/抗氧化生物标志和炎性因子的影响[J/OL]. 北京大学学报(医学版), ( 2018- 11- 09) [2019-12-28]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.4691.R.20181108.1357.010.html. |
| [12] | Turnbaugh PJ, Ley RE, Mahowald MA, et al. An obesity-associated gut microbiome with increased capacity for energy harvest[J]. Nature, 2006,444(7122):1027-1031. |
| [13] | Brun E, Barreau F, Veronesi G, et al. Titanium dioxide nanoparticle impact and translocation through ex vivo, in vivo and in vitro gut epithelia[J]. Part Fibre Toxicol, 2014(11):13. |
| [14] | Guo Z, Martucci NJ, Moreno-Olivas F, et al. Titanium dioxide nanoparticle ingestion alters nutrient absorption in an in vitro model of the small intestine[J]. NanoImpact, 2017(5):70-82. |
| [15] | Pinget G, Tan J, Janac B, et al. Impact of the food additive titanium dioxide (E171) on gut microbiota-host interaction[J]. Front Nutr, 2019(6):57. |
| [16] | Di Z, Shuo H, Tenglong Y, et al. Toxicity of titanium dioxide nanoparticles induced by reactive oxygen species[J]. Reactive Oxygen Species, 2019,8(23):267-275. |
| [17] | Chen Z, Wang Y, Wang X, et al. Effect of titanium dioxide nanoparticles on glucose homeostasis after oral administration[J]. J Appl Toxicol, 2018,38(6):810-823. |
| [18] | Bull MJ, Plummer NT. Part 1: The human gut microbiome in health and disease[J]. Integr Med (Encinitas), 2014,13(6):17-22. |
| [19] | Weissbach H, Redfield BG, Axelrod J. The exzymic acetylation of serotonin and other naturally occurring amines[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta, 1961(54):190-192. |
| [20] | Xiao F, Yu J, Guo Y, et al. Effects of individual branched-chain amino acids deprivation on insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism in mice[J]. Metabolism, 2014,63(6):841-850. |
| [21] |
Taya Y, Ota Y, Wilkinson AC, et al. Depleting dietary valine permits nonmyeloablative mouse hematopoietic stem cell transplantation[J]. Science, 2016,354(6316):1152-1155.
pmid: 27934766 |
| [22] |
Duan Y, Liu J, Ma L, et al. Toxicological characteristics of nanoparticulate anatase titanium dioxide in mice[J]. Biomaterials, 2010,31(5):894-899.
pmid: 19857890 |
| [23] |
Lee BC, Dikiy A, Kim HY, et al. Functions and evolution of selenoprotein methionine sulfoxide reductases[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta, 2009,1790(11):1471-1477.
pmid: 19406207 |
| [24] | Zierer J, Jackson MA, Kastenmüller G, et al. The fecal metabolome as a functional readout of the gut microbiome[J]. Nat Genet, 2018,50(6):790-795. |
| [25] | Vernocchi P, Del Chierico F, Putignani L. Gut microbiota profiling: Metabolomics based approach to unravel compounds affecting human health[J]. Front Microbiol, 2016(7):1144. |
| [26] | Xia Y, Dawson VL, Dawson TM, et al. Nitric oxide synthase generates superoxide and nitric oxide in arginine-depleted cells leading to peroxynitrite-mediated cellular injury[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 1996,93(13):6770-6774. |
| [27] | Tiwari S, van Tonder AJ, Vilchèze C, et al. Arginine-deprivation-induced oxidative damage sterilizes Mycobacterium tuberculosis[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2018,115(39):9779-9784. |
| [1] | 张展奕,张帆,颜野,曹财广,李长剑,邓绍晖,孙悦皓,黄天亮,管允鹤,李楠,陆敏,胡振华,张树栋. 近红外荧光靶向探针用于前列腺神经血管束术中成像[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 843-850. |
| [2] | 孟令玮,李雪,高胜寒,李悦,曹瑞涛,张毅,潘韶霞. 三种方法建立大鼠种植体周炎模型的比较[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(1): 22-29. |
| [3] | 王雪萍,张于亚楠,卢天兰,卢喆,康哲维,孙瑶瑶,岳伟华. 首发精神分裂症肠道微生物多态性与临床症状及血清代谢组学的关联[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(5): 863-873. |
| [4] | 马媛,张玥,李蕊,邓书伟,秦秋实,朱鏐娈. 脓毒症小鼠髓源性抑制细胞氨基酸代谢特点[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(3): 532-540. |
| [5] | 何伟,杨思雯,陈娟,朱晓俊,陈志忠,马文军. 275 nm和310 nm紫外线对去卵巢骨质疏松大鼠骨代谢的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(2): 236-243. |
| [6] | 陈章健,韩硕,郑湃,贾光. 锐钛矿型纳米二氧化钛经口暴露90天对Sprague-Dawley大鼠血常规指标的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(6): 1205-1208. |
| [7] | 王贵红,左婷,李然,左正才. 瑞巴派特在大鼠痛风性关节炎急性发作中的作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(4): 716-720. |
| [8] | 尹雪倩, 张晓玄, 文婧, 刘思奇, 刘欣然, 周若宇, 王军波. 荞麦、燕麦、豌豆复配对糖尿病大鼠血糖的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(3): 447-452. |
| [9] | 白枫,何倚帆,牛亚楠,杨若娟,曹静. 超细颗粒物对大鼠离体灌注心脏功能的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(2): 240-245. |
| [10] | 周迪,陈章健,胡贵平,阎腾龙,龙昌茂,冯慧敏,贾光. 纳米二氧化钛亚急性经口暴露对大鼠氧化/抗氧化生物标志和炎性因子的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(5): 821-827. |
| [11] | 陈章健,韩硕,郑湃,周淑佩,贾光. 纳米二氧化钛与葡萄糖亚慢性联合经口暴露对幼年大鼠血清叶酸和维生素B12水平的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(3): 451-456. |
| [12] | 白珊珊,莫思怡,徐啸翔,刘云,谢秋菲,曹烨. 大鼠咬合干扰致口颌面痛敏的自我赏罚实验行为学特点[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(1): 51-57. |
| [13] | 何姣,袁戈恒,张俊清,郭晓蕙. 早期糖尿病周围神经病变大鼠模型的建立[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(6): 1150-1154. |
| [14] | 王伟,侯进,黄文强. 运动导致兴奋脑区组织液流动一过性加速[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(2): 206-209. |
| [15] | 王玉洁,郭向阳,王军. 重复异丙酚麻醉对新生大鼠海马细胞凋亡及远期学习记忆能力的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(2): 310-314. |
|
||