北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2020, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (4): 726-729. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2020.04.025
Swanson人工跖趾关节置换术治疗第2~5跖趾关节疾病的疗效评价
- 北京大学人民医院创伤骨科,北京大学人民医院创伤救治中心,北京 100044
Evaluation of therapeutic efficacy of arthroplasty with Swanson prosthesis in the surgical treatment of 2-5 metatarsophalangeal joint diseases
Zhong-di LIU,Hao LU,Yu-song YUAN,Hai-lin XU( )
)
- Department of Trauma and Orthopedics, Trauma Medical Center, Peking University People’s Hospital, Beijing 100044, China
摘要:
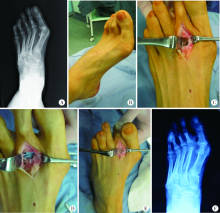
目的: 探讨使用Swanson双柄硅胶假体行跖趾关节置换治疗骨性关节炎、类风湿关节炎等引起的第2~5跖趾关节病变的中长期临床疗效。方法: 2010年1月至2015年10月应用Swanson双柄硅胶假体实施第2~5跖趾关节置换术21例,成功随访16例,其中,男性2例,女性14例,平均年龄(66.7±5.5)岁,类风湿关节炎9例,严重骨性关节炎5例,跖骨头骨软骨病2例。采用美国足踝外科协会Maryland足部评分系统、视觉模拟评分(visual analogue score, VAS)和影像学检查等方法对手术前后行走及跖趾关节活动度、疼痛程度等进行临床评价。结果: 随访时间17个月至5年,平均3.2年。Maryland足部评分:术前为(60.69±6.12)分,术后末次随访时为(88.13±5.84)分。术前跖趾关节活动度:背伸5.4°±3.1°,跖屈4.4°±2.7°;术后:背伸15.7°±4.5°,跖屈12.2°±4.3°,术后跖趾关节活动度较术前有明显改善,数据对比差异有统计学意义(P<0.01)。VAS评分:术前评分为(6.8±0.9)分,术后末次随访为(2.3±0.8)分,术后跖趾关节疼痛症状得到明显改善。根据美国足踝外科协会Maryland足部评分系统,术后评分较术前评分有显著性提高(P<0.01),优良率达到81.3%。结论: Swanson双柄硅胶假体跖趾关节置换术能够较好地缓解疼痛, 增加关节活动范围及稳定性,维持前足正常的行走能力,是重建第2~5跖趾关节结构、恢复关节功能的有效方法,但仍存在一些不良反应的发生概率,需要进一步改进。
中图分类号:
- R649.9
| [1] |
Nery C, Baumfeld D. Lesser metatarsophalangeal joint instability: Treatment with tendon transfers[J]. Foot Ankle Clin, 2018,23(1):103-126.
pmid: 29362027 |
| [2] | Swanson AB, de Groot Swanson G. Use of grommets for flexible hinge implant arthroplasty of the great toe[J]. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1997(340):87-94. |
| [3] |
Phisitkul P. Managing complications of lesser toe and metatarsophalangeal joint surgery[J]. Foot Ankle Clin, 2018,23(1):145-156.
pmid: 29362029 |
| [4] | Davies MS, Saxby TS. Metatarsal neck osteotomy with rigid internal fixation for the treatment of lesser toe metatarsophalangeal joint pathology[J]. Foot Ankle Int, 1999,20(10):630-635. |
| [5] |
Stevens J, de Bot R, Hermus J, et al. Clinical outcome following total joint replacement and arthrodesis for hallux rigidus: A systematic review[J]. JBJS Rev, 2017,5(11):e2.
pmid: 29135720 |
| [6] |
Erdil M, Elmadaǧ NM, Polat G, et al. Comparison of arthrodesis, resurfacing hemiarthroplasty, and total joint replacement in the treatment of advanced hallux rigidus[J]. J Foot Ankle Surg, 2013,52(5):588-593.
doi: 10.1053/j.jfas.2013.03.014 pmid: 23659913 |
| [7] | O'Malley MJ, Basran HS, Gu Y, et al. Treatment of advanced stages of hallux rigidus with cheilectomy and phalangeal osteotomy[J]. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 2013,95(7):606-610. |
| [8] |
Swanson AB, Lumsden RM, Swanson GD. Silicone implant arthroplasty of the great toe. A review of single stem and flexible hinge implants[J]. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1979, (142):30-43.
pmid: 387324 |
| [9] |
Moeckel BH, Sculco TP, Alexiades MM, et al. The double-stemmed silicone-rubber implant for rheumatoid arthritis of the first metatarsophalangeal joint. Long-term results[J]. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1992,74(4):564-570.
pmid: 1583051 |
| [10] |
Peace RA, Hamilton GA. End-stage hallux rigidus: cheilectomy, implant, or arthrodesis?[J]. Clin Podiatr Med Surg, 2012,29(3):341-353.
pmid: 22727376 |
| [11] | Valentini R, de Fabrizio G, Piovan G. First metatarsophalangeal joint replacement with total arthroplasty in the surgical treatment of the hallux rigidus[J]. Acta Biomed, 2014,85(Suppl 2):113-117. |
| [12] |
Stone OD, Ray R, Thomson CE, et al. Long-term follow-up of arthrodesis vs total joint arthroplasty for hallux rigidus[J]. Foot Ankle Int, 2017,38(4):375-380.
doi: 10.1177/1071100716682994 pmid: 28367694 |
| [13] |
Brewster M. Does total joint replacement or arthrodesis of the first metatarsophalangeal joint yield better functional results? A syste-matic review of the literature[J]. J Foot Ankle Surg, 2010,49(6):546-552.
doi: 10.1053/j.jfas.2010.07.003 pmid: 20833566 |
| [14] |
Shereff MJ, Jahss MH. Complications of silastic implant arthroplasty in the hallux[J]. Foot Ankle, 1980,1(2):95-101.
pmid: 7274905 |
| [15] |
Erkocak OF, Senaran H, Altan E, et al. Short-term functional outcomes of first metatarsophalangeal total joint replacement for hallux rigidus[J]. Foot Ankle Int, 2013,34(11):1569-1579.
doi: 10.1177/1071100713496770 pmid: 23877170 |
| [1] | 安思兰,郑群怡,王锴,高姗. 全膝关节置换术后患者早期疼痛的特点及其影响因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 167-173. |
| [2] | 王鑫光,耿霄,李杨,吴天晨,李子剑,田华. 便携式导航与计算机导航辅助在全膝关节置换力线对准和手术时间的比较[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(4): 728-733. |
| [3] | 柯岩,张蔷,马云青,李儒军,陶可,桂先革,李克鹏,张洪,林剑浩. 全髋关节置换术治疗脊柱骨骺发育不良患者Tönnis 3级髋关节骨关节炎的早期疗效[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(1): 175-182. |
| [4] | 李森磊,杨先腾,田晓滨,孙立. 直接前入路和前外侧入路全髋关节置换术后的早期功能恢复对比[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(2): 268-272. |
| [5] | 王军锋, 李沼, 张克石, 袁峰, 李儒军, 钟群杰, 关振鹏. 双膝关节置换术中髌骨置换与否的左右侧随机对照研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(5): 861-866. |
| [6] | 赵旻暐, 王宁, 曾琳, 李民, 赵中凯, 张菡, 田华. 膝关节置换术后连续收肌管阻滞与股神经阻滞的疗效比较[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(1): 142-147. |
|
||