北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2020, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (5): 875-880. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2020.05.013
短期头盆环牵引配合手术治疗重度脊柱畸形的临床疗效
徐贝宇1,漆龙涛1,王宇1,∆( ),李淳德1,∆(
),李淳德1,∆( ),孙浩林1,王诗军1,于峥嵘1,赵耀1,刘龙龙2
),孙浩林1,王诗军1,于峥嵘1,赵耀1,刘龙龙2
- 1.北京大学第一医院骨科,北京 100034
2.临汾市第二人民医院,山西临汾 041000
Clinical efficacy of short-term halo-pelvic traction combined with surgery in the treatment of severe spinal deformities
Bei-yu XU1,Long-tao QI1,Yu WANG1,∆( ),Chun-de LI1,∆(
),Chun-de LI1,∆( ),Hao-lin SUN1,Shi-jun WANG1,Zheng-rong YU1,Yao ZHAO1,Long-long LIU2
),Hao-lin SUN1,Shi-jun WANG1,Zheng-rong YU1,Yao ZHAO1,Long-long LIU2
- 1. Department of Orthopedics, Peking University First Hospital, Beijing 100034, China
2. Department of Orthopedics, Linfen Second People’s Hospital, Shanxi 041000, China
摘要:
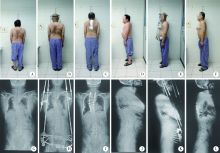
目的:探讨短期头盆环牵引配合手术治疗重度脊柱畸形的临床疗效。方法:选择北京大学第一医院2015年1月—2018年5月应用一期头盆环牵引配合二期手术治疗的重度脊柱畸形患者病例资料进行回顾性分析,共收集到病例24例,其中男性9例,女性15例,平均年龄(28.8±10.0)岁(12~48岁)。分别测量牵引前、一期牵引后及矫形手术后身高、脊柱侧凸Cobb角、脊柱后凸Cobb角,比较患者牵引前、牵引后及手术后的身高、脊柱侧凸Cobb角和脊柱后凸Cobb角变化情况。结果:24例患者牵引时间(2.5±1.1)周(1~5周), 牵引前及牵引后身高分别为(141.7±11.2) cm(116~167 cm)和(154.1±9.5) cm(136~176 cm), 牵引后身高增加值为(12.4±4.6) cm(4~20 cm), 牵引后身高与牵引前差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。牵引前、牵引后及手术后脊柱侧凸Cobb角分别为104.9°±35.0°(25°~158°)、64.8°±21.0°(19°~92°)、39.3°±17.0°(10°~70°), 牵引后及手术后脊柱侧凸Cobb角与牵引前差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),冠状位牵引矫形率为37.2%±10.9%(11.9%~51.2%),冠状位总矫形率为61.9%±12.6%(26.9%~79.0%)。牵引前、牵引后及手术后脊柱后凸Cobb角分别为106.9°±29.2°(54°~163°)、63.1°±17.1°(32°~92°)、39.0°±16.8°(10°~68°), 牵引后及手术后脊柱后凸Cobb角与牵引前差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),矢状位牵引矫形率为40.0%±10.7%(16.7%~55.5%),矢状位总矫形率为64.3%±10.7%(49.0%~87.5%)。结论:一期短期头盆环牵引配合二期手术是治疗重度脊柱侧凸一种安全、有效的方法,其临床矫形效果满意。
中图分类号:
- R682.1+3
| [1] |
Hamzaoglu A, Alanay A, Ozturk C, et al. Posterior vertebral column resection in severe spinal deformities: a total of 102 cases[J]. Spine (Phila Pa 1976), 2011,36(5):E340-E344.
doi: 10.1097/BRS.0b013e3182015712 |
| [2] | Bouchoucha S, Khelifi A, Saied W, et al. Progressive correction of severe spinal deformities with halo-gravity traction[J]. Acta Orthop Belg, 2011,77(4):529-534. |
| [3] |
Gollogly S, Smith JT, Campbell RM. Determining lung volume with three-dimensional reconstructions of CT scan data: a pilot study to evaluate the effects of expansion thoracoplasty on children with severe spinal deformities[J]. J Pediatr Orthop, 2004,24(3):323-328.
pmid: 15105731 |
| [4] |
Zhang Y, Xie J, Wang Y, et al. Thoracic pedicle classification determined by inner cortical width of pedicles on computed tomography images: its clinical significance for posterior vertebral column resection to treat rigid and severe spinal deformities-a retrospective review of cases[J]. BMC Musculoskelet Disord, 2014,15:278.
doi: 10.1186/1471-2474-15-278 pmid: 25124922 |
| [5] |
O’Brien JP, Yac ACMC, Hodgson AR. Halo pelvic traction: a technic for severe spinal deformities[J]. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1973,93:179-190.
doi: 10.1097/00003086-197306000-00018 |
| [6] |
Arlet V, Papin P, Marchesi D. Halo femoral traction and sliding rods in the treatment of a neurologically compromised congenital scoliosis: technique[J]. Eur Spine J, 1999,8(4):329-331.
doi: 10.1007/s005860050182 pmid: 10483837 |
| [7] |
Qiu Y, Liu Z, Zhu F, et al. Comparison of effectiveness of Halo-femoral traction after anterior spinal release in severe idiopathic and congenital scoliosis: a retrospective study[J]. J Orthop Surg Res, 2007,2:23.
doi: 10.1186/1749-799X-2-23 pmid: 18047681 |
| [8] | Zhang HQ, Gao QL, Ge L, et al. Strong halo-femoral traction with wide posterior spinal release and three dimensional spinal correction for the treatment of severe adolescent idiopathic scoliosis[J]. Chin Med J (Engl), 2012,125(7):1297-1302. |
| [9] | 李彩红, 张梅清, 李晔, 等. 严重脊柱畸形患者术前颅-股骨牵引的护理[J]. 世界最新医学信息文摘:电子版, 2016,16(18):297-298. |
| [10] |
Hsu LC. Halo-pelvic traction: a means of correcting severe spinal deformities[J]. Hong Kong Med J, 2014,20(4):358-359.
pmid: 25243266 |
| [11] |
Yang C, Wang H, Zheng Z, et al. Halo-gravity traction in the treatment of severe spinal deformity: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Eur Spine J, 2017,26(7):1810-1816.
pmid: 27858237 |
| [12] |
Pourtaheri S, Shah SA, Ditro CP, et al. Preoperative halo-gravity traction with and without thoracoscopic anterior release for skeletal dysplasia patients with severe kyphoscoliosis[J]. J Child Orthop, 2016,10(2):135-142.
doi: 10.1007/s11832-016-0721-0 pmid: 27016925 |
| [13] |
Kim NH, Kim HJ, Moon SH, et al. 20-year-follow up of treatment using spine osteotomy and halo-pelvic traction for tuberculous kyphosis[J]. Asian Spine J, 2009,3(1):27-31.
pmid: 20404943 |
| [14] |
Hodgson AR. Halo-pelvic traction in scoliosis[J]. Isr J Med Sci, 1973,9(6):767-770.
pmid: 4724284 |
| [15] | Dove J, Hsu LC, Yau AC. The cervical spine after halo-pelvic traction. An analysis of the complications of 83 patients[J]. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 1980,62B(2):158-161. |
| [16] | 赵聚峰, 杜志伟. 严重脊柱侧后凸畸形头盆环支撑牵引预治疗31例体会[J]. 实用骨科杂志, 2005,11(3):265-266. |
| [17] | 田慧中, 吕霞, 马原. 头盆环牵引全脊柱截骨内固定治疗重度脊柱弯曲[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志, 2007,15(3):167-172. |
| [18] |
Rozario RA, Stein BM. Complications of halo-pelvic traction. Case report[J]. J Neurosurg, 1976,45(6):716-718.
doi: 10.3171/jns.1976.45.6.0716 pmid: 978245 |
| [19] |
Ransford AO, Manning CW. Complications of halo-pelvic distraction for scoliosis[J]. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 1975,57(2):131-137.
pmid: 1141278 |
| [20] |
Ma JK, Ning LH. Posterior instrumentation and spondylodesis for scoliosis under halo-pelvic distraction with local anesthesia[J]. Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi, 1987,25(7):390-393, 444.
pmid: 3677941 |
| [21] |
Zielke K, Pellin B. Halo-pelvic traction. How to reduce its dangers by simplifying its use[J]. Z Orthop Ihre Grenzgeb, 1974,112(2):351-354.
pmid: 4276749 |
| [22] |
Tredwell SJ, O’Brien JP. Avascular necrosis of the proximal end of the dens. A complication of halo-pelvic distraction[J]. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1975,57(3):332-336.
pmid: 1123386 |
| [23] |
Tredwell SJ, O’Brien JP. Apophyseal joint degeneration in the cervical spine following halo-pelvic distraction[J]. Spine (Phila Pa 1976), 1980,5(6):497-501.
doi: 10.1097/00007632-198011000-00002 |
| [24] |
Dove J, Hsu LC, Yau AC. Spontaneous cervical spinal fusion. A complication of halo-pelvic traction[J]. Spine (Phila Pa 1976), 1981,6(1):45-48.
doi: 10.1097/00007632-198101000-00008 |
| [25] | Ransford AO, Manning CW. Halo-pelvic apparatus: peritoneal penetration by pelvic pins[J]. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 1978,60B(3):404-405. |
| [26] |
O’Brien JP, Yau AC, Smith TK, et al. Halo pelvic traction. A preliminary report on a method of external skeletal fixation for correcting deformities and maintaining fixation of the spine[J]. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 1971,53(2):217-229.
pmid: 5578217 |
| [1] | 陈逸凡,刘中砥,张鹏,黄伟. 严重创伤患者损伤严重度评分的一致性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 157-160. |
| [2] | 闫乐,王宪娥,詹雅琳,苗莉莉,韩烨,张楚人,岳兆国,胡文杰,侯建霞. 超声龈下清创联合手工根面平整术治疗重度牙周炎的临床效果[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(1): 64-70. |
| [3] | 侯磊,叶国华,刘筱菁,李自力. 下颌后缩伴颞下颌关节重度骨关节病患者正颌术后颌骨稳定性及髁突体积变化的评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(1): 113-118. |
| [4] | 李熠,徐莉,周彦恒,欧阳翔英,曹甜. 牙周正畸牙体联合治疗1例预后无望上前牙患者的长期疗效观察#br#[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(4): 740-744. |
| [5] | 郭艳利, 游珂, 耿力, 张小为, 沈晓野, 姚燕君, 范晓红. 不典型鳞状细胞和低度鳞状上皮内病变中高危型人乳头瘤状病毒检测的作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2006, 38(5): 480-482. |
|
||