北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (2): 273-278. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2021.02.007
中国崇礼某大型雪场大众滑雪者损伤情况分析
杨渝平1,2,马骁1,陈拿云1,蒋艳芳1,张晓伟2,丁中伟2,敖英芳1,Δ( )
)
- 1.北京大学第三医院运动医学科,北京大学运动医学研究所,运动医学关节伤病北京市重点实验室,北京 100191
2.北京大学第三医院崇礼院区运动医学科,河北张家口 076350
Analysis of the mass skiers’ injury in a large ski resort in Chongli, China
YANG Yu-ping1,2,MA Xiao1,CHEN Na-yun1,JIANG Yan-fang1,ZHANG Xiao-wei2,DING Zhong-wei2,AO Ying-fang1,Δ( )
)
- 1. Department of Sports Medicine, Peking University Third Hospital; Institute of Sports Medicine of Peking University; Beijing Key Laboratory of Sports Injuries, Beijing 100191, China
2. Department of Sports Medicine,Peking University Third Hospital-Chongli,Zhangjiakou 076350, Hebei, China
摘要:
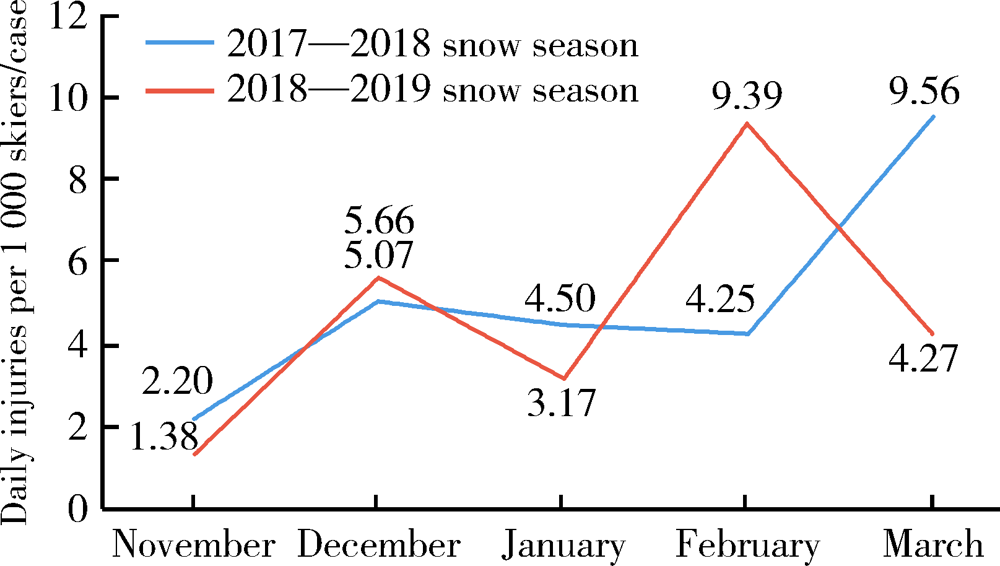
目的: 对中国崇礼某大型雪场滑雪人群的损伤情况进行回顾性分析,为预测2022年冬季奥林匹克运动会背景下快速增长的滑雪损伤救治医疗需求提供依据。方法: 收集2017年11月至2018年3月雪季和2018年11月至2019年3月雪季在崇礼某大型雪场医疗站就诊的所有受伤滑雪者的基本资料。比较两个雪季滑雪人数、受伤人数、受伤原因、损伤类型和受伤部位等情况。结果: 两个雪季共发生753例损伤,每1 000例滑雪者平均日损伤分别为4.53例和4.46例。两个雪季11月份的每1 000例滑雪者平均日损伤例数均比较低,分别为2.20例和1.38例,而不同月份受伤率差异可能与降雪关系不大,更有可能与客流量多少相关。两个雪季的所有受伤者中,男性占比均高于女性。21~30岁的受伤滑雪者占比最大,达到了36.8%。受伤原因以摔伤(76.6%)为主,受伤概率最高的部位是头颈部(17.9%), 其次为膝关节(17.4%)和手腕手指(13.3%)。损伤类型以挫伤及外伤(29.5%)、关节和(或)韧带损伤(22.2%)最为常见。所有受伤者中,儿童(2~12岁)占比12.7%。大于50岁的受伤患者的中重度损伤(包括骨折、脑震荡等)率为34.8%。结论: 雪场应重点关注儿童和老年滑雪者的受伤情况,针对性地开展指导和救援工作;为更好地保障滑雪人群医疗安全,雪场医疗站和附近救治医院应配备相应数量的医疗人员和设备,雪场应进一步完善其安全管理和救护体系。
中图分类号:
- R648
| [1] |
Carús L, Escorihuela M. Feature-specific ski injuries in snow parks[J]. Accid Anal Prev, 2016,95(Pt A):86-90.
doi: 10.1016/j.aap.2016.06.023 pmid: 27415812 |
| [2] |
Pierpoint LA, Kerr ZY, Grunwald G, et al. Effect of environmental conditions on injury rates at a Colorado ski resort[J]. Inj Prev, 2020,26(4):324-329.
pmid: 31324655 |
| [3] | Castellani C, Singer G, Eibisberger M, et al. An epidemiologic analysis of winter sport accidents on ski slopes comparing two seasons[J]. J Sports Med Phys Fit, 2019,59(4):648-654. |
| [4] |
Hunter RE. Skiing injuries[J]. Am J Sports Med, 1999,27(3):381-389.
pmid: 10352778 |
| [5] |
Laver L, Pengas IP, Mei-Dan O. Injuries in extreme sports[J]. J Orthop Surg Res, 2017,12(1):59.
pmid: 28420431 |
| [6] |
Pons-Villanueva J, Seguí-Gómez M, Martínez-González MA. Risk of injury according to participation in specific physical activities: a 6-year follow-up of 14 356 participants of the SUN cohort[J]. Int J Epidemiol, 2010,39(2):580-587.
doi: 10.1093/ije/dyp319 pmid: 19897466 |
| [7] |
Torbjørn S, Debbie P, Kathrin S, et al. Sports injury and illness incidence in the PyeongChang 2018 Olympic Winter Games: a prospective study of 2914 athletes from 92 countries[J]. Br J Sports Med, 2019,53(17):1085-1092.
pmid: 31235615 |
| [8] | 张莹, 叶海波. 北京冬奥会影响下我国滑雪产业变化与发展趋势研究[C]// 第十一届全国体育科学大会论文摘要汇编. 北京: 中国体育科学学会, 2019: 1276-1278. |
| [9] | 李宏, 王诚民. “三亿人上冰雪”引领冰雪文化发展研究[J]. 边疆经济与文化, 2019(3):105-106. |
| [10] | 王艳兵, 王文霞, 樊晓兵, 等. 高山滑雪场游客安全救护模式研究:以张家口崇礼区为例[J]. 河北北方学院学报(社会科学版), 2017,33(2):109-112. |
| [11] | 曹国林. 高山滑雪初学者运动损伤原因调查分析[J]. 辽宁体育科技, 2014,36(2):32-33, 37. |
| [12] |
Greenspan L, McLellan BA, Greig H. Abbreviated Injury Scale and injury severity score: a scoring chart[J]. J Trauma, 1985,25(1):60-64.
pmid: 3965737 |
| [13] |
Martin B, Gerhard R. Favourable changes of the risk-benefit ratio in alpine skiing[J]. Int J Environ Res Public Health, 2015,12(6):6092-6097.
pmid: 26035659 |
| [14] |
Hosaka N, Arai K, Otsuka H, et al. Incidence of recreational snowboarding-related spinal injuries over an 11-year period at a ski resort in Niigata, Japan[J]. BMJ Open Sport Exerc Med, 2020,6(1):e000742.
doi: 10.1136/bmjsem-2020-000742 pmid: 32419953 |
| [15] |
Stenroos A, Handolin L. Incidence of recreational Alpine skiing and snowboarding injuries: Six years experience in the largest ski resort in Finland[J]. Scand J Surg, 2015,104(2):127-131.
pmid: 24786173 |
| [16] | Posch M, Schranz A, Lener M, et al. Incidences of fatalities on Austrian ski slopes: A 10-year analysis[J]. Int J Environ Res Public Health, 2020,17(8):2916. |
| [17] |
Annabelle D, Nathan KE, Robert JJ. Alpine skiing injuries[J]. Sports Health, 2019,11(1):18-26.
pmid: 30782106 |
| [18] |
Paolo G, Marco B, Giuseppe S, et al. Factors affecting injury severity among recreational skiers and snowboarders: an epidemi-ology study[J]. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc, 2010,18(12):1804-1809.
pmid: 20390247 |
| [19] | Arne E, Andreas R, Stig H. Injuries among children and adults in alpine skiing and snowboarding[J]. J Sci Med Sport, 2019,22(Suppl 1):S3-S6. |
| [20] |
Jason SM, Dana K. Let it snow: how snowfall and injury mechanism affect ski and snowboard injuries in Vail, Colorado, 2011—2012[J]. J Trauma Acute Care Surg, 2013,75(2):334-338.
pmid: 23887567 |
| [21] | Tim C, Anthony MN, Matthew W, et al. Injury patterns in recreational alpine skiing and snowboarding at a mountainside clinic[J]. Wildern Environ Med, 2013,24(4):417-421. |
| [22] |
Jordan MJ, Aagaard P, Herzog W. Anterior cruciate ligament injury/reinjury in alpine ski racing: a narrative review[J]. Open Access J Sports Med, 2017,8:71-83.
pmid: 28435336 |
| [23] | Jannelli E, Calderoni EF, Ivone A, et al. From the central pivot to the peripheal knee injuries in the skier: a narrative review[J]. Acta Biomed, 2019,90(12):39-42. |
| [24] |
Steenstrup SE, Bakken A, Bere T, et al. Head injury mechanisms in FIS World Cup alpine and freestyle skiers and snowboarders[J]. Br J Sports Med, 2018,52(1):61-69.
pmid: 29133295 |
| [25] |
Milan M, Jhajj S, Stewart C, et al. Helmet use and injury severity among pediatric skiers and snowboarders in Colorado[J]. J Pediatr Surg, 2017,52(2):349-353.
pmid: 27876383 |
| [26] | Nicolas B, Jean-Dominique L, Sanae A, et al. Effect of helmet use on traumatic brain injuries and other head injuries in alpine sport[J]. Wildern Environ Med, 2018,29(2):151-158. |
| [27] |
Andrew WR, Paul CB, Craig MR. Ulnar collateral ligament injury of the thumb metacarpophalangeal joint[J]. Clin J Sport Med, 2010,20(2):106-112.
pmid: 20215892 |
| [28] |
Suezie K, Nathan KE, Robert JJ, et al. Snowboarding injuries: trends over time and comparisons with alpine skiing injuries[J]. Am J Sports Med, 2012,40(4):770-776.
pmid: 22268231 |
| [29] |
On MG, Oh JR, Jang YH, et al. Epidemiologic study of shoulder injuries in the PyeongChang 2018 Winter Olympic Games[J]. Clin Orthop Surg, 2019,11(2):187-191.
pmid: 31156771 |
| [30] | Jörg S, Josef K, Matej S, et al. Reducing the back overuse-related risks in alpine ski racing: let’s put research into sports practice[J]. Br J Sports Med, 2019,53(1):2-3. |
| [31] | 王梦. 河北崇礼2018-2019年雪季滑雪游客首次突破百万人次[EB/OL]. (2019-05-02) [2020-03-15]. http://sports.xinhuanet.com/c/2019-05/02/c_1124443390.htm. |
| [1] | 康志宇,王磊磊,韩永正,郭向阳. 北京冬季奥林匹克运动会运动员手术的麻醉管理[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(4): 770-773. |
| [2] | 白鹏,怀伟,夏天,杨钟玮,郭向阳,周方. 气管插管和喉罩在手术室与滑雪场雪道建立人工气道时间的比较[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(1): 166-169. |
| [3] | 杨渝平,孔思敏,邓佳良,蒋艳芳,敖英芳. 休闲滑雪者和滑雪运动员急性运动损伤的比较[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(5): 838-842. |
| [4] | 蒋青,张雨. 新形势下运动损伤特点及细胞生物治疗的应用前景和挑战[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(5): 828-831. |
| [5] | 杨渝平,马骁,陈拿云,蒋艳芳,张晓伟,丁中伟,刘涛,敖英芳. 冬奥会雪场医疗站和近地医疗保障医院在滑雪运动伤救治体系中的作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(3): 580-585. |
|
||