北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (3): 598-601. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2021.03.027
碘液浸染在Micro-CT下识别小鼠颅底-颞下区肿瘤组织中的应用
杨榕1,李庆祥1,王逸飞1,周闻2,王雯3,郭传瑸1,刘浩2,Δ( ),郭玉兴1,Δ(
),郭玉兴1,Δ( )
)
- 1.北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院,口腔颌面外科 国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心 口腔数字化医疗技术和材料国家工程实验室 口腔数字医学北京市重点实验室,北京 100081
2.北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院中心实验室,北京 100081
3.河北医科大学口腔医院正畸科,石家庄 050017
Application of iodine staining technique for tumor identification in Micro-CT of mouse model with skull base-infratemporal fossa tumor
YANG Rong1,LI Qing-xiang1,WANG Yi-fei1,ZHOU Wen2,WANG Wen3,GUO Chuan-bin1,LIU Hao2,Δ( ),GUO Yu-xing1,Δ(
),GUO Yu-xing1,Δ( )
)
- 1. Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery,Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Laboratory for Digital and Material Technology of Stomatology & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
2. Central Laboratory,Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
3. Department of Orthodontics, Hospital of Stomotology, Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang 050017, China
摘要:
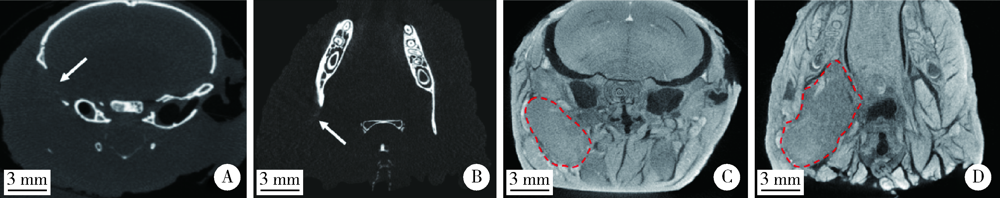
目的: 建立颅底-颞下区恶性肿瘤动物模型,探索碘液浸染技术在Micro-CT图像中识别肿瘤组织的作用。方法: 对12只BABL/c裸鼠采用异氟烷吸入镇静麻醉,在小动物超声系统引导下经颌下区注射头颈鳞状细胞癌WSU-HN6细胞至右侧颞下窝。观察3周后解剖头颅标本,用4%多聚甲醛固定,并行Micro-CT扫描,3.75%复方碘液浸染后重复扫描。将头部标本包埋、切片,进行苏木精-伊红染色和免疫组织化学染色分析肿瘤形成情况。结果: 经Micro-CT分析发现颅骨有明显破坏,但无法辨别肿瘤组织;经3.75%复方碘液浸染后,在Micro-CT阅读软件中可以清晰观察肿瘤及周围软组织形态。经苏木精-伊红染色和免疫组织化学染色分析证实,颅底-颞下区形成鳞状细胞癌,同时伴有明显颅骨破坏。结论: 采用颌下注射方式可以成功构建颅底-颞下区肿瘤动物模型;Micro-CT可以观察到颅骨骨质改变,采用复方碘液浸染后有利于观察肿瘤及周围软组织结构。
中图分类号:
- R329.4
| [1] | 阮彩莲, 杨延庆, 薛涛, 等. 经耳前颞叶底入路显露中颅底和岩斜区的便携式视频显微解剖[J]. 解剖学报, 2016,47(4):507-509. |
| [2] |
Guo Y, Guo C. Maxillary-fronto-temporal approach for removal of recurrent malignant infratemporal fossa tumors: Anatomical and clinical study[J]. J Craniomaxillofac Surg, 2014,42(3):206-212.
doi: 10.1016/j.jcms.2013.05.001 |
| [3] | 杨榕, 李庆祥, 毛驰, 等. 多模态影像融合技术与颅底-颞下区肿瘤的诊断和治疗[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019,51(1):53-58. |
| [4] | 郭玉兴, 彭歆, 刘筱菁, 等. 导航技术在颅底-颞下区肿瘤手术中的应用[J]. 中华口腔医学杂志, 2013,48(11):645-647. |
| [5] | 郭玉兴, 郭传瑸. 增强CT三维重建在颞下咽旁间隙肿瘤中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2011,43(1):148-150. |
| [6] | 郭玉兴, 郭传瑸, 俞光岩, 等. 影响颞下咽旁间隙恶性肿瘤预后的因素分析[J]. 中华神经外科杂志, 2012,28(8):775-779. |
| [7] | 毛以华, 朱昭炜, 丁茂超, 等. 应用高分辨率显微CT进行大鼠周围神经微血管三维可视化研究[J]. 解剖学报, 2013,44(3):353-356. |
| [8] |
Faraj KA, Cuijpers VM, Wismans RG, et al. Micro-computed tomographical imaging of soft biological materials using contrast techniques[J]. Tissue Eng Part C Methods, 2009,15(3):493-499.
doi: 10.1089/ten.tec.2008.0436 |
| [9] |
Degenhardt K, Wright AC, Horng D, et al. Rapid 3D phenotyping of cardiovascular development in mouse embryos by micro-CT with iodine staining[J]. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging, 2010,3(3):314-322.
doi: 10.1161/CIRCIMAGING.109.918482 pmid: 20190279 |
| [10] |
Jeffery NS, Stephenson RS, Gallagher JA, et al. Micro-computed tomography with iodine staining resolves the arrangement of muscle fibres[J]. J Biomech, 2011,44(1):189-192.
doi: 10.1016/j.jbiomech.2010.08.027 pmid: 20846653 |
| [11] |
Metscher BD. MicroCT for developmental biology: a versatile tool for high-contrast 3D imaging at histological resolutions[J]. Dev Dyn, 2009,238(3):632-640.
doi: 10.1002/dvdy.v238:3 |
| [12] |
Wu J, Yin N. Anatomy research of nasolabial muscle structure in fetus with cleft lip: an iodine staining technique based on microcomputed tomography[J]. J Craniofac Surg, 2014,25(3):1056-1061.
doi: 10.1097/SCS.0000000000000651 |
| [13] |
Wu J, Yin N. Detailed anatomy of the nasolabial muscle in human fetuses as determined by Micro-CT combined with iodine staining[J]. Ann Plast Surg, 2016,76(1):111-116.
doi: 10.1097/SAP.0000000000000219 |
| [14] | 崔国峰, 魏戎, 武军龙, 等. 骨关节炎动物模型的综合评估[J]. 中华骨与关节外科杂志, 2019,12(1):68-74. |
| [1] | 李志存, 吴天俣, 梁磊, 范宇, 孟一森, 张骞. 穿刺活检单针阳性前列腺癌术后病理升级的危险因素分析及列线图模型构建[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 896-901. |
| [2] | 刘家骏, 刘国康, 朱玉虎. 免疫相关性重症肺炎1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 932-937. |
| [3] | 黄教悌,胡菁,韩博. 治疗相关神经内分泌前列腺癌机制研究与靶向治疗新进展[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 557-561. |
| [4] | 田宇轩,阮明健,刘毅,李德润,吴静云,沈棋,范宇,金杰. 双参数MRI改良PI-RADS评分4分和5分病灶的最大径对临床有意义前列腺癌的预测效果[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 567-574. |
| [5] | 姚凯烽,阮明健,李德润,田宇轩,陈宇珂,范宇,刘毅. 靶向穿刺联合区域系统穿刺对PI-RADS 4~5分患者的前列腺癌诊断效能[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 575-581. |
| [6] | 欧俊永,倪坤明,马潞林,王国良,颜野,杨斌,李庚午,宋昊东,陆敏,叶剑飞,张树栋. 肌层浸润性膀胱癌合并中高危前列腺癌患者的预后因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 582-588. |
| [7] | 王滨帅,邱敏,张前进,田茂锋,刘磊,王国良,陆敏,田晓军,张树栋. 6例肾尤文肉瘤伴静脉瘤栓的诊治[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 636-639. |
| [8] | 虞乐,邓绍晖,张帆,颜野,叶剑飞,张树栋. 具有低度恶性潜能的多房囊性肾肿瘤的临床病理特征及预后[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 661-666. |
| [9] | 舒帆,郝一昌,张展奕,邓绍晖,张洪宪,刘磊,王国良,田晓军,赵磊,马潞林,张树栋. 肾部分切除术治疗囊性肾癌的功能学和肿瘤学结果:单中心回顾性研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 667-672. |
| [10] | 方杨毅,李强,黄志高,陆敏,洪锴,张树栋. 睾丸鞘膜高分化乳头状间皮肿瘤1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 741-744. |
| [11] | 柴晓东,孙子文,李海爽,朱靓怡,刘小旦,刘延涛,裴斐,常青. 髓母细胞瘤分子亚型中CD8+T淋巴细胞浸润的临床病理特点[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 512-518. |
| [12] | 林国中,马长城,吴超,司雨,杨军. 微通道技术在颈椎管肿瘤微创切除术中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 318-321. |
| [13] | 俞光岩. 儿童唾液腺疾病[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 1-3. |
| [14] | 薛蔚,董樑,钱宏阳,费笑晨. 前列腺癌新辅助治疗与辅助治疗的现状及进展[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 775-780. |
| [15] | 薛子璇,唐世英,邱敏,刘承,田晓军,陆敏,董靖晗,马潞林,张树栋. 青年肾肿瘤伴瘤栓的临床病理特征及预后分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 802-811. |
|
||