北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (5): 990-994. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2021.05.030
牙周健康的上颌前牙唇侧嵴顶上牙龈的三维形态分析
- 北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院, 1.牙周科,北京 100081
2.放射科 国家口腔医学中心 国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心 口腔数字化医疗技术和材料国家工程实验室,北京 100081
Three-dimensional morphology analysis of the supraosseous gingival profile of periodontally healthy maxillary anterior teeth
YANG Gang1,HU Wen-jie1,△( ),CAO Jie1,LIU Deng-gao2
),CAO Jie1,LIU Deng-gao2
- 1. Department of Periodontology, Beijing 100081, China
2. Department of Radiology, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Center of Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Laboratory for Digital and Material Technology of Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
摘要:
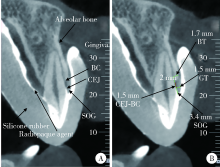
目的: 利用锥形束体层摄影术(cone-beam computed tomography,CBCT)分析牙周健康的汉族青年上颌前牙唇侧中央嵴顶上牙龈(supraosseous gingiva,SOG)的三维形态及相关解剖结构。方法: 选取25名牙周健康的汉族青年共计150颗上颌前牙纳入研究,受试者男性11名,女性14名,平均年龄(24.5±1.6)岁,佩戴含有显影剂的硅橡胶印模拍摄软组织间接显影CBCT。对影像资料进行三维重建并测量分析唇侧中央嵴顶上牙龈的形态,包括SOG高度、釉牙骨质界(cemento-enamel junction,CEJ)到骨嵴顶的距离、CEJ处牙龈厚度、骨嵴顶下2 mm牙槽骨厚度等。数据用SPSS 22.0软件进行统计分析,比较各牙位参数之间的差异,分析其相互之间的相关关系。结果: 上颌前牙唇侧中央SOG高度测量结果,中切牙为(3.54±0.67) mm、侧切牙为(3.48±0.81) mm、尖牙为(3.49±0.70) mm,各牙位SOG高度差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。上颌前牙唇侧中央CEJ水平牙龈平均厚度测量结果,中切牙为(1.45±0.23) mm,侧切牙为(1.13±0.24) mm,尖牙为(1.14±0.22) mm,中切牙牙龈最厚,与侧切牙和尖牙相比差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。唇侧中央SOG与CEJ处牙龈厚度在所有牙位上均无明显相关性(P>0.05)。结论: 牙周健康的上颌前牙唇侧嵴顶上牙龈中,中切牙牙龈最厚,未发现上颌前牙区唇侧中央SOG高度与厚度存在相关性。
中图分类号:
- R783
| [1] |
Arora R, Narula S, Sharma R, et al. Supracrestal gingival tissue: Assessing relation with periodontal biotypes in a healthy periodon-tium [J]. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent, 2013, 33(6):763-771.
doi: 10.11607/prd.1501 |
| [2] |
Perez JR, Smukler H, Nunn M E. Clinical evaluation of the supraosseous gingivae before and after crown lengthening [J]. J Periodontol, 2007, 78(6):1023-1030.
pmid: 17539715 |
| [3] |
Gargiulo AW, Wentz FM, Orban B. Dimensions and relations of the dentogingival junction in humans [J]. J Periodontol, 1961, 32(3):261-267.
doi: 10.1902/jop.1961.32.3.261 |
| [4] |
Kois JC. Altering gingival levels: The restorative connection part I: Biologic variables [J]. J Esthet Restor Dent, 1994, 6(1):3-7.
doi: 10.1111/j.1708-8240.1994.tb00825.x |
| [5] | Vacek JS, Gher ME, Assad DA, et al. The dimensions of the human dentogingival junction [J]. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent, 1994, 14(2):154-165. |
| [6] |
Fischer KR, Grill E, Jockel-Schneider Y, et al. On the relationship between gingival biotypes and supracrestal gingival height, crown form and papilla height [J]. Clin Oral Implants Res, 2014, 25(8):894-898.
doi: 10.1111/clr.2014.25.issue-8 |
| [7] | 乐迪, 张豪, 胡文杰, 等. 牙周探诊法判断牙龈生物型的初步研究 [J]. 中华口腔医学杂志, 2012, 47(2):81-84. |
| [8] | 曹洁, 胡文杰, 张豪, 等. 基于锥形束计算机体层摄影术测量牙龈厚度 [J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2013, 45(1):135-139. |
| [9] | 张艳玲, 张豪, 胡文杰, 等. 120名汉族青年前段牙弓唇侧角化龈宽度的测量 [J]. 中华口腔医学杂志, 2010, 45(8):477-481. |
| [10] |
Zhang YL, Le D, Hu WJ, et al. Assessment of dynamic smile and gingival contour in young Chinese people [J]. Int Dent J, 2015, 65(4):182-187.
doi: 10.1111/idj.12174 |
| [11] |
Perez JR, Smukler H, Nunn ME. Clinical dimensions of the supraosseous gingivae in healthy periodontium [J]. J Periodontol, 2008, 79(12):2267-2272.
doi: 10.1902/jop.2008.080101 pmid: 19053916 |
| [12] |
Cao J, Hu WJ, Zhang H, et al. A novel technique for measurement of dentogingival tissue by cone beam computed tomography [J]. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol, 2015, 119(2):e82-e87.
doi: 10.1016/j.oooo.2014.10.022 |
| [13] |
Alves PHM, Alves TCLP, Pegoraro TA, et al. Measurement pro-perties of gingival biotype evaluation methods [J]. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res, 2018, 20(3):280-284.
doi: 10.1111/cid.2018.20.issue-3 |
| [14] |
Hausmann E, Allen K, Clerehugh V. What alveolar crest level on a bite-wing radiograph represents bone loss? [J]. J Periodontol, 1991, 62(9):570-572.
pmid: 1941497 |
| [15] |
Ghassemian M, Nowzari H, Lajolo C, et al. The thickness of facial alveolar bone overlying healthy maxillary anterior teeth [J]. J Periodontol, 2012, 83(2):187-197.
doi: 10.1902/jop.2011.110172 pmid: 21692627 |
| [16] |
Nowzari H, Molayem S, Chiu CH, et al. Cone beam computed tomographic measurement of maxillary central incisors to determine prevalence of facial alveolar bone width ≥2 mm [J]. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res, 2012, 14(4):595-601.
doi: 10.1111/cid.2012.14.issue-4 |
| [17] |
Taylor R. Interpretation of the correlation coefficient: A basic review [J]. J Diagn Med Sonogr, 1990, 6(1):35-39.
doi: 10.1177/875647939000600106 |
| [18] | Kao RT, Fagan MC, Conte GJ. Thick vs thin gingival biotypes: A key determinant in treatment planning for dental implants [J]. J Calif Dent Assoc, 2008, 36(3):193-198. |
| [19] |
Müller HP, Könönen E. Variance components of gingival thickness [J]. J Periodontal Res, 2005, 40(3):239-244
pmid: 15853970 |
| [20] |
Fu JH, Yeh CY, Chan HL, et al. Tissue biotype and its relation to the underlying bone morphology [J]. J Periodontol, 2010, 81(4):569-574.
doi: 10.1902/jop.2009.090591 |
| [21] |
La Rocca AP, Alemany AS, Levi P Jr. Anterior maxillary and mandibular biotype: Relationship between gingival thickness and width with respect to underlying bone thickness [J]. Implant Dent, 2012, 21(6):507-515.
doi: 10.1097/ID.0b013e318271d487 |
| [22] | Frumkin N, Via S, Klinger A. Evaluation of the width of the alveolar bone in subjects with different gingival biotypes: A prospective cohort study using cone beam computed tomography [J]. Quintessence Int, 2017, 48(3):209-216. |
| [23] | Cook DR, Mealey BL, Verrett RG, et al. Relationship between clinical periodontal biotype and labial plate thickness: An in vivo study [J]. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent, 2011, 31(4):345-354. |
| [24] |
Batista EL, Moreira CC, Batista FC, et al. Altered passive eruption diagnosis and treatment: A cone beam computed tomography-based reappraisal of the condition [J]. J Clin Periodontol, 2012, 39(11):1089-1096.
doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051X.2012.01940.x pmid: 22966787 |
| [1] | 邢念增,王明帅,杨飞亚,尹路,韩苏军. 前列腺免活检创新理念的临床实践及其应用前景[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 565-566. |
| [2] | 田宇轩,阮明健,刘毅,李德润,吴静云,沈棋,范宇,金杰. 双参数MRI改良PI-RADS评分4分和5分病灶的最大径对临床有意义前列腺癌的预测效果[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 567-574. |
| [3] | 唐祖南,胡耒豪,陈震,于尧,章文博,彭歆. 增强现实技术在口腔颌面颈部解剖识别中的应用评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 541-545. |
| [4] | 吕梁,张铭津,温奧楠,赵一姣,王勇,李晶,杨庚辰,柳大为. 应用三维软组织空间线角模板法评价颏部对称性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 106-110. |
| [5] | 毛渤淳,田雅婧,王雪东,李晶,周彦恒. 骨性Ⅱ类高角患者拔牙矫治前后的面部软硬组织变化[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 111-119. |
| [6] | 凌晓彤,屈留洋,郑丹妮,杨静,闫雪冰,柳登高,高岩. 牙源性钙化囊肿与牙源性钙化上皮瘤的三维影像特点[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 131-137. |
| [7] | 段登辉,WANGHom-Lay,王恩博. 可吸收胶原膜在颊侧袋形瓣引导性骨再生手术中的作用: 一项回顾性影像学队列研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 1097-1104. |
| [8] | 刘毅,袁昌巍,吴静云,沈棋,肖江喜,赵峥,王霄英,李学松,何志嵩,周利群. 靶向穿刺+6针系统穿刺对PI-RADS 5分患者的前列腺癌诊断效能[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 812-817. |
| [9] | 袁昌巍,李德润,李志华,刘毅,山刚志,李学松,周利群. 多参数磁共振成像中动态对比增强状态在诊断PI-RADS 4分前列腺癌中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 838-842. |
| [10] | 刘颖,霍然,徐慧敏,王筝,王涛,袁慧书. 磁共振血管壁成像评估颈动脉中重度狭窄患者斑块特征与脑血流灌注的相关性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 646-651. |
| [11] | 傅强,高冠英,徐雁,林卓华,孙由静,崔立刚. 无症状髋关节前上盂唇撕裂超声与磁共振检查的对比研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 665-669. |
| [12] | 刘想,谢辉辉,许玉峰,张晓东,陶晓峰,柳林,王霄英. 人工智能对提高放射科住院医生诊断胸部肋骨骨折一致性的价值[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 670-675. |
| [13] | 卢汉,张建运,杨榕,徐乐,李庆祥,郭玉兴,郭传瑸. 下颌牙龈鳞状细胞癌患者预后的影响因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 702-707. |
| [14] | 黄莹,吴志远,周行红,蔡志刚,张杰. 股前外侧皮瓣修复上颌骨缺损术后面部软组织对称性感观分级[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 708-715. |
| [15] | 张雯,刘筱菁,李自力,张益. 基于解剖标志的鼻翼基底缩窄缝合术对正颌患者术后鼻唇部形态的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 736-742. |
|
||