北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (2): 299-303. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2022.02.017
术前及术后膜性尿道长度与腹腔镜根治性前列腺切除术后控尿功能恢复的相关性
- 北京大学第三医院泌尿外科,北京 100191
Relationship between recovery of urinary continence after laparoscopic radical prostatectomy and preoperative/postoperative membranous urethral length
ZHANG Fan,CHEN Qu,HAO Yi-chang,YAN Ye,LIU Cheng,HUANG Yi( ),MA Lu-lin
),MA Lu-lin
- Department of Urology, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
摘要:
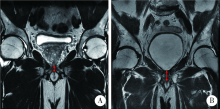
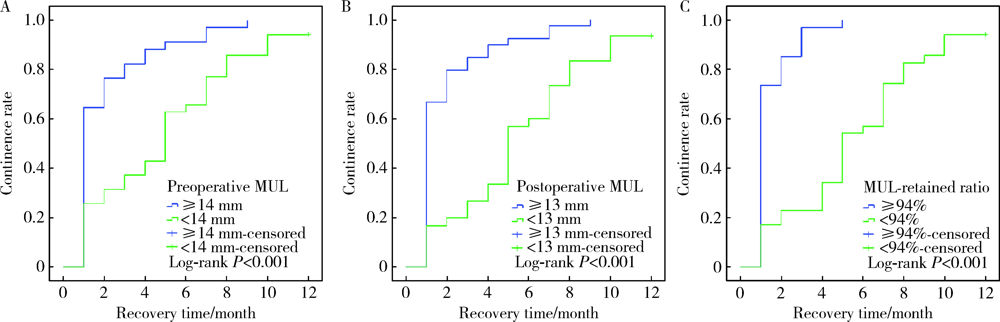
目的: 探讨术前及术后膜性尿道长度(membranous urethral length,MUL)与腹腔镜根治性前列腺切除术(laparoscopic radical prostatectomy,LRP)后控尿功能恢复的相关性。方法: 回顾性分析经组织病理学诊断为前列腺腺癌并于北京大学第三医院行LRP的患者69例,患者均于LRP术前及术后行磁共振检查。术前MUL定义为前列腺尖部尿道至阴茎球部尿道之间的距离,术后MUL定义为膀胱颈口至阴茎球部尿道之间的距离,MUL留存比定义为术后MUL占术前MUL的百分比。所有患者均行腹膜外LRP,自术后第1个月起每月对患者的控尿功能恢复情况进行随访,以全天不需要使用尿垫为控尿功能恢复标准。应用Logistic多因素回归分析影响术后3个月控尿功能恢复的危险因素,Kaplan-Meier法绘制LRP术后患者控尿功能恢复曲线,Log-rank检验比较各组间术后控尿功能恢复曲线的统计学意义。结果: 69例患者平均年龄(71.4±8.6)岁;穿刺前平均前列腺特异抗原(23.40±30.31) μg/L;术前磁共振测量前列腺体积(prostatic volume,PV)为12.20~128.48 mL,平均(39.48±22.73) mL;术前MUL为5~22 mm,平均(13.0±3.3) mm;术后MUL为4~22 mm,平均(12.3±3.4) mm;MUL留存比为80%~100%,平均93.9%±6.2%。LRP术后3个月和12个月69例患者控尿率分别为57.9%(40/69)和97.1%(67/69)。单因素分析表明,PV(P=0.028)、术前MUL(P<0.001)和术后MUL(P<0.001)是LRP术后3个月尿失禁的影响因素;多因素分析显示,术后MUL<13 mm是LRP术后3个月尿失禁发生的独立危险因素(P<0.001)。Log-rank检验提示,术前MUL≥14 mm、术后MUL≥13 mm和MUL留存比≥94%的患者术后控尿功能恢复分别优于术前MUL<14 mm、术后MUL<13 mm和MUL留存比<94%的患者,差异具有统计学意义(P=0.001)。结论: 术前MUL、术后MUL和MUL留存比与LRP术后控尿功能恢复存在相关性,术后MUL较短是术后3个月尿失禁发生的独立危险因素。
中图分类号:
- R737.25
| [1] |
Mottet N, Bellmunt J, Bolla M, et al. EAU-ESTRO-SIOG guidelines on prostate cancer. Part 1: Screening, diagnosis, and local treatment with curative intent[J]. Euro Urol, 2017, 71(4):618-629.
doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2016.08.003 |
| [2] |
Heesakkers J, Farag F, Bauer RM, et al. Pathophysiology and contributing factors in postprostatectomy incontinence: A review[J]. Eur Urol, 2017, 71(6):936-944.
doi: S0302-2838(16)30666-2 pmid: 27720536 |
| [3] |
Walz J, Epstein JI, Ganzer R, et al. A critical analysis of the current knowledge of surgical anatomy of the prostate related to optimisation of cancer control and preservation of continence and erection in candidates for radical prostatectomy: An update[J]. Eur Urol, 2016, 70(2):301-311.
doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2016.01.026 |
| [4] |
Bessede T, Sooriakumaran P, Takenaka A, et al. Neural supply of the male urethral sphincter: Comprehensive anatomical review and implications for continence recovery after radical prostatectomy[J]. World J Urol, 2017, 35(4):549-565.
doi: 10.1007/s00345-016-1901-8 pmid: 27484205 |
| [5] |
Mungovan SF, Sandhu JS, Akin O, et al. Preoperative membranous urethral length measurement and continence recovery following radical prostatectomy: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Eur Urol, 2017, 71(3):368-378.
doi: S0302-2838(16)30341-4 pmid: 27394644 |
| [6] | Song W, Kim CK, Park BK, et al. Impact of preoperative and postoperative membranous urethral length measured by 3 Tesla magnetic resonance imaging on urinary continence recovery after robotic-assisted radical prostatectomy[J]. Can Urol Assoc J, 2017, 11(3/4):E93-E99. |
| [7] |
Paparel P, Akin O, Sandhu JS, et al. Recovery of urinary continence after radical prostatectomy: Association with urethral length and urethral fibrosis measured by preoperative and postoperative endorectal magnetic resonance imaging[J]. Eur Urol, 2009, 55(3):629-639.
doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2008.08.057 |
| [8] |
Myers RP, Cahill DR, Devine RM, et al. Anatomy of radical prostatectomy as defined by magnetic resonance imaging[J]. J Urol, 1998, 159(6):2148-2158.
pmid: 9598561 |
| [9] |
Coakley FV, Eberhardt S, Kattan MW, et al. Urinary continence after radical retropubic prostatectomy: Relationship with membranous urethral length on preoperative endorectal magnetic resonance imaging[J]. J Urol, 2002, 168(3):1032-1035.
doi: 10.1097/01.ju.0000025881.75827.a5 pmid: 12187216 |
| [10] |
Vordermark D. Quality of life and satisfaction with outcome among prostate-cancer survivors[J]. N Engl J Med, 2008, 359(2):200-202.
doi: 10.1056/NEJMc080867 |
| [11] |
Mohler JL, Antonarakis ES, Armstrong AJ, et al. Prostate can-cer, version 2. 2019, NCCN clinical practice guidelines in onco-logy[J]. J Natl Compr Canc Netw, 2019, 17(5):479-505.
doi: 10.6004/jnccn.2019.0023 |
| [12] | 张帆, 马潞林, 黄毅, 等. 腹腔镜前列腺癌根治术后控尿功能恢复与术前膜性尿道长度的相关性研究[J]. 中华泌尿外科杂志, 2013, 34(1):41-44. |
| [13] |
Nguyen L, Jhaveri J, Tewari A. Surgical technique to overcome anatomical shortcoming: Balancing post-prostatectomy continence outcomes of urethral sphincter lengths on preoperative magnetic resonance imaging[J]. J Urol, 2008, 179(5):1907-1911.
doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2008.01.036 pmid: 18353395 |
| [14] |
Kadono Y, Nohara T, Kawaguchi S, et al. Investigating the me-chanism underlying urinary continence recovery after radical prostatectomy: Effectiveness of a longer urethral stump to prevent urinary incontinence[J]. BJU Int, 2018, 122(3):456-462.
doi: 10.1111/bju.14181 |
| [15] | 张帆, 肖春雷, 张树栋, 等. 前列腺体积及前列腺突入膀胱长度与腹腔镜前列腺癌根治术后控尿功能恢复的相关性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(4):621-625. |
| [16] |
Lee H, Kim K, Hwang SI, et al. Impact of prostatic apical shape and protrusion on early recovery of continence after robot-assisted radical prostatectomy[J]. Urology, 2014, 84(4):844-849.
doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2014.06.011 |
| [17] |
Sauer M, Tennstedt P, Berliner C, et al. Predictors of short and long term urinary incontinence after radical prostatectomy in prostate MRI: Significance and reliability of standardized measurements[J]. Eur J Radiol, 2019, 120:108668.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2019.108668 |
| [18] | Kim M, Park M, Pak S, et al. Integrity of the urethral sphincter complex, nerve-sparing, and long-term continence status after robotic-assisted radical prostatectomy[J]. Eur Urol Focus, 2019, 5(5):823-830. |
| [1] | 邢念增,王明帅,杨飞亚,尹路,韩苏军. 前列腺免活检创新理念的临床实践及其应用前景[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 565-566. |
| [2] | 田宇轩,阮明健,刘毅,李德润,吴静云,沈棋,范宇,金杰. 双参数MRI改良PI-RADS评分4分和5分病灶的最大径对临床有意义前列腺癌的预测效果[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 567-574. |
| [3] | 于书慧,韩佳凝,钟丽君,陈聪语,肖云翔,黄燕波,杨洋,车新艳. 术前盆底肌电生理参数对前列腺癌根治性切除术后早期尿失禁的预测价值[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 594-599. |
| [4] | 李雨清,王飚,乔鹏,王玮,关星. 经耻骨后尿道中段悬吊带术治疗女性复发性压力性尿失禁的中长期疗效[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 600-604. |
| [5] | 刘毅,袁昌巍,吴静云,沈棋,肖江喜,赵峥,王霄英,李学松,何志嵩,周利群. 靶向穿刺+6针系统穿刺对PI-RADS 5分患者的前列腺癌诊断效能[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 812-817. |
| [6] | 毛海,张帆,张展奕,颜野,郝一昌,黄毅,马潞林,褚红玲,张树栋. 基于MRI前列腺腺体相关参数构建腹腔镜前列腺癌术后尿失禁的预测模型[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 818-824. |
| [7] | 邱敏,宗有龙,王滨帅,杨斌,徐楚潇,孙争辉,陆敏,赵磊,卢剑,刘承,田晓军,马潞林. 腹腔镜肾部分切除术治疗中高复杂程度肾肿瘤的效果[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 833-837. |
| [8] | 袁昌巍,李德润,李志华,刘毅,山刚志,李学松,周利群. 多参数磁共振成像中动态对比增强状态在诊断PI-RADS 4分前列腺癌中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 838-842. |
| [9] | 张展奕,张帆,颜野,曹财广,李长剑,邓绍晖,孙悦皓,黄天亮,管允鹤,李楠,陆敏,胡振华,张树栋. 近红外荧光靶向探针用于前列腺神经血管束术中成像[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 843-850. |
| [10] | 刘慧丽,吕彦函,王晓晓,李民. 老年患者腹腔镜泌尿系肿瘤根治术后慢性疼痛的影响因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 851-856. |
| [11] | 刘颖,霍然,徐慧敏,王筝,王涛,袁慧书. 磁共振血管壁成像评估颈动脉中重度狭窄患者斑块特征与脑血流灌注的相关性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 646-651. |
| [12] | 傅强,高冠英,徐雁,林卓华,孙由静,崔立刚. 无症状髋关节前上盂唇撕裂超声与磁共振检查的对比研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 665-669. |
| [13] | 许素环,王蓓蓓,庞秋颖,钟丽君,丁炎明,黄燕波,车新艳. 等体温膀胱冲洗对经尿道前列腺电切术患者干预效果的meta分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 676-683. |
| [14] | 叶珊,金萍萍,张楠,邬海博,石林,赵强,杨坤,袁慧书,樊东升. 肌萎缩侧索硬化患者认知功能改变与脑皮层厚度分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1158-1162. |
| [15] | 张铃福,侯纯升,徐智,王立新,凌晓锋,王港,崔龙,修典荣. 腹腔镜下经胆囊管胆管引流联合胆总管探查取石术治疗复杂胆管结石的临床效果[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1185-1189. |
|
||